Abstract
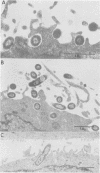
Bordetella parapertussis, a respiratory tract pathogen commonly regarded as noninvasive, was found to invade HeLa 229 cell monolayers. Following treatment of the monolayers with gentamicin, numbers of viable B. parapertussis recovered were comparable to those of invasive Salmonella and Shigella isolates. Invasion occurs through a cytochalasin-sensitive process which appears to be distinct from receptor-mediated endocytosis. Hyperimmune antisera raised against filaments hemagglutinin, a major adhesion of B. pertussis, did not inhibit invasion by B. parapertussis, suggesting that alternate adhesin(s) are required for invasion. In addition, B. parapertussis was found to invade human respiratory epithelial cells in primary culture, as demonstrated in ultrathin sections viewed by transmission electron microscopy. Although viable intracellular B. parapertussis persist within HeLa cells, they do not multiply there and the monolayers remain intact, suggesting a possible mechanism of carriage for these organisms.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRAWFORD J. G., FISHEL C. W. Growth of Bordetella pertussis in tissue culture. J Bacteriol. 1959 Apr;77(4):465–474. doi: 10.1128/jb.77.4.465-474.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheers C., Gray D. F. Macrophage behaviour during the complaisant phase of murine pertussis. Immunology. 1969 Dec;17(6):875–887. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daskaleros P. A., Payne S. M. Cloning the gene for Congo red binding in Shigella flexneri. Infect Immun. 1985 Apr;48(1):165–168. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.1.165-168.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies P. J., Davies D. R., Levitzki A., Maxfield F. R., Milhaud P., Willingham M. C., Pastan I. H. Transglutaminase is essential in receptor-mediated endocytosis of alpha 2-macroglobulin and polypeptide hormones. Nature. 1980 Jan 10;283(5743):162–167. doi: 10.1038/283162a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falkow S., Small P., Isberg R., Hayes S. F., Corwin D. A molecular strategy for the study of bacterial invasion. Rev Infect Dis. 1987 Sep-Oct;9 (Suppl 5):S450–S455. doi: 10.1093/clinids/9.supplement_5.s450. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goudswaard J., van der Donk J. A., Noordzij A., van Dam R. H., Vaerman J. P. Protein A reactivity of various mammalian immunoglobulins. Scand J Immunol. 1978;8(1):21–28. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1978.tb00492.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krantz I., Alestig K., Trollfors B., Zackrisson G. The carrier state in pertussis. Scand J Infect Dis. 1986;18(2):121–123. doi: 10.3109/00365548609032317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LACEY B. W. Antigenic modulation of Bordetella pertussis. J Hyg (Lond) 1960 Mar;58:57–93. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400038134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linnemann C. C., Jr, Bass J. W., Smith M. H. The carrier state in pertussis. Am J Epidemiol. 1968 Nov;88(3):422–427. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchitto K. S., Smith S. G., Locht C., Keith J. M. Nucleotide sequence homology to pertussis toxin gene in Bordetella bronchiseptica and Bordetella parapertussis. Infect Immun. 1987 Mar;55(3):497–501. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.3.497-501.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh M., Helenius A. Adsorptive endocytosis of Semliki Forest virus. J Mol Biol. 1980 Sep 25;142(3):439–454. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90281-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson S., Oxford J. S., Dourmashkin R. R. Studies on the mechanism of influenza virus entry into cells. J Gen Virol. 1979 Apr;43(1):223–229. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-43-1-223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romanus V., Jonsell R., Bergquist S. O. Pertussis in Sweden after the cessation of general immunization in 1979. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1987 Apr;6(4):364–371. doi: 10.1097/00006454-198704000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R., Munoz J., Cameron C. Histamine-sensitizing factor, mouse-protective antigens, and other antigens of some members of the genus Bordetella. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jul;99(1):57–64. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.1.57-64.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato Y., Izumiya K., Sato H., Cowell J. L., Manclark C. R. Role of antibody to leukocytosis-promoting factor hemagglutinin and to filamentous hemagglutinin in immunity to pertussis. Infect Immun. 1981 Mar;31(3):1223–1231. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.3.1223-1231.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlegel R., Dickson R. B., Willingham M. C., Pastan I. H. Amantadine and dansylcadaverine inhibit vesicular stomatitis virus uptake and receptor-mediated endocytosis of alpha 2-macroglobulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(7):2291–2295. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.7.2291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. M., Frasch C. E. A sensitive silver stain for detecting lipopolysaccharides in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 1;119(1):115–119. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90673-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuomanen E., Weiss A. Characterization of two adhesins of Bordetella pertussis for human ciliated respiratory-epithelial cells. J Infect Dis. 1985 Jul;152(1):118–125. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.1.118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urisu A., Cowell J. L., Manclark C. R. Filamentous hemagglutinin has a major role in mediating adherence of Bordetella pertussis to human WiDr cells. Infect Immun. 1986 Jun;52(3):695–701. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.3.695-701.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varughese P. Incidence of pertussis in Canada. Can Med Assoc J. 1985 May 1;132(9):1041–1042. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A. A., Falkow S. Genetic analysis of phase change in Bordetella pertussis. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):263–269. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.263-269.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang N. S., Kube D., Park C., Furmanski P. Growth of human mammary epithelial cells on collagen gel surfaces. Cancer Res. 1981 Oct;41(10):4093–4100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]