Abstract
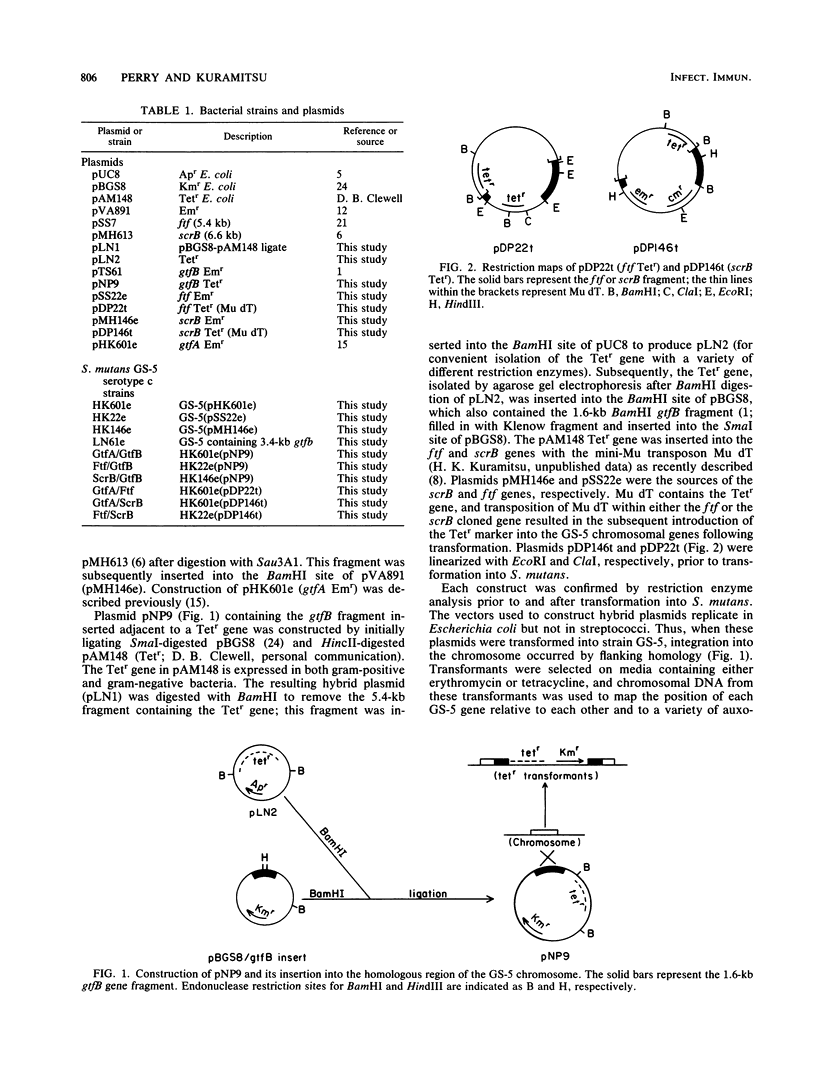
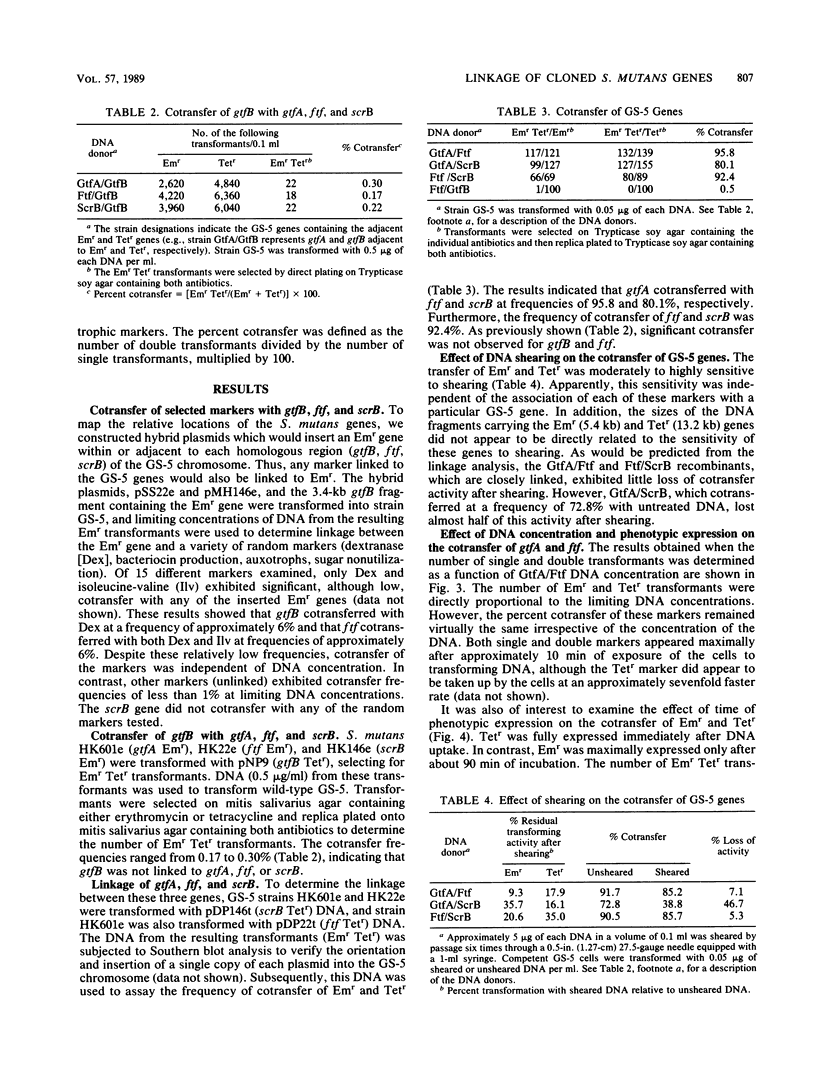
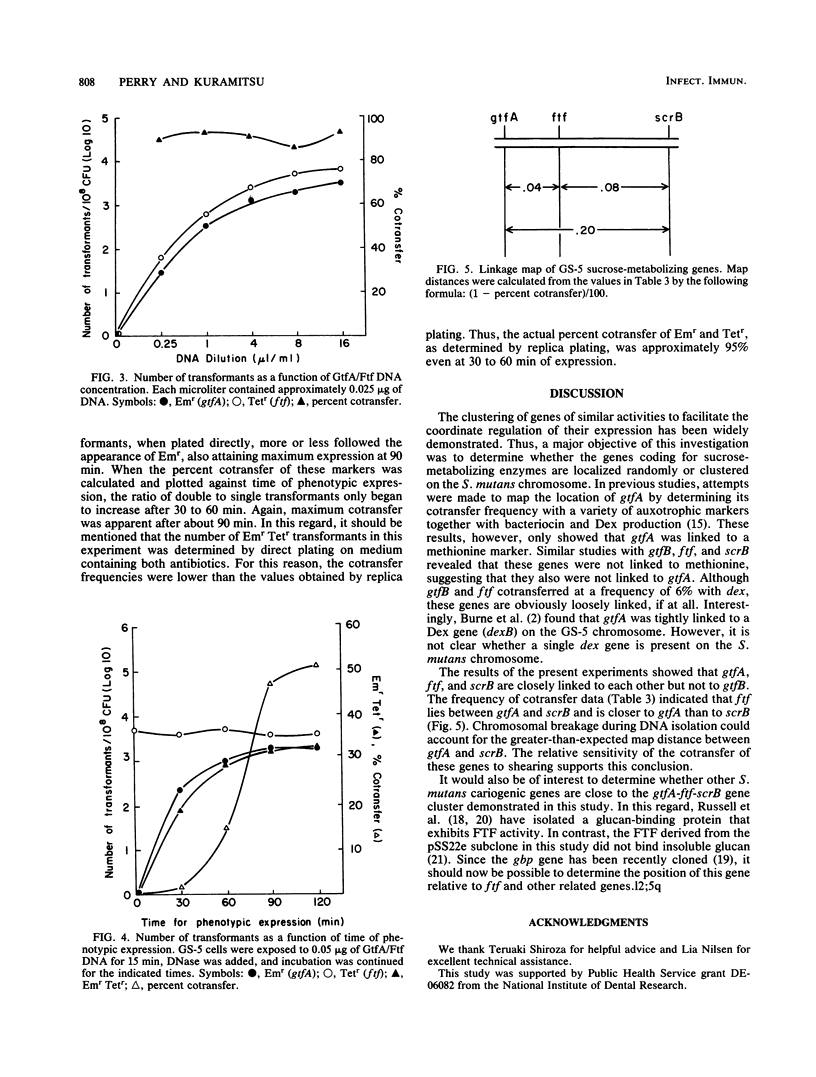
Mapping vectors containing antibiotic resistance markers inserted adjacent to or within different cloned genes from Streptococcus mutans were used to determine the relative positions of these genes on the chromosome. The gtfA, ftf, and scrB genes were inserted into streptococcal mapping vector pVA891 adjacent to an Emr gene, whereas the Emr marker was inserted directly into the gtfB gene. These chimeric plasmids were transformed into S. mutans GS-5, selecting for Emr transformants. To determine the positions of the cloned genes relative to each other, it was necessary to construct plasmids labeled with a different antibiotic resistance marker. Thus, a Tetr gene was inserted adjacent to gtfB in the appropriate mapping vector and within the ftf and scrB genes with a mini-Mu transposon (Mu dT). The chimeric plasmids were transformed into the appropriate Emr recipients, and the DNA from the resulting Emr Tetr transformants was used in linkage studies. Based on the cotransfer data, gtfB was not closely linked to gtfA, ftf, or scrB. However, gtfA cotransferred with ftf and scrB at frequencies of approximately 96 and 80%, respectively. The percent cotransfer of ftf and scrB was approximately 92. These data indicate that the three genes are clustered on the GS-5 chromosome, with ftf located between gtfA and scrB. Little, if any, linkage was observed between these genes and a variety of other random markers.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aoki H., Shiroza T., Hayakawa M., Sato S., Kuramitsu H. K. Cloning of a Streptococcus mutans glucosyltransferase gene coding for insoluble glucan synthesis. Infect Immun. 1986 Sep;53(3):587–594. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.3.587-594.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burne R. A., Rubinfeld B., Bowen W. H., Yasbin R. E. Tight genetic linkage of a glucosyltransferase and dextranase of Streptococcus mutans GS-5. J Dent Res. 1986 Dec;65(12):1392–1401. doi: 10.1177/00220345860650120301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chassy B. M., Porter E. V. Initial characterization of sucrose-6-phosphate hydrolase from Streptococcus mutans and its apparent identity with intracellular invertase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Jul 12;89(1):307–314. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)90979-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamada S., Slade H. D. Biology, immunology, and cariogenicity of Streptococcus mutans. Microbiol Rev. 1980 Jun;44(2):331–384. doi: 10.1128/mr.44.2.331-384.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanna Z., Fregeau C., Préfontaine G., Brousseau R. Construction of a family of universal expression plasmid vectors. Gene. 1984 Oct;30(1-3):247–250. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90128-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayakawa M., Aoki H., Kuramitsu H. K. Isolation and characterization of the sucrose 6-phosphate hydrolase gene from Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1986 Sep;53(3):582–586. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.3.582-586.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue M., Koga T., Sato S., Hamada S. Synthesis of adherent insoluble glucan by the concerted action of the two glucosyltransferase components of Streptococcus mutans. FEBS Lett. 1982 Jun 21;143(1):101–104. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80282-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuramitsu H. K. Recent advances in defining the cariogenicity of mutans streptococci: molecular genetic approaches. Eur J Epidemiol. 1987 Sep;3(3):257–260. doi: 10.1007/BF00149733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuramitsu H. K. Utilization of a mini-mu transposon to construct defined mutants in Streptococcus mutans. Mol Microbiol. 1987 Sep;1(2):229–232. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1987.tb00516.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuramitsu H. K., Wondrack L. Insoluble glucan synthesis by Streptococcus mutans serotype c strains. Infect Immun. 1983 Nov;42(2):763–770. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.2.763-770.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loesche W. J. Role of Streptococcus mutans in human dental decay. Microbiol Rev. 1986 Dec;50(4):353–380. doi: 10.1128/mr.50.4.353-380.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macrina F. L., Jones K. R., Wood P. H. Chimeric streptococcal plasmids and their use as molecular cloning vehicles in Streptococcus sanguis (Challis). J Bacteriol. 1980 Sep;143(3):1425–1435. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.3.1425-1435.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukasa H., Tsumori H., Shimamura A. Isolation and characterization of an extracellular glucosyltransferase synthesizing insoluble glucan from Streptococcus mutans serotype c. Infect Immun. 1985 Sep;49(3):790–796. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.3.790-796.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry D., Nilsen L. J., Kuramitsu H. K. Mapping of a cloned glucosyltransferase gene in Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1985 Oct;50(1):130–135. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.1.130-135.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pucci M. J., Macrina F. L. Cloned gtfA gene of Streptococcus mutans LM7 alters glucan synthesis in Streptococcus sanguis. Infect Immun. 1985 Jun;48(3):704–712. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.3.704-712.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robeson J. P., Barletta R. G., Curtiss R., 3rd Expression of a Streptococcus mutans glucosyltransferase gene in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):211–221. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.211-221.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell R. R., Coleman D., Dougan G. Expression of a gene for glucan-binding protein from Streptococcus mutans in Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1985 Feb;131(2):295–299. doi: 10.1099/00221287-131-2-295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell R. R., Donald A. C., Douglas C. W. Fructosyltransferase activity of a glucan-binding protein from Streptococcus mutans. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Oct;129(10):3243–3250. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-10-3243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell R. R. Glucan-binding proteins of Streptococcus mutans serotype c. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 May;112(1):197–201. doi: 10.1099/00221287-112-1-197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato S., Kuramitsu H. K. Isolation and characterization of a fructosyltransferase gene from Streptococcus mutans GS-5. Infect Immun. 1986 Apr;52(1):166–170. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.1.166-170.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schachtele C. F., Loken A. E., Schmitt M. K. Use of specifically labeled sucrose for comparison of extracellular glucan and fructan metabolism by oral streptococci. Infect Immun. 1972 Feb;5(2):263–266. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.2.263-266.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spratt B. G., Hedge P. J., te Heesen S., Edelman A., Broome-Smith J. K. Kanamycin-resistant vectors that are analogues of plasmids pUC8, pUC9, pEMBL8 and pEMBL9. Gene. 1986;41(2-3):337–342. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90117-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Martin E. J., Wittenberger C. L. Characterization of a phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent sucrose phosphotransferase system in Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1979 Jun;24(3):865–868. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.3.865-868.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



