Abstract
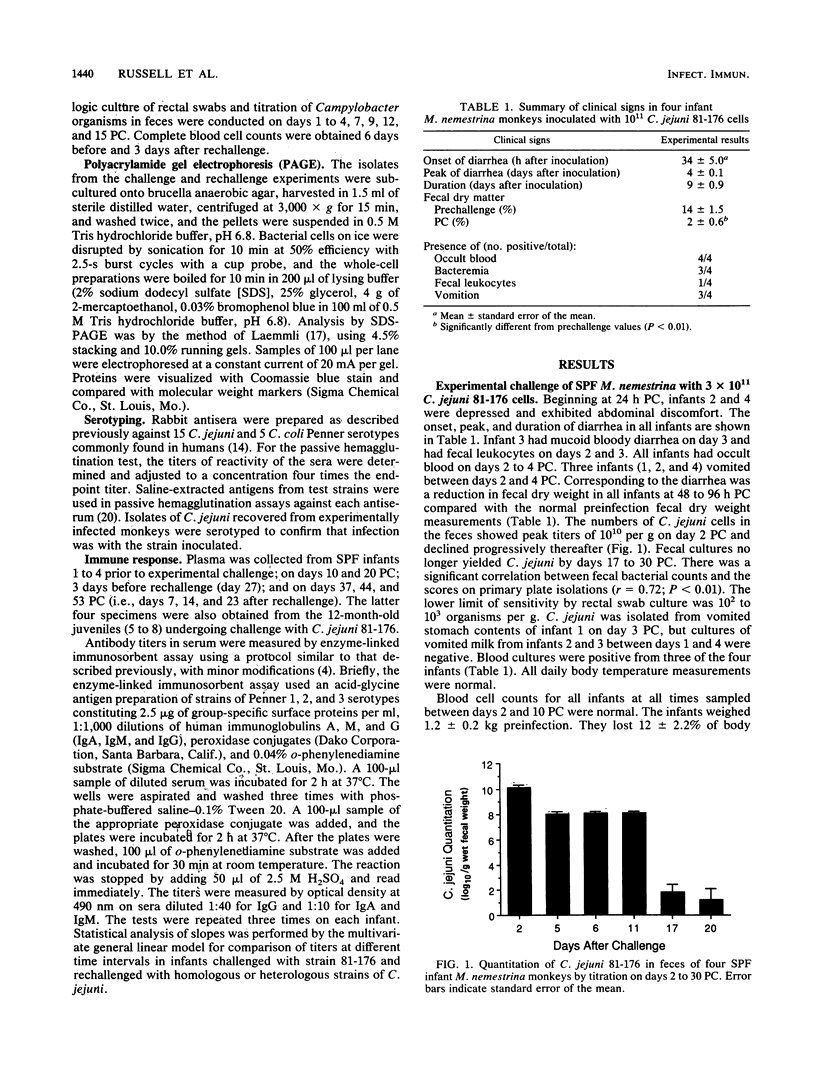
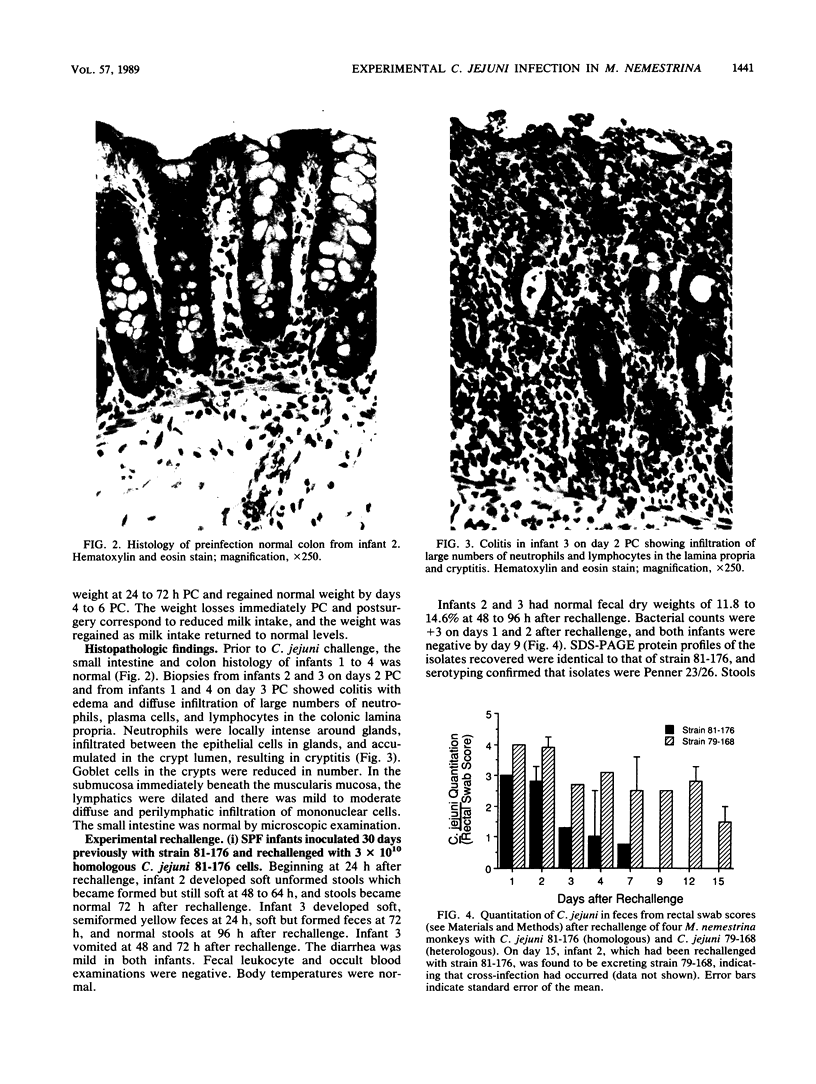
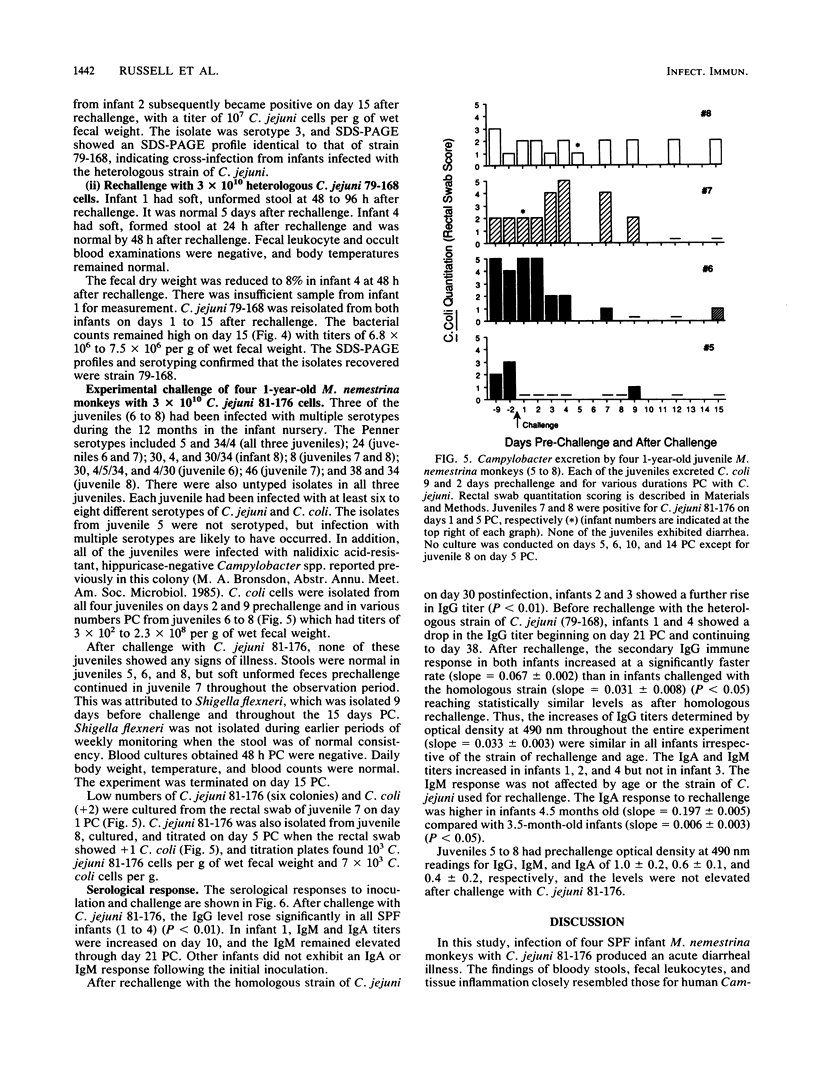
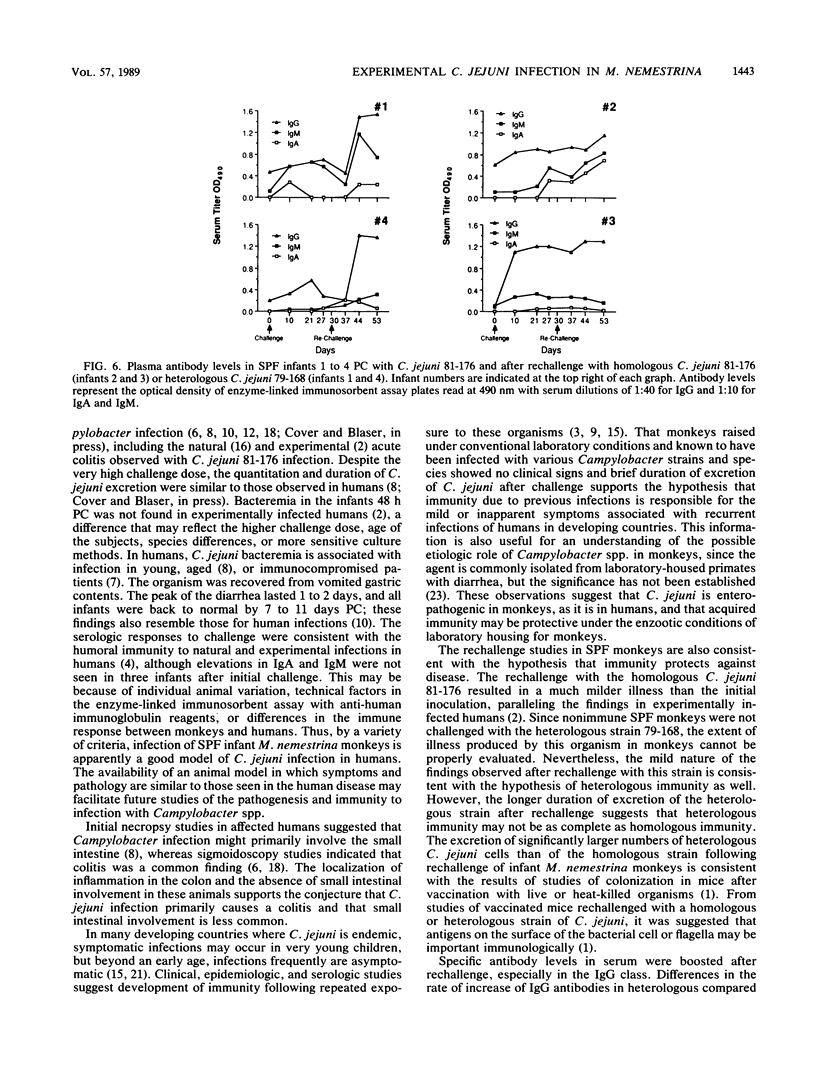
Experimental infection of four specific-pathogen-free Macaca nemestrina monkeys (aged 3.5 and 4.5 months) with Campylobacter jejuni 81-176 caused acute diarrheal illness, characterized by fluid diarrhea, bloody stools, and fecal leukocytes, which lasted for approximately 7 to 11 days. Histologic examination of intestinal biopsies showed acute colitis characterized by infiltration of the mucosa with neutrophils and lymphocytes, and cryptitis. There were no histologic changes in the small intestine. Excretion of C. jejuni was demonstrated for 2 to 4 weeks postchallenge. Plasma antibodies to C. jejuni group antigen were elevated after challenge. Only mild diarrhea occurred after rechallenge with the same strain or with a heterologous C. jejuni strain (79-168) followed by further elevation in specific immunoglobulins A, M, and G. Four 1-year-old juvenile M. nemestrina monkeys which had experienced multiple infections with Campylobacter spp. did not exhibit illness when challenged with C. jejuni 81-176. All had elevated immunoglobulin A, M, and G plasma antibodies prior to challenge, and these humoral antibody levels were indicative of the immunity to challenge. The results demonstrate that C. jejuni infection in M. nemestrina caused colitis with clinical and pathologic results similar to those found in humans and indicate that prior infection protects against subsequent challenge.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abimiku A. G., Dolby J. M. Cross-protection of infant mice against intestinal colonisation by Campylobacter jejuni: importance of heat-labile serotyping (Lior) antigens. J Med Microbiol. 1988 Aug;26(4):265–268. doi: 10.1099/00222615-26-4-265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black R. E., Levine M. M., Clements M. L., Hughes T. P., Blaser M. J. Experimental Campylobacter jejuni infection in humans. J Infect Dis. 1988 Mar;157(3):472–479. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.3.472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaser M. J., Black R. E., Duncan D. J., Amer J. Campylobacter jejuni-specific serum antibodies are elevated in healthy Bangladeshi children. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Feb;21(2):164–167. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.2.164-167.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaser M. J., Duncan D. J. Human serum antibody response to Campylobacter jejuni infection as measured in an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Infect Immun. 1984 May;44(2):292–298. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.2.292-298.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaser M. J., Parsons R. B., Wang W. L. Acute colitis caused by Campylobacter fetus ss. jejuni. Gastroenterology. 1980 Mar;78(3):448–453. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaser M. J., Perez G. P., Smith P. F., Patton C., Tenover F. C., Lastovica A. J., Wang W. I. Extraintestinal Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli infections: host factors and strain characteristics. J Infect Dis. 1986 Mar;153(3):552–559. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.3.552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaser M. J., Reller L. B. Campylobacter enteritis. N Engl J Med. 1981 Dec 10;305(24):1444–1452. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198112103052404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaser M. J., Taylor D. N., Echeverria P. Immune response to Campylobacter jejuni in a rural community in Thailand. J Infect Dis. 1986 Feb;153(2):249–254. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.2.249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaser M. J., Taylor D. N., Feldman R. A. Epidemiology of Campylobacter jejuni infections. Epidemiol Rev. 1983;5:157–176. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.epirev.a036256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant J. L., Stills H. F., Lentsch R. H., Middleton C. C. Campylobacter jejuni isolated from patas monkeys with diarrhea. Lab Anim Sci. 1983 Jun;33(3):303–305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colgan T., Lambert J. R., Newman A., Luk S. C. Campylobacter jejuni enterocolitis. A clinicopathologic study. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1980 Nov;104(11):571–574. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgeorge R. B., Baskerville A., Lander K. P. Experimental infection of Rhesus monkeys with a human strain of Campylobacter jejuni. J Hyg (Lond) 1981 Jun;86(3):343–351. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400069096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox J. G., Claps M. C., Taylor N. S., Maxwell K. O., Ackerman J. I., Hoffman S. B. Campylobacter jejuni/coli in commercially reared beagles: prevalence and serotypes. Lab Anim Sci. 1988 Jun;38(3):262–265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass R. I., Stoll B. J., Huq M. I., Struelens M. J., Blaser M., Kibriya A. K. Epidemiologic and clinical features of endemic Campylobacter jejuni infection in Bangladesh. J Infect Dis. 1983 Aug;148(2):292–296. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.2.292. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korlath J. A., Osterholm M. T., Judy L. A., Forfang J. C., Robinson R. A. A point-source outbreak of campylobacteriosis associated with consumption of raw milk. J Infect Dis. 1985 Sep;152(3):592–596. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.3.592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert M. E., Schofield P. F., Ironside A. G., Mandal B. K. Campylobacter colitis. Br Med J. 1979 Mar 31;1(6167):857–859. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6167.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris G. K., el Sherbeeny M. R., Patton C. M., Kodaka H., Lombard G. L., Edmonds P., Hollis D. G., Brenner D. J. Comparison of four hippurate hydrolysis methods for identification of thermophilic Campylobacter spp. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Nov;22(5):714–718. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.5.714-718.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penner J. L., Hennessy J. N. Passive hemagglutination technique for serotyping Campylobacter fetus subsp. jejuni on the basis of soluble heat-stable antigens. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Dec;12(6):732–737. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.6.732-737.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson N. J., Koornhof H. J., Bokkenheuser V. D., Mayet Z., Rosen E. U. Age related susceptibility to Campylobacter jejuni infection in a high prevalance population. Arch Dis Child. 1983 Aug;58(8):616–619. doi: 10.1136/adc.58.8.616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell R. G., Krugner L., Tsai C. C., Ekstrom R. Prevalence of Campylobacter in infant, juvenile and adult laboratory primates. Lab Anim Sci. 1988 Dec;38(6):711–714. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell R. G., Rosenkranz S. L., Lee L. A., Howard H., DiGiacomo R. F., Bronsdon M. A., Blakley G. A., Tsai C. C., Morton W. R. Epidemiology and etiology of diarrhea in colony-born Macaca nemestrina. Lab Anim Sci. 1987 Jun;37(3):309–316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skirrow M. B. Campylobacter enteritis - the first five years. J Hyg (Lond) 1982 Oct;89(2):175–184. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400070704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. N., Echeverria P., Pitarangsi C., Seriwatana J., Bodhidatta L., Blaser M. J. Influence of strain characteristics and immunity on the epidemiology of Campylobacter infections in Thailand. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 May;26(5):863–868. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.5.863-868.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tribe G. W., Fleming M. P. Biphasic enteritis in imported cynomolgus (Macaca fascicularis) monkeys infected with Shigella, Salmonella and Campylobacter species. Lab Anim. 1983 Jan;17(1):65–69. doi: 10.1258/002367783781070957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker R. I., Caldwell M. B., Lee E. C., Guerry P., Trust T. J., Ruiz-Palacios G. M. Pathophysiology of Campylobacter enteritis. Microbiol Rev. 1986 Mar;50(1):81–94. doi: 10.1128/mr.50.1.81-94.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





