Abstract
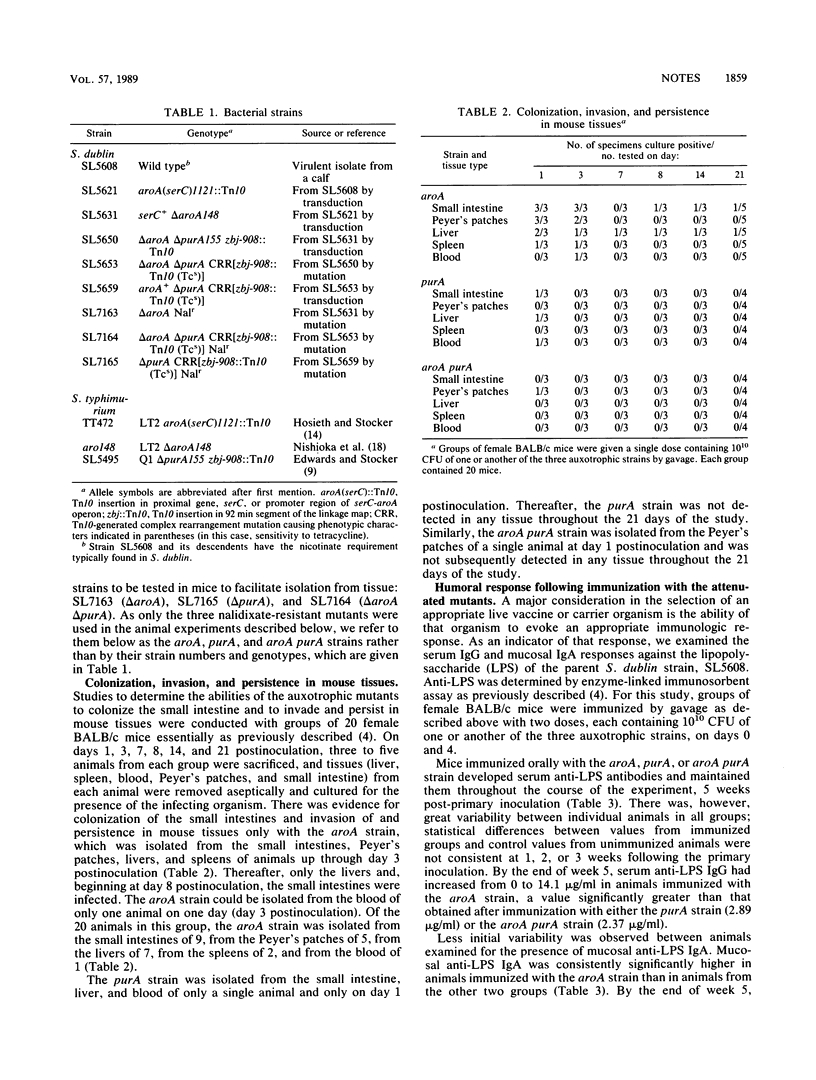
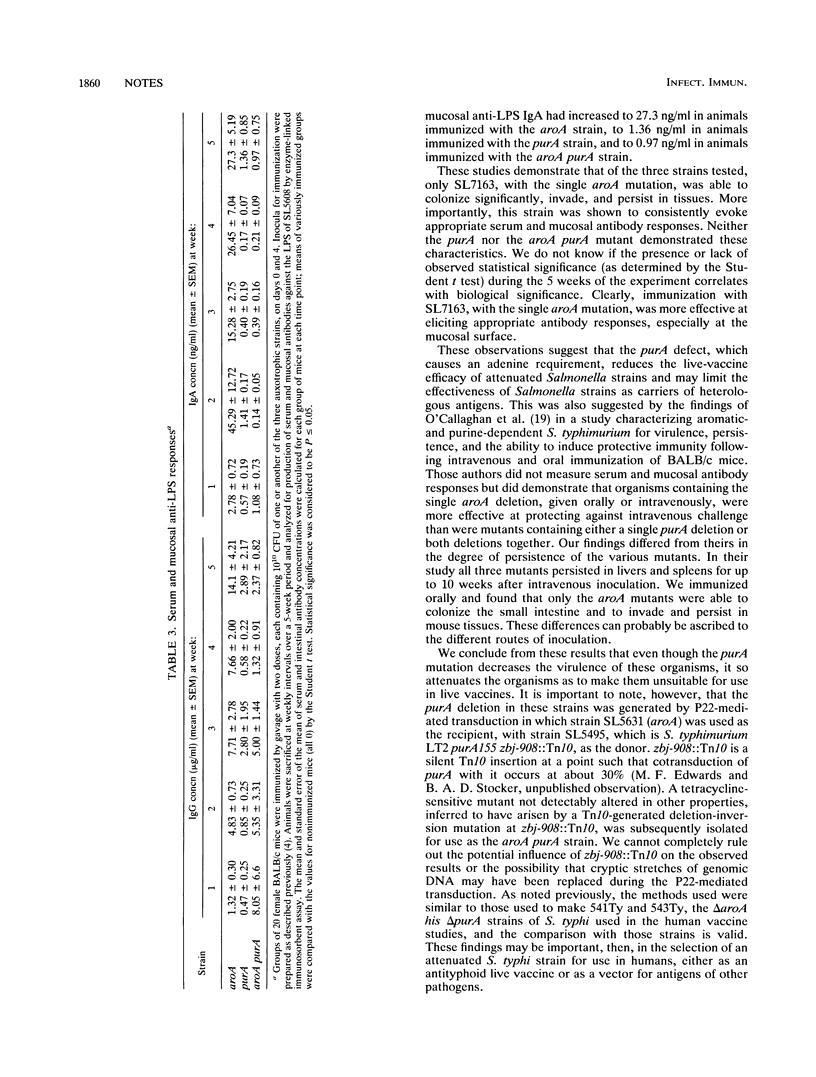
We made delta aroA, delta purA, and delta aroA delta purA derivatives of a strain of Salmonella dublin and isolated a nalidixate-resistant mutant of each construct. An inoculum of each of the nearly isogenic nalidixate-resistant auxotrophs was administered to BALB/c mice by gavage. The ability of each strain to colonize, invade, persist in tissues, and evoke serum and mucosal antibody responses to the lipopolysaccharide of the parent strain was examined. Only the delta aroA strain colonized, invaded, persisted, and (more importantly) evoked sustained significant serum and mucosal antibody responses. Neither the delta purA nor the delta aroA delta purA strain showed any of these abilities. These observations demonstrate that the purA defect, which causes a requirement for adenine, reduces the live-vaccine efficacy of attenuated Salmonella strains and may limit the effectiveness of Salmonella strains as carriers of heterologous antigens. These findings may be important in the selection of attenuated S. typhi strains for use in humans either as antityphoid live vaccines or as vectors for antigens of other pathogens.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown A., Hormaeche C. E., Demarco de Hormaeche R., Winther M., Dougan G., Maskell D. J., Stocker B. A. An attenuated aroA Salmonella typhimurium vaccine elicits humoral and cellular immunity to cloned beta-galactosidase in mice. J Infect Dis. 1987 Jan;155(1):86–92. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.1.86. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements J. D., El-Morshidy S. Construction of a potential live oral bivalent vaccine for typhoid fever and cholera-Escherichia coli-related diarrheas. Infect Immun. 1984 Nov;46(2):564–569. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.2.564-569.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements J. D., Lyon F. L., Lowe K. L., Farrand A. L., el-Morshidy S. Oral immunization of mice with attenuated Salmonella enteritidis containing a recombinant plasmid which codes for production of the B subunit of heat-labile Escherichia coli enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1986 Sep;53(3):685–692. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.3.685-692.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements J. D. Use of attenuated mutants of Salmonella as carriers for delivery of heterologous antigens to the secretory immune system. Pathol Immunopathol Res. 1987;6(2):137–146. doi: 10.1159/000157055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtiss R., 3rd 1984 Kreshover lecture. Genetic analysis of Streptococcus mutans virulence and prospects for an anticaries vaccine. J Dent Res. 1986 Aug;65(8):1034–1045. doi: 10.1177/00220345860650080101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtiss R., 3rd, Kelly S. M. Salmonella typhimurium deletion mutants lacking adenylate cyclase and cyclic AMP receptor protein are avirulent and immunogenic. Infect Immun. 1987 Dec;55(12):3035–3043. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.12.3035-3043.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dougan G., Sellwood R., Maskell D., Sweeney K., Liew F. Y., Beesley J., Hormaeche C. In vivo properties of a cloned K88 adherence antigen determinant. Infect Immun. 1986 Apr;52(1):344–347. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.1.344-347.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards M. F., Stocker B. A. Construction of delta aroA his delta pur strains of Salmonella typhi. J Bacteriol. 1988 Sep;170(9):3991–3995. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.9.3991-3995.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Formal S. B., Baron L. S., Kopecko D. J., Washington O., Powell C., Life C. A. Construction of a potential bivalent vaccine strain: introduction of Shigella sonnei form I antigen genes into the galE Salmonella typhi Ty21a typhoid vaccine strain. Infect Immun. 1981 Dec;34(3):746–750. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.3.746-750.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germanier R., Füer E. Isolation and characterization of Gal E mutant Ty 21a of Salmonella typhi: a candidate strain for a live, oral typhoid vaccine. J Infect Dis. 1975 May;131(5):553–558. doi: 10.1093/infdis/131.5.553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman R. H., Hornick R. B., Woodard W. E., DuPont H. L., Snyder M. J., Levine M. M., Libonati J. P. Evaluation of a UDP-glucose-4-epimeraseless mutant of Salmonella typhi as a liver oral vaccine. J Infect Dis. 1977 Dec;136(6):717–723. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.6.717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoiseth S. K., Stocker B. A. Aromatic-dependent Salmonella typhimurium are non-virulent and effective as live vaccines. Nature. 1981 May 21;291(5812):238–239. doi: 10.1038/291238a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoiseth S. K., Stocker B. A. Genes aroA and serC of Salmonella typhimurium constitute an operon. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jul;163(1):355–361. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.1.355-361.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Herrington D., Murphy J. R., Morris J. G., Losonsky G., Tall B., Lindberg A. A., Svenson S., Baqar S., Edwards M. F. Safety, infectivity, immunogenicity, and in vivo stability of two attenuated auxotrophic mutant strains of Salmonella typhi, 541Ty and 543Ty, as live oral vaccines in humans. J Clin Invest. 1987 Mar;79(3):888–902. doi: 10.1172/JCI112899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning P. A., Heuzenroeder M. W., Yeadon J., Leavesley D. I., Reeves P. R., Rowley D. Molecular cloning and expression in Escherichia coli K-12 of the O antigens of the Inaba and Ogawa serotypes of the Vibrio cholerae O1 lipopolysaccharides and their potential for vaccine development. Infect Immun. 1986 Aug;53(2):272–277. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.2.272-277.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishioka Y., Demerec M., Eisenstark A. Genetic analysis of aromatic mutants of Salmonella typhimurium. Genetics. 1967 Jun;56(2):341–351. doi: 10.1093/genetics/56.2.341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Callaghan D., Maskell D., Liew F. Y., Easmon C. S., Dougan G. Characterization of aromatic- and purine-dependent Salmonella typhimurium: attention, persistence, and ability to induce protective immunity in BALB/c mice. Infect Immun. 1988 Feb;56(2):419–423. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.2.419-423.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertsson J. A., Lindberg A. A., Hoiseth S., Stocker B. A. Salmonella typhimurium infection in calves: protection and survival of virulent challenge bacteria after immunization with live or inactivated vaccines. Infect Immun. 1983 Aug;41(2):742–750. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.2.742-750.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadoff J. C., Ballou W. R., Baron L. S., Majarian W. R., Brey R. N., Hockmeyer W. T., Young J. F., Cryz S. J., Ou J., Lowell G. H. Oral Salmonella typhimurium vaccine expressing circumsporozoite protein protects against malaria. Science. 1988 Apr 15;240(4850):336–338. doi: 10.1126/science.3281260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith B. P., Reina-Guerra M., Hoiseth S. K., Stocker B. A., Habasha F., Johnson E., Merritt F. Aromatic-dependent Salmonella typhimurium as modified live vaccines for calves. Am J Vet Res. 1984 Jan;45(1):59–66. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith B. P., Reina-Guerra M., Stocker B. A., Hoiseth S. K., Johnson E. Aromatic-dependent Salmonella dublin as a parenteral modified live vaccine for calves. Am J Vet Res. 1984 Nov;45(11):2231–2235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stocker B. A., Hoiseth S. K., Smith B. P. Aromatic-dependent "Salmonella sp." as live vaccine in mice and calves. Dev Biol Stand. 1983;53:47–54. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahdan M. H., Serie C., Germanier R., Lackany A., Cerisier Y., Guerin N., Sallam S., Geoffroy P., el Tantawi A. S., Guesry P. A controlled field trial of liver oral typhoid vaccine Ty21a. Bull World Health Organ. 1980;58(3):469–474. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Tamura Y., Yokota T. Enteroadhesion fimbriae and enterotoxin of Escherichia coli: genetic transfer to a streptomycin-resistant mutant of the galE oral-route live-vaccine Salmonella typhi Ty21a. Infect Immun. 1985 Dec;50(3):925–928. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.3.925-928.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



