Abstract
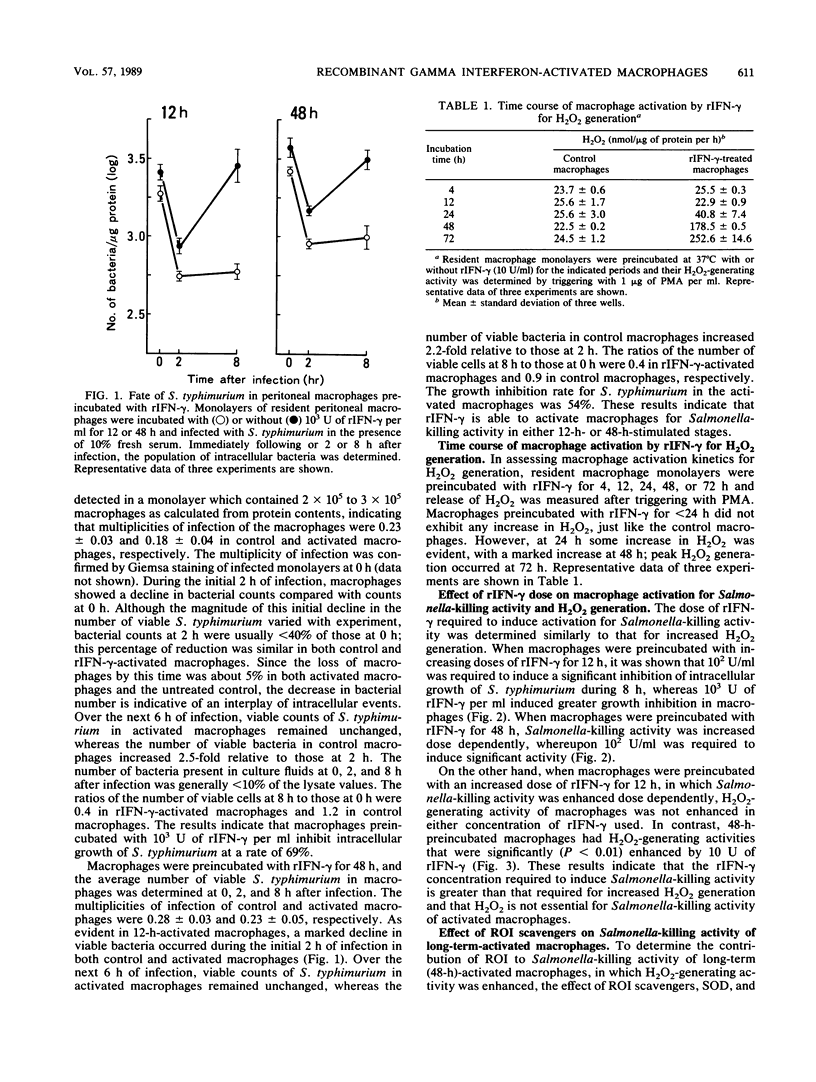
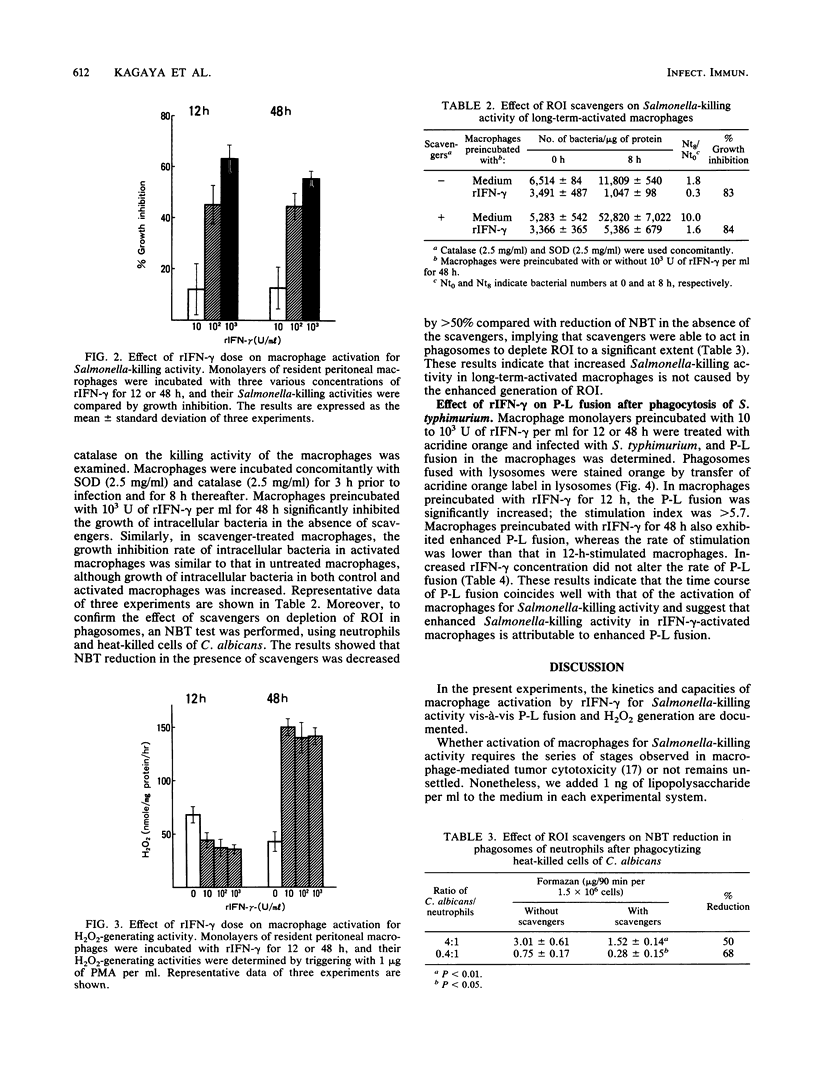
The ability of recombinant gamma interferon (rIFN-gamma) to activate macrophages for Salmonella-killing activity was kinetically examined in relation to phagosome-lysosome fusion and H2O2 generation. Resident peritoneal macrophages of BALB/c mice incubated with 10(2) to 10(3) U of rIFN-gamma per ml for 12 h exhibited enhanced bactericidal activity against Salmonella typhimurium, although H2O2 generation was unaltered. In contrast, macrophages incubated with equal doses of rIFN-gamma for 48 h showed both an enhanced Salmonella-killing activity and an increased generation of H2O2. To evaluate Salmonella-killing activities of macrophages, intracellular bacteria were assayed at 0, 2, and 8 h after infection. During the initial 2 h of infection, 12-h-activated macrophages, as well as the unstimulated control macrophages, showed a decline in bacterial population at the same rate. Over the next 6 h of infection, however, the number of viable bacteria in activated macrophages remained unchanged, whereas the number of bacteria in control macrophages significantly (P less than 0.05) increased. Similar results were obtained in 48-h-activated macrophages. On the other hand, macrophages incubated with 10 to 10(3) U of rIFN-gamma exhibited enhanced fusion of lysosomes to Salmonella-containing phagosomes in both the 12-h- and 48-h-stimulated stages. Moreover, when 48-h-activated macrophages were incubated concomitantly with superoxide dismutase and catalase, Salmonella-killing activity was not affected. These results indicate that rIFN-gamma per se is able to activate peritoneal macrophages to induce Salmonella-killing activity and suggest that increased phagosome-lysosome fusion followed by an oxygen-independent killing mechanism is primarily responsible for the enhanced Salmonella-killing activity in rIFN-gamma-activated macrophages.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong J. A., Hart P. D. Response of cultured macrophages to Mycobacterium tuberculosis, with observations on fusion of lysosomes with phagosomes. J Exp Med. 1971 Sep 1;134(3 Pt 1):713–740. doi: 10.1084/jem.134.3.713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baehner R. L., Murrmann S. K., Davis J., Johnston R. B., Jr The role of superoxide anion and hydrogen peroxide in phagocytosis-associated oxidative metabolic reactions. J Clin Invest. 1975 Sep;56(3):571–576. doi: 10.1172/JCI108126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaman L., Benjamini E., Pappagianis D. Activation of macrophages by lymphokines: enhancement of phagosome-lysosome fusion and killing of Coccidioides immitis. Infect Immun. 1983 Mar;39(3):1201–1207. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.3.1201-1207.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black C. M., Catterall J. R., Remington J. S. In vivo and in vitro activation of alveolar macrophages by recombinant interferon-gamma. J Immunol. 1987 Jan 15;138(2):491–495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brummer E., Morrison C. J., Stevens D. A. Recombinant and natural gamma-interferon activation of macrophages in vitro: different dose requirements for induction of killing activity against phagocytizable and nonphagocytizable fungi. Infect Immun. 1985 Sep;49(3):724–730. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.3.724-730.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrol M. E., Jackett P. S., Aber V. R., Lowrie D. B. Phagolysosome formation, cyclic adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate and the fate of Salmonella typhimurium within mouse peritoneal macrophages. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 Feb;110(2):421–429. doi: 10.1099/00221287-110-2-421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catterall J. R., Sharma S. D., Remington J. S. Oxygen-independent killing by alveolar macrophages. J Exp Med. 1986 May 1;163(5):1113–1131. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.5.1113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M., Mackaness G. B. Delayed hypersensitivity and arthus reactivity in relation to host resistance in salmonella-infected mice. J Immunol. 1968 Nov;101(5):830–845. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M. Vaccines and cell-mediated immunity. Bacteriol Rev. 1974 Dec;38(4):371–402. doi: 10.1128/br.38.4.371-402.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelson P. J., Erbs C. Biochemical and functional characteristics of the plasma membrane of macrophages from BCG-infected mice. J Immunol. 1978 May;120(5):1532–1536. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenstein T. K., Killar L. M., Sultzer B. M. Immunity to infection with Salmonella typhimurium: mouse-strain differences in vaccine- and serum-mediated protection. J Infect Dis. 1984 Sep;150(3):425–435. doi: 10.1093/infdis/150.3.425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flesch I. E., Kaufmann S. H. Attempts to characterize the mechanisms involved in mycobacterial growth inhibition by gamma-interferon-activated bone marrow macrophages. Infect Immun. 1988 Jun;56(6):1464–1469. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.6.1464-1469.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flesch I., Kaufmann S. H. Mycobacterial growth inhibition by interferon-gamma-activated bone marrow macrophages and differential susceptibility among strains of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Immunol. 1987 Jun 15;138(12):4408–4413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukazawa Y., Kagaya K., Ishibashi Y. Effect of delayed-type hypersensitivity reaction and transferred lymphokine on the resistance of mice to Salmonella typhimurium infection. Infect Immun. 1983 Feb;39(2):986–989. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.2.986-989.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray P. W., Goeddel D. V. Cloning and expression of murine immune interferon cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(19):5842–5846. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.19.5842. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn H., Kaufmann S. H. The role of cell-mediated immunity in bacterial infections. Rev Infect Dis. 1981 Nov-Dec;3(6):1221–1250. doi: 10.1093/clinids/3.6.1221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibbs J. B., Jr, Taintor R. R., Chapman H. A., Jr, Weinberg J. B. Macrophage tumor killing: influence of the local environment. Science. 1977 Jul 15;197(4300):279–282. doi: 10.1126/science.327547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochadel J. F., Keller K. F. Protective effects of passively transferred immune T- or B-lymphocytes in mice infected with Salmonella typhimurium. J Infect Dis. 1977 May;135(5):813–823. doi: 10.1093/infdis/135.5.813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoover D. L., Finbloom D. S., Crawford R. M., Nacy C. A., Gilbreath M., Meltzer M. S. A lymphokine distinct from interferon-gamma that activates human monocytes to kill Leishmania donovani in vitro. J Immunol. 1986 Feb 15;136(4):1329–1333. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz M. A. The Legionnaires' disease bacterium (Legionella pneumophila) inhibits phagosome-lysosome fusion in human monocytes. J Exp Med. 1983 Dec 1;158(6):2108–2126. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.6.2108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Killar L. M., Eisenstein T. K. Delayed-type hypersensitivity and immunity to Salmonella typhimurium. Infect Immun. 1986 May;52(2):504–508. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.2.504-508.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. C., Rebar L., Young P., Ruscetti F. W., Hanna N., Poste G. Identification and characterization of a human T cell line-derived lymphokine with MAF-like activity distinct from interferon-gamma. J Immunol. 1986 Feb 15;136(4):1322–1328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lissner C. R., Swanson R. N., O'Brien A. D. Genetic control of the innate resistance of mice to Salmonella typhimurium: expression of the Ity gene in peritoneal and splenic macrophages isolated in vitro. J Immunol. 1983 Dec;131(6):3006–3013. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackaness G. B. Resistance to intracellular infection. J Infect Dis. 1971 Apr;123(4):439–445. doi: 10.1093/infdis/123.4.439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mor N., Goren M. B. Discrepancy in assessment of phagosome-lysosome fusion with two lysosomal markers in murine macrophages infected with Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1987 Jul;55(7):1663–1667. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.7.1663-1667.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray H. W., Byrne G. I., Rothermel C. D., Cartelli D. M. Lymphokine enhances oxygen-independent activity against intracellular pathogens. J Exp Med. 1983 Jul 1;158(1):234–239. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.1.234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray H. W. Pretreatment with phorbol myristate acetate inhibits macrophage activity against intracellular protozoa. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1982 Jun;31(6):479–487. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray H. W., Spitalny G. L., Nathan C. F. Activation of mouse peritoneal macrophages in vitro and in vivo by interferon-gamma. J Immunol. 1985 Mar;134(3):1619–1622. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nacy C. A., James S. L., Benjamin W. R., Farrar J. J., Hockmeyer W. T., Meltzer M. S. Activation of macrophages for microbicidal and tumoricidal effector functions by soluble factors from EL-4, a continuous T cell line. Infect Immun. 1983 May;40(2):820–824. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.2.820-824.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F., Murray H. W., Wiebe M. E., Rubin B. Y. Identification of interferon-gamma as the lymphokine that activates human macrophage oxidative metabolism and antimicrobial activity. J Exp Med. 1983 Sep 1;158(3):670–689. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.3.670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ornellas E. P., Roantree R. J., Steward J. P. The specificity and importance of humoral antibody in the protection of mice against intraperitoneal challenge with complement-sensitive and complement-resistant Salmonella. J Infect Dis. 1970 Feb;121(2):113–123. doi: 10.1093/infdis/121.2.113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pace J. L., Russell S. W., Torres B. A., Johnson H. M., Gray P. W. Recombinant mouse gamma interferon induces the priming step in macrophage activation for tumor cell killing. J Immunol. 1983 May;130(5):2011–2013. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pick E., Keisari Y. A simple colorimetric method for the measurement of hydrogen peroxide produced by cells in culture. J Immunol Methods. 1980;38(1-2):161–170. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90340-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plant J., Glynn A. A. Genetics of resistance to infection with Salmonella typhimurium in mice. J Infect Dis. 1976 Jan;133(1):72–78. doi: 10.1093/infdis/133.1.72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothermel C. D., Rubin B. Y., Jaffe E. A., Murray H. W. Oxygen-independent inhibition of intracellular Chlamydia psittaci growth by human monocytes and interferon-gamma-activated macrophages. J Immunol. 1986 Jul 15;137(2):689–692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber R. D., Hicks L. J., Celada A., Buchmeier N. A., Gray P. W. Monoclonal antibodies to murine gamma-interferon which differentially modulate macrophage activation and antiviral activity. J Immunol. 1985 Mar;134(3):1609–1618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Dissel J. T., Stikkelbroeck J. J., Michel B. C., van den Barselaar M. T., Leijh P. C., van Furth R. Inability of recombinant interferon-gamma to activate the antibacterial activity of mouse peritoneal macrophages against Listeria monocytogenes and Salmonella typhimurium. J Immunol. 1987 Sep 1;139(5):1673–1678. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




