Abstract
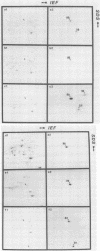
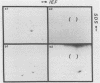
Endotoxic lipopolysaccharide (LPS), a common structural component of all gram-negative bacteria, is well recognized for its capacity to interact with and perturb immunologically relevant cells. Using a radioiodinated, photoactivatable LPS probe, we have recently identified an 80-kilodalton LPS-specific binding protein on murine B lymphocytes. We now have extended these studies to determine if other mammalian species, as well as representative endotoxin-resistant species (frog and chicken), have a similar LPS-binding protein. We have identified what appears to be a relatively conserved 80-kilodalton LPS-binding protein on mononuclear cells of all mammalian species tested. However, both frog and chicken leukocytes failed to show the presence of a similar LPS-binding protein. It is possible that the presence of specific LPS-binding proteins may be important for endotoxin sensitivity of most mammalian species.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson B., Augustinsson O., Holst H., Jónasson H. ACTH-mediated aldosterone hypersecretion during endotoxin-induced fever with apparent influence upon renal sodium excretion. Acta Physiol Scand. 1987 Apr;129(4):451–458. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-201x.1987.tb10617.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumgartner J. D., Glauser M. P., McCutchan J. A., Ziegler E. J., van Melle G., Klauber M. R., Vogt M., Muehlen E., Luethy R., Chiolero R. Prevention of gram-negative shock and death in surgical patients by antibody to endotoxin core glycolipid. Lancet. 1985 Jul 13;2(8446):59–63. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)90176-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berczi I., Bertók L., Bereznai T. Comparative studies on the toxicity of Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharide endotoxin in various animal species. Can J Microbiol. 1966 Oct;12(5):1070–1071. doi: 10.1139/m66-143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Milsark I. W., Cerami A. C. Passive immunization against cachectin/tumor necrosis factor protects mice from lethal effect of endotoxin. Science. 1985 Aug 30;229(4716):869–871. doi: 10.1126/science.3895437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bleicher P. A., Rollins-Smith L. A., Jacobs D. M., Cohen N. Mitogenic responses of frog lymphocytes to crude and purified preparations of bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS). Dev Comp Immunol. 1983 Summer;7(3):483–496. doi: 10.1016/0145-305x(83)90033-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brigham K. L., Meyrick B. Endotoxin and lung injury. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1986 May;133(5):913–927. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A., Cannon J. G., Wolff S. M., Bernheim H. A., Beutler B., Cerami A., Figari I. S., Palladino M. A., Jr, O'Connor J. V. Tumor necrosis factor (cachectin) is an endogenous pyrogen and induces production of interleukin 1. J Exp Med. 1986 Jun 1;163(6):1433–1450. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.6.1433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FINKELSTEIN R. A. OBSERVATIONS ON MODE OF ACTION OF ENDOTOXIN IN CHICK EMBRYOS. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1964 Mar;115:702–707. doi: 10.3181/00379727-115-29012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JORDAN M. M., HINSHAW L. B. SPECIES RESISTANCE TO HISTAMINE AND ENDOTOXIN: THE RESPONSE OF THE CHICKEN. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1964 Feb;115:455–458. doi: 10.3181/00379727-115-28940. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lei M. G., Morrison D. C. Specific endotoxic lipopolysaccharide-binding proteins on murine splenocytes. I. Detection of lipopolysaccharide-binding sites on splenocytes and splenocyte subpopulations. J Immunol. 1988 Aug 1;141(3):996–1005. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lei M. G., Morrison D. C. Specific endotoxic lipopolysaccharide-binding proteins on murine splenocytes. II. Membrane localization and binding characteristics. J Immunol. 1988 Aug 1;141(3):1006–1011. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyrick B., Brigham K. L. Acute effects of Escherichia coli endotoxin on the pulmonary microcirculation of anesthetized sheep structure:function relationships. Lab Invest. 1983 Apr;48(4):458–470. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michie H. R., Manogue K. R., Spriggs D. R., Revhaug A., O'Dwyer S., Dinarello C. A., Cerami A., Wolff S. M., Wilmore D. W. Detection of circulating tumor necrosis factor after endotoxin administration. N Engl J Med. 1988 Jun 9;318(23):1481–1486. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198806093182301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore J. N., Garner H. E., Shapland J. E., Schaub R. G. Equine endotoxemia: an insight into cause and treatment. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1981 Sep 1;179(5):473–477. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. C., Leive L. Fractions of lipopolysaccharide from Escherichia coli O111:B4 prepared by two extraction procedures. J Biol Chem. 1975 Apr 25;250(8):2911–2919. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. C., Rudbach J. A. Endotoxin-cell-membrane interactions leading to transmembrane signaling. Contemp Top Mol Immunol. 1981;8:187–218. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-3917-5_6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. C., Ryan J. L. Bacterial endotoxins and host immune responses. Adv Immunol. 1979;28:293–450. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60802-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. C., Ryan J. L. Endotoxins and disease mechanisms. Annu Rev Med. 1987;38:417–432. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.38.020187.002221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson N. C. Role of 5-hydroxytryptamine in endotoxin-induced respiratory failure of pigs. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987 Jan;135(1):93–99. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1987.135.1.93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss N., Du Pasquier L. Factors affecting the reactivity of amphibian lymphocytes in a miniaturized technique of the mixed lymphocyte culture. J Immunol Methods. 1973 Nov;3(3):273–285. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(73)90023-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winn R., Maunder R., Chi E., Harlan J. Neutrophil depletion does not prevent lung edema after endotoxin infusion in goats. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1987 Jan;62(1):116–121. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1987.62.1.116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wollenweber H. W., Morrison D. C. Synthesis and biochemical characterization of a photoactivatable, iodinatable, cleavable bacterial lipopolysaccharide derivative. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 5;260(28):15068–15074. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]