Abstract
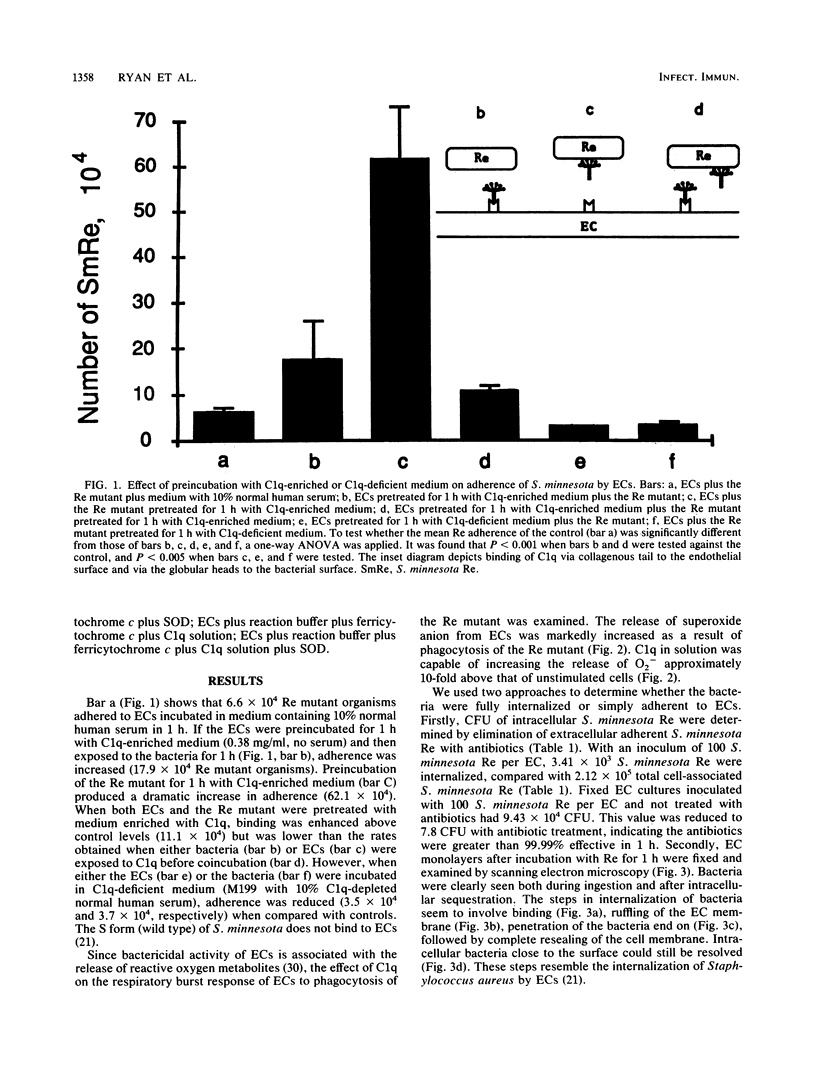
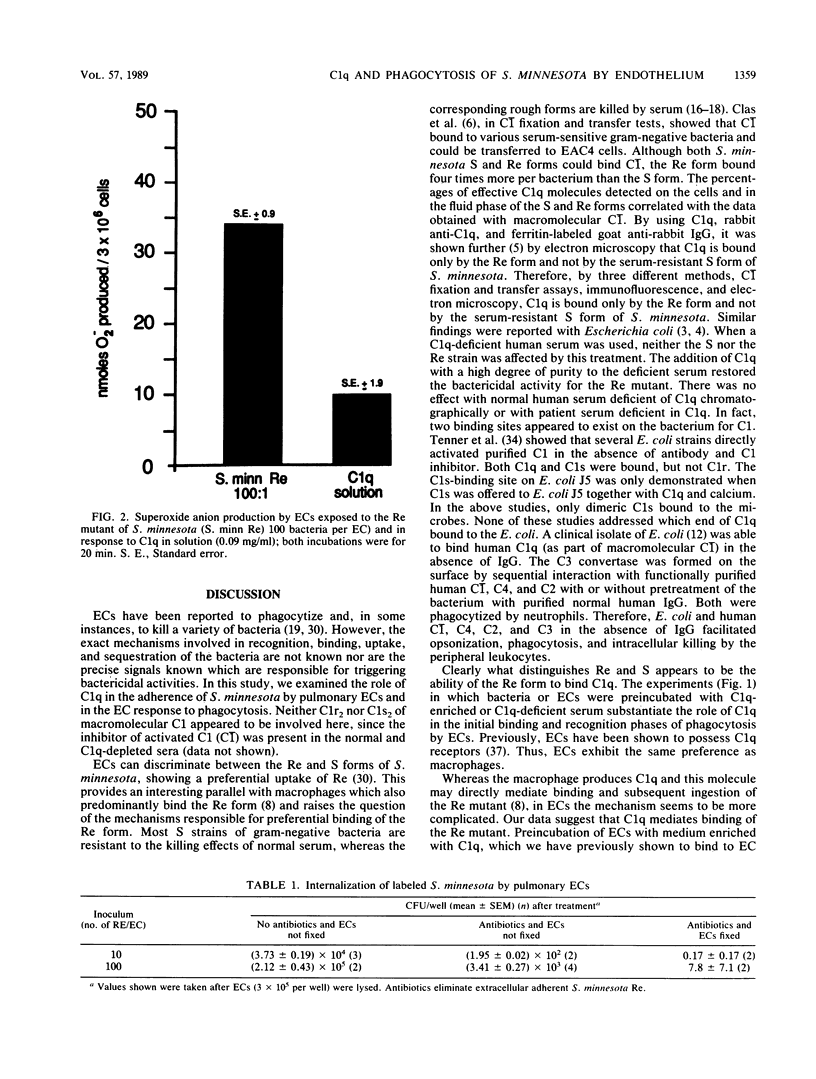
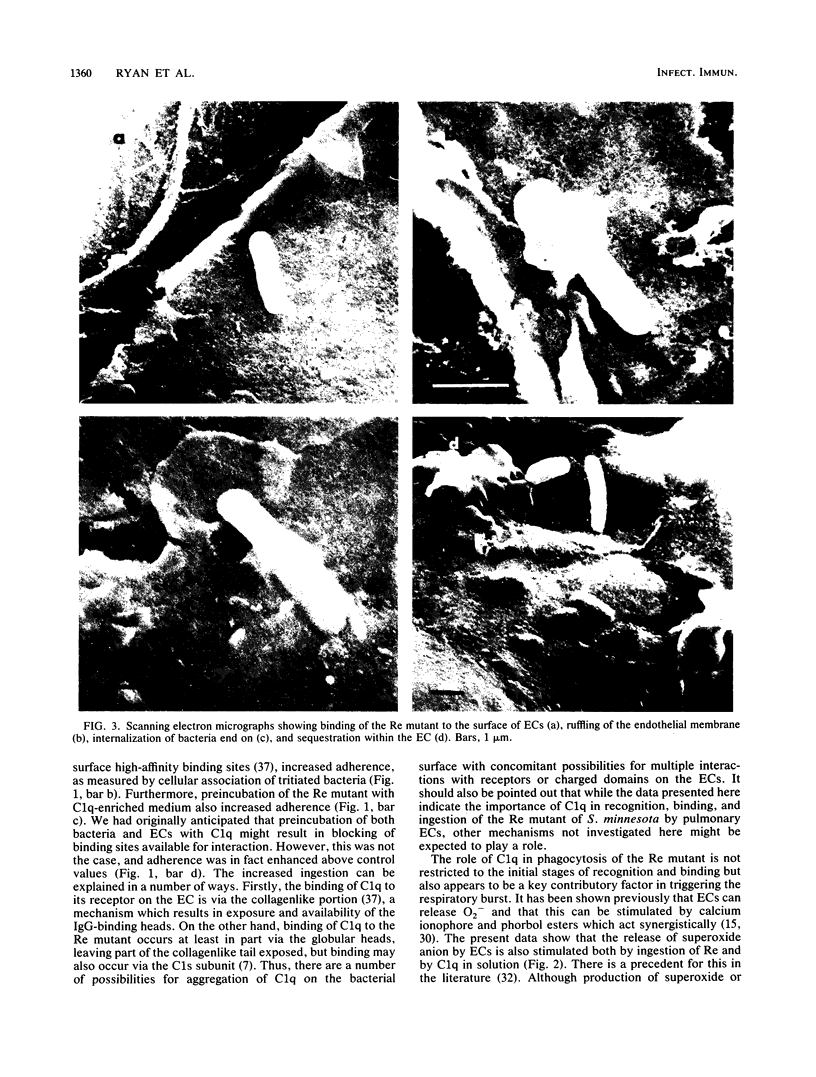
The Re mutant of Salmonella minnesota adheres in much greater numbers than the wild type to endothelial cells derived from the bovine pulmonary artery. Since the Re mutant is distinguished from wild-type S. minnesota by its ability to bind C1q and since endothelial cells possess receptors for C1q, we examined the role of C1q in the phagocytosis of the S. minnesota Re mutant. First, preincubating endothelial cells with C1q-enriched medium resulted in increased adherence of the Re mutant (17.9 x 10(4) versus 6.6 x 10(4]. Second, preincubating the Re mutant with C1q-enriched medium resulted in increased numbers of adherent bacteria (62.1 x 10(4) versus 6.6 x 10(4]. Preincubation of both endothelial cells and bacteria with C1q-enriched medium resulted in increased adherence above control levels but less adherence than when either cells or bacteria were preincubated separately in C1q-enriched medium. If serum depleted of C1q was used for preincubation of endothelial cells or bacteria, adherence was reduced below control levels. Thus, C1q plays an important role in the initial steps (recognition, binding, and ingestion) of phagocytosis. Next, the role of C1q was investigated in the respiratory burst response. Levels of superoxide anion released from endothelial cells 15 min after phagocytosis of the Re mutant (100 bacteria per endothelial cell) were assayed by measurement of the superoxide dismutase-inhibitable reduction of ferricytochrome c. Superoxide anion release was increased during phagocytosis of the Re mutant (35 nmol of O2- per 3 x 10(6) endothelial cells) and was also elevated above control values by incubation with soluble C1q (10 nmol of O2- per 3 x 10(6) endothelial cells). These results indicate a role for C1q in both the ingestion and the response of endothelial cells to the S. minnesota Re mutant.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Avrameas S., Ternynck T. The cross-linking of proteins with glutaraldehyde and its use for the preparation of immunoadsorbents. Immunochemistry. 1969 Jan;6(1):53–66. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(69)90178-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergamini T. M., Bandyk D. F., Govostis D., Kaebnick H. W., Towne J. B. Infection of vascular prostheses caused by bacterial biofilms. J Vasc Surg. 1988 Jan;7(1):21–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betz S. J., Isliker H. Antibody-independent interactions between Escherichia coli J5 and human complement components. J Immunol. 1981 Nov;127(5):1748–1754. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betz S. J., Page N., Estrade C., Isliker H. The effect of specific antibody on antibody-independent interactions between E. coli J5 and human complement. J Immunol. 1982 Feb;128(2):707–711. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clas F., Golecki J. R., Loos M. Electron microscopic study showing antibody-independent binding of C1q, a subcomponent of the first component of complement, to serum-sensitive salmonellae. Infect Immun. 1984 Sep;45(3):795–797. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.3.795-797.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clas F., Loos M. Antibody-independent binding of the first component of complement (C1) and its subcomponent C1q to the S and R forms of Salmonella minnesota. Infect Immun. 1981 Mar;31(3):1138–1144. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.3.1138-1144.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clas F., Schmidt G., Loos M. The role of the classical pathway for the bactericidal effect of normal sera against gram-negative bacteria. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1985;121:19–72. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-45604-6_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Euteneuer B., Störkel S., Loos M. Differences in attachment and phagocytosis of Salmonella minnesota strains (S form, Re mutant) by mouse peritoneal macrophages: participation of endogenous C1q and bacterial surface components (LPS, porins). Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1985;121:85–97. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-45604-6_5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Guerrero M. L., Muelas J. M., Aguado J. M., Renedo G., Fraile J., Soriano F., De Villalobos E. Q fever endocarditis on porcine bioprosthetic valves. Clinicopathologic features and microbiologic findings in three patients treated with doxycycline, cotrimoxazole, and valve replacement. Ann Intern Med. 1988 Feb;108(2):209–213. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-108-2-209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fry W. J. Vascular prosthesis infections. Surg Clin North Am. 1972 Dec;52(6):1419–1424. doi: 10.1016/s0039-6109(16)39886-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. D., Hand W. L., Francis J. B., King-Thompson N., Corwin R. W. Antibiotic uptake by alveolar macrophages. J Lab Clin Med. 1980 Mar;95(3):429–439. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leist-Welsh P., Bjornson A. B. Immunoglobulin-independent utilization of the classical complement pathway in opsonophagocytosis of Escherichia coli by human peripheral leukocytes. J Immunol. 1982 Jun;128(6):2643–2651. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macneal W. J., Spence M. J., Slavkin A. E. Early Lesions of Experimental Endocarditis Lenta. Am J Pathol. 1943 Sep;19(5):735–749. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malick L. E., Wilson R. B. Modified thiocarbohydrazide procedure for scanning electron microscopy: routine use for normal, pathological, or experimental tissues. Stain Technol. 1975 Jul;50(4):265–269. doi: 10.3109/10520297509117069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsubara T., Ziff M. Superoxide anion release by human endothelial cells: synergism between a phorbol ester and a calcium ionophore. J Cell Physiol. 1986 May;127(2):207–210. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041270203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muschel L. H., Larsen L. J. The sensitivity of smooth and rough gram-negative bacteria to the immune bactericidal reaction. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1970 Jan;133(1):345–348. doi: 10.3181/00379727-133-34472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowley D. Sensitivity of rough gram-negative bacteria to the bactericidal action of serum. J Bacteriol. 1968 May;95(5):1647–1650. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.5.1647-1650.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan U. S., Clements E., Habliston D., Ryan J. W. Isolation and culture of pulmonary artery endothelial cells. Tissue Cell. 1978;10(3):535–554. doi: 10.1016/s0040-8166(16)30347-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan U. S., Mortara M., Whitaker C. Methods for microcarrier culture of bovine pulmonary artery endothelial cells avoiding the use of enzymes. Tissue Cell. 1980;12(4):619–635. doi: 10.1016/0040-8166(80)90017-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan U. S. The endothelial surface and responses to injury. Fed Proc. 1986 Feb;45(2):101–108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUTER E. Multiplication of tubercle bacilli within phagocytes cultivated in vitro, and effect of streptomycin and isonicotinic acid hydrazide. Am Rev Tuberc. 1952 Jun;65(6):775–776. doi: 10.1164/art.1952.65.6.775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenner A. J., Ziccardi R. J., Cooper N. R. Antibody-independent C1 activation by E. coli. J Immunol. 1984 Aug;133(2):886–891. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volanakis J. E., Stroud R. M. Rabbit C1q: purification, functional and structural studies. J Immunol Methods. 1972 Nov;2(1):25–34. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(72)90014-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voyta J. C., Via D. P., Butterfield C. E., Zetter B. R. Identification and isolation of endothelial cells based on their increased uptake of acetylated-low density lipoprotein. J Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;99(6):2034–2040. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.6.2034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang S. C., Schultz D. R., Ryan U. S. Receptor-mediated binding of C1q on pulmonary endothelial cells. Tissue Cell. 1986;18(1):13–18. doi: 10.1016/0040-8166(86)90003-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]