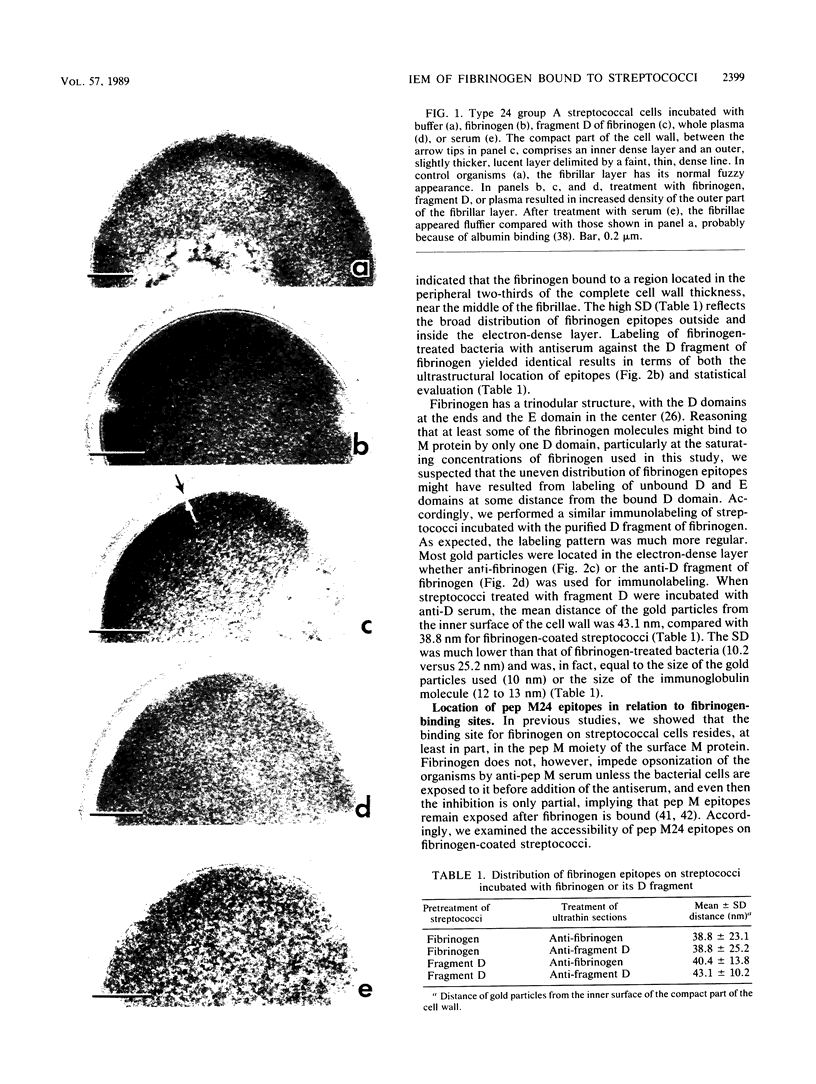
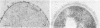Abstract
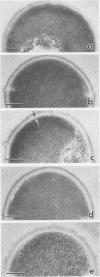
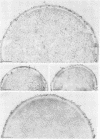
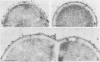
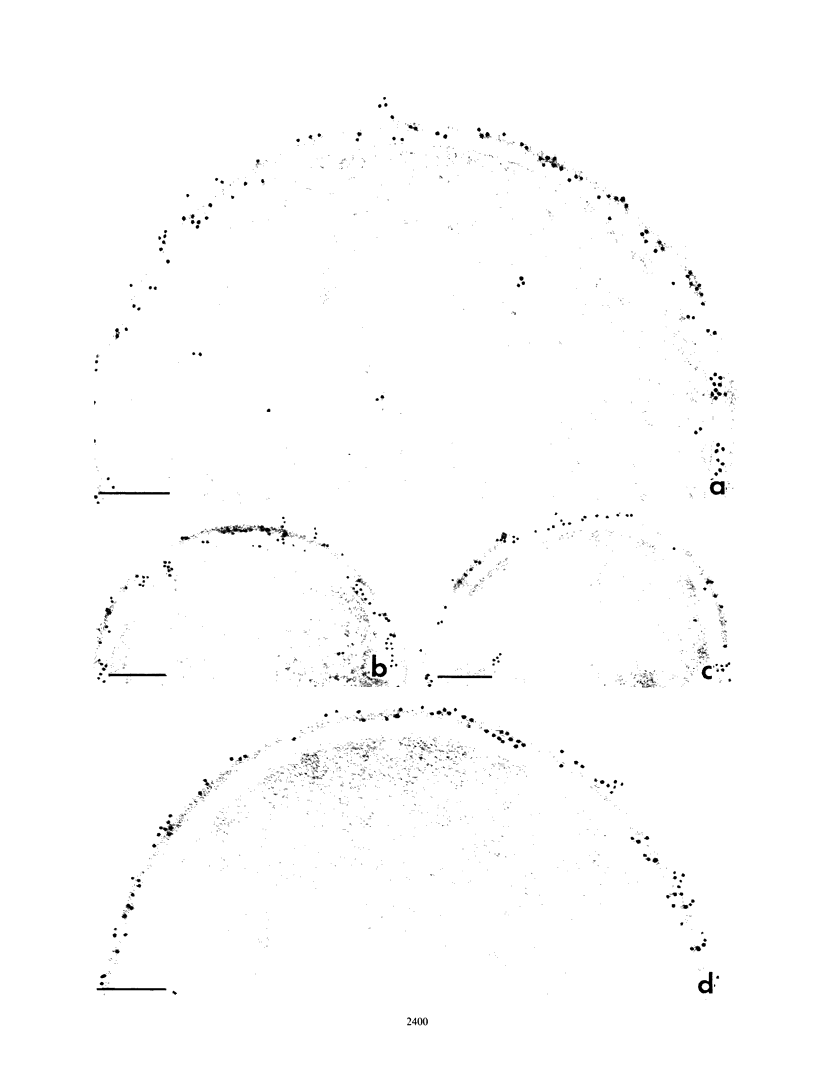
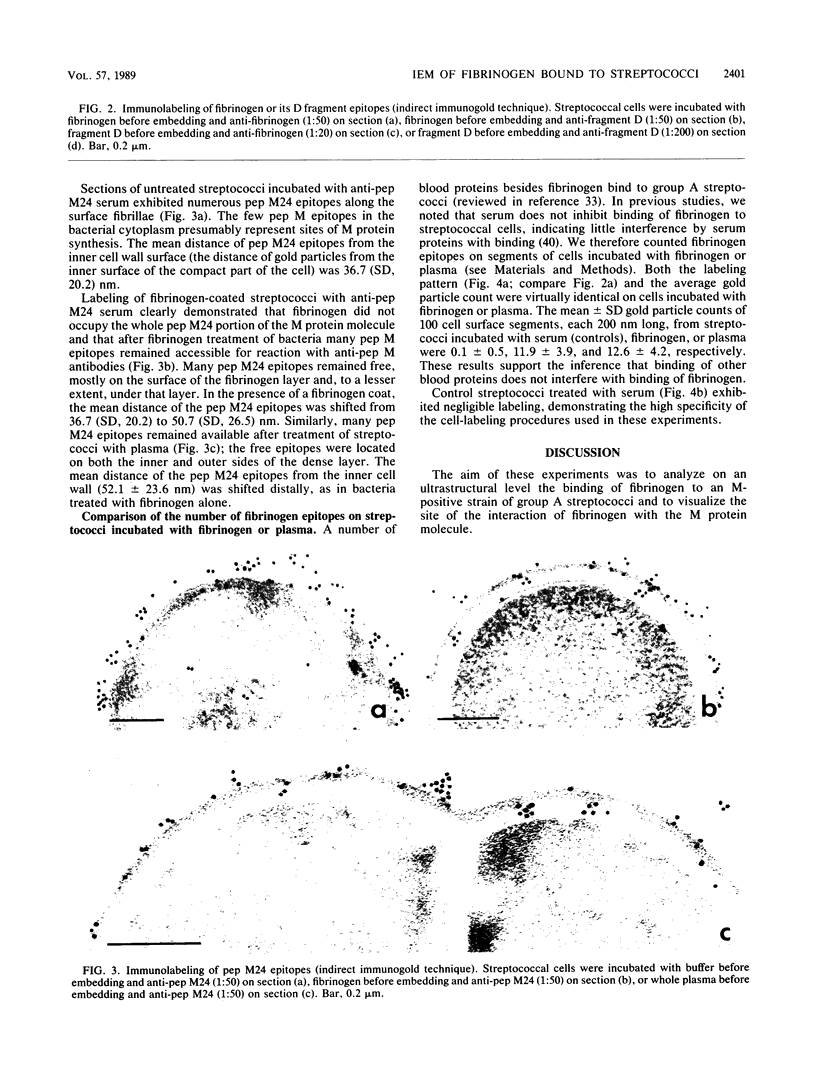
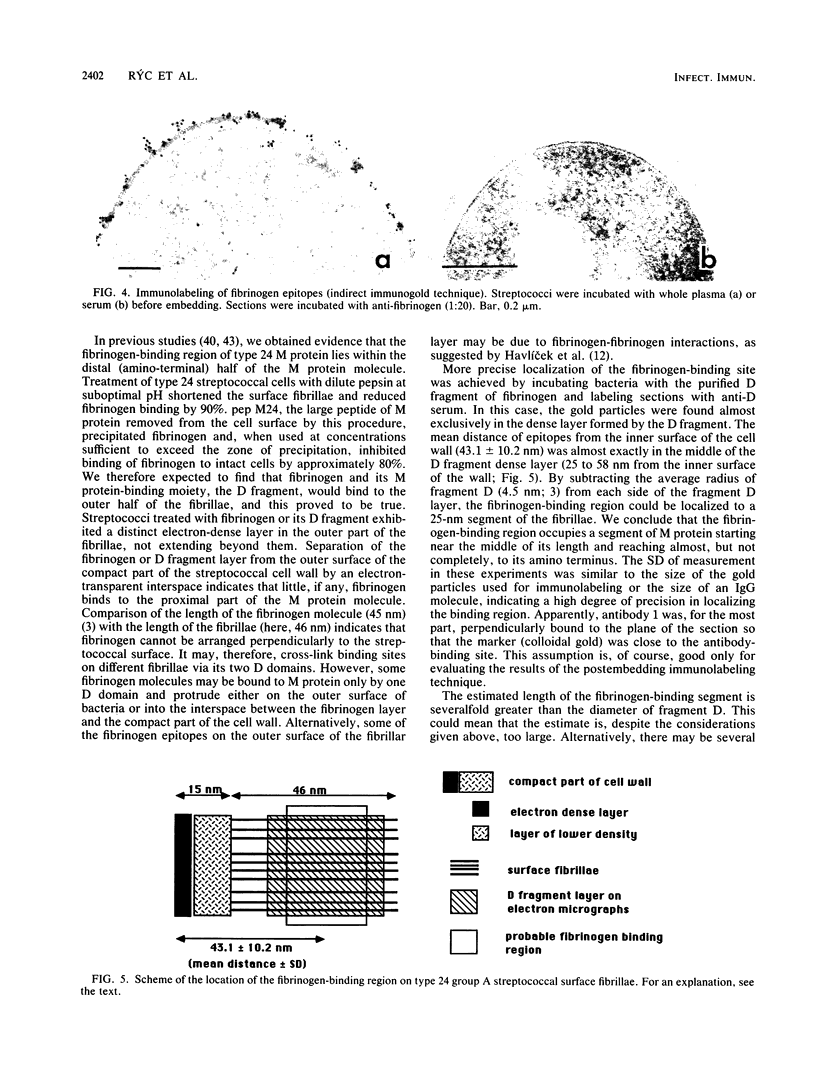
Binding of fibrinogen to the M protein located on the surface fibrillae of group A streptococci impedes deposition of complement and thus contributes to the virulence of these organisms. We investigated this binding by electron microscopy using postembedding immunogold labeling. Both fibrinogen and its D fragment formed a distinct dense layer in the surface fibrillae, separated by 10 nm from the compact part of the cell wall. Labeling the sections with anti-fibrinogen or anti-fragment D showed that the fibrinogen-binding region lay within a 25-nm segment of the fibrillae beginning approximately 30 nm from the inner surface of the cell wall. The outer surface of the fibrinogen layer could be labeled with antibody to the amino-terminal half of type 24 M protein, indicating that the fibrillar tips remained exposed after fibrinogen binding. The degree of labeling with anti-fibrinogen, determined by gold particle counting, was the same whether the bacterial cells had been incubated with purified fibrinogen or whole plasma. These results indicate that the fibrinogen-binding region lies in the distal (amino-terminal) half of the M protein molecule but excludes the most distal portion, which is the site of epitopes that interact with opsonic anti-M antibody, and that plasma proteins other than fibrinogen, a number of which are known to bind to group A streptococci, do not interfere with fibrinogen binding.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acetarin J. D., Carlemalm E., Villiger W. Developments of new Lowicryl resins for embedding biological specimens at even lower temperatures. J Microsc. 1986 Jul;143(Pt 1):81–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1986.tb02766.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beachey E. H., Stollerman G. H., Chiang E. Y., Chiang T. M., Seyer J. M., Kang A. H. Purification and properties of M protein extracted from group A streptococci with pepsin: covalent structure of the amino terminal region of type 24 M antigen. J Exp Med. 1977 Jun 1;145(6):1469–1483. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.6.1469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beijbom L., Larsson U., Kavéus U., Hebert H. Structure analysis of fibrinogen by electron microscopy and image processing. J Ultrastruct Mol Struct Res. 1988 Mar;98(3):312–319. doi: 10.1016/s0889-1605(88)80923-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bendayan M., Nanci A., Kan F. W. Effect of tissue processing on colloidal gold cytochemistry. J Histochem Cytochem. 1987 Sep;35(9):983–996. doi: 10.1177/35.9.3302022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlemalm E., Villiger W., Hobot J. A., Acetarin J. D., Kellenberger E. Low temperature embedding with Lowicryl resins: two new formulations and some applications. J Microsc. 1985 Oct;140(Pt 1):55–63. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1985.tb02660.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chhatwal G. S., Dutra I. S., Blobel H. Fibrinogen binding inhibits the fixation of the third component of human complement on surface of groups A, B, C, and G streptococci. Microbiol Immunol. 1985;29(10):973–980. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1985.tb02961.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtney H. S., Ofek I., Simpson W. A., Hasty D. L., Beachey E. H. Binding of Streptococcus pyogenes to soluble and insoluble fibronectin. Infect Immun. 1986 Sep;53(3):454–459. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.3.454-459.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischetti V. A., Jones K. F., Scott J. R. Size variation of the M protein in group A streptococci. J Exp Med. 1985 Jun 1;161(6):1384–1401. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.6.1384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischetti V. A., Parry D. A., Trus B. L., Hollingshead S. K., Scott J. R., Manjula B. N. Conformational characteristics of the complete sequence of group A streptococcal M6 protein. Proteins. 1988;3(1):60–69. doi: 10.1002/prot.340030106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox E. N. M proteins of group A streptococci. Bacteriol Rev. 1974 Mar;38(1):57–86. doi: 10.1128/br.38.1.57-86.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havlícek J., Pokorný J., Havlícková H. Quantitative character of fibrinogen uptake by M+ and M- variants of Streptococcus pyogenes. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1987 Jun;265(1-2):1–11. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(87)80147-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollingshead S. K., Fischetti V. A., Scott J. R. Complete nucleotide sequence of type 6 M protein of the group A Streptococcus. Repetitive structure and membrane anchor. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 5;261(4):1677–1686. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hryniewicz W., Lipinski B., Jeljaszewicz J. Nature of the interaction between M protein of Streptococcus pyogenes and fibrinogen. J Infect Dis. 1972 Jun;125(6):626–630. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.6.626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KANTOR F. S., COLE R. M. A fibrinogen precipitating factor (FPF) of group A streptococci. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1959 Oct;102:146–150. doi: 10.3181/00379727-102-25172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KANTOR F. S. FIBRINOGEN PRECIPITATION BY STREPTOCOCCAL M PROTEIN. I. IDENTITY OF THE REACTANTS, AND STOICHIOMETRY OF THE REACTION. J Exp Med. 1965 May 1;121:849–859. doi: 10.1084/jem.121.5.849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronvall G. A surface component in group A, C, and G streptococci with non-immune reactivity for immunoglobulin G. J Immunol. 1973 Nov;111(5):1401–1406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronvall G., Schönbeck C., Myhre E. Fibrinogen binding structures in beta-hemolytic streptococci group A, C, and G. Comparisons with receptors for IgG and aggregated beta 2-microglobulin. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1979 Oct;87(5):303–310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronvall G., Simmons A., Myhre E. B., Jonsson S. Specific absorption of human serum albumin, immunoglobulin A, and immunoglobulin G with selected strains of group A and G streptococci. Infect Immun. 1979 Jul;25(1):1–10. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.1.1-10.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler W., Prokop O. Relationship between haptoglobin and Streptococcus pyogenes T4 antigens. Nature. 1978 Jan 26;271(5643):373–373. doi: 10.1038/271373a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kühnemund O., Havlicek J., Knöll H., Sjöquist J., Köhler W. Interaction of group A type 1 streptococcal M protein with fibrinogen. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand B. 1985 Jun;93(3):201–209. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1985.tb02877.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANCEFIELD R. C. Current knowledge of type-specific M antigens of group A streptococci. J Immunol. 1962 Sep;89:307–313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lämmler C., Chhatwal G. S., Blobel H. Variations in the binding of mammalian fibrinogens to streptococci of different animal origin. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1983;172(3):191–196. doi: 10.1007/BF02123805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mouw A. R., Beachey E. H., Burdett V. Molecular evolution of streptococcal M protein: cloning and nucleotide sequence of the type 24 M protein gene and relation to other genes of Streptococcus pyogenes. J Bacteriol. 1988 Feb;170(2):676–684. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.2.676-684.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pancholi V., Fischetti V. A. Isolation and characterization of the cell-associated region of group A streptococcal M6 protein. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jun;170(6):2618–2624. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.6.2618-2624.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips G. N., Jr, Flicker P. F., Cohen C., Manjula B. N., Fischetti V. A. Streptococcal M protein: alpha-helical coiled-coil structure and arrangement on the cell surface. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4689–4693. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:208–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuterswärd A., Miörner H., Wagner M., Kronvall G. Variations in binding of mammalian fibrinogens to streptococci groups A, B, C, E, G and to Staphylococcus aureus. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand B. 1985 Apr;93(2):77–82. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1985.tb02855.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Runehagen A., Schönbeck C., Hedner U., Hessel B., Kronvall G. Binding of fibrinogen degradation products to S. aureus and to beta-hemolytic streptococci group A, C and G. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1981 Apr;89(2):49–55. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1981.tb00151_89b.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rýc M., Wagner B., Wagner M., Petrás P., Havlicek J. Binding of horse-spleen ferritin to group A streptococci. Microbios. 1985;44(181S):261–269. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J. R., Pulliam W. M., Hollingshead S. K., Fischetti V. A. Relationship of M protein genes in group A streptococci. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(6):1822–1826. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.6.1822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J., Hsu K. C., Gotschlich E. C. Electron microscopic studies on streptococci. I. M antigen. J Exp Med. 1969 Nov 1;130(5):1063–1091. doi: 10.1084/jem.130.5.1063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Switalski L. M., Ljungh A., Rydén C., Rubin K., Hök M., Wadström T. Binding of fibronectin to the surface of group A, C, and G streptococci isolated from human infections. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Dec;1(6):381–387. doi: 10.1007/BF02019939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner B., Schmidt K. H., Wagner M., Köhler W. Albumin bound to the surface of M protein-positive streptococci increased their phagocytosis by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes in the absence of complement and bactericidal antibodies. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1986 Jul;261(4):432–446. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(86)80075-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitnack E., Beachey E. H. Antiopsonic activity of fibrinogen bound to M protein on the surface of group A streptococci. J Clin Invest. 1982 Apr;69(4):1042–1045. doi: 10.1172/JCI110508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitnack E., Beachey E. H. Biochemical and biological properties of the binding of human fibrinogen to M protein in group A streptococci. J Bacteriol. 1985 Oct;164(1):350–358. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.1.350-358.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitnack E., Beachey E. H. Inhibition of complement-mediated opsonization and phagocytosis of Streptococcus pyogenes by D fragments of fibrinogen and fibrin bound to cell surface M protein. J Exp Med. 1985 Dec 1;162(6):1983–1997. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.6.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitnack E., Dale J. B., Beachey E. H. Common protective antigens of group A streptococcal M proteins masked by fibrinogen. J Exp Med. 1984 Apr 1;159(4):1201–1212. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.4.1201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitnack E., Dale J. B., Beachey E. H. Streptococcal defenses against host immune attack: the M protein-fibrinogen interaction. Trans Assoc Am Physicians. 1983;96:197–202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]