Abstract
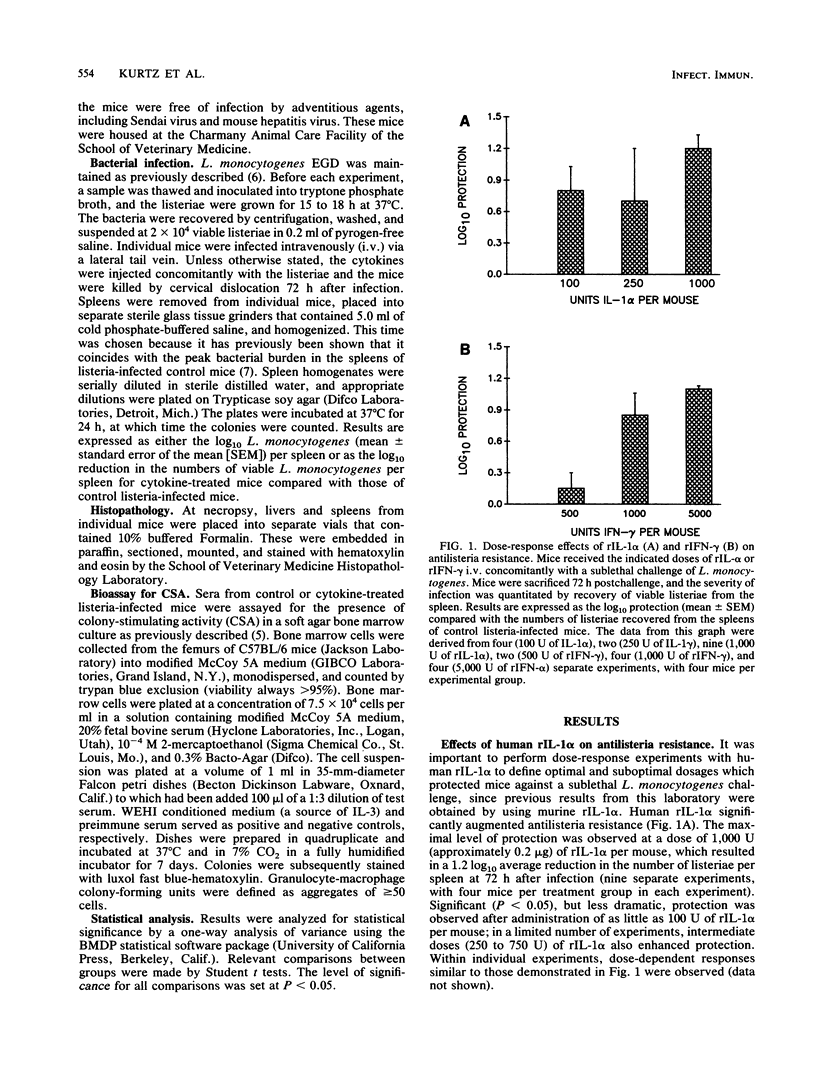
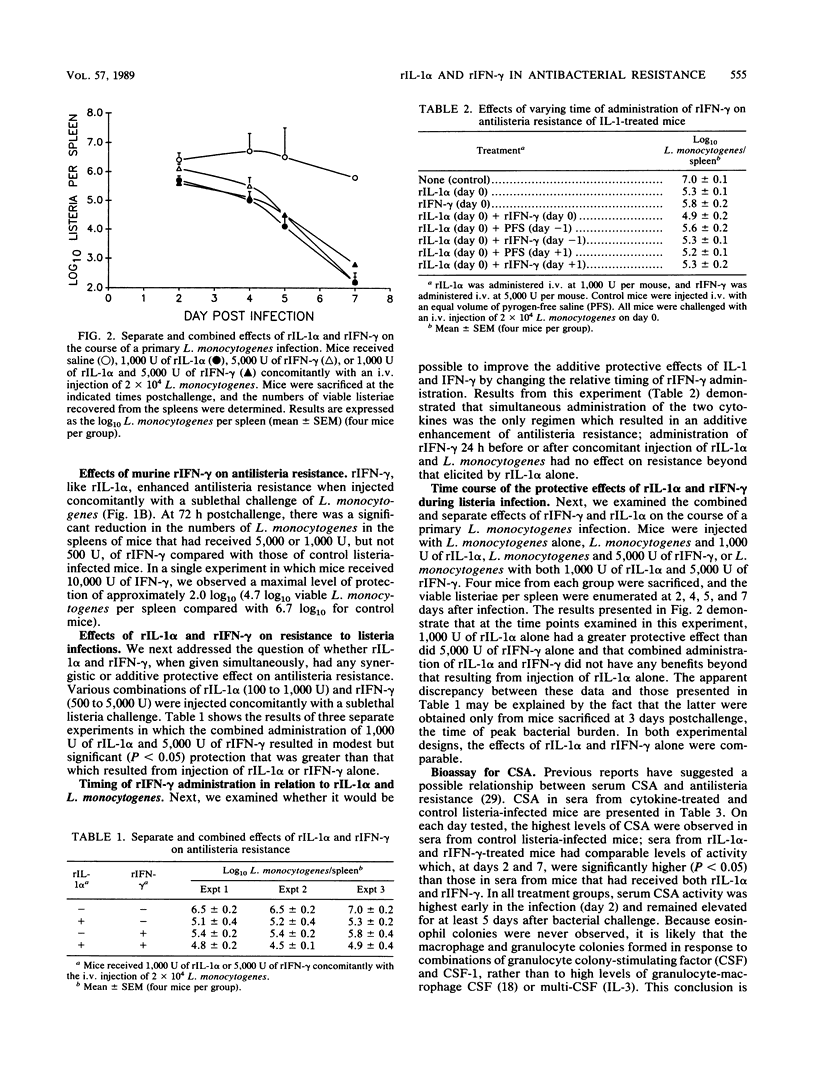
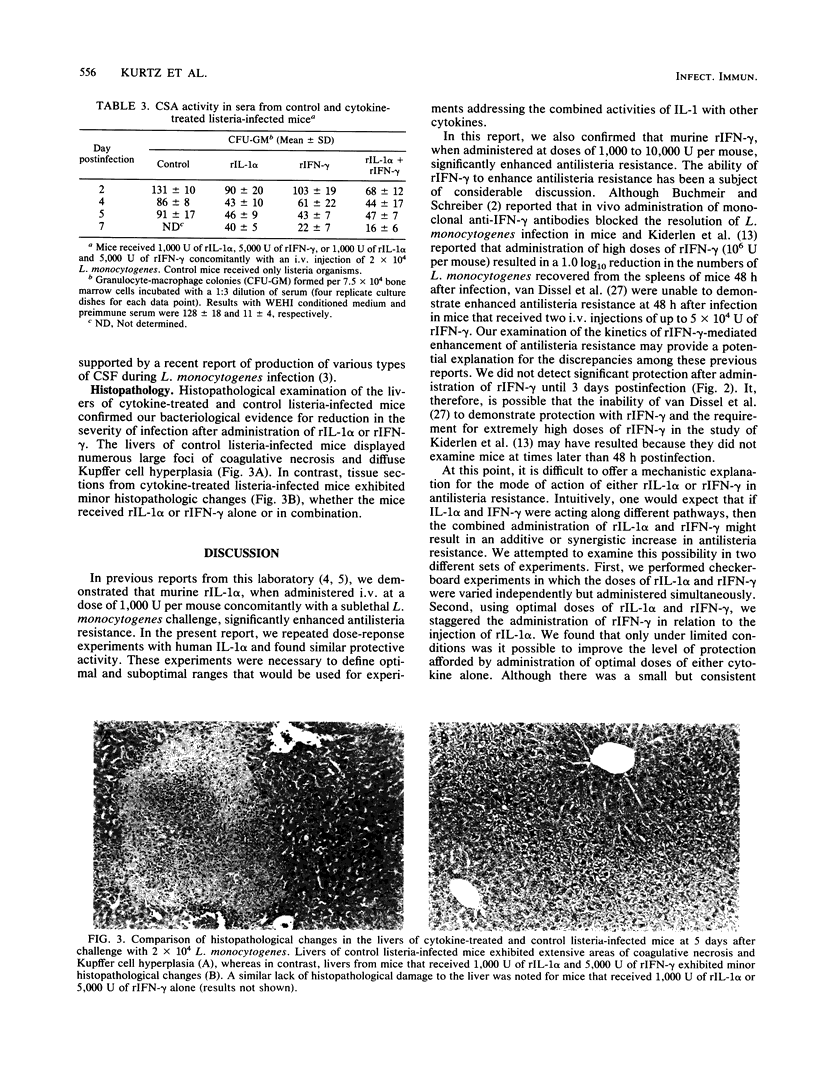
Our laboratory has previously reported that administration of murine recombinant interleukin 1 alpha (rIL-1 alpha) substantially enhanced the resistance of mice to Listeria monocytogenes infection. Other investigators have reported that gamma interferon (IFN-gamma) plays a pivotal role in antilisteria resistance. In the present study, we have defined doses of human rIL-1 alpha that enhanced the antilisteria resistance of mice. We then addressed the possibility that combined immunotherapy with rIL-1 alpha and recombinant IFN-gamma (rIFN-gamma) might result in an additive or synergistic enhancement of antibacterial resistance. Simultaneous administration of rIL-1 alpha and rIFN-gamma enhanced antilisteria resistance (at 3 days after infection) to a greater extent than did either cytokine alone, although the results did not imply a synergistic action between the two cytokines. Experiments which examined the effects of the timing of cytokine administration indicated that maximal protection was observed when rIL-1 alpha and rIFN-gamma were administered together concomitantly with the L. monocytogenes challenge. When we compared the separate and combined protective effects of rIL-1 alpha and rIFN-gamma throughout the course of a primary L. monocytogenes infection, we observed an additive effect of the two cytokines only at 3 days after challenge, the time at which the peak bacterial burden occurs in the spleens and livers of infected mice. Histopathological comparisons of livers and spleens from cytokine-treated and control listeria-infected mice verified that cytokine treatment reduced the severity of tissue damage in cytokine-treated listeria-infected mice. In an attempt to provide a potential mechanism for the protective effects of rIL-1 alpha and rIFN-gamma administration, we compared levels of colony-stimulating activity in sera from cytokine-treated and control listeria-infected mice. The highest levels of colony-stimulating activity were detected in sera from control listeria-infected mice; somewhat lower levels were found in sera from listeria-infected mice that received rIL-1 alpha and rIFN-gamma either alone or in combination.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beller D. I., Kiely J. M., Unanue E. R. Regulation of macrophage populations. I. Preferential induction of Ia-rich peritoneal exudates by immunologic stimuli. J Immunol. 1980 Mar;124(3):1426–1432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchmeier N. A., Schreiber R. D. Requirement of endogenous interferon-gamma production for resolution of Listeria monocytogenes infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(21):7404–7408. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.21.7404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheers C., Haigh A. M., Kelso A., Metcalf D., Stanley E. R., Young A. M. Production of colony-stimulating factors (CSFs) during infection: separate determinations of macrophage-, granulocyte-, granulocyte-macrophage-, and multi-CSFs. Infect Immun. 1988 Jan;56(1):247–251. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.1.247-251.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czuprynski C. J., Brown J. F. Recombinant murine interleukin-1 alpha enhancement of nonspecific antibacterial resistance. Infect Immun. 1987 Sep;55(9):2061–2065. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.9.2061-2065.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czuprynski C. J., Brown J. F., Young K. M., Cooley A. J., Kurtz R. S. Effects of murine recombinant interleukin 1 alpha on the host response to bacterial infection. J Immunol. 1988 Feb 1;140(3):962–968. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czuprynski C. J., Canono B. P., Henson P. M., Campbell P. A. Genetically determined resistance to listeriosis is associated with increased accumulation of inflammatory neutrophils and macrophages which have enhanced listericidal activity. Immunology. 1985 Jul;55(3):511–518. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czuprynski C. J., Henson P. M., Campbell P. A. Killing of Listeria monocytogenes by inflammatory neutrophils and mononuclear phagocytes from immune and nonimmune mice. J Leukoc Biol. 1984 Feb;35(2):193–208. doi: 10.1002/jlb.35.2.193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esparza I., Männel D., Ruppel A., Falk W., Krammer P. H. Interferon gamma and lymphotoxin or tumor necrosis factor act synergistically to induce macrophage killing of tumor cells and schistosomula of Schistosoma mansoni. J Exp Med. 1987 Aug 1;166(2):589–594. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.2.589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havell E. A. Augmented induction of interferons during Listeria monocytogenes infection. J Infect Dis. 1986 May;153(5):960–969. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.5.960. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havell E. A. Production of tumor necrosis factor during murine listeriosis. J Immunol. 1987 Dec 15;139(12):4225–4231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann S. H., Brinkmann V. Attempts to characterize the T-cell population and lymphokine involved in the activation of macrophage oxygen metabolism in murine listeriosis. Cell Immunol. 1984 Oct 15;88(2):545–550. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(84)90186-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiderlen A. F., Kaufmann S. H., Lohmann-Matthes M. L. Protection of mice against the intracellular bacterium Listeria monocytogenes by recombinant immune interferon. Eur J Immunol. 1984 Oct;14(10):964–967. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830141019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koestler T. P., Badger A. M., Rieman D. J., Greig R., Poste G. Induction by immunomodulatory agents of a macrophage antigen recognized by monoclonal antibody 158.2 and correlation with macrophage function. Cell Immunol. 1985 Nov;96(1):113–125. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(85)90344-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le J., Vilcek J. Tumor necrosis factor and interleukin 1: cytokines with multiple overlapping biological activities. Lab Invest. 1987 Mar;56(3):234–248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lederman H. M., Brill C. R., Murphy P. A. Interleukin 1-driven secretion of interleukin 2 is highly temperature-dependent. J Immunol. 1987 Jun 1;138(11):3808–3811. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto M., Matsubara S., Matsuno T., Tamura M., Hattori K., Nomura H., Ono M., Yokota T. Protective effect of human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor on microbial infection in neutropenic mice. Infect Immun. 1987 Nov;55(11):2715–2720. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.11.2715-2720.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalf D. The molecular biology and functions of the granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factors. Blood. 1986 Feb;67(2):257–267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neta R., Oppenheim J. J., Douches S. D. Interdependence of the radioprotective effects of human recombinant interleukin 1 alpha, tumor necrosis factor alpha, granulocyte colony-stimulating factor, and murine recombinant granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor. J Immunol. 1988 Jan 1;140(1):108–111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Old L. J. Tumour necrosis factor. Polypeptide mediator network. 1987 Mar 26-Apr 1Nature. 326(6111):330–331. doi: 10.1038/326330a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onozaki K., Urawa H., Tamatani T., Iwamura Y., Hashimoto T., Baba T., Suzuki H., Yamada M., Yamamoto S., Oppenheim J. J. Synergistic interactions of interleukin 1, interferon-beta, and tumor necrosis factor in terminally differentiating a mouse myeloid leukemic cell line (M1). Evidence that interferon-beta is an autocrine differentiating factor. J Immunol. 1988 Jan 1;140(1):112–119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozaki Y., Ohashi T., Minami A., Nakamura S. Enhanced resistance of mice to bacterial infection induced by recombinant human interleukin-1a. Infect Immun. 1987 Jun;55(6):1436–1440. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.6.1436-1440.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peck R. A one-plate assay for macrophage bactericidal activity. J Immunol Methods. 1985 Sep 3;82(1):131–140. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(85)90232-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philip R., Epstein L. B. Tumour necrosis factor as immunomodulator and mediator of monocyte cytotoxicity induced by itself, gamma-interferon and interleukin-1. Nature. 1986 Sep 4;323(6083):86–89. doi: 10.1038/323086a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal G. M., McCall E., Stueve T., Bagby G. C., Jr Interleukin 1 stimulates endothelial cells to release multilineage human colony-stimulating activity. J Immunol. 1987 Mar 15;138(6):1772–1778. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsujimoto M., Yip Y. K., Vilcek J. Interferon-gamma enhances expression of cellular receptors for tumor necrosis factor. J Immunol. 1986 Apr 1;136(7):2441–2444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel S. N., Douches S. D., Kaufman E. N., Neta R. Induction of colony stimulating factor in vivo by recombinant interleukin 1 alpha and recombinant tumor necrosis factor alpha 1. J Immunol. 1987 Apr 1;138(7):2143–2148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wing E. J., Barczynski L. C., Waheed A., Shadduck R. K. Effect of Listeria monocytogenes infection on serum levels of colony-stimulating factor and number of progenitor cells in immune and nonimmune mice. Infect Immun. 1985 Aug;49(2):325–328. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.2.325-328.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wing E. J., Magee D. M., Pearson A. C., Waheed A., Shadduck R. K. Peritoneal macrophages exposed to purified macrophage colony-stimulating factor (M-CSF) suppress mitogen- and antigen-stimulated lymphocyte proliferation. J Immunol. 1986 Nov 1;137(9):2768–2773. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong G. H., Clark-Lewis I., McKimm-Breschkin L., Harris A. W., Schrader J. W. Interferon-gamma induces enhanced expression of Ia and H-2 antigens on B lymphoid, macrophage, and myeloid cell lines. J Immunol. 1983 Aug;131(2):788–793. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young A. M., Cheers C. Colony-forming cells and colony-stimulating activity during listeriosis in genetically resistant or susceptible mice. Cell Immunol. 1986 Feb;97(2):227–237. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(86)90393-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Dissel J. T., Stikkelbroeck J. J., Michel B. C., van den Barselaar M. T., Leijh P. C., van Furth R. Inability of recombinant interferon-gamma to activate the antibacterial activity of mouse peritoneal macrophages against Listeria monocytogenes and Salmonella typhimurium. J Immunol. 1987 Sep 1;139(5):1673–1678. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]