Abstract
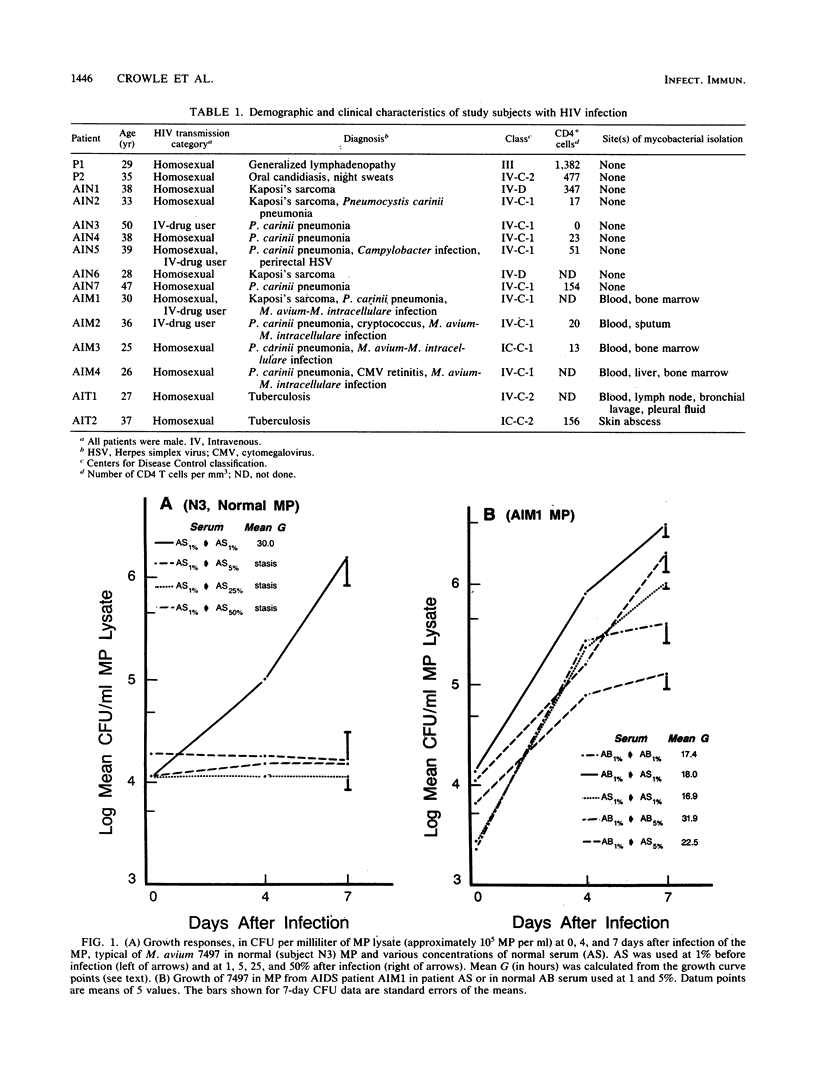
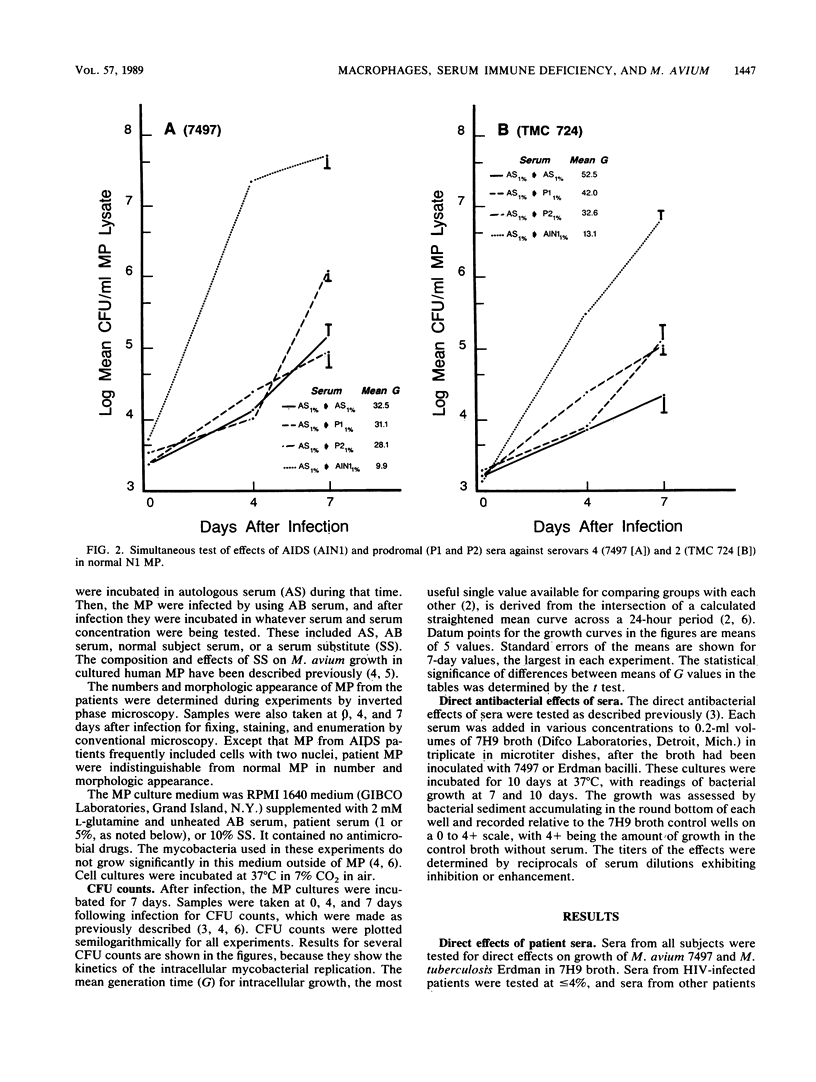
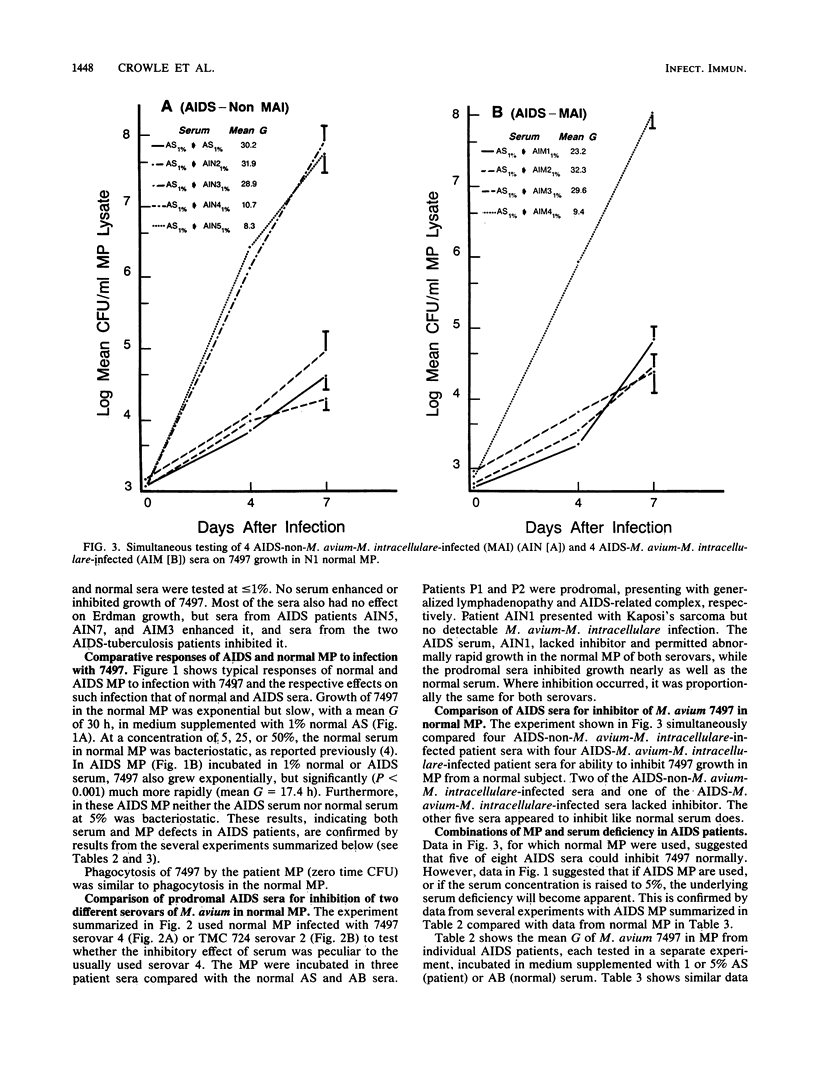
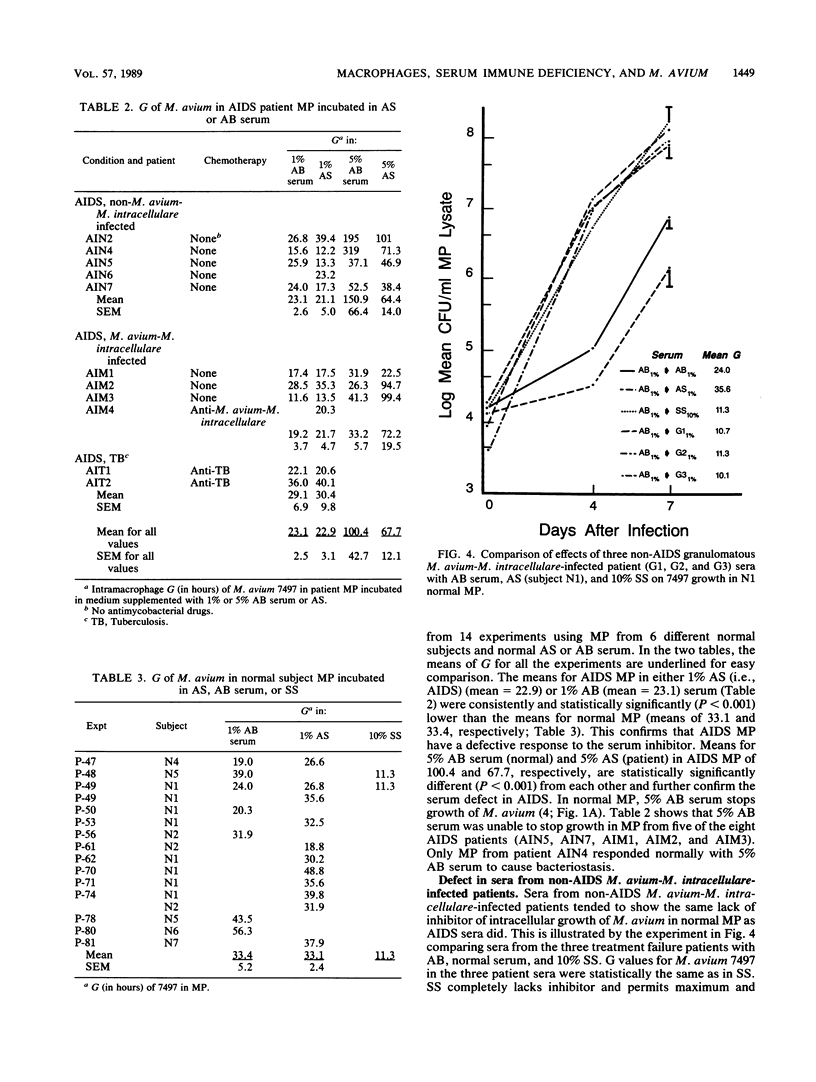
Some characteristics of the sera and macrophages (MP) of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-infected patients which might contribute to their unusual susceptibility to Mycobacterium avium infection were studied. Cultures of patient peripheral blood MP in medium supplemented with their sera or normal subject sera were infected with M. avium and compared with similar cultures of normal MP. Intracellular mycobacterial replication was measured in the infected MP by CFU counts of the bacteria made from lysed samples of the MP at 0, 4, and 7 days after MP infection. Sera from patients with chronic granulomatous infection with M. avium, but no HIV infection, also were studied. The sera from all of the patients with chronic granulomatous infection and from several HIV-infected patients were deficient or lacking in an inhibitor that in normal serum acts within normal MP to suppress intracellular growth of M. avium. Most of the HIV-infected patients also had MP that were abnormally permissive for M. avium because they responded poorly to the serum inhibitor. Elucidation of these associated defects in native defenses against M. avium may result in better prevention and therapy of M. avium infections.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Crowle A. J., Elkins N., May M. H. Effectiveness of ofloxacin against Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Mycobacterium avium, and rifampin against M. tuberculosis in cultured human macrophages. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1988 May;137(5):1141–1146. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/137.5.1141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowle A. J., Poche P. Inhibition by normal human serum of Mycobacterium avium multiplication in cultured human macrophages. Infect Immun. 1989 Apr;57(4):1332–1335. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.4.1332-1335.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowle A. J., Ross E. J., May M. H. Inhibition by 1,25(OH)2-vitamin D3 of the multiplication of virulent tubercle bacilli in cultured human macrophages. Infect Immun. 1987 Dec;55(12):2945–2950. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.12.2945-2950.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowle A. J., Tsang A. Y., Vatter A. E., May M. H. Comparison of 15 laboratory and patient-derived strains of Mycobacterium avium for ability to infect and multiply in cultured human macrophages. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Nov;24(5):812–821. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.5.812-821.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flepp M., Rhyner K., Lüthy R., Greminger P., Vurma-Rapp U., Wolfisberg C., Burnens A., Siegenthaler W. Mykobakteriosen bei Patienten mit HIV-Infektion. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 1988 May 6;113(18):711–718. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1067708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mycobacterioses and the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Joint Position Paper of the American Thoracic Society and the Centers for Disease Control. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987 Aug;136(2):492–496. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/136.2.492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orenstein J. M., Meltzer M. S., Phipps T., Gendelman H. E. Cytoplasmic assembly and accumulation of human immunodeficiency virus types 1 and 2 in recombinant human colony-stimulating factor-1-treated human monocytes: an ultrastructural study. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):2578–2586. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.2578-2586.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pauza C. D. HIV persistence in monocytes leads to pathogenesis and AIDS. Cell Immunol. 1988 Apr 1;112(2):414–424. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(88)90310-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perfect J. R. Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare complex infections in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. J Electron Microsc Tech. 1988 Jan;8(1):105–113. doi: 10.1002/jemt.1060080107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnittman S., Lane H. C., Witebsky F. G., Gosey L. L., Hoggan M. D., Fauci A. S. Host defense against Mycobacterium-avium complex. J Clin Immunol. 1988 Jul;8(4):234–243. doi: 10.1007/BF00916551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



