Abstract
The purpose of this study was to investigate the effect of cyclodextrins (CDs) on aqueous solubility, stability, and in vitro corneal permeability of delta-8-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ8-THC). Phase solubility of Δ8-THC was studied in the presence of 2-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin (HPβCD), randomly methylated-β-cyclodextrin (RMβCD) and sulfobutyl ether-β-cyclodextrin sodium salt (SβCD). Stability of Δ8-THC in 5% w/v aqueous CD solutions, as a function of pH, was studied following standard protocols. In vitro corneal permeation of Δ8-THC (with and without CDs) across excised rabbit cornea was also determined. Phase-solubility profile of Δ8-THC in the presence of both HPβCD and RMβCD was of the AP type, whereas, with SβCD an AL type was apparent. Aqueous solubility of Δ8-THC increased to 1.65, 2.4, and 0.64 mg/mL in the presence of 25% w/v HPβCD, RMβCD, and SβCD, respectively. Significant degradation of Δ8-THC was not observed within the study period at the pH values studied, except for at pH 1.2. Transcorneal permeation of Δ8-THC was dramatically improved in the presence of CDs. The results demonstrate that CDs significantly increase aqueous solubility, stability, and transcorneal permeation of Δ8-THC. Thus, topical ophthalmic formulations containing Δ8-THC and modified beta CDs may show markedly improved ocular bioavailability.
Key words: cyclodextrins, glaucoma, ocular, tetrahydrocannabinol
INTRODUCTION
Cannabinoids have attracted a great deal of attention as a potential new class of antiglaucoma agents (1,2). Delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9-THC), the biologically active chemical component of Cannabis sativa (marijuana), is responsible for a majority of the plant's pharmacological effects. Currently, Δ9-THC is marketed in the USA as Marinol® for the control of nausea and vomiting caused by antineoplastic drugs, and to retard weight reduction syndrome associated with HIV/AIDS (3). However, Δ9-THC is gaining recognition as a treatment option for a host of other medical disorders including glaucoma (4). Earlier studies demonstrate that smoking of marijuana and intravenous and oral administration of Δ9-THC and Δ8-THC (delta-8-tetrahydrocannabinol) reduces the intraocular pressure (IOP), in animals and in humans (5). However, since the mechanism surrounding their effect on IOP was initially thought to involve the central nervous system, issues such as psychoactivity and side effects associated with these routes of administration hindered progress. Recent discovery of CB1 receptor expression in various ocular tissues has renewed interest in the study of topical administration of cannabinoids in the treatment of glaucoma (1,2). A number of pharmacological and histological studies strongly suggest direct role of ocular CB1 receptors in the lowering of the IOP by the cannabinoids (1,2). Additionally, Δ9-THC has also been reported to reduce glutamate and N-methyl-D-aspartate-induced retinal ganglionic cell death through its CB1 agonist activity (1–3,6–9). Moreover, the antioxidant property of Δ9-THC protects neurons against oxidative stress associated with glutamate-induced excitotoxicity (2,8,9). Therefore, in contrast to currently available drugs, topical administration of Δ9-THC would not only reduce the IOP but would also protect the retinal ganglionic cells against glutamate and N-methyl-D-aspartate-induced neurotoxicity. However, Δ9-THC is psychotropic, poorly soluble in aqueous media, and has undesirable side effects (10,11). Moreover, susceptibility to oxidation, hydrolysis, thermal, and photolytic degradation in the solution form make the design of Δ9-THC ophthalmic formulations a challenging task (11–14).
Δ8-THC, an isomer of Δ9-THC, has also been shown to be pharmacologically active as an antiglaucoma agent (1,15). The stereochemistry and in vivo and in vitro metabolism profiles of both compounds (Δ8-THC and Δ9-THC) are similar. However, Δ8-THC is easier and less expensive to prepare and is considered to be less psychotropic than Δ9-THC (15–18). Additionally, Δ8-THC is chemically more stable, does not undergo oxidation to cannabinol and has a much longer shelf life than Δ9-THC (15). Moreover, it has been shown to exhibit negligible side effects when administered prior to antineoplastic therapy in cancer patients (18). Taking this into consideration, Δ8-THC may be a better choice for topical glaucoma therapy.
Although more stable, utility of Δ8-THC as a topical ophthalmic agent is limited, just like Δ9-THC by its lipophilicity, low aqueous solubility, and resinous nature. Additionally, a host of physiological factors limit ocular bioavailability of topically administered compounds (1,19,20). The multilayered and varied corneal structure severely limits penetration of xenobiotics across the corneal membrane. For efficient transcorneal permeation, the therapeutic agents must possess optimum hydrophilic and hydrophobic characteristics (1). Moreover, adsorption of cannabinoids to glass and plastics poses a significant challenge in formulation, analysis, and topical delivery of these drugs (21–25).
In recent years, cyclodextrins (CDs) have been used in ophthalmics for the delivery of water-insoluble drugs (1,19). CDs are a group of cyclic oligosaccharides with a relative lipophilic central cavity and a hydrophilic outer surface. The hydrophobic central cavity is able to form non-covalent inclusion complexes with various drug molecules. CDs have been reported to increase the aqueous solubility, chemical stability, and bioavailability of ophthalmic drugs. Moreover, inclusion of CDs in ophthalmic formulations has been shown to reduce drug-induced ocular irritation. Complexation with CDs also improves the ocular permeability of lipophilic drugs, without affecting their inherent permeability, by making greater concentration of the free drug available at the surface of cornea (1,19). Additionally, modified beta CDs such as sulfobutyl ether-β-cyclodextrin sodium salt (SβCD) and 2-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin (HPβCD) have been reported to be safe for ocular application, even at concentrations as high as 10% and 45% w/v, respectively (19,26,27). Furthermore, topical eye drop formulations containing CDs and drugs (HPβCD/Indomethacin, randomly methylated-β-cyclodextrin (RMβCD)/chloramphenicol) are commercially available in the European market (28).
Till date there are no literature reports with respect to the interaction of CDs with Δ8-THC. Therefore, the objectives of this project were to determine the physiochemical characteristic of Δ8-THC and to investigate the effect of three different modified CDs (HPβCD, RMβCD, and SβCD) on aqueous solubility, stability, and in vitro corneal permeability of Δ8-THC.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Materials
Δ8-THC was isolated from a mixture of Δ9-THC and Δ8-THC which was produced when Δ9-THC was exposed to acidic conditions. HPβCD and RMβCD were purchased form Sigma Chemical Co. (St Louis, MO, USA) with a degree of substitution of 0.6 and 1.7, respectively. SβCD (degree of substitution 6.6), 20- and 5-mL clear glass vials were procured from Fisher Scientific (St. Louis, Missouri, USA). One-milliliter clear high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) vials and 200 μL polypropylene inserts were purchased from Waters Corporation (Milford, MA, USA). Ultra-high grade polypropylene micro centrifuge tubes, 1.6 mL, were obtained from MidSci (St.Louis, Missouri, USA). Polyethylene inserts, 250 μL, were obtained from VWR International (West Chester, PA, USA). All glass vials used in this study conformed to USP type I standards (Table I). HPLC grade solvents and other chemicals (analytical grade) were obtained from Fisher Scientific (St. Louis, Missouri, USA). Whole eyes from male albino New Zealand rabbits were obtained from Pel-Freez Biologicals (Rogers, AK). Eyes were shipped overnight in solution (Hanks' balanced salt solutions) over wet ice and were used immediately on receipt.
Table I.
Container Types, Capacity and Approximate Nominal and Fill Volumes Used in the Binding Studies
| Type of containers | Purchased from | Catalog number | Volume | Volume filled |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyethylene inserts | VWR International | 4025 | 250 μL | 200 μL |
| Polypropylene inserts | Waters Corporation | 186001728 | 200 μL | 150 μL |
| Ultrahigh-grade polypropylene | MidSci | MIC1004 | 1.6 ml | 1.5 ml |
| Clear glass vial | Fisher Scientific | 033715, 0337525 | 20 ml | 19 ml |
| Clear glass vial | Fisher Scientific | 03338B | 5 ml | 4 ml |
| HPLC vials | Waters Corporation | WAT025054c | 1 ml | 0.8 ml |
Methods
Binding of Δ8-THC to Glass and Plastics
Binding of Δ8-THC to glass and plastics was studied at two different concentrations. Δ8-THC in ethanolic stock was spiked in deionized water to yield Δ8-THC concentrations of 0.5 and 0.15 μg/mL. Final concentration of ethanol, in these primary stock solutions, was 5% and 0.5% v/v, respectively. Primary stock solutions were sampled immediately for analysis and also transferred into glass and plastic containers for binding studies (Table I). The solutions were exposed to the containers for a period of 30 min at room temperature and then analyzed for drug content. Care was taken to avoid contact with the caps. The container type, their capacity and approximate nominal and fill volumes are described in Table I. Each experiment was carried out in sets of six. Change in Δ8-THC concentration in the samples from the corresponding initial assay of the primary stock solution was determined. To avoid evaporation of ethanol, the surface-to-volume ratio in the glass and plastic containers were minimized and the vials were tightly capped. As a control, the drug content in the primary stock solution was also monitored as a function of time.
Saturation Solubility Studies
Saturation solubility studies were carried out using standard shake flask method. Briefly, Δ8-THC (in hexane) was purged with nitrogen to evaporate the hexane. Water or the respective buffers were then added to dried sample and capped. The samples were continuously agitated at 100 rpm for 24 h at 25°C in a reciprocating water bath. At the end of 24 h, the samples were centrifuged and the supernatant was analyzed for drug content. Solubility studies were carried out in water and in buffers at four pH values: phosphate (pH 3.0 and 7.4), acetate (pH 5.0), and borate (pH 9.0) buffers (buffer strength and ionic strength were 15 and 0.03 mM, respectively)
Stability in Aqueous Solutions
Stability of Δ8-THC as a function of pH was studied in the buffer solutions described above. Aliquots (19 mL) of the buffer were placed in glass vials and were allowed to equilibrate at 25°C. Δ8-THC stock solution in ethanol (1 mL) was added to the buffers, such that the final concentration of ethanol was 5% v/v. From these aliquots, 900 μL were added to several 1-mL HPLC vials (USP type I glass). The HPLC vials were tightly sealed to avoid any evaporation of ethanol and stored in a vertical position at 25°C. At predetermined intervals, these vials were taken out and analyzed for Δ8-THC content. Additionally, using a similar protocol, stability of Δ8-THC at 40°C in phosphate buffer (pH 7.4) was also investigated. Experiments were conducted at least in triplicate. Log percent drug remaining was plotted against time and the apparent degradation rate constants were calculated from the slope of the line of best-fit. Stability of Δ8-THC was also determined in buffer solutions containing 5% w/v CDs and 5% v/v ethanol.
Determination of Octanol–Water Partition Coefficient and Ionization Constant
Predicted values of Moriguchi log P (mlog P) and pKa of Δ8-THC were determined using ACD Lab/I-Lab web service (ACD/Log P 8.02, ACD/pKa 8.03).
Phase-Solubility Studies
Complexation of Δ8-THC with various CDs was determined using phase-solubility studies according to the method of Higuchi and Connors (29). Excess amount of Δ8-THC was added to 5 mL aqueous solutions, in screw-capped vials, containing increasing concentrations of CDs. The concentrations ranged from 0.72 to 181 mM for HPβCD; 0.76 to 190 mM for RMβCD; and 0.46 to 116 mM for SβCD. The resulting suspensions were shaken at 25°C for 24 h in a reciprocating water bath. Following equilibration, the suspensions were centrifuged at 13,000 rpm for 20 min at 4°C and the supernatant thus obtained was analyzed using an HPLC system. Phase-solubility profile was obtained by plotting the solubility of Δ8-THC against the concentration of CDs used. Each experiment was carried out at least in triplicate, and the binding constants (K1:1) for the drug-cyclodextrin complex were calculated from the linear region of the solubility curves using Eq. 1:
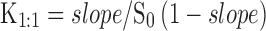 |
1 |
Where, S0 = intrinsic solubility of the drug.
In Vitro Corneal Permeation Studies
Corneas excised from whole eyes, obtained from Pel-Freez Biologicals (Roger, AK), were used for the determination of in vitro transcorneal permeability. Whole eyes were shipped overnight in Hanks' balanced salt solution, over wet ice, and were used immediately upon receipt. The corneas were excised with some scleral portion adhering to help secure the membrane between the diffusion half-cells during the course of a transport study. After excision, the corneas were washed with ice-cold Dulbecco's phosphate buffer saline (DPBS, pH 7.4) and mounted on side-bi-side diffusion half-cells (PermeGear Inc., Bethlehem, PA, USA) with the epithelial side facing the donor chamber. Temperature of the half-cells, were maintained at 34°C with the help of a circulating water bath. Excess Δ8-THC was pre-equilibrated, for 24 h at 25°C, with DPBS containing 5% w/v of HPβCD, RMβCD, or SβCD, separately. The supernatants were analyzed for drug content and 3 mL of these solutions were added to the donor chamber of the diffusion apparatus, in separate sets of experiment. The receiver chamber contained 3.2 mL of the respective 5% w/v HPβCD, RMβCD, or SβCD in DPBS solutions. CDs were added to the receiver chamber to maintain sink condition throughout the duration of the experiment. Additionally, in vitro corneal permeability of a Δ8-THC suspension formulation (200 μg/mL) was also determined as a control. In this case, the donor solution consisted of 3 mL of a 200 μg/mL Δ8-THC suspension and the receiver chamber contained 3.2 mL of a 5% HPβCD in DPBS solution. A slight difference in the donor and receiver chamber volumes maintained the normal shape of the cornea through marginally elevated hydrostatic pressure. The contents of both chambers were stirred continuously with a magnetic stirrer. Aliquots, 600 μL, were withdrawn from the receiver chamber at predetermined time points (30, 60, 90, 120, 150, and 180 min), and replaced with an equal volume of the respective CD solutions. Samples were analyzed immediately for drug content. All experiments were carried out at least in quadruplicates.
Data Analysis
Rate of Δ8-THC transport across excised rabbit cornea was obtained from the slope of a “cumulative amount of Δ8-THC transported” versus “time” plot. Steady-state flux (SSF) were determined by dividing the rate of transport by the surface area as described in Eq. 2
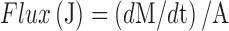 |
2 |
Where, M is the cumulative amount of drug transported and A is the corneal surface area exposed to the permeant.
Corneal membrane permeability was determined by normalizing the SSF to the donor concentration, Cd according to Eq. 3
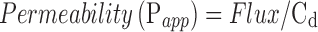 |
3 |
Analytical Method
Samples were analyzed for drug content using an HPLC system which comprised a Waters 717 plus autosampler, Waters 2487 Dual λ Absorbance detector, Waters 600 controller pump, and Agilent 3395 integrator. A Symmetry® C18 4.6 × 250-mm column was used and the mobile phase consisted of 20% of a 25 mM phosphate buffer (pH 3.0) with 0.1% triethylamine mixture and 80% acetonitrile. The wavelength (λ) and flow rate was set at 215 nm and 1.5 mL/min, respectively. The limit of detection and limit of quantification of Δ8-THC was 5 and 10 ng/mL, respectively, and the precision RSD at the limit of quantification was 4%.
RESULTS
Binding of Δ8-THC to Glass and Plastics
The majority of research laboratories and pharmaceutical companies use glass that conforms to USP type I standards (30). Therefore binding of THC to USP type I glass and plastic containers was investigated. Binding was evaluated at two different Δ8-THC concentrations (0.5 and 0.15 μg/mL). The solutions were exposed to the containers (Table I) for a period of 30 min at room temperature and analyzed for drug content. Chemical degradation of the drug was not observed in the 30-min study period and any change in Δ8-THC content was attributed to sticking of the compound to the walls of the glass vials or plastic containers. Table II summarizes the percentage loss of Δ8-THC in the different containers at the two different concentrations studied. Δ8-THC demonstrated greatest binding to the plastic containers at 0.15 μg/mL, with the polyethylene and polypropylene inserts not showing any detectable Δ8-THC levels at the end of 30 min. Δ8-THC concentration was below the limit of quantification in four out of the six polyethylene inserts used when the primary stock solution concentration was 0.5 μg/mL. In the remaining two polyethylene inserts, the concentration of Δ8-THC remaining was only 0.07 and 0.12 μg/mL. About 78.7% and 41.2% losses in drug content were observed in the polypropylene inserts and ultrahigh-grade polypropylene containers, respectively, at the 0.5 μg/mL drug concentration within 30 min. At 0.15 μg/mL Δ8-THC, 47% drug loss was observed in the ultrahigh-grade polypropylene containers. Δ8-THC did not stick to glass vials meeting the USP Type I standards at the concentrations tested, 0.15 and 0.5 μg/mL. The percent drug loss in the glass vials was observed to be within the RSD of the analytical method. The surface-to-volume ratio of the vials, however, had an impact on the binding of Δ8-THC to glass (data not provided). On the basis of these results, further studies were carried out in glass vials meeting USP type I specifications only.
Table II.
Percent Δ8-THC Loss of in Different Containers at Two Different Concentrations
| Type of container | Percentage of drug loss in 30 min (0.5 μg/ml, 5%v/v ethanol) | Percentage of drug loss in 30 min (0.15 μg/ml, 0.5% v/v ethanol) |
|---|---|---|
| Polyethylene inserts | 86.4 and 76.0 (n = 2) | ND |
| Polypropylene inserts | 78.7 ± 8.1 | ND |
| Ultra high grade Polypropylene | 41.2 ± 4.7 | 47.0 ± 2.3 |
| Clear glass vial (20 mL) | 1.8 ± 1.6 | 1.7 ± 1.3 |
| Clear glass vial (5 mL) | 0.9 ± 1.1 | 1.9 ± 1.4 |
| HPLC vials (1 mL) | 0 | 1.4 ± 1.8 |
These studies were carried out for 30 min at room temperature. Values are represented as mean ± sd (n = 6). All glass vials used in this study met USP Type I specification
ND not detectable
Saturation Solubility Studies
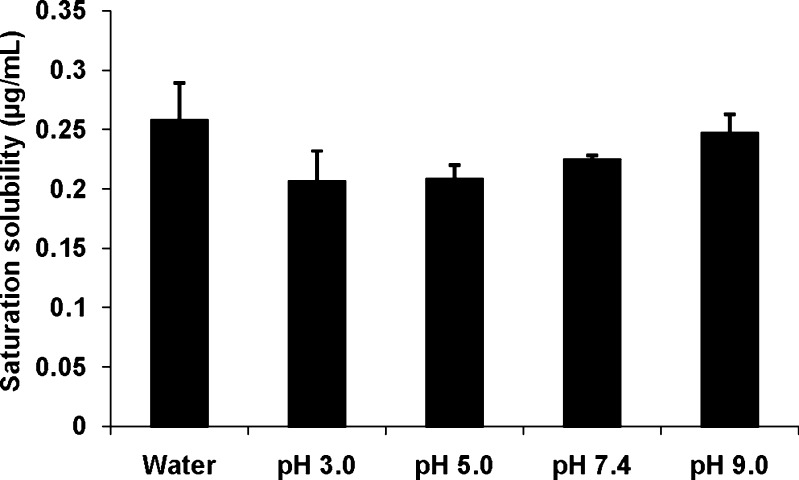
Saturation solubility of Δ8-THC in water and as a function of pH is illustrated in Fig. 1. These studies were carried out at 25°C for 24 h in a reciprocating water bath. Aqueous solubility of Δ8-THC was observed to be 0.26 ± 0.03 μg/mL. The pH dependent solubility studies (pH 3.0–9.0) indicated that solubility of Δ8-THC was independent of solution pH.
Fig. 1.
Solubility of Δ8-THC in water and as a function of pH. The solubility studies were carried out at 25°C for a period of 24 h. Values are represented as mean ± SD (n = 3)
Stability in Aqueous Solutions
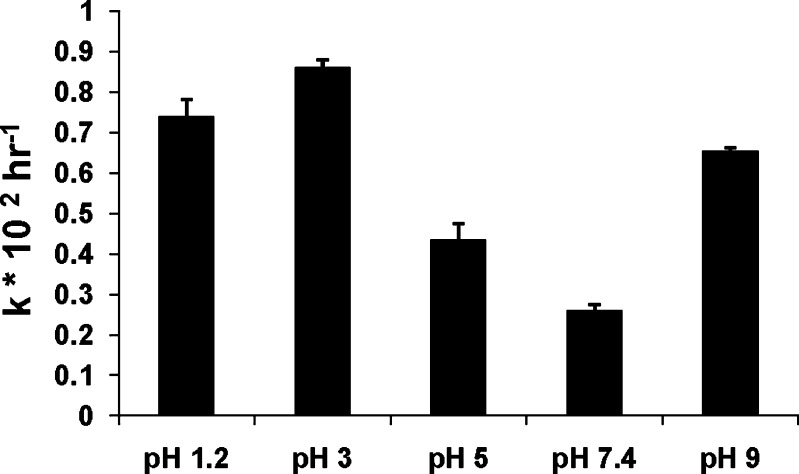
Aqueous stability of Δ8-THC was determined within the pH range of 1.2 to 9.0 at 25°C. Δ8-THC exhibited pseudo-first order degradation kinetics at all the pH values tested. Half-lives of Δ8-THC in pH 5.0, 7.4, and 9.0 were 195.0 ± 4.2, 266.5 ± 14.0 and 105.0 ± 1.2 h, respectively. In pH 1.2 and 3.0 buffers, the half-lives were 84.0 ± 2.6 and 94.0 ± 5.4 h, respectively (Fig. 2). A 1.5-fold increase in the degradation rate (from 0.0027 ± 0.00026 to 0.0042 ± 0.00016 h−1) of Δ8-THC was observed when the studies were carried out at 40°C in phosphate buffer pH 7.4
Fig. 2.
Apparent first order degradation rate constant (k × 102 h−1) of Δ8-THC at 25°C as a function of pH. Results are depicted as mean ± SD (n = 3)
pH-Stability Profile in the Presence of Cyclodextrins
Table III depicts the pH-stability profile of Δ8-THC in the presence of 5% w/v CDs. HPβCD, RMβCD, and SβCD were tested for their ability to improve the solution stability of Δ8-THC. Stability was determined in buffer solutions containing 5% w/v CDs at five pH values: pH 1.2, 3.0, and 7.4 (phosphate); pH 5.0 (acetate); and pH 9.0 (borate). The buffers also contained 5% v/v ethanol since preparation of the Δ8-THC controls needed 5% v/v ethanol. All three beta cyclodextrins tested dramatically improved the chemical stability of Δ8-THC at all the pH values tested. Significant degradation of Δ8-THC was not observed for a period of 2 months (last time point tested) in pH 3.0, 5.0, 7.4, and 9 buffers. However, at pH 1.2, 20.0% and 75% of Δ8-THC degraded in the 5% w/v SβCD and HPβCD solutions, respectively.
Table III.
Effect of pH on the degradation of Δ8-THC in the absence or in the presence of CDs
| pH | Percent delta-8-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ8-THC) degraded | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Without CD in 4 days | In the presence of 5% w/v HPβCD in 2 months | In the presence of 5% w/v RMβCD in 2 months | In the presence of 5% w/v SβCD in 2 months | |
| 1.2 | 53.0 ± 1.2 | 20.0 ± 2.3 | 0 | 75 ± 4.0 |
| 3.0 | 63.0 ± 2.1 | 4.0 ± 0.8 | 0 | 0 |
| 5.0 | 40.0 ± 0.8 | 2.8 ± 1.2 | 0 | 0 |
| 7.4 | 36.0 ± 1.2 | 3.0 ± 0.6 | 0 | 0 |
| 9.0 | 54.0 ± 0.9 | 3.0 ± 1.8 | 0 | 0 |
These studies were carried out at room temperature. Results are depicted as mean ± SD (n = 3).
Determination of Octanol–Water Partition Coefficient and Ionization Constant
Predicted values of mlog P (Moriguchi log P) and pKa determined using ACD Lab/I-Lab web service (ACD/Log P 8.02, ACD/Pka 8.03, respectively) were 7.53 ± 0.36 and 9.83 ± 0.6, respectively.
Phase-Solubility Studies
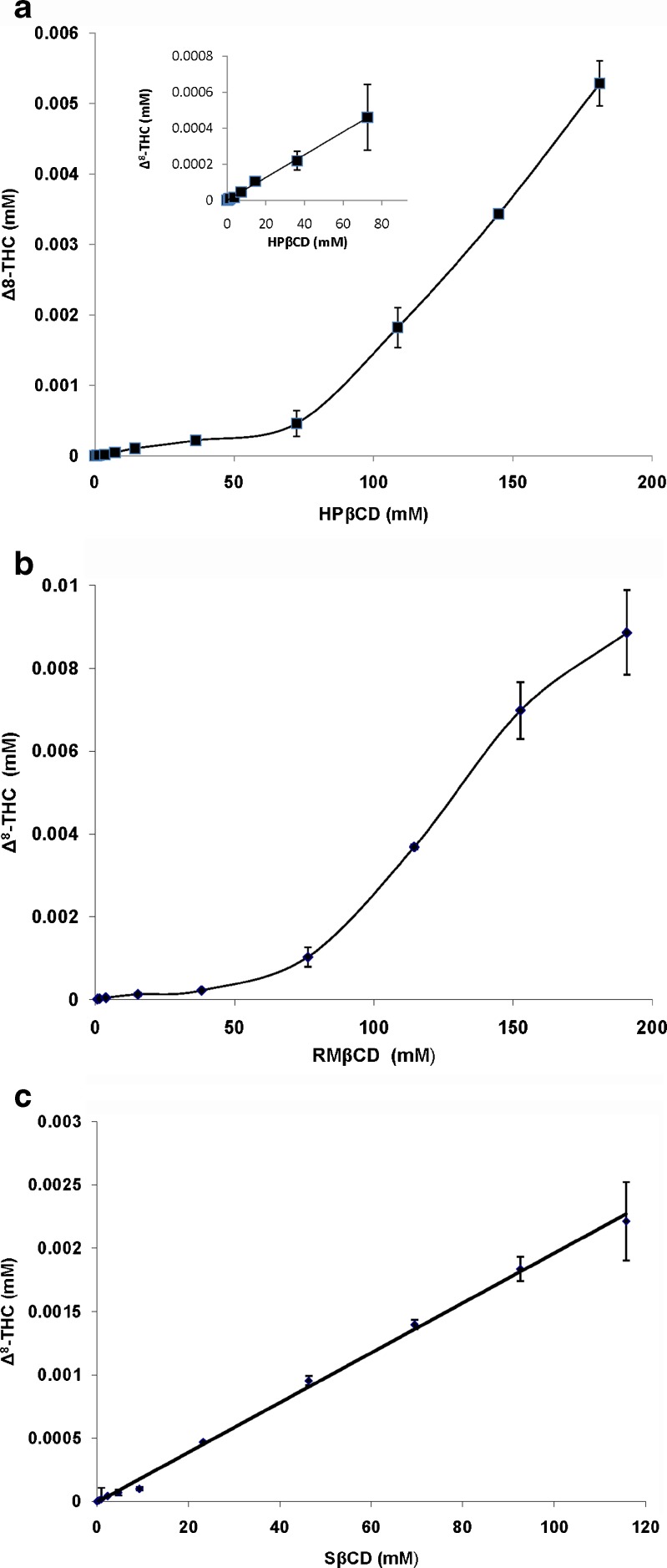
The phase-solubility studies are useful for studying the complexation of poorly soluble drugs with CDs because it not only determines the solubilizing capacity of the CDs but also provides an insight into the stoichiometry of the inclusion complexes formed. Figure 3 represents the phase-solubility diagrams of Δ8-THC with HPβCD, RMβCD, and SβCD, respectively. Phase-solubility studies were conducted for a period of 24 h. Binding constants (Table IV) were calculated from the slopes of the linear phase-solubility plots using Eq. 1. All the CDs tested, dramatically improved the aqueous solubility of Δ8-THC. A 8,250-fold (1.65 mg/mL) and 12,000-fold (2.4 mg/mL) increase in solubility was observed in the presence of 25% w/v HPβCD and RMβCD, respectively. In the presence of 25% w/v SβCD, aqueous solubility of Δ8-THC was 640 μg/mL. The phase-solubility data of Δ8-THC with both HPβCD and RMβCD resulted in an AP-type Higuchi plot. The curve showed positive deviation from linearity, indicating the formation of higher order complexes (Fig. 3a and b). In contrast, aqueous solubility of Δ8-THC increased linearly as a function of SβCD concentration (AL-type plot) indicating the stoichiometry of Δ8-THC: SΒCD complex is probably 1:1 (Fig. 3c). The binding constant values were 11,555, 12,200, and 31,000 M−1 for HPβCD, RMβCD, and SβCD, respectively.
Fig. 3.
a Phase solubility of Δ8-THC in the presence of HPβCD at 25°C, following 24-h equilibration. Each point represents mean ± SD (n = 6). Insert represents that the phase solubility of Δ8-THC as AL type up to a concentration of 80 mM HPβCD. The total diagram is classified as AP type. b Phase solubility of Δ8-THC in the presence of RMβCD at 25°C, following 24-h equilibration. Each point represents mean ± SD (n = 6). The diagram is classified as AP type. c Phase solubility of Δ8-THC in the presence of SβCD at 25°C, following 24-h equilibration. Each point represents mean ± SD (n = 6). The diagram is classified as AL type
Table IV.
Slope, Apparent Stability Constant (K 1:1) and Correlation Coefficient (R 2) Determined from the Δ8-THC: HPβCD, Δ8-THC: RMβCD and Δ8-THC: SβCD Aqueous Phase-Solubility Diagrams
| Cyclodextrins | Slope × 106 | K 1:1 (M−1) | R 2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| HPΒCD | 7.36 | 11,555 | 0.997 |
| RMΒCD | 7.76 | 12,200 | 0.994 |
| SΒCD | 19.20 | 31,000 | 0.998 |
The solubility of Δ8-THC in the absences of CD (S0) was found to be 0.64 ± 0.01 × 10−6 mM
In Vitro Corneal Permeation Studies
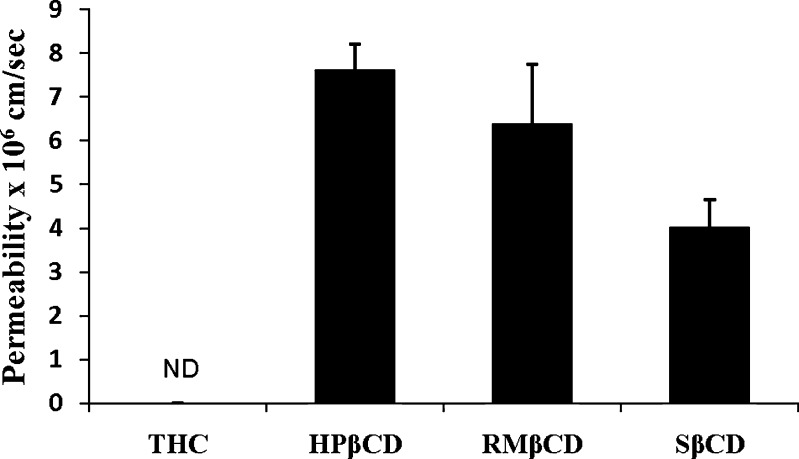
In these studies, the donor solution (3.0 mL) consisted of supernatants of Δ8-THC solutions, pre-equilibrated for 24 h at 25°C in DPBS (pH 7.4) containing 5% w/v HPβCD, RMβCD, or SβCD. The receiver chamber contained 3.2 mL of the respective solutions of 5% HPβCD, 5% RMβCD, or 5% SβCD in DPBS. The supernatants of the 5% w/v HPβCD, RMβCD, and SβCD in DPBS contained 86 μg/mL, 70 μg/mL and 168 μg/mL of Δ8-THC, respectively. The permeability of Δ8-THC, with or without CDs across the excised rabbit cornea is depicted in Fig. 4. In the case of the Δ8-THC suspension, the drug was not detectable in the receiver chamber till the last time point tested (3 h). However, corneal permeation of the resinous, unstable, and poorly soluble Δ8-THC was dramatically improved in the presence of CDs. The apparent permeability of Δ8-THC in the presence of 5% w/v HPβCD, RMβCD, and SβCD was determined to be 7.6 ± 0.6 × 10−6, 6.3 ± 1.3 × 10−6, and 4.0 ± 0.6 × 10−6 cm/s, respectively.
Fig. 4.
Transcorneal permeation of Δ8-THC from Δ8-THC suspension and Δ8-THC in the presence of 5% w/v cyclodextrin formulation. Results are depicted as mean ± SD (n = 4). ND not detectable
DISCUSSION
The goal of this study was to determine the physiochemical characteristic of Δ8-THC and to evaluate the effect of CD on the solubility, stability, and corneal permeation of Δ8-THC. Δ8-THC, an isomer of Δ9-THC, has shown promise as an antiglaucoma agent (1,15). However, similar to Δ9-THC, the utility of Δ8-THC as a topical ophthalmic agent is limited by its lipophilic nature, poor aqueous solubility, and resinous nature.
Highly lipophilic compounds can adsorb to glass and plastic containers and cause difficulties in handling and processing and lead to significant loss of content on storage. Additionally, adsorption can cause misinterpretation of the data and lack of reproducibility. The results from this study indicate that the extent of Δ8-THC adsorption to polyethylene is significantly greater than its adsorption to polypropylene surfaces. The most striking observation was that Δ8-THC did not stick to glass vials meeting the USP type I standards at the drug concentrations tested (Table II). The percentage loss of Δ8-THC in the glass vials was observed to be within the RSD of the method. Therefore, glass that met USP type I specification were used in the subsequent studies. The surface-to-volume ratio of the vials (data not provided), consistent with earlier reports on Δ9-THC by Blanc et al. (25), had an impact on binding of Δ8-THC to glass. Increase in the surface-to-volume ratio (low fill volumes in the vials) resulted in a significantly greater loss of Δ8-THC in comparison to vials that had a low surface-to-volume ratio (high fill volumes).
Solubility is an important parameter affecting drug permeation across biological membranes. Δ8-THC demonstrated very low aqueous solubility (0.26 ± 0.03 μg/mL), consistent with its high hydrophobicity (log P 7.53 ± 0.6). Wide ranges of aqueous solubility (1–2.8 μg/mL) and n-octanol/water partition (6,000–9,440,000) coefficient have been reported for Δ9-THC (24,31). This variation can be attributed to the difficulty in uniformly dissolving the resinous molecule, adsorption to glass and plastics, and analytical techniques used for quantification. Δ8-THC demonstrated pH independent solubility within the pH range tested (pH 1–9; Fig. 1) which was expected since the drug is known to be weakly acidic in nature and exists predominantly in the unionized state below pH 9.0.
Δ8-THC demonstrated linear pseudo-first order degradation kinetics in aqueous solutions. In earlier studies with Δ9-THC, by Garrett et al. (32), Δ9-THC was found to exhibit a biphasic semilogarithmic degradation profile with time, in acidic aqueous solutions below pH 4.0, and followed a first order decay above pH 4.0. These studies, however, were carried out at a temperature of 60.8°C and at such high temperatures there is a possibility of multiple degradation mechanisms operating in conjunction. In the present study, hydrolysis of Δ8-THC in an acidic pH range was observed to be much faster than that in neutral and basic buffers (Fig. 2). Expectedly, a 1.5-fold increase in the degradation rate (from 0.0027 ± 0.00026 to 0.0042 ± 0.00016 h−1) was observed when the studies were carried out at 40°C in phosphate buffer of pH 7.4.
Effect of increasing concentration of CDs on aqueous solubility of the therapeutic agent is usually determined using phase-solubility studies according to the method of Higuchi and Connors (33,34). A-type phase-solubility profiles are obtained when apparent solubility of the therapeutic agent increases with increasing concentration of CDs. When the complex is first order with respect to CDs then AL-type phase-solubility (linear increase in solubility of the compound as a function of CDs concentration) profiles are obtained. If the complex is first order with respect to therapeutic agent, but second or higher order with respect to the CDs then AP-type curve is obtained (positive deviation from linearity with increasing concentration of CDs) (33,34). Phase-solubility studies demonstrate that HPβCD, RMβCD, and SβCD, through their ability to form inclusion complexes, dramatically improved the solubility of Δ8-THC (Fig. 3a, b, and c). The plots suggest that SβCD forms a 1:1 inclusion complex (AL type) with Δ8-THC. With HPβCD or RMβCD the results from this study suggest formation of higher order complexes and depict an AP-type phase-solubility curve. Recently Mannila et al. (35) demonstrated that Δ9-THC yields an AL-type phase-solubility curve with HPβCD, indicating the formation of 1:1 inclusion complexes between HPβCD and Δ9-THC. Besides differences in the chemical structure a possible reason for the variations observed in the phase-solubility plots could be differences in the experimental protocol. While Mannila and coworkers used HPβCD in the concentration range of 0–80 mM with a 72 h equilibration period, in the current study the HPβCD concentration ranged from 0 to 181 mM with a 24 h of equilibration time. If concentrations up to 80 mM were to be considered both studies demonstrate an AL-type phase-solubility plot (Fig. 3a, insert). Phase-solubility studies with RMβCD indicate the formation of higher order complexes with Δ8-THC, which is consistent with an earlier report by Hazekamp and Verpoorte with Δ9-THC (36). However, the observed solubility of Δ8-THC (2.8 mg/mL) in the presence of RMβCD (190 mM) and the stability constant (K1:1; 12,200 M−1) were significantly less than the values reported for Δ9-THC by Hazekamp and Verpoorte (14 mg/mL in the presence of 187 mM RMβCD and K1:1 = 15,600 M−1). This drastic difference could be attributed to differences in experimental protocols between the two studies. In the latter study, ethanolic stock solutions of both Δ9-THC and RMβCD were used to prepare the complex and the equilibration time was 72 h. Additionally, Δ8-THC and Δ9-THC may interact differently with RMβCD. The binding constant of Δ8-THC was greater with SβCD than with HPβCD or RMβCD (Table IV) suggesting that SβCD forms more stable inclusion complexes with Δ8-THC. These results are consistent with the reports by Okimoto et al. (37) wherein neutral drugs were shown to exhibit greater binding constant with SβCD than with HPβCD.
Stability in aqueous solution is critical for topical ophthalmic formulation (19). The ability of CDs to reduce hydrolysis, oxidation and enzymatic decomposition of drugs is well documented (38). In this study, Δ8-THC exhibited dramatically improved chemical stability at almost all pH values in the presences of CD. (Table III). Δ8-THC, in the presence of 5% w/v HPβCD, RMβCD, and SβCD demonstrated insignificant degradation in pH 3.0, 5.0, 7.4, and 9 buffers up to a period of 2 months (last point tested) at room temperature. However, at pH 1.2, 5% w/v SΒCD and 5% w/v HPβCD failed to prevent the degradation of Δ8-THC which could be due to chemical instability of these CDs under strongly acidic conditions (39). The mechanism of enhanced stability of Δ8-THC in the presence of 5% w/v RMβCD, at pH 1.2, is unknown at this point but may be explained by strong steric hindrance created by RMβCD complexation or by greater inclusion of Δ8-THC in the RMβCD cavity at pH 1.2.
Cornea is the major pathway for intraocular penetration of topically instilled medications (1). In vitro corneal permeability data suggests that the complexation of Δ8-THC with HPβCD, RMβCD, and SβCD significantly improves transcorneal diffusion of Δ8-THC. Complexation of Δ8-THC with HPβCD resulted in a twofold increase (from 3.77 × 10−6 to 7.6 × 10−6 cm/s) in corneal permeability compared to that of Δ8-THC: SβCD complex. Lower corneal permeability of Δ8-THC in the presence of SβCD can be attributed to the higher magnitude of the binding constant with SβCD (Table IV). A number of reports indicate that the magnitude of the binding constant plays an important role in oral bioavailability of drug–cyclodextrin complexes (40). A very high binding constant value can lead to the presence of decreased free drug fraction at the corneal surface, leading to reduced membrane permeability. Statistically significant difference in the corneal permeability of Δ8-THC from Δ8-THC: HPβCD complex (7.6 ± 0.6 × 10−6 cm/s), and Δ8-THC: RMβCD complex (6.3 ± 1.3 × 10−6 cm/s) was not observed. This observation could be attributed to almost similar binding constants of Δ8-THC with HPβCD and RMβCD (Table IV). Recently, Kearse and Green (41) evaluated transcorneal permeability of Δ9-THC, in vitro, from various vehicles including light mineral oil (LMO) (41). With LMO as the vehicle, corneal permeability of Δ9-THC was only 0.018 × 10−6 cm/s, which is extremely poor and could explain the observed lack of any IOP lowering effect in vivo (42,43). Incidentally, the authors observed that transcorneal permeation of Δ9-THC in the presence of 30% HPβCD was only 0.033 × 10 − 6 cm/s. In the present study, Δ8-THC demonstrated a 230-fold higher permeability (7.6 × 10−6 cm/s) in the presence of 5% w/v HPβCD (Fig. 4).
Osmolality of DPBS containing 5% w/v HPβCD was 293 ± 4 mOsm/kg H2O (Osmette S, model 4002 (Precision Systems Inc., Natick, MA)). This solution is isotonic indicating that corneal integrity would not be affected on exposure to this solution, which is consistent with results from previous report from our laboratory (26), wherein Trans-epithelial electrical resistance (TEER) values of corneas exposed to DPBS alone or in presence of 5% w/v HPβCD for a period of 3 h were observed to be similar. Additionally, transcorneal transport of [14 C]mannitol, a paracellular marker, and [3H]diazepam, a transcellular marker in the presence of DPBS alone or in the presence of 5% w/v HPβCD remained the same indicating the integrity and viability of the corneal tissues are maintained during the experimental protocol (26). Osmolality of DPBS containing 5% w/v SβCD and 5% w/v RMβCD were 316 ± 4, 366 ± 4 mOsm/kg H2O, respectively. Although the RMβCD solutions were hypertonic, compared to that of HPβCD, which could affect the corneal integrity, the transcorneal permeation of Δ8-THC was similar or less than that of HPβCD. RMβCD was thus not studied any further. However, further studies evaluating the integrity of cornea in the presence of RMβCD and SβCD are warranted.
Conclusions
Ocular bioavailability of Δ8-THC is low because of its lipophilicity, resinous nature, and its limited aqueous solubility and stability. Therefore, there is a need for solubility and stability enhancing agents to deliver Δ8-THC into the deeper ocular tissues. Till date there are no reports on interaction of CDs (which can act as a solubilizer as well as stabilizer) with Δ8-THC. Results from this study demonstrate that all the CDs tested dramatically increase the aqueous solubility, stability, and transcorneal permeation of Δ8-THC. Thus, topical ophthalmic formulations containing Δ8-THC and CDs may show markedly greater ocular bioavailability and IOP lowering activity and could add to the treatment options in glaucoma. However, further studies evaluating the effect of RMβCD and SβCD on corneal integrity are warranted.
Acknowledgment
The project was partially supported by grant numbers 5P20RR021929 from the National Center for Research Resources and 1R41EY020042-01A1 from the National Eye Institute (NEI), National Institutes of Health. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Center for Research Resources or NEI.
References
- 1.Jarvinen T, Pate DW, Laine K. Cannabinoids in the treatment of glaucoma. Pharmacol Ther. 2002;95:203–20. doi: 10.1016/S0163-7258(02)00259-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Tomida I, Pertwee RG, Azuara-Blanco A. Cannabinoids and glaucoma. Br J Ophthalmol. 2004;88:708–13. doi: 10.1136/bjo.2003.032250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Thumma S, Majumdar S, Elsohly MA, Gul W, Repka MA. Chemical stability and bioadhesive properties of an ester prodrug of delta (9)-tetrahydrocannabinol in poly(ethylene oxide) matrices: effect of formulation additives. Int J Pharm. 2008;362:126–32. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2008.06.025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Williamson EM, Evans FJ. Cannabinoids in clinical practice. Drugs. 2000;60:1303–14. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200060060-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Porcella A, Maxia C, Gessa GL, Pani L. The synthetic cannabinoid WIN55212-2 decreases the intraocular pressure in human glaucoma resistant to conventional therapies. Eur J Neurosci. 2001;13:409–12. doi: 10.1046/j.0953-816X.2000.01401.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Marquis RE, Whitson JT. Management of glaucoma: focus on pharmacological therapy. Drugs Aging. 2005;22:1–21. doi: 10.2165/00002512-200522010-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Williams PB (2007) Invention: Novel Cannabinoids and method of use,WO/2007/130361
- 8.Crandall J, Matragoon S, Khalifa YM, Borlongan C, Tsai NT, Caldwell RB, et al. Neuroprotective and intraocular pressure-lowering effects of (−)Delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol in a rat model of glaucoma. Ophthalmic Res. 2007;39:69–75. doi: 10.1159/000099240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Szczesniak AM, Kelly ME, Whynot S, Shek PN, Hung O. Ocular hypotensive effects of an intratracheally delivered liposomal delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol preparation in rats. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2006;22:160–7. doi: 10.1089/jop.2006.22.160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Repka MA, ElSohly MA, Munjal M, Ross SA. Temperature stability and bioadhesive properties of delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol incorporated hydroxypropylcellulose polymer matrix systems. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2006;32:21–32. doi: 10.1080/03639040500387914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.van Drooge DJ, Hinrichs WL, Wegman KA, Visser MR, Eissens AC, Frijlink HW. Solid dispersions based on inulin for the stabilisation and formulation of delta 9-tetrahydrocannabinol. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2004;21:511–8. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2003.11.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Mechoulam R. Marihuana chemistry. Science. 1970;168:1159–66. doi: 10.1126/science.168.3936.1159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Mechoulam R, Hanus L. A historical overview of chemical research on cannabinoids. Chem Phys Lipids. 2000;108:1–13. doi: 10.1016/S0009-3084(00)00184-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Fairbairn JW, Liebmann JA, Rowan MG. The stability of cannabis and its preparations on storage. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1976;28:1–7. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1976.tb04014.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Muchtar S, Almog S, Torracca MT, Saettone MF, Benita S. A submicron emulsion as ocular vehicle for delta-8-tetrahydrocannabinol: effect on intraocular pressure in rabbits. Ophthalmic Res. 1992;24:142–9. doi: 10.1159/000267160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Avraham Y, Ben-Shushan D, Breuer A, Zolotarev O, Okon A, Fink N, et al. Very low doses of delta 8-THC increase food consumption and alter neurotransmitter levels following weight loss. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2004;77:675–84. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2004.01.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Stinchcomb AL, Valiveti S, Hammell DC, Ramsey DR. Human skin permeation of delta8-tetrahydrocannabinol, cannabidiol and cannabinol. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2004;56:291–7. doi: 10.1211/0022357022791. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Valiveti S, Hammell DC, Earles DC, Stinchcomb AL. In vitro/in vivo correlation studies for transdermal delta 8-THC development. J Pharm Sci. 2004;93:1154–64. doi: 10.1002/jps.20036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Kaur IP, Chhabra S, Aggarwal D. Role of cyclodextrins in ophthalmics. Curr Drug Deliv. 2004;1:351–60. doi: 10.2174/1567201043334623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Loftsson T, Stefansson E. Cyclodextrins in eye drop formulations: enhanced topical delivery of corticosteroids to the eye. Acta Ophthalmol Scand. 2002;80:144–50. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0420.2002.800205.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Wong AS, Orbanosky MW, Reeve VC, Beede JD. Stability of delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol in stored blood and serum. NIDA Res Monogr. 1982;42:119–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Johnson JR, Jennison TA, Peat MA, Foltz RL. Stability of delta 9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), 11-hydroxy-THC, and 11-nor-9-carboxy-THC in blood and plasma. J Anal Toxicol. 1984;8:202–4. doi: 10.1093/jat/8.5.202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Christophersen AS. Tetrahydrocannabinol stability in whole blood: plastic versus glass containers. J Anal Toxicol. 1986;10:129–31. doi: 10.1093/jat/10.4.129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Garrett ER, Hunt CA. Physiochemical properties, solubility, and protein binding of delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol. J Pharm Sci. 1974;63:1056–64. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600630705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Blanc JA, Manneh VA, Ernst R, Berger DE, de Keczer SA, Chase C, et al. Adsorption losses from urine-based cannabinoid calibrators during routine use. Clin Chem. 1993;39:1705–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Majumdar S, Srirangam R. Solubility, stability, physicochemical characteristics and in vitro ocular tissue permeability of hesperidin: a natural bioflavonoid. Pharm Res. 2009;26:1217–25. doi: 10.1007/s11095-008-9729-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Rajewski RA, Stella VJ. Pharmaceutical applications of cyclodextrins. 2. In vivo drug delivery. J Pharm Sci. 1996;85:1142–69. doi: 10.1021/js960075u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Davis ME, Brewster ME. Cyclodextrin-based pharmaceutics: past, present and future. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2004;3:1023–35. doi: 10.1038/nrd1576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Dollo G, Le Corre P, Chevanne F, Le Verge R. Inclusion complexation of amide-typed local anaesthetics with [beta]-cyclodextrin and its derivatives. ii. evaluation of affinity constants and in vitro transfer rate constants. Int J Pharm. 1996;136:165–74. doi: 10.1016/0378-5173(96)04512-7. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Mizutani T, Mizutani A. Estimation of adsorption of drugs and proteins on glass surfaces with controlled pore glass as a reference. J Pharm Sci. 1978;67:1102–5. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600670820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Grotenhermen F. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of cannabinoids. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2003;42:327–60. doi: 10.2165/00003088-200342040-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Garrett ER, Tsau J. Stability of tetrahydrocannabinols I. J Pharm Sci. 1974;63:1563–74. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600631016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Loftsson T, Jarho P, Masson M, Jarvinen T. Cyclodextrins in drug delivery. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2005;2:335–51. doi: 10.1517/17425247.2.1.335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Brewster ME, Loftsson T. Cyclodextrins as pharmaceutical solubilizers. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2007;59:645–66. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2007.05.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Mannila J, Jarvinen T, Jarvinen K, Tarvainen M, Jarho P. Effects of RM-beta-CD on sublingual bioavailability of Delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol in rabbits. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2005;26:71–7. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2005.04.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Hazekamp A, Verpoorte R. Structure elucidation of the tetrahydrocannabinol complex with randomly methylated beta-cyclodextrin. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2006;29:340–7. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2006.07.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Okimoto K, Rajewski RA, Uekama K, Jona JA, Stella VJ. The interaction of charged and uncharged drugs with neutral (HP-beta-CD) and anionically charged (SBE7-beta-CD) beta-cyclodextrins. Pharm Res. 1996;13:256–64. doi: 10.1023/A:1016047215907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Challa R, Ahuja A, Ali J, Khar RK. Cyclodextrins in drug delivery: an updated review. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2005;6:E329–57. doi: 10.1208/pt060243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Loftsson T, Masson M. Cyclodextrins in topical drug formulations: theory and practice. Int J Pharm. 2001;225:15–30. doi: 10.1016/S0378-5173(01)00761-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Carrier RL, Miller LA, Ahmed I. The utility of cyclodextrins for enhancing oral bioavailability. J Control Release. 2007;123:78–99. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2007.07.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Kearse EC, Green K. Effect of vehicle upon in vitro transcorneal permeability and intracorneal content of Delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol. Curr Eye Res. 2000;20:496–501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.ElSohly MA, Harland EC, Benigni DA, Waller CW. Cannabinoids in glaucoma II: the effect of different cannabinoids on intraocular pressure of the rabbit. Curr Eye Res. 1984;3:841–50. doi: 10.3109/02713688409000797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Green K, Roth M. Ocular effects of topical administration of delta 9-tetrahydrocannabinol in man. Arch Ophthalmol. 1982;100:265–7. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1982.01030030267006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]