Abstract
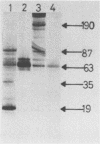
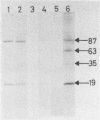
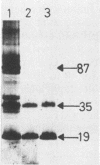
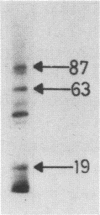
The binding of staphylococcal components to fibrinogen was studied. Fibrinogen-binding material from lysed staphylococcal cells or culture supernatants was affinity purified on fibrinogen-Sepharose and analyzed on Western (immuno-) blots by the use of fibrinogen and antifibrinogen antibodies. Two main bands of 87 and 19 kilodaltons (kDa) and a weaker band of 35 kDa bound specifically to fibrinogen. A monoclonal antibody bound to all three bands, indicating that these were of the same origin. The yield of these components was much higher in the culture supernatant than on washed cells, suggesting that these molecules are essentially extracellular products. In a plasma coagulase test, the 87-kDa band, but not the 19-kDa band, clotted rabbit plasma, demonstrating that the 87-kDa molecule is coagulase. This was further confirmed by the fact that the 87-kDa band binds specifically to prothrombin. It was shown that the 87- and the 19-kDa molecules were present on the cell surface by surface labeling the cells with 125I. In addition, the fact that killed and washed cells could induce plasma clotting demonstrates that staphylococci have coagulase exposed on the surface. It was concluded that cell-bound coagulase has affinity for fibrinogen also in the absence of prothrombin and thus is responsible for the clumping of staphylococci in fibrinogen.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altenbern R. A. On the nature of albumin-promoted coagulase release by Staphylococcus aureus. J Infect Dis. 1966 Dec;116(5):593–600. doi: 10.1093/infdis/116.5.593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beachey E. H. Bacterial adherence: adhesin-receptor interactions mediating the attachment of bacteria to mucosal surface. J Infect Dis. 1981 Mar;143(3):325–345. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.3.325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell G. I. Models for the specific adhesion of cells to cells. Science. 1978 May 12;200(4342):618–627. doi: 10.1126/science.347575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackstock R., Kelly F. C. Comparison of staphylococcal clumping factor and protein A. J Bacteriol. 1968 Sep;96(3):855–856. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.3.855-856.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brückler J., Schaeg W., Blobel H. Isolierung des "Clumping Factors" von Staphylococcus aureus. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig A. 1974 Sep;228(4):465–473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr M. E., Jr, Gabriel D. A., Herion J. C., Roberts H. R. Granulocyte lysosomal cationic protein alters fibrin assembly: a possible mechanism for granulocyte control of clot structure. J Lab Clin Med. 1986 Mar;107(3):199–203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chhatwal G. S., Preissner K. T., Müller-Berghaus G., Blobel H. Specific binding of the human S protein (vitronectin) to streptococci, Staphylococcus aureus, and Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1987 Aug;55(8):1878–1883. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.8.1878-1883.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUTHIE E. S. Evidence for two forms of staphylococcal coagulase. J Gen Microbiol. 1954 Jun;10(3):427–436. doi: 10.1099/00221287-10-3-427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison V. E., Sanford B. A. Factors influencing adherence of Staphylococcus aureus to influenza A virus-infected cell cultures. Infect Immun. 1982 Sep;37(3):946–955. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.3.946-955.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn D. L., Simmons R. L. Fibrin in peritonitis. III. The mechanism of bacterial trapping by polymerizing fibrin. Surgery. 1982 Sep;92(3):513–519. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engels W., Kamps M. A. Secretion of staphylocoagulase be Staphylococcus aureus: the role of a cell-bound intermediate. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1981;47(6):509–524. doi: 10.1007/BF00443238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espersen F., Clemmensen I., Barkholt V. Isolation of Staphylococcus aureus clumping factor. Infect Immun. 1985 Sep;49(3):700–708. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.3.700-708.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espersen F., Schiøtz P. O. Normally-occurring precipitating antibodies against Staphylococcus aureus in human serum and colostrum. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand C. 1981 Apr;89(2):93–98. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1981.tb02670.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fröman G., Switalski L. M., Speziale P., Hök M. Isolation and characterization of a fibronectin receptor from Staphylococcus aureus. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 15;262(14):6564–6571. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapral F. A. Factors involved in experimental staphylococcal peritonitis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1965 Jul 23;128(1):259–273. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1965.tb11643.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopec M., Wegrzynowicz Z., Latallo Z. S. Precipitation of soluble fibrin monomer complexes SFMC by cellular basic proteins, and the antagonistic effect of sulfonated mycopolysaccharides. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1970 Dec;135(3):675–679. doi: 10.3181/00379727-135-35119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanser M. E., Saba T. M. Fibronectin as a co-factor necessary for optimal granulocyte phagocytosis of Staphylococcus aureus. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1981 Nov;30(5):415–424. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopes J. D., dos Reis M., Brentani R. R. Presence of laminin receptors in Staphylococcus aureus. Science. 1985 Jul 19;229(4710):275–277. doi: 10.1126/science.3160113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millar M. R., Inglis T. Influence of lysozyme on aggregation of Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Sep;25(9):1587–1590. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.9.1587-1590.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller K. D., Hetrick D. L., Bielefeldt D. J. Production and properties of Staphylococcus aureus (strain Newman D2C) with uniform clumping factor activity. Thromb Res. 1977 Feb;10(2):203–211. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(77)90002-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proctor R. A., Christman G., Mosher D. F. Fibronectin-induced agglutination of Staphylococcus aureus correlates with invasiveness. J Lab Clin Med. 1984 Oct;104(4):455–469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotter J., Kelly F. C. Serological reactions associated with the clumping factor of Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1966 Feb;91(2):588–594. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.2.588-594.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schenkein I., Levy M., Uhr J. W. The use of glucose oxidase as a generator of H 2 O 2 in the enzymatic radioiodination of components of cell surfaces. Cell Immunol. 1972 Nov;5(3):490–493. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(72)90076-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toy P. T., Lai L. W., Drake T. A., Sande M. A. Effect of fibronectin on adherence of Staphylococcus aureus to fibrin thrombi in vitro. Infect Immun. 1985 Apr;48(1):83–86. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.1.83-86.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umeda A., Ikebuchi T., Amako K. Localization of bacteriophage receptor, clumping factor, and protein A on the cell surface of Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1980 Feb;141(2):838–844. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.2.838-844.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Usui Y. Biochemical properties of fibrinogen binding protein (clumping factor) of the staphylococcal cell surface. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1986 Sep;262(3):287–297. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(86)80001-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vercellotti G. M., McCarthy J. B., Lindholm P., Peterson P. K., Jacob H. S., Furcht L. T. Extracellular matrix proteins (fibronectin, laminin, and type IV collagen) bind and aggregate bacteria. Am J Pathol. 1985 Jul;120(1):13–21. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wegrzynowicz Z., Heczko P. B., Jeljaszewicz J., Neugebauer M., Pulverer G. Pseudocoagulase activity of staphylococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Jan;9(1):15–19. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.1.15-19.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodward M. P., Young W. W., Jr, Bloodgood R. A. Detection of monoclonal antibodies specific for carbohydrate epitopes using periodate oxidation. J Immunol Methods. 1985 Apr 8;78(1):143–153. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(85)90337-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]