Abstract
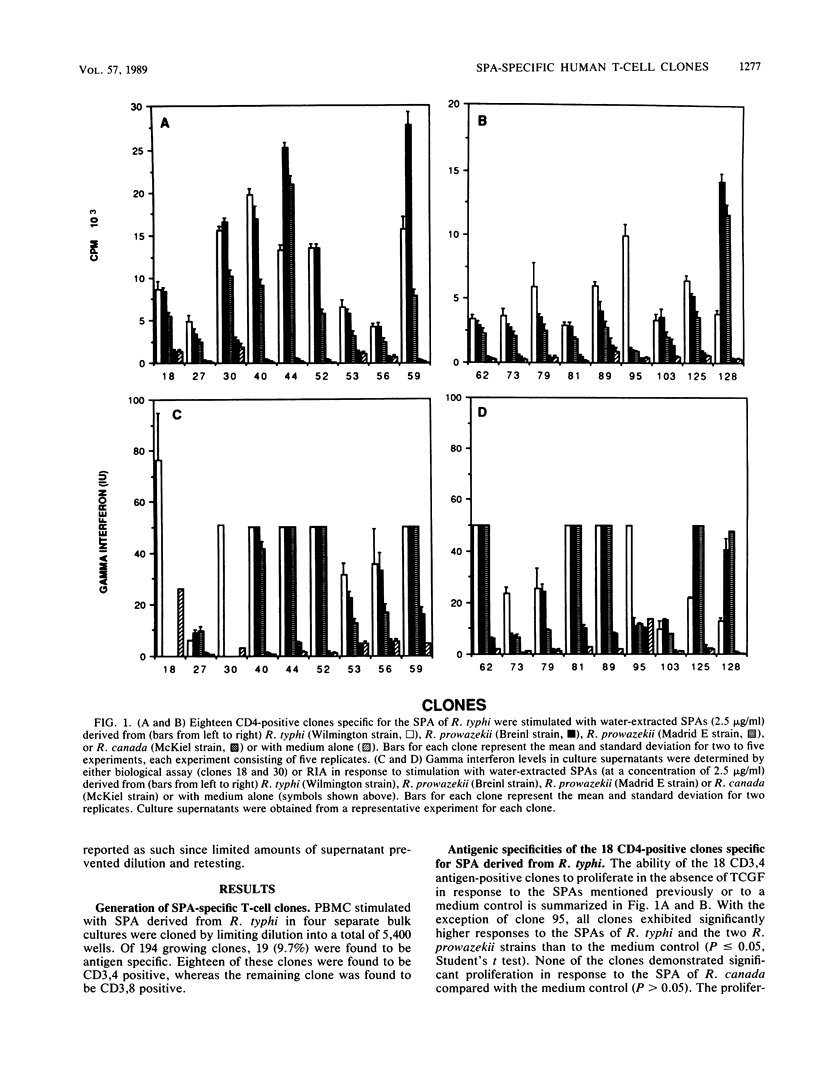
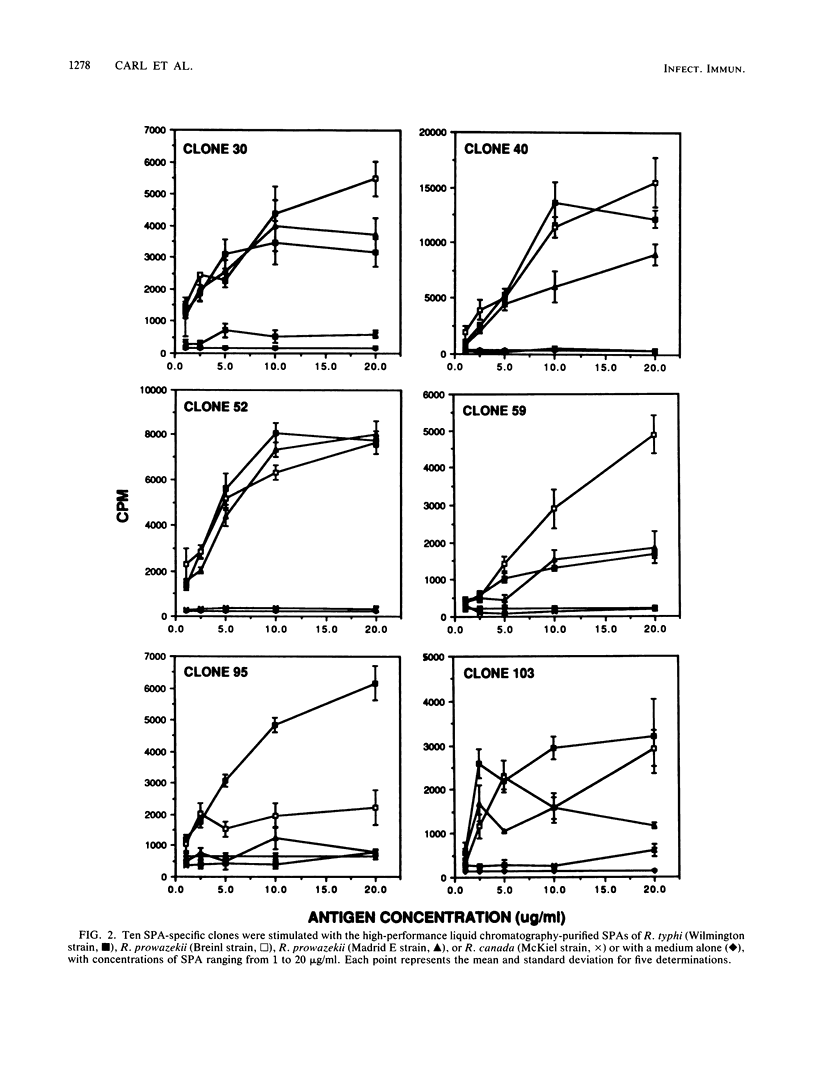
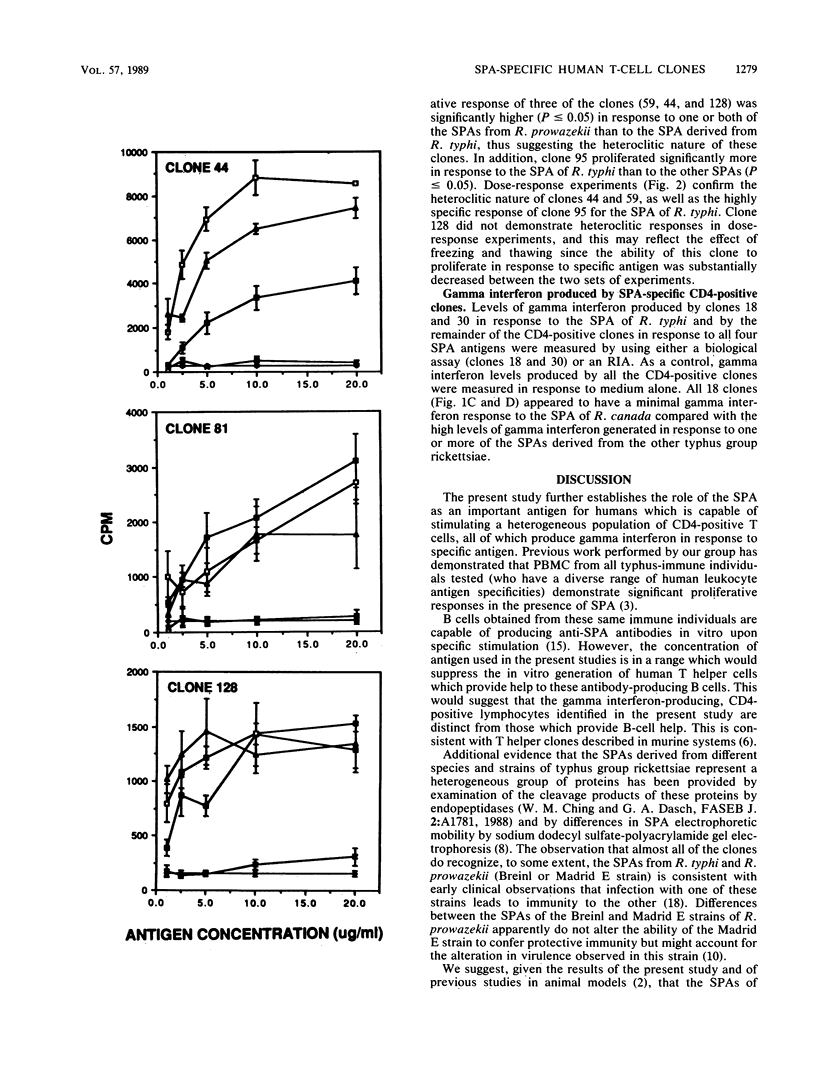
Immunity to the typhus group of rickettsiae is largely dependent on the effector function of several classes of T lymphocytes, including those which produce gamma interferon. Since the surface protein antigen (SPA) derived from typhus group rickettsiae has been shown to be an effective immunogen in animal models, human T-cell clones specific for the SPA of Rickettsia typhi were isolated and tested for their antigenic specificity, as well as for their ability to produce gamma interferon. Eighteen CD4-positive clones specific for the SPA of R. typhi exhibited considerable diversity in their response to the SPAs derived from two strains of Rickettsia prowazekii and from Rickettsia canada. The vast majority of clones also recognized the SPAs from R. prowazekii but not from R. canada. Two heteroclitic clones demonstrated significantly higher proliferative responses to the SPAs derived from one or both of the R. prowazekii strains than to the SPA of R. typhi, and one clone demonstrated a significantly higher response to the SPA of R. typhi than to the other SPAs. All 18 clones produced gamma interferon in response to SPA stimulation. We conclude that the SPAs from typhus group rickettsiae can elicit both a diverse T-cell response in humans and the efficient stimulation of gamma interferon-mediated immunity.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Biddison W. E., Sharrow S. O., Shearer G. M. T cell subpopulations required for the human cytotoxic T lymphocyte response to influenza virus: evidence for T cell help. J Immunol. 1981 Aug;127(2):487–491. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourgeois A. L., Dasch G. A., Strong D. M. In vitro stimulation of human peripheral blood lymphocytes by soluble and membrane fractions of renografin-purified typhus group rickettsiae. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):483–491. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.483-491.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carl M., Dasch G. A. Characterization of human cytotoxic lymphocytes directed against cells infected with typhus group rickettsiae: evidence for lymphokine activation of effectors. J Immunol. 1986 Apr 1;136(7):2654–2661. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carl M., Robbins F. M., Hartzman R. J., Dasch G. A. Lysis of cells infected with typhus group rickettsiae by a human cytotoxic T cell clone. J Immunol. 1987 Dec 15;139(12):4203–4207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherwinski H. M., Schumacher J. H., Brown K. D., Mosmann T. R. Two types of mouse helper T cell clone. III. Further differences in lymphokine synthesis between Th1 and Th2 clones revealed by RNA hybridization, functionally monospecific bioassays, and monoclonal antibodies. J Exp Med. 1987 Nov 1;166(5):1229–1244. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.5.1229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crist A. E., Jr, Wisseman C. L., Jr, Murphy J. R. Characteristics of lymphoid cells that adoptively transfer immunity to Rickettsia mooseri infection in mice. Infect Immun. 1984 Apr;44(1):55–60. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.1.55-60.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Blas A. L., Ratnaparkhi M. V., Mosimann J. E. Estimation of the number of monoclonal hybridomas in a cell-fusion experiment. Methods Enzymol. 1983;92:36–39. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)92007-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOX J. P., JORDAN M. E., GELFAND H. M. Immunization of man against epidemic typhus by infection with avirulent Rickettsia prowazeki strain E. IV. Persistence of immunity and a note as to differing complement-fixation antigen requirements in post-infection and post-vaccination sera. J Immunol. 1957 Oct;79(4):348–354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock W. S., Bishop C. A., Prestidge R. L., Harding D. R., Hearn M. T. Reversed-phase, high-pressure liquid chromatography of peptides and proteins with ion-pairing reagents. Science. 1978 Jun 9;200(4346):1168–1170. doi: 10.1126/science.206966. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb J. R., Eckels D. D., Lake P., Johnson A. H., Hartzman R. J., Woody J. N. Antigen-specific human T lymphocyte clones: induction, antigen specificity, and MHC restriction of influenza virus-immune clones. J Immunol. 1982 Jan;128(1):233–238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maheshwari R. K., Friedman R. M. Effect of interferon treatment on vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV): release of unusual particles with low infectivity. Virology. 1980 Mar;101(2):399–407. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90453-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald G. A., Anacker R. L., Garjian K. Cloned gene of Rickettsia rickettsii surface antigen: candidate vaccine for Rocky Mountain spotted fever. Science. 1987 Jan 2;235(4784):83–85. doi: 10.1126/science.3099387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misiti J., Dasch G. A. In vitro antigen-specific antibody response to the species-specific surface protein antigens of typhus group rickettsiae by human peripheral blood mononuclear cells: generation of an antigen-dependent suppressor T cell. J Immunol. 1985 Apr;134(4):2689–2694. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turco J., Winkler H. H. Inhibition of the growth of Rickettsia prowazekii in cultured fibroblasts by lymphokines. J Exp Med. 1983 Mar 1;157(3):974–986. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.3.974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisseman C. L., Jr, Waddell A. Interferonlike factors from antigen- and mitogen-stimulated human leukocytes with antirickettsial and cytolytic actions on Rickettsia prowazekii. Infected human endothelial cells, fibroblasts, and macrophages. J Exp Med. 1983 Jun 1;157(6):1780–1793. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.6.1780. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodward T. E. Murine and epidemic typhus rickettsiae: how close is their relationship? Yale J Biol Med. 1982 May-Aug;55(3-4):335–341. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



