Abstract
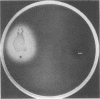
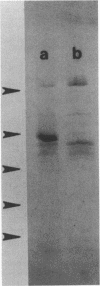
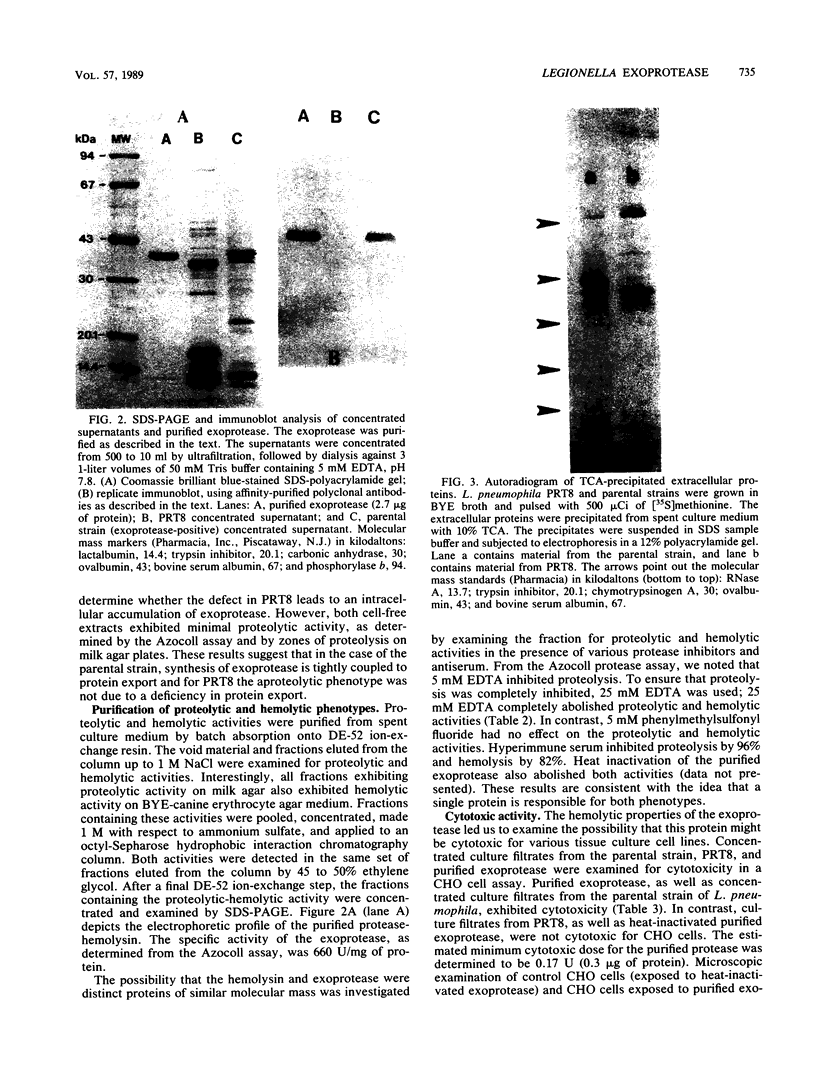
A preliminary screening of selected Legionella species for proteolytic and hemolytic phenotypes suggested a correlation between these activities. To investigate the relationship of these phenotypes, a mutant strain of Legionella pneumophila deficient in the expression of a 38-kilodalton (kDa) exoprotease was isolated and characterized. This strain, designated PRT8, was also found to be nonhemolytic when screened on blood agar composed of 5% canine or guinea pig erythrocytes. Strain PRT8 was serologically and biochemically identical to the parental strain with the exception of the expression of the exoprotease. Immunoblot analysis of concentrated culture filtrates from PRT8 probed with polyclonal anti-38-kDa exoprotease serum revealed no cross-reactive peptides. To resolve the role of the exoprotease in the hemolytic phenotype, the exoprotease was purified from the culture supernatant of the parental strain by a combination of ion-exchange and hydrophobic interaction chromatography steps. The hemolytic activity was found to copurify with the proteolytic activity, and analyses by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and immunoblot revealed a single protein species exhibiting an apparent molecular mass of 38 kDa. Finally, the purified exoprotease and concentrated culture supernatant from the parental strain, but not from PRT8, exhibited cytotoxicity (minimum cytotoxic activity of 0.17 U of protease activity) in a Chinese hamster ovary cell assay. These data suggest that the exoprotease is responsible for the hemolytic and cytotoxic phenotypes described for this species and therefore may be one of several determinants associated with virulence.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baskerville A., Conlan J. W., Ashworth L. A., Dowsett A. B. Pulmonary damage caused by a protease from Legionella pneumophila. Br J Exp Pathol. 1986 Aug;67(4):527–536. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berdal B. P., Olsvik O., Ogaard A. A. A heat-labile necrotic activity in supernatants from cultures of Legionella pneumophila. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand B. 1982 Apr;90(2):169–171. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1982.tb00100.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conlan J. W., Baskerville A., Ashworth L. A. Separation of Legionella pneumophila proteases and purification of a protease which produces lesions like those of Legionnaires' disease in guinea pig lung. J Gen Microbiol. 1986 Jun;132(6):1565–1574. doi: 10.1099/00221287-132-6-1565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conlan J. W., Williams A., Ashworth L. A. In vivo production of a tissue-destructive protease by Legionella pneumophila in the lungs of experimentally infected guinea-pigs. J Gen Microbiol. 1988 Jan;134(1):143–149. doi: 10.1099/00221287-134-1-143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyfus L. A., Iglewski B. H. Purification and characterization of an extracellular protease of Legionella pneumophila. Infect Immun. 1986 Mar;51(3):736–743. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.3.736-743.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Perlmann P. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, Elisa. 3. Quantitation of specific antibodies by enzyme-labeled anti-immunoglobulin in antigen-coated tubes. J Immunol. 1972 Jul;109(1):129–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields B. S., Barbaree J. M., Shotts E. B., Jr, Feeley J. C., Morrill W. E., Sanden G. N., Dykstra M. J. Comparison of guinea pig and protozoan models for determining virulence of Legionella species. Infect Immun. 1986 Sep;53(3):553–559. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.3.553-559.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman R. L., Iglewski B. H., Miller R. D. Identification of a cytotoxin produced by Legionella pneumophila. Infect Immun. 1980 Jul;29(1):271–274. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.1.271-274.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gul'nik S. V., Yusupova M. P., Lavrenova G. I., Tartakovsky I. S., Prozorovsky S. V., Stepanov V. M. Proteinases of Legionella: phenylalanineaminopeptidase of L. pneumophila. J Gen Microbiol. 1986 Feb;132(2):387–392. doi: 10.1099/00221287-132-2-387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedlund K. W. Legionella toxin. Pharmacol Ther. 1981;15(1):123–130. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(81)90021-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iglewski B. H., Sadoff J. C. Toxin inhibitors of protein synthesis: production, purification, and assay of Pseudomonas aeruginosa toxin A. Methods Enzymol. 1979;60:780–793. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(79)60071-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keen M. G., Street E. D., Hoffman P. S. Broad-host-range plasmid pRK340 delivers Tn5 into the Legionella pneumophila chromosome. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jun;162(3):1332–1335. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.3.1332-1335.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenard J. Protein components of erythrocyte membranes from different animal species. Biochemistry. 1970 Dec 8;9(25):5037–5040. doi: 10.1021/bi00827a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McHugh G. L., Swartz M. N. Elimination of plasmids from several bacterial species by novobiocin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Sep;12(3):423–426. doi: 10.1128/aac.12.3.423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olmsted J. B. Affinity purification of antibodies from diazotized paper blots of heterogeneous protein samples. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 10;256(23):11955–11957. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasculle A. W., Feeley J. C., Gibson R. J., Cordes L. G., Myerowitz R. L., Patton C. M., Gorman G. W., Carmack C. L., Ezzell J. W., Dowling J. N. Pittsburgh pneumonia agent: direct isolation from human lung tissue. J Infect Dis. 1980 Jun;141(6):727–732. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.6.727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne N. R., Horwitz M. A. Phagocytosis of Legionella pneumophila is mediated by human monocyte complement receptors. J Exp Med. 1987 Nov 1;166(5):1377–1389. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.5.1377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamm L. V., Bassford P. J., Jr Cellular and extracellular protein antigens of Treponema pallidum synthesized during in vitro incubation of freshly extracted organisms. Infect Immun. 1985 Mar;47(3):799–807. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.3.799-807.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thacker W. L., Wilkinson H. W., Plikaytis B. B., Steigerwalt A. G., Mayberry W. R., Moss C. W., Brenner D. J. Second serogroup of Legionella feeleii strains isolated from humans. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jul;22(1):1–4. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.1.1-4.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson M. R., Miller R. D., Iglewski B. H. In vitro production of an extracellular protease by Legionella pneumophila. Infect Immun. 1981 Oct;34(1):299–302. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.1.299-302.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorpe T. C., Miller R. D. Extracellular enzymes of Legionella pneumophila. Infect Immun. 1981 Aug;33(2):632–635. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.2.632-635.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinbaum D. L., Benner R. R., Dowling J. N., Alpern A., Pasculle A. W., Donowitz G. R. Interaction of Legionella micdadei with human monocytes. Infect Immun. 1984 Oct;46(1):68–73. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.1.68-73.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams A., Baskerville A., Dowsett A. B., Conlan J. W. Immunocytochemical demonstration of the association between Legionella pneumophila, its tissue-destructive protease, and pulmonary lesions in experimental legionnaires' disease. J Pathol. 1987 Nov;153(3):257–264. doi: 10.1002/path.1711530310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winn W. C., Jr, Myerowitz R. L. The pathology of the Legionella pneumonias. A review of 74 cases and the literature. Hum Pathol. 1981 May;12(5):401–422. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(81)80021-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]