Abstract
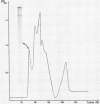
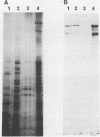
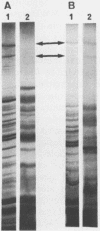
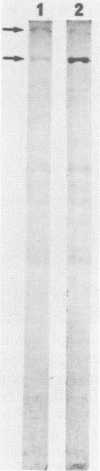
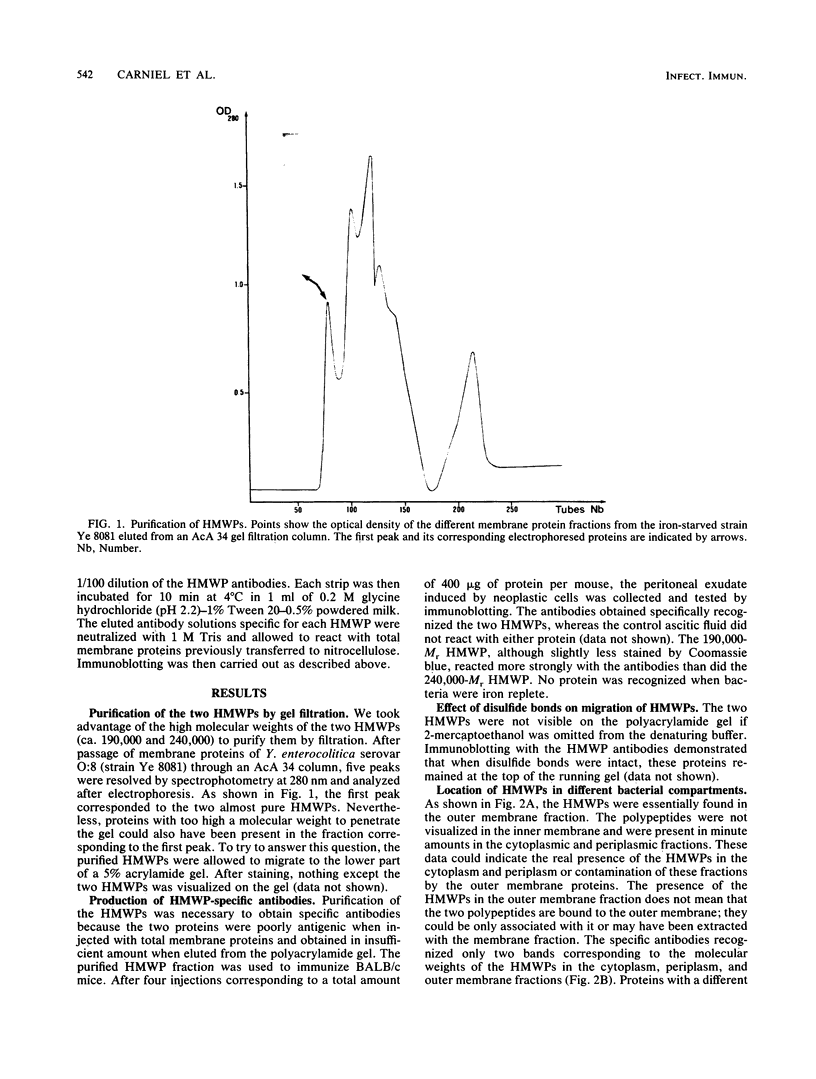
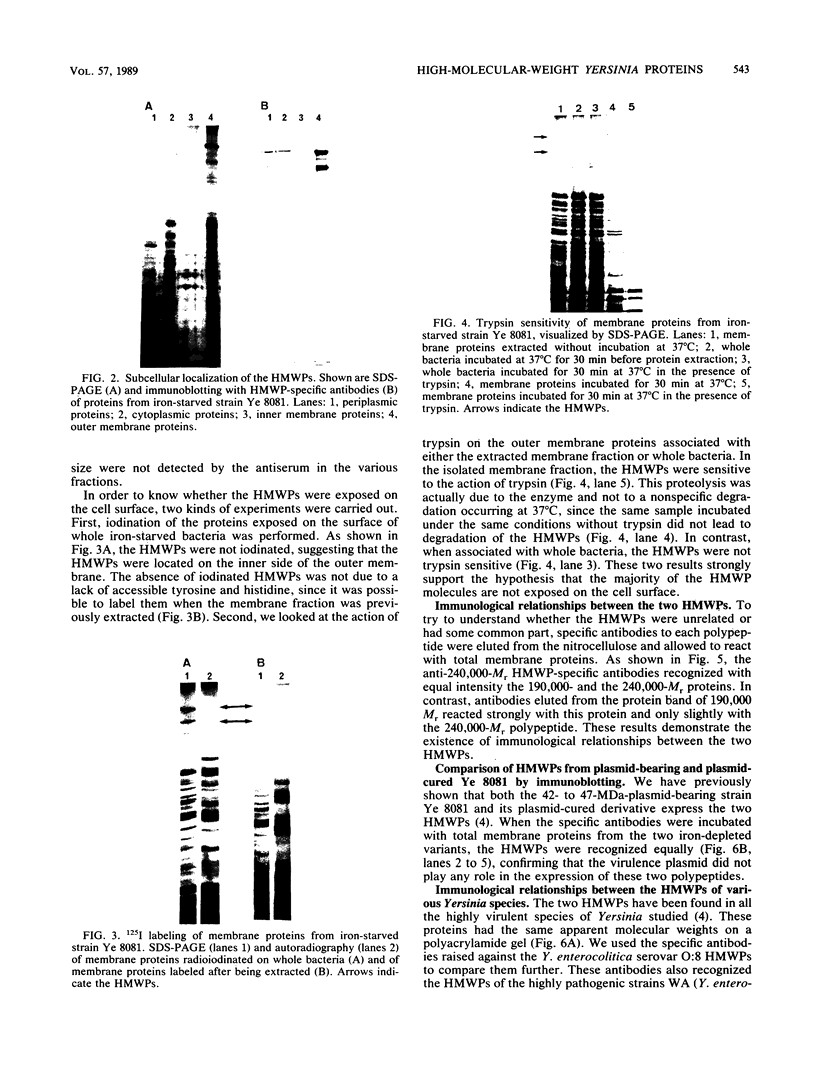
We have previously shown that under iron limitation, different Yersinia species synthesize new polypeptides. Two of them, the high-molecular-weight proteins (HMWPs), are expressed only by the highly pathogenic strains. In the present study, the HMWPs from Y. enterocolitica serovar O:8 were purified by gel filtration, and specific antibodies were obtained. Using these antibodies, we show that the two polypeptides were synthesized de novo during iron starvation and that they were found essentially in the bacterial outer membrane fractions, although the majority of the molecules were not exposed on the cell surface. We also demonstrate that the two proteins had common epitopes and that the HMWPs of the high-virulence-phenotype species Y. pestis, Y. pseudotuberculosis, and Y. enterocolitica serovar O:8 (a strain different from the one used to purify the proteins) are antigenically related. The less pathogenic and nonpathogenic strains did not exhibit cross-reacting material, suggesting that these strains do not synthesize even an altered form of the HMWPs.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BURROWS T. W., JACKSON S. The virulence-enhancing effect of iron on nonpigmented mutants of virulent strains of Pasteurella pestis. Br J Exp Pathol. 1956 Dec;37(6):577–583. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bölin I., Norlander L., Wolf-Watz H. Temperature-inducible outer membrane protein of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis and Yersinia enterocolitica is associated with the virulence plasmid. Infect Immun. 1982 Aug;37(2):506–512. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.2.506-512.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capron J. P., Capron-Chivrac D., Tossou H., Delamarre J., Eb F. Spontaneous Yersinia enterocolitica peritonitis in idiopathic hemochromatosis. Gastroenterology. 1984 Dec;87(6):1372–1375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carniel E., Mazigh D., Mollaret H. H. Expression of iron-regulated proteins in Yersinia species and their relation to virulence. Infect Immun. 1987 Jan;55(1):277–280. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.1.277-280.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallant T., Freedman M. H., Vellend H., Francombe W. H. Yersinia sepsis in patients with iron overload treated with deferoxamine. N Engl J Med. 1986 Jun 19;314(25):1643–1643. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198606193142515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leighton P. M., MacSween H. M. Yersinia hepatic abscesses subsequent to long-term iron therapy. JAMA. 1987 Feb 20;257(7):964–965. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melby K., Slørdahl S., Gutteberg T. J., Nordbø S. A. Septicaemia due to Yersinia enterocolitica after oral overdoses of iron. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1982 Aug 14;285(6340):467–468. doi: 10.1136/bmj.285.6340.467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mofenson H. C., Caraccio T. R., Sharieff N. Iron sepsis: Yersinia enterocolitica septicemia possibly caused by an overdose of iron. N Engl J Med. 1987 Apr 23;316(17):1092–1093. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C., Heppel L. A. The release of enzymes from Escherichia coli by osmotic shock and during the formation of spheroplasts. J Biol Chem. 1965 Sep;240(9):3685–3692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olmsted J. B. Affinity purification of antibodies from diazotized paper blots of heterogeneous protein samples. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 10;256(23):11955–11957. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnoy D. A., Wolf-Watz H., Bolin I., Beeder A. B., Falkow S. Characterization of common virulence plasmids in Yersinia species and their role in the expression of outer membrane proteins. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):108–114. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.108-114.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabson A. R., Hallett A. F., Koornhof H. J. Generalized Yersinia enterocolitica infection. J Infect Dis. 1975 Apr;131(4):447–451. doi: 10.1093/infdis/131.4.447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robins-Browne R. M., Prpic J. K. Effects of iron and desferrioxamine on infections with Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1985 Mar;47(3):774–779. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.3.774-779.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roche G., Leheup B., Gérard A., Canton P., Lion C., Leichtmann G., Dureux J. B. Septicémies à Yersinia enterocolitica. Revue générale à propos d'un nouvaeu cas chez une jeune femme présentant une thalassémie majeure. Rev Med Interne. 1982 Mar;3(1):65–74. doi: 10.1016/s0248-8663(82)80010-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sartorelli A. C., Fischer D. S., Downs W. G. Use of sarcoma 180/TG to prepare hyperimmune ascitic fluid in the mouse. J Immunol. 1966 Apr;96(4):676–682. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart S. J., Prpic J. K., Robins-Browne R. M. Production of aerobactin by some species of the genus Yersinia. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jun;166(3):1131–1133. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.3.1131-1133.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan K. H., Williams R. P. Use of iodo-gen and iodine-125 to label the outer membrane proteins of whole cells of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Anal Biochem. 1982 Mar 1;120(2):254–258. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90344-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]