Abstract
Increased sensitivity to killing by human serum complement occurs in Salmonella typhimurium strains in which the 95-kilobase virulence plasmid is integrated into the chromosome. This phenotypic change appears to be due to alterations in plasmid gene expression and is reversed by the presence of an autonomous plasmid bearing a cloned region of the virulence plasmid. Accordingly, this region has been termed rsk for reduced serum killing. Sequence analysis of the region reveals that rsk is composed of a series of direct 10-base-pair (bp) repeats with a 21-nucleotide periodicity. Two adjacent repeats are identical, but increasing loss of conservation is apparent with increased distance both 5' and 3' of these highly conserved 10-mers. The smallest isolated sequence which restores the serum-resistant phenotype is only 66 bp long and contains the two identical 10-mers and one degenerate 10-mer (8 of 10 bp conserved) 3' of these. The minimal rsk region of 66 bp does not appear to contain a coding sequence, or a promoter, for a structural gene. It is proposed that the minimal rsk is an isolated regulatory site involved in the regulation of the serum resistance of S. typhimurium. Integration of the 95-kilobase plasmid disrupts the normal regulation of virulence plasmid genes, resulting in an increase in the killing of the bacteria by complement activated by the classical pathway. The introduction of the minimal rsk on a multiple-copy plasmid restores resistance to serum killing, possibly through the titration of a trans-acting regulatory factor.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abeles A. L., Snyder K. M., Chattoraj D. K. P1 plasmid replication: replicon structure. J Mol Biol. 1984 Mar 5;173(3):307–324. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90123-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Backhaus H., Petri J. B. Sequence analysis of a region from the early right operon in phage P22 including the replication genes 18 and 12. Gene. 1984 Dec;32(3):289–303. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90004-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baird G. D., Manning E. J., Jones P. W. Evidence for related virulence sequences in plasmids of Salmonella dublin and Salmonella typhimurium. J Gen Microbiol. 1985 Jul;131(7):1815–1823. doi: 10.1099/00221287-131-7-1815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckingham K. A plasmid cloning vector for Kpnl-cleaved DNA. Plasmid. 1980 Nov;4(3):354–356. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(80)90074-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dandanell G., Hammer K. Two operator sites separated by 599 base pairs are required for deoR repression of the deo operon of Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 1;4(12):3333–3338. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04085.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dlabac V. The sensitivity of smooth and rough mutants of Salmonella typhimurium to bactericidal and bacteriolytic action of serum, lysozyme and to phagocytosis. Folia Microbiol (Praha) 1968;13(5):439–449. doi: 10.1007/BF02869196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorman C. J., Barr G. C., Ni Bhriain N., Higgins C. F. DNA supercoiling and the anaerobic and growth phase regulation of tonB gene expression. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jun;170(6):2816–2826. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.6.2816-2826.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn T. M., Hahn S., Ogden S., Schleif R. F. An operator at -280 base pairs that is required for repression of araBAD operon promoter: addition of DNA helical turns between the operator and promoter cyclically hinders repression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(16):5017–5020. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.16.5017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Tjian R. The promoter-specific transcription factor Sp1 binds to upstream sequences in the SV40 early promoter. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):79–87. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90210-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gulig P. A., Curtiss R., 3rd Plasmid-associated virulence of Salmonella typhimurium. Infect Immun. 1987 Dec;55(12):2891–2901. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.12.2891-2901.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackett J., Kotlarski I., Mathan V., Francki K., Rowley D. The colonization of Peyer's patches by a strain of Salmonella typhimurium cured of the cryptic plasmid. J Infect Dis. 1986 Jun;153(6):1119–1125. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.6.1119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackett J., Wyk P., Reeves P., Mathan V. Mediation of serum resistance in Salmonella typhimurium by an 11-kilodalton polypeptide encoded by the cryptic plasmid. J Infect Dis. 1987 Mar;155(3):540–549. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.3.540. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helmuth R., Stephan R., Bunge C., Hoog B., Steinbeck A., Bulling E. Epidemiology of virulence-associated plasmids and outer membrane protein patterns within seven common Salmonella serotypes. Infect Immun. 1985 Apr;48(1):175–182. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.1.175-182.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins C. F., Dorman C. J., Stirling D. A., Waddell L., Booth I. R., May G., Bremer E. A physiological role for DNA supercoiling in the osmotic regulation of gene expression in S. typhimurium and E. coli. Cell. 1988 Feb 26;52(4):569–584. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90470-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho Y. S., Wulff D. L., Rosenberg M. Bacteriophage lambda protein cII binds promoters on the opposite face of the DNA helix from RNA polymerase. Nature. 1983 Aug 25;304(5928):703–708. doi: 10.1038/304703a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irani M. H., Orosz L., Adhya S. A control element within a structural gene: the gal operon of Escherichia coli. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):783–788. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90064-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones G. W., Rabert D. K., Svinarich D. M., Whitfield H. J. Association of adhesive, invasive, and virulent phenotypes of Salmonella typhimurium with autonomous 60-megadalton plasmids. Infect Immun. 1982 Nov;38(2):476–486. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.2.476-486.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kado C. I., Liu S. T. Rapid procedure for detection and isolation of large and small plasmids. J Bacteriol. 1981 Mar;145(3):1365–1373. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.3.1365-1373.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitagawa Y., Akaboshi E., Shinagawa H., Horii T., Ogawa H., Kato T. Structural analysis of the umu operon required for inducible mutagenesis in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4336–4340. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krikos A., Mutoh N., Boyd A., Simon M. I. Sensory transducers of E. coli are composed of discrete structural and functional domains. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):615–622. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90442-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krämer H., Niemöller M., Amouyal M., Revet B., von Wilcken-Bergmann B., Müller-Hill B. lac repressor forms loops with linear DNA carrying two suitably spaced lac operators. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1481–1491. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02390.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majumdar A., Adhya S. Demonstration of two operator elements in gal: in vitro repressor binding studies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(19):6100–6104. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.19.6100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pal S. K., Chattoraj D. K. P1 plasmid replication: initiator sequestration is inadequate to explain control by initiator-binding sites. J Bacteriol. 1988 Aug;170(8):3554–3560. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.8.3554-3560.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardon P., Popoff M. Y., Coynault C., Marly J., Miras I. Virulence-associated plasmids of Salmonella serotype Typhimurium in experimental murine infection. Ann Inst Pasteur Microbiol. 1986 Jul-Aug;137B(1):47–60. doi: 10.1016/s0769-2609(86)80093-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M. Gene regulation by proteins acting nearby and at a distance. Nature. 1986 Aug 21;322(6081):697–701. doi: 10.1038/322697a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reitzer L. J., Magasanik B. Transcription of glnA in E. coli is stimulated by activator bound to sites far from the promoter. Cell. 1986 Jun 20;45(6):785–792. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90553-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spratt B. G., Rowbury R. J. The plasmid of Salmonella typhimurium LT2. Mol Gen Genet. 1973 Mar 19;121(4):347–353. doi: 10.1007/BF00433233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi K., Vigneron M., Matthes H., Wildeman A., Zenke M., Chambon P. Requirement of stereospecific alignments for initiation from the simian virus 40 early promoter. Nature. 1986 Jan 9;319(6049):121–126. doi: 10.1038/319121a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
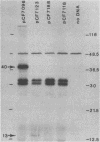
- Tsutsui H., Fujiyama A., Murotsu T., Matsubara K. Role of nine repeating sequences of the mini-F genome for expression of F-specific incompatibility phenotype and copy number control. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jul;155(1):337–344. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.1.337-344.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandenbosch J. L., Rabert D. K., Jones G. W. Plasmid-associated resistance of Salmonella typhimurium to complement activated by the classical pathway. Infect Immun. 1987 Nov;55(11):2645–2652. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.11.2645-2652.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]