Abstract
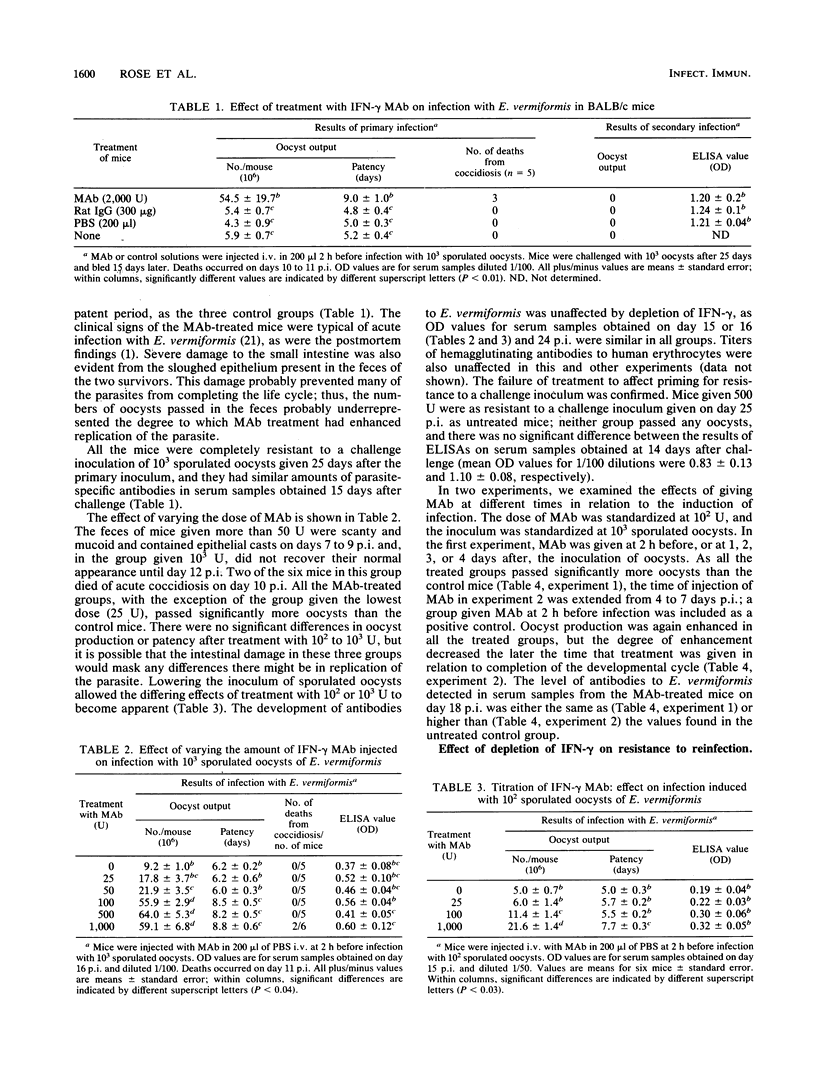
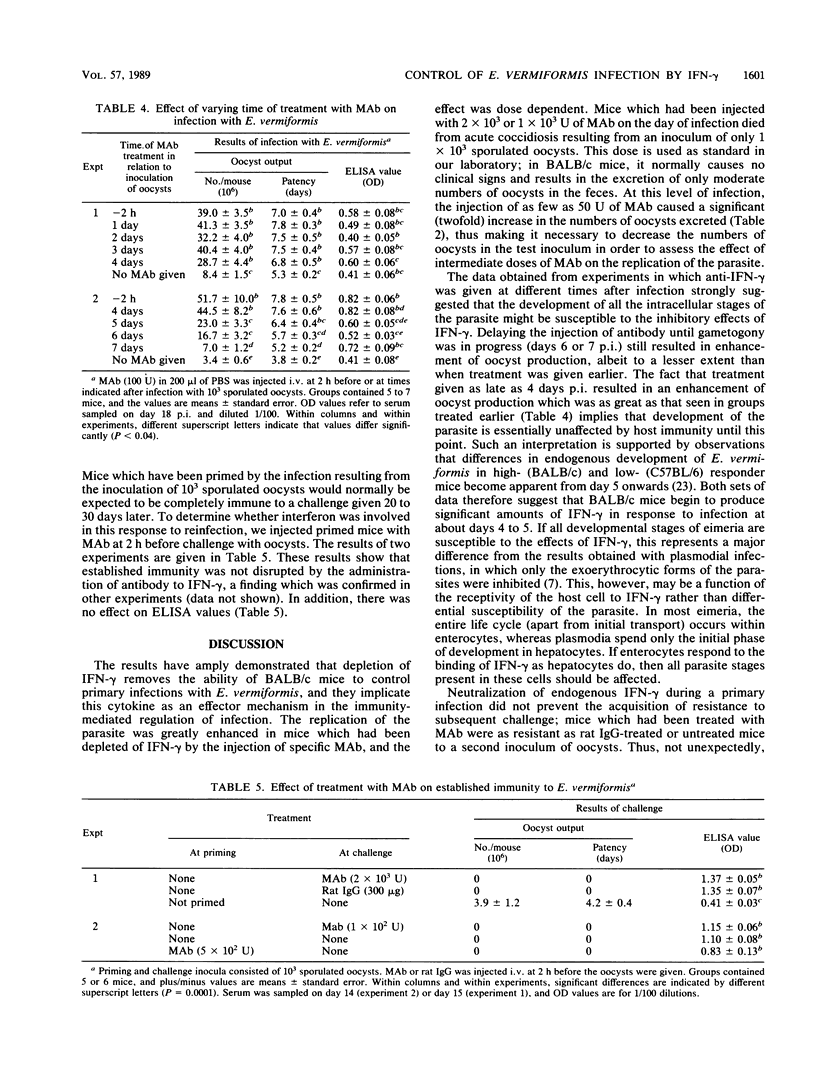
Neutralization of endogenous gamma interferon by treatment with a rat monoclonal antibody caused enhancement of infection with the protozoon Eimeria vermiformis in naive BALB/c mice. The effect was dose dependent and was apparent when a monoclonal antibody was given at 2 h before infection or up to 7 days postinfection, but it decreased with increasing time postinfection between days 4 and 7. The titers of parasite-specific antibodies in the serum were not significantly affected by the injection of monoclonal antibodies. Treatment during priming did not prevent the development of resistance to challenge, and treatment at the time of challenge did not abrogate established immunity. The results indicate that gamma interferon is involved in the control of primary infection with E. vermiformis in BALB/c mice but not in the expression of immunity to challenge.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blagburn B. L., Todd K. S., Jr Pathological changes and immunity associated with experimental Eimeria vermiformis infections in Mus musculus. J Protozool. 1984 Nov;31(4):556–561. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1984.tb05502.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bland P. MHC class II expression by the gut epithelium. Immunol Today. 1988 Jun;9(6):174–178. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(88)91293-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman H. D. Drug resistance in avian coccidia (a review). Vet Parasitol. 1984 Jul;15(1):11–27. doi: 10.1016/0304-4017(84)90106-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira A., Schofield L., Enea V., Schellekens H., van der Meide P., Collins W. E., Nussenzweig R. S., Nussenzweig V. Inhibition of development of exoerythrocytic forms of malaria parasites by gamma-interferon. Science. 1986 May 16;232(4752):881–884. doi: 10.1126/science.3085218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes H. P., Thomas K. R., Speer C. A. Antigen-specific lymphocyte transformation induced by oocyst antigens of Eimeria bovis. Infect Immun. 1988 Jun;56(6):1518–1525. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.6.1518-1525.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kogut M. H., Lange C. Effect of lymphokine treatment on the invasion of cultured animal cells by Eimeria tenella. Lymphokine Res. 1988 Spring;7(1):31–44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer J. D., Bogitsh B. J. Schistosoma japonicum: biochemistry and cytochemistry of dipeptidyl aminopeptidase-II-like activity in adults. Exp Parasitol. 1985 Oct;60(2):163–170. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(85)90019-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long P. L., Millard B. J., Joyner L. P., Norton C. C. A guide to laboratory techniques used in the study and diagnosis of avian coccidiosis. Folia Vet Lat. 1976 Jul-Sep;6(3):201–217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long P. L., Milne B. S. The effect of an interferon inducer on Eimeria maxima in the chicken. Parasitology. 1971 Apr;62(2):295–302. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000071523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maheshwari R. K., Czarniecki C. W., Dutta G. P., Puri S. K., Dhawan B. N., Friedman R. M. Recombinant human gamma interferon inhibits simian malaria. Infect Immun. 1986 Sep;53(3):628–630. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.3.628-630.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCabe R. E., Luft B. J., Remington J. S. Effect of murine interferon gamma on murine toxoplasmosis. J Infect Dis. 1984 Dec;150(6):961–962. doi: 10.1093/infdis/150.6.961. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellouk S., Maheshwari R. K., Rhodes-Feuillette A., Beaudoin R. L., Berbiguier N., Matile H., Miltgen F., Landau I., Pied S., Chigot J. P. Inhibitory activity of interferons and interleukin 1 on the development of Plasmodium falciparum in human hepatocyte cultures. J Immunol. 1987 Dec 15;139(12):4192–4195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Momburg F., Koch N., Möller P., Moldenhauer G., Butcher G. W., Hämmerling G. J. Differential expression of Ia and Ia-associated invariant chain in mouse tissues after in vivo treatment with IFN-gamma. J Immunol. 1986 Feb 1;136(3):940–948. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray H. W., Spitalny G. L., Nathan C. F. Activation of mouse peritoneal macrophages in vitro and in vivo by interferon-gamma. J Immunol. 1985 Mar;134(3):1619–1622. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onaga H., Tajima M., Ishii T. Activation of macrophages by culture fluid of antigen-stimulated spleen cells collected from chickens immunized with Eimeria tenella. Vet Parasitol. 1983 Aug;13(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0304-4017(83)90015-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfefferkorn E. R., Guyre P. M. Inhibition of growth of Toxoplasma gondii in cultured fibroblasts by human recombinant gamma interferon. Infect Immun. 1984 May;44(2):211–216. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.2.211-216.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose M. E., Hesketh P. Eimerian life cycles: the patency of eimeria vermiformis, but not Eimeria pragensis, is subject to host (Mus musculus) influence. J Parasitol. 1986 Dec;72(6):949–954. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose M. E., Joysey H. S., Hesketh P., Grencis R. K., Wakelin D. Mediation of immunity to Eimeria vermiformis in mice by L3T4+ T cells. Infect Immun. 1988 Jul;56(7):1760–1765. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.7.1760-1765.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose M. E., Owen D. G., Hesketh P. Susceptibility to coccidiosis: effect of strain of mouse on reproduction of Eimeria vermiformis. Parasitology. 1984 Feb;88(Pt 1):45–54. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000054330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose M. E., Wakelin D., Joysey H. S., Hesketh P. Immunity to coccidiosis: adoptive transfer in NIH mice challenged with Eimeria vermiformis. Parasite Immunol. 1988 Jan;10(1):59–69. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1988.tb00203.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schofield L., Ferreira A., Altszuler R., Nussenzweig V., Nussenzweig R. S. Interferon-gamma inhibits the intrahepatocytic development of malaria parasites in vitro. J Immunol. 1987 Sep 15;139(6):2020–2025. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schofield L., Villaquiran J., Ferreira A., Schellekens H., Nussenzweig R., Nussenzweig V. Gamma interferon, CD8+ T cells and antibodies required for immunity to malaria sporozoites. Nature. 1987 Dec 17;330(6149):664–666. doi: 10.1038/330664a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speer C. A., Reduker D. W., Burgess D. E., Whitmire W. M., Splitter G. A. Lymphokine-induced inhibition of growth of Eimeria bovis and Eimeria papillata (Apicomplexa) in cultured bovine monocytes. Infect Immun. 1985 Nov;50(2):566–571. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.2.566-571.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki Y., Orellana M. A., Schreiber R. D., Remington J. S. Interferon-gamma: the major mediator of resistance against Toxoplasma gondii. Science. 1988 Apr 22;240(4851):516–518. doi: 10.1126/science.3128869. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



