Abstract
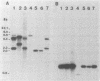
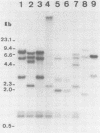
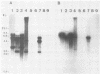
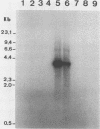
A number of DNA probes which hybridize to highly abundant DNA sequences of Entamoeba histolytica were developed. Variations in the hybridization patterns of different E. histolytica strains were detected with selected probes. Four types of restriction fragment length patterns were obtained. Of these, the first class belonged to E. invadens and E. histolytica-like var. Laredo. The next two classes consisted of various strains of E. histolytica which were originally isolated from symptomatic patients and possessed pathogenic patterns of isoenzymes (zymodemes), whereas the fourth group contained E. histolytica strains with nonpathogenic zymodemes obtained from asymptomatic carriers. DNA probes, based on DNA sequences specific to E. histolytica isolates with pathogenic and nonpathogenic zymodemes were isolated, and their nucleotide sequences were determined. These probes (P145 and B133) hybridized selectively to DNA of isolates possessing either pathogenic or nonpathogenic isoenzyme patterns. The newly developed probes could be useful for diagnostic purposes and could serve as tools to investigate the molecular basis of pathogenicity and the genetic mechanisms which regulate the variable aggressive behavior of the parasite.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bhattacharya S., Bhattacharya A., Diamond L. S. Comparison of repeated DNA from strains of Entamoeba histolytica and other Entamoeba. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1988 Jan 15;27(2-3):257–262. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(88)90045-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond L. S. A new liquid medium for xenic cultivation of Entamoeba histolytica and other lumen-dwelling protozoa. J Parasitol. 1982 Oct;68(5):958–959. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond L. S., Harlow D. R., Cunnick C. C. A new medium for the axenic cultivation of Entamoeba histolytica and other Entamoeba. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1978;72(4):431–432. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(78)90144-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Entner N. "Mating" in Entamoeba histolytica? Nat New Biol. 1971 Aug 25;232(34):256–256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erttmann K. D., Unnasch T. R., Greene B. M., Albiez E. J., Boateng J., Denke A. M., Ferraroni J. J., Karam M., Schulz-Key H., Williams P. N. A DNA sequence specific for forest form Onchocerca volvulus. Nature. 1987 Jun 4;327(6121):415–417. doi: 10.1038/327415a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrant R. L. Amebiasis: introduction, current status, and research questions. Rev Infect Dis. 1986 Mar-Apr;8(2):218–227. doi: 10.1093/clinids/8.2.218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber M., Garfinkel L., Gitler C., Mirelman D., Revel M., Rozenblatt S. Entamoeba histolytica: cloning and characterization of actin cDNA. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1987 Jul;24(3):227–235. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(87)90154-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber M., Koller B., Gitler C., Mirelman D., Revel M., Rozenblatt S., Garfinkel L. Entamoeba histolytica ribosomal RNA genes are carried on palindromic circular DNA molecules. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1989 Jan 15;32(2-3):285–296. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(89)90077-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipman D. J., Pearson W. R. Rapid and sensitive protein similarity searches. Science. 1985 Mar 22;227(4693):1435–1441. doi: 10.1126/science.2983426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macina R. A., Arauzo S., Reyes M. B., Sanchez D. O., Basombrio M. A., Montamat E. E., Solari A., Frasch A. C. Trypanosoma cruzi isolates from Argentina and Chile grouped with the aid of DNA probes. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1987 Aug;25(1):45–53. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(87)90017-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirelman D., Bracha R., Chayen A., Aust-Kettis A., Diamond L. S. Entamoeba histolytica: effect of growth conditions and bacterial associates on isoenzyme patterns and virulence. Exp Parasitol. 1986 Aug;62(1):142–148. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(86)90017-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirelman D., Bracha R., Wexler A., Chayen A. Changes in isoenzyme patterns of a cloned culture of nonpathogenic Entamoeba histolytica during axenization. Infect Immun. 1986 Dec;54(3):827–832. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.3.827-832.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirelman D. Effect of culture conditions and bacterial associates on the zymodemes of Entamoeba histolytica. Parasitol Today. 1987 Feb;3(2):37–37. doi: 10.1016/0169-4758(87)90210-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargeaunt P. G. The reliability of Entamoeba histolytica zymodemes in clinical diagnosis. Parasitol Today. 1987 Feb;3(2):40–37. doi: 10.1016/0169-4758(87)90211-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strachan W. D., Chiodini P. L., Spice W. M., Moody A. H., Ackers J. P. Immunological differentiation of pathogenic and non-pathogenic isolates of Entamoeba histolytica. Lancet. 1988 Mar 12;1(8585):561–563. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)91355-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh J. A. Problems in recognition and diagnosis of amebiasis: estimation of the global magnitude of morbidity and mortality. Rev Infect Dis. 1986 Mar-Apr;8(2):228–238. doi: 10.1093/clinids/8.2.228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wirth D. F., Rogers W. O., Barker R., Jr, Dourado H., Suesebang L., Albuquerque B. Leishmaniasis and malaria: new tools for epidemiologic analysis. Science. 1986 Nov 21;234(4779):975–979. doi: 10.1126/science.3535070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]