Abstract
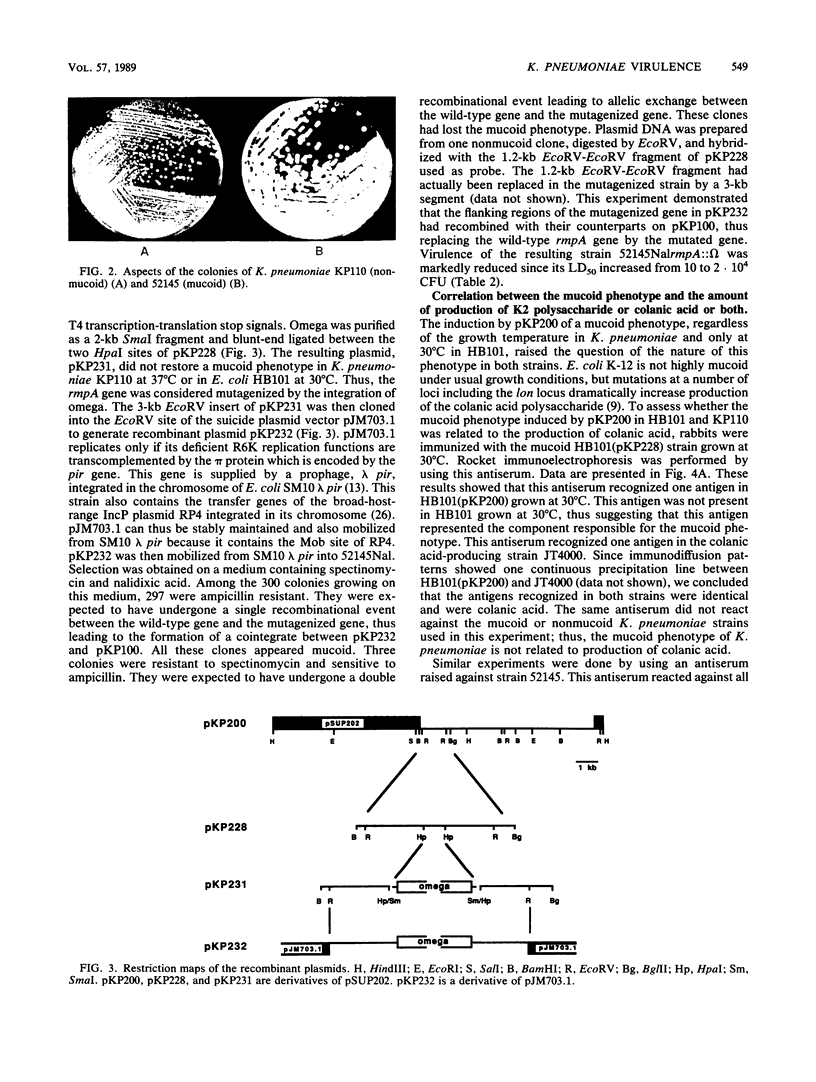
We have previously reported that the presence of a 180-kilobase plasmid encoding production of aerobactin was correlated with the virulence of Klebsiella pneumoniae K1 and K2 isolates. This work demonstrates that a variant of a K2 strain which has lost this plasmid, pKP100, becomes avirulent. Labeling of this plasmid with the mobilizable, replication-defective element pME28, used here as a mobilizable transposon, allowed the transfer of this plasmid into a plasmidless derivative. Virulence was restored upon reacquisition of this tagged plasmid, pKP101. In addition to aerobactin production, another phenotype could be correlated with the presence of this virulence plasmid: the mucoid phenotype of the bacterial colonies. Both wild-type and plasmidless strains are encapsulated, but only the former presented mucoid colonies. Participation of this phenotype in the virulence of K. pneumoniae was demonstrated by constructing a mutant altered in the plasmid gene encoding this phenotype. The resulting strain demonstrated a 1,000-fold decrease in virulence. Introduction of the recombinant plasmid pKP200 carrying the gene encoding this mucoid phenotype into Escherichia coli HB101 also led to the production of a mucoid phenotype. Rocket immunoelectrophoresis demonstrated that in E. coli this phenotype was due to the production of colanic acid. On the other hand, neither the overproduction of K2 capsular polysaccharide nor the presence of colanic acid was detected in mucoid strains of K. pneumoniae. We conclude that this mucoid phenotype is definitely an important virulence factor of K. pneumoniae. It is due to the plasmid-encoded production of a substance which is different from colanic acid and the capsular polysaccharide of K. pneumoniae.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen P., Hart C. A., Saunders J. R. Isolation from Klebsiella and characterization of two rcs genes that activate colanic acid capsular biosynthesis in Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Feb;133(2):331–340. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-2-331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer H. W., Roulland-Dussoix D. A complementation analysis of the restriction and modification of DNA in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1969 May 14;41(3):459–472. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90288-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. N., Chang A. C., Hsu L. Nonchromosomal antibiotic resistance in bacteria: genetic transformation of Escherichia coli by R-factor DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Aug;69(8):2110–2114. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.8.2110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Figurski D. H., Helinski D. R. Replication of an origin-containing derivative of plasmid RK2 dependent on a plasmid function provided in trans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1648–1652. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fournier J. M., Jolivet-Reynaud C., Riottot M. M., Jouin H. Murine immunoprotective activity of Klebsiella pneumoniae cell surface preparations: comparative study with ribosomal preparations. Infect Immun. 1981 May;32(2):420–426. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.2.420-426.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fournier J. M., Vann W. F., Karakawa W. W. Purification and characterization of Staphylococcus aureus type 8 capsular polysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1984 Jul;45(1):87–93. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.1.87-93.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottesman S., Trisler P., Torres-Cabassa A. Regulation of capsular polysaccharide synthesis in Escherichia coli K-12: characterization of three regulatory genes. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jun;162(3):1111–1119. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.3.1111-1119.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottesman S., Zipser D. Deg phenotype of Escherichia coli lon mutants. J Bacteriol. 1978 Feb;133(2):844–851. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.2.844-851.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kado C. I., Liu S. T. Rapid procedure for detection and isolation of large and small plasmids. J Bacteriol. 1981 Mar;145(3):1365–1373. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.3.1365-1373.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LENNOX E. S. Transduction of linked genetic characters of the host by bacteriophage P1. Virology. 1955 Jul;1(2):190–206. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(55)90016-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller V. L., Mekalanos J. J. A novel suicide vector and its use in construction of insertion mutations: osmoregulation of outer membrane proteins and virulence determinants in Vibrio cholerae requires toxR. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jun;170(6):2575–2583. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.6.2575-2583.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuta K., Ohta M., Mori M., Hasegawa T., Nakashima I., Kato N. Virulence for mice of Klebsiella strains belonging to the O1 group: relationship to their capsular (K) types. Infect Immun. 1983 Apr;40(1):56–61. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.1.56-61.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nassif X., Sansonetti P. J. Correlation of the virulence of Klebsiella pneumoniae K1 and K2 with the presence of a plasmid encoding aerobactin. Infect Immun. 1986 Dec;54(3):603–608. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.3.603-608.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prentki P., Krisch H. M. In vitro insertional mutagenesis with a selectable DNA fragment. Gene. 1984 Sep;29(3):303–313. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90059-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruzzo C., Valisena S., Satta G. Laboratory and wild-type Klebsiella pneumoniae strains carrying mannose-inhibitable adhesins and receptors for coliphages T3 and T7 are more pathogenic for mice than are strains without such receptors. Infect Immun. 1983 Feb;39(2):520–527. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.2.520-527.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reimmann C., Haas D. IS21 insertion in the trfA replication control gene of chromosomally integrated plasmid RP1: a property of stable Pseudomonas aeruginosa Hfr strains. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Jun;203(3):511–519. doi: 10.1007/BF00422078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reimmann C., Haas D. Mode of replicon fusion mediated by the duplicated insertion sequence IS21 in Escherichia coli. Genetics. 1987 Apr;115(4):619–625. doi: 10.1093/genetics/115.4.619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riottot M. M., Fournier J. M., Jouin H. Direct evidence for the involvement of capsular polysaccharide in the immunoprotective activity of Klebsiella pneumoniae ribosomal preparations. Infect Immun. 1981 Jan;31(1):71–77. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.1.71-77.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simoons-Smit A. M., Verweij-van Vught A. M., MacLaren D. M. The role of K antigens as virulence factors in Klebsiella. J Med Microbiol. 1986 Mar;21(2):133–137. doi: 10.1099/00222615-21-2-133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson J. A., Smith S. E., Dean R. T. Alginate inhibition of the uptake of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by macrophages. J Gen Microbiol. 1988 Jan;134(1):29–36. doi: 10.1099/00221287-134-1-29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi M., Yoshida K., San Clemente C. L. Relation of colonial morphologies in soft agar to morphological and biological properties of the K-9 strain of Klebsiella pneumoniae and its variants. Can J Microbiol. 1977 Apr;23(4):448–451. doi: 10.1139/m77-066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torres-Cabassa A. S., Gottesman S. Capsule synthesis in Escherichia coli K-12 is regulated by proteolysis. J Bacteriol. 1987 Mar;169(3):981–989. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.3.981-989.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torres-Cabassa A., Gottesman S., Frederick R. D., Dolph P. J., Coplin D. L. Control of extracellular polysaccharide synthesis in Erwinia stewartii and Escherichia coli K-12: a common regulatory function. J Bacteriol. 1987 Oct;169(10):4525–4531. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.10.4525-4531.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILKINSON J. F. The extracellualr polysaccharides of bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1958 Mar;22(1):46–73. doi: 10.1128/br.22.1.46-73.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams P., Lambert P. A., Brown M. R., Jones R. J. The role of the O and K antigens in determining the resistance of Klebsiella aerogenes to serum killing and phagocytosis. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Jul;129(7):2181–2191. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-7-2181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams P., Lambert P. A., Haigh C. G., Brown M. R. The influence of the O and K antigens of Klebsiella aerogenes on surface hydrophobicity and susceptibility to phagocytosis and antimicrobial agents. J Med Microbiol. 1986 Mar;21(2):125–132. doi: 10.1099/00222615-21-2-125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]