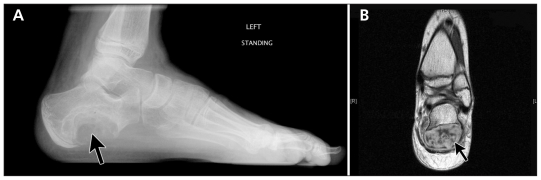
A 17-year-old boy presented with pain in his left foot that had progressed over a six-month period. He had no history of trauma or systemic illness. On examination, he was tender over the left calcaneus; there was no swelling or warmth over this area. Radiography showed an eccentric, lytic lesion in the calcaneus, with a classic “soap-bubble” appearance (Figure 1A). Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) showed a low–signal intensity rim and nonhomogenous areas in the cyst (Figure 1B). A diagnosis of aneurysmal bone cyst of the calcaneus was made, and the lesion was treated with intralesional sclerotherapy.
Figure 1:
(A) Plain radiograph of the left foot of a 17-year-old boy showing a solitary eccentric, lytic lesion (arrow) in the left calcaneus, consistent with an aneurysmal bone cyst. (B) Magnetic resonance scan of the left foot showing a subperiosteal multicystic lesion (arrow) with a hypointense signal on T1-weighted images.
Aneurysmal bone cysts are solitary benign, osteolytic lesions, constituting 1% of all primary bone tumours. The incidence is 0.14 per 100 000 population, and they are slightly more common in women than men (1.04:1).1 They often affect people during their second decade of life. The most common locations are the metaphyses of long bones, vertebrae and flat bones. The etiology of primary aneurysmal bone cysts is not clear; however, secondary cysts may arise from pre-existing bone lesions, such as giant cell tumours, osteoblastomas, chondroblastomas or angiomas.2 Patients may present with heel pain, mass, swelling, deformity or pathologic fracture.
Aneurysmal bone cyst is primarily a radiologic diagnosis. On radiographs, it appears as an eccentrically placed osteolytic lesion with elevated periosteum reflected by a “soap bubble” appearance, as in our patient. Magnetic resonance imaging typically shows a nonhomogenous lesion with a low-signal rim encircling the cystic lesion on both T1 and T2 images. Combined use of radiography and MRI increases the diagnostic accuracy.3 Because the differential diagnosis includes malignant bone tumours, such as telangiectatic osteosarcoma, biopsy may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis.2 Histology shows honeycomb-like spaces filled with hemorrhagic fluid without endothelial lining.
The treatment depends on the location and aggressiveness of the lesion. In the quiescent form, follow-up is possible. In rapidly expanding aggressive lesions, conventional treatment is surgical curettage with or without adjuvant therapy and bone grafting.2 Percutaneous sclerotherapy and embolization are safe alternatives and have shown equally good results in one case series.4
Footnotes
This article has been peer reviewed.
Competing interests: None declared.
References
- 1.Leithner A, Windhager R, Lang S, et al. Aneurysmal bone cyst: a population based epidemiological study and literature review. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1999;363:176–9 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Mankin HJ, Hornicek FJ, Ortiz-Cruz E, et al. Aneurysmal bone cyst: a review of 150 patients. J Clin Oncol 2005;23:6756–62 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Mahnken AH, Nolte-Ernsting CC, Wildberger JE, et al. Aneurysmal bone cyst: value of MR imaging and conventional radiography. Eur Radiol 2003;13:1118–24 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Rastogi S, Varshney MK, Trikha V, et al. Treatment of aneurysmal bone cysts with percutaneous sclerotherapy using polidocanol. A review of 72 cases with long-term follow-up. J Bone Joint Surg Br 2006;88:1212–6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]