Abstract
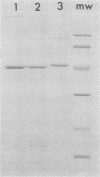
The phospholipase C gene from Clostridium perfringens was isolated, and its sequence was determined. It was found that the structural gene codes for a protein of 399 amino acid residues. The NH2-terminal residues have the typical features of a signal peptide and are probably cleaved after secretion. Escherichia coli cells harboring the phospholipase C gene-containing plasmid expressed high levels of this protein in the periplasmic space. Phospholipase C purified from E. coli transformants was enzymatically active, hemolytic to erythrocytes, and toxic to animals when injected intravenously. The phospholipase C gene from a related organism, Clostridium bifermentans, was also isolated. The two phospholipase C genes were found to be 64% homologous in coding sequence. The C. bifermentans protein, however, was 50-fold less active enzymatically than the C. perfringens enzyme.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk R. S., Brown D., Coutinho I., Meyers D. In vivo studies with two phospholipase C fractions from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1987 Jul;55(7):1728–1730. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.7.1728-1730.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird R. A., Low M. G., Stephen J. Immunopurification of phospholipase C (alpha-toxin) from Clostridium perfringens. FEBS Lett. 1974 Aug 30;44(3):279–281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dente L., Cesareni G., Cortese R. pEMBL: a new family of single stranded plasmids. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 25;11(6):1645–1655. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.6.1645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eloy C., Fardel G., Flandrois J. P. Fast protein liquid chromatography for the isolation of Clostridium perfringens type A alpha-toxin. J Chromatogr. 1985 Mar 8;321(1):235–239. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)90440-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M., Hogness D. S. Colony hybridization: a method for the isolation of cloned DNAs that contain a specific gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3961–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansen T., Holm T., Guddal P. H., Sletten K., Haugli F. B., Little C. Cloning and sequencing of the gene encoding the phosphatidylcholine-preferring phospholipase C of Bacillus cereus. Gene. 1988 May 30;65(2):293–304. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90466-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krug E. L., Kent C. Phospholipase C from Clostridium perfringens: preparation and characterization of homogeneous enzyme. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1984 Jun;231(2):400–410. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(84)90403-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macfarlane M. G., Knight B. C. The biochemistry of bacterial toxins: The lecithinase activity of Cl. welchii toxins. Biochem J. 1941 Sep;35(8-9):884–902. doi: 10.1042/bj0350884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitsui K., Mitsui N., Hase J. Clostridium perfringens exotoxins. II. Purification and some properties of theta-toxin. Jpn J Exp Med. 1973 Oct;43(5):377–391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C., Heppel L. A. The release of enzymes from Escherichia coli by osmotic shock and during the formation of spheroplasts. J Biol Chem. 1965 Sep;240(9):3685–3692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pritchard A. E., Vasil M. L. Nucleotide sequence and expression of a phosphate-regulated gene encoding a secreted hemolysin of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jul;167(1):291–298. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.1.291-298.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato H., Kameyama S., Murata R. Immunogenicity of highly purified -toxoid of Clostridium perfringens. Jpn J Med Sci Biol. 1972 Feb;25(1):53–56. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smyth C. J., Arbuthnott J. P. Properties of Clostridium perfringens (welchii) type-A alpha-toxin (phospholipase C) purified by electrofocusing. J Med Microbiol. 1974 Feb;7(1):41–66. doi: 10.1099/00222615-7-1-41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smyth C. J. The identification and purification of multiple forms of theta-haemolysin (theta-toxin) of Clostridium perfringens type A. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 Apr;87(2):219–238. doi: 10.1099/00221287-87-2-219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi T., Sugahara T., Ohsaka A. Purification of Clostridium perfringens phospholipase C (alpha-toxin) by affinity chromatography on agarose-linked egg-yolk lipoprotein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 May 10;351(1):155–171. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(74)90074-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]