Abstract
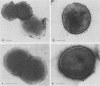
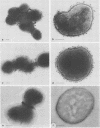
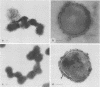
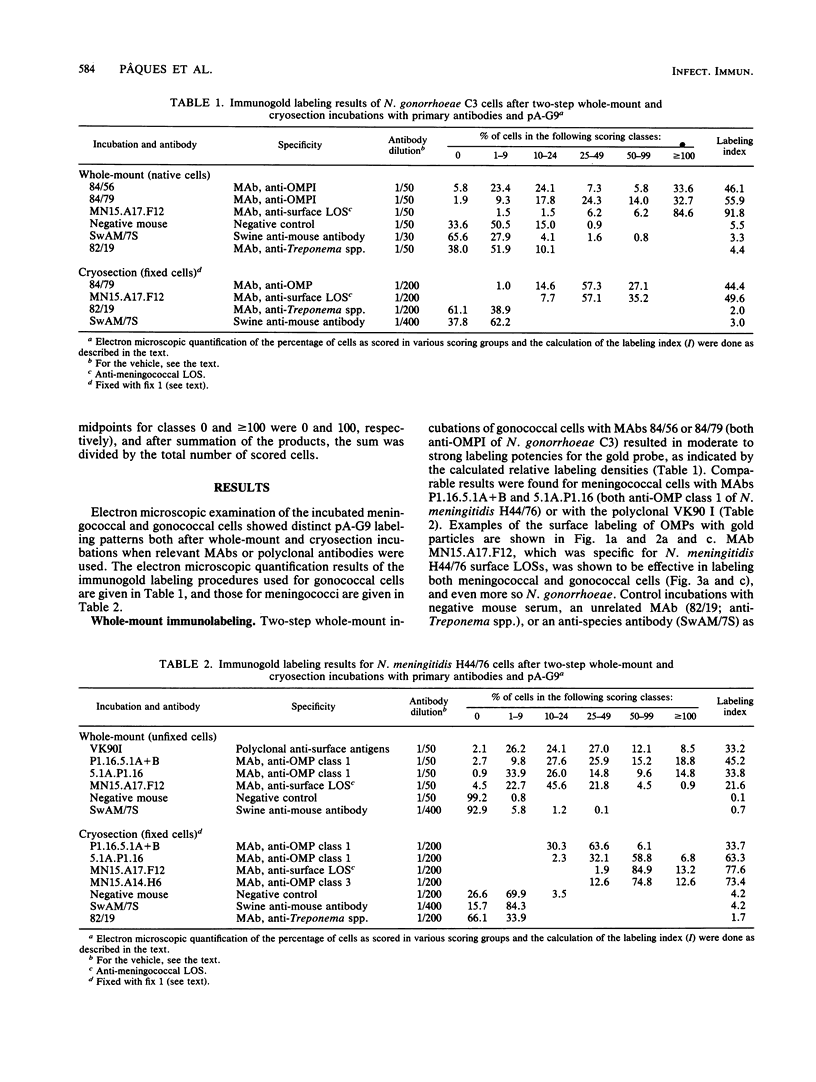
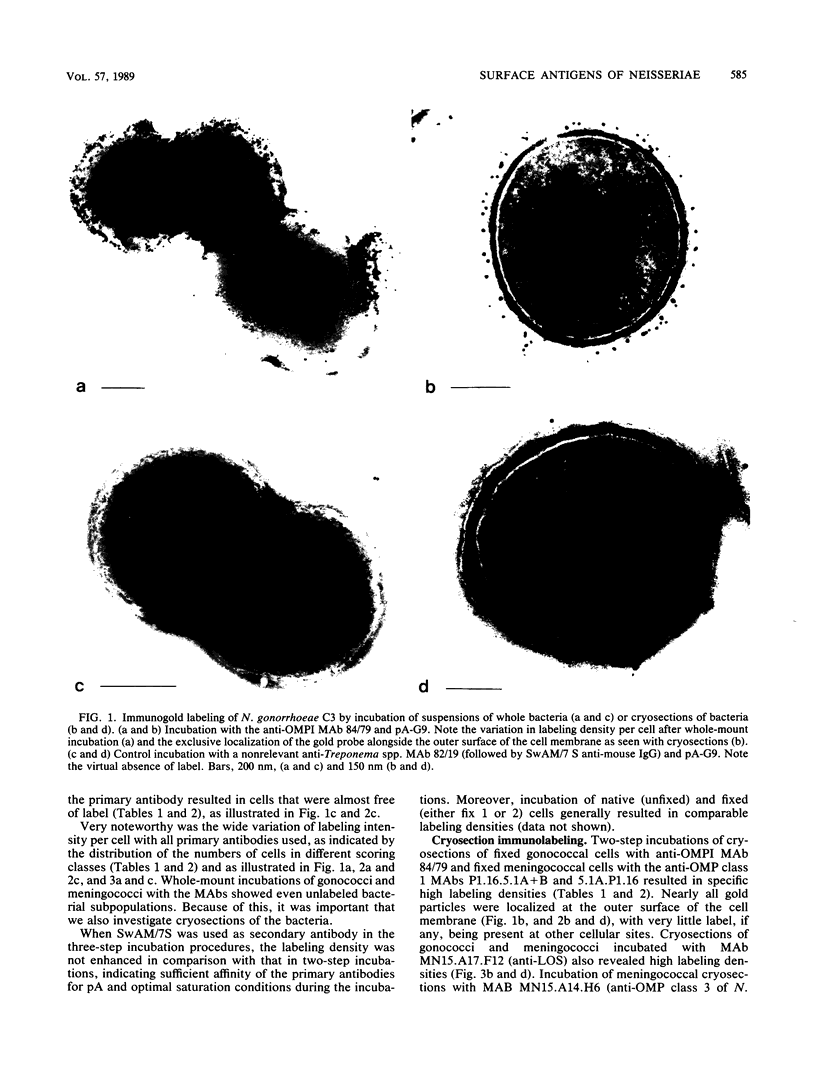
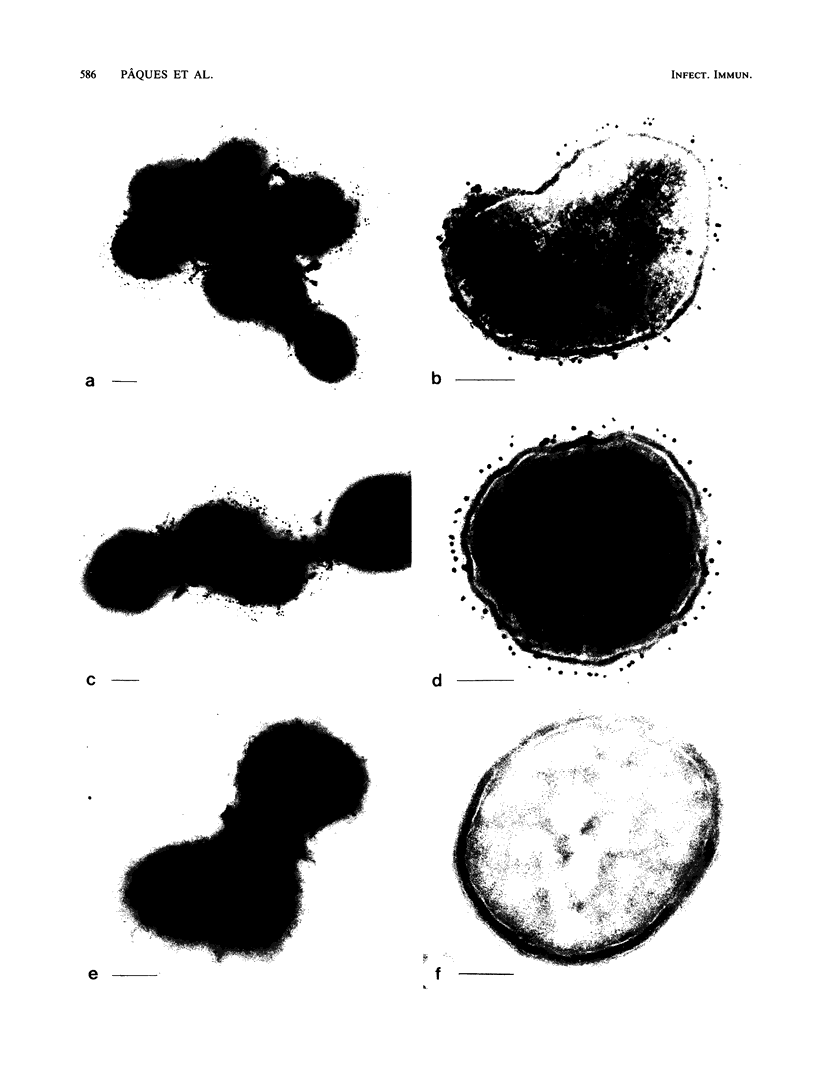
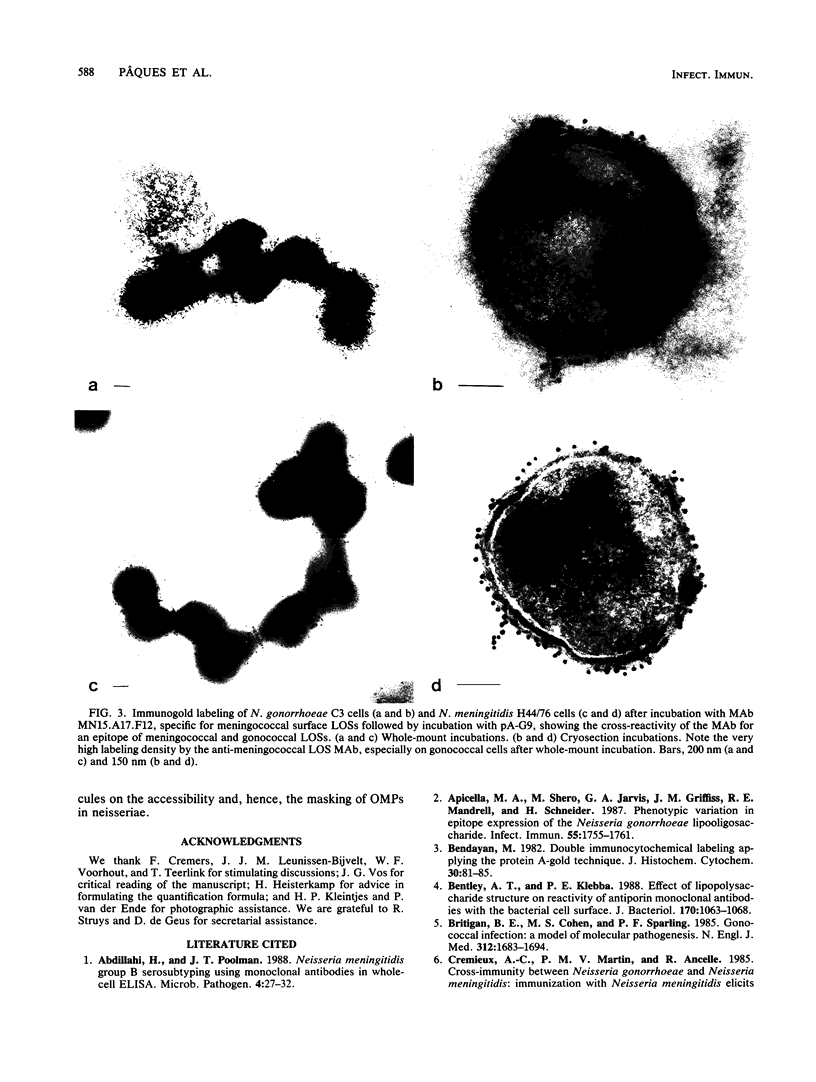
The parallel application of two electron microscopic immunogold labeling procedures was used to assess the surface exposure and accessibility of gonococcal and meningococcal surface antigens. Monoclonal antibodies were used as markers for the surface antigens, i.e., outer membrane proteins and lipooligosaccharides. To evaluate the labeling densities obtained after incubation of whole bacteria in suspension or ultrathin cryosections of bacteria, a method of electron microscopic quantitation was developed. Incubation of whole bacterial suspensions with monoclonal antibodies and protein A-gold resulted in specific labeling of the bacterial surfaces. However, the labeling densities varied largely in each cell. By contrast, cryosections showed uniform heavy labeling densities at the surface of the outer membranes of all cells. Apparently, by sectioning the cells the antigen-masking barrier could be evaded, and steric hindrance was no longer restrictive. Thus, a better estimate of both the presence and the surface exposure, i.e., the accessibility of antigens, could be made. Such information is essential for us to better understand host-bacterial interactions and to develop new vaccines.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abdillahi H., Poolman J. T. Neisseria meningitidis group B serosubtyping using monoclonal antibodies in whole-cell ELISA. Microb Pathog. 1988 Jan;4(1):27–32. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(88)90045-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Apicella M. A., Shero M., Jarvis G. A., Griffiss J. M., Mandrell R. E., Schneider H. Phenotypic variation in epitope expression of the Neisseria gonorrhoeae lipooligosaccharide. Infect Immun. 1987 Aug;55(8):1755–1761. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.8.1755-1761.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bendayan M. Double immunocytochemical labeling applying the protein A-gold technique. J Histochem Cytochem. 1982 Jan;30(1):81–85. doi: 10.1177/30.1.6172469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentley A. T., Klebba P. E. Effect of lipopolysaccharide structure on reactivity of antiporin monoclonal antibodies with the bacterial cell surface. J Bacteriol. 1988 Mar;170(3):1063–1068. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.3.1063-1068.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Britigan B. E., Cohen M. S., Sparling P. F. Gonococcal infection: a model of molecular pathogenesis. N Engl J Med. 1985 Jun 27;312(26):1683–1694. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198506273122606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frasch C. E., Zollinger W. D., Poolman J. T. Serotype antigens of Neisseria meningitidis and a proposed scheme for designation of serotypes. Rev Infect Dis. 1985 Jul-Aug;7(4):504–510. doi: 10.1093/clinids/7.4.504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geoghegan W. D., Ackerman G. A. Adsorption of horseradish peroxidase, ovomucoid and anti-immunoglobulin to colloidal gold for the indirect detection of concanavalin A, wheat germ agglutinin and goat anti-human immunoglobulin G on cell surfaces at the electron microscopic level: a new method, theory and application. J Histochem Cytochem. 1977 Nov;25(11):1187–1200. doi: 10.1177/25.11.21217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horisberger M., Rosset J. Colloidal gold, a useful marker for transmission and scanning electron microscopy. J Histochem Cytochem. 1977 Apr;25(4):295–305. doi: 10.1177/25.4.323352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiskoot W., Teerlink T., Van Hoof M. M., Bartels K., Kanhai V., Crommelin D. J., Beuvery E. C. Immunogenic activity of gonococcal protein I in mice with three different lipoidal adjuvants delivered in liposomes and in complexes. Infect Immun. 1986 Nov;54(2):333–338. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.2.333-338.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature. 1975 Aug 7;256(5517):495–497. doi: 10.1038/256495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morein B., Sundquist B., Höglund S., Dalsgaard K., Osterhaus A. Iscom, a novel structure for antigenic presentation of membrane proteins from enveloped viruses. 1984 Mar 29-Apr 4Nature. 308(5958):457–460. doi: 10.1038/308457a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poolman J. T., Buchanan T. M. Monoclonal antibody activity against native and denatured forms of gonococcal outer membrane proteins as detected within ultrathin, longitudinal slices of polyacrylamide gels. J Immunol Methods. 1984 Dec 31;75(2):265–274. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(84)90110-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poolman J. T., Timmermans H. A., Hopman C. T., Teerlink T., Van Vught P. A., Witvliet M. H., Beuvery E. C. Comparison of meningococcal outer membrane protein vaccines solubilized with detergent or C polysaccharide. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1987;53(6):413–419. doi: 10.1007/BF00415495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson E. N., Jr, Clemens C. M., McGee Z. A., Cannon J. G. Immunoelectron microscopic localization of outer membrane proteins II on the surface of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infect Immun. 1988 Apr;56(4):1003–1006. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.4.1003-1006.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson E. N., Jr, McGee Z. A., Buchanan T. M., Blake M. S., Hitchcock P. J. Probing the surface of Neisseria gonorrhoeae: simultaneous localization of protein I and H.8 antigens. Infect Immun. 1987 May;55(5):1190–1197. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.5.1190-1197.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson E. N., Jr, McGee Z. A., Clemens C. M. Probing the surface of bacteria: use of gold sphere immunological probes. Microb Pathog. 1987 Mar;2(3):159–169. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(87)90018-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson E. N., Jr, McGee Z. A., Kaplan J., Hammond M. E., Larson J. K., Buchanan T. M., Schoolnik G. K. Ultrastructural localization of specific gonococcal macromolecules with antibody-gold sphere immunological probes. Infect Immun. 1984 Nov;46(2):361–366. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.2.361-366.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shafer W. M. Lipopolysaccharide masking of gonococcal outer-membrane proteins modulates binding of bacterial cathepsin G to gonococci. J Gen Microbiol. 1988 Mar;134(3):539–545. doi: 10.1099/00221287-134-3-539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J. Surface-exposed protein antigens of the gonococcal outer membrane. Infect Immun. 1981 Dec;34(3):804–816. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.3.804-816.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teerlink T., Beuvery E. C., Evenberg D., van Wezel T. L. Synergistic effect of detergents and aluminium phosphate on the humoral immune response to bacterial and viral membrane proteins. Vaccine. 1987 Dec;5(4):307–314. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(87)90157-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teerlink T., Versantvoort H., Beuvery E. C. Antigenic and immunogenic properties of cyanogen bromide peptides from gonococcal outer membrane protein IB. Evidence for the existence of a surface-exposed conserved epitope. J Exp Med. 1987 Jul 1;166(1):63–76. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.1.63. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tommassen J., Leunissen J., van Damme-Jongsten M., Overduin P. Failure of E. coli K-12 to transport PhoE-LacZ hybrid proteins out of the cytoplasm. EMBO J. 1985 Apr;4(4):1041–1047. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03736.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virji M., Zak K., Heckels J. E. Monoclonal antibodies to gonococcal outer membrane protein IB: use in investigation of the potential protective effect of antibodies directed against conserved and type-specific epitopes. J Gen Microbiol. 1986 Jun;132(6):1621–1629. doi: 10.1099/00221287-132-6-1621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voorhout W. F., Leunissen-Bijvelt J. J., Leunissen J. L., Verkleij A. J. Steric hindrance in immunolabelling. J Microsc. 1986 Mar;141(Pt 3):303–310. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1986.tb02724.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]