Abstract
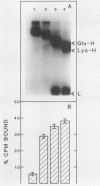
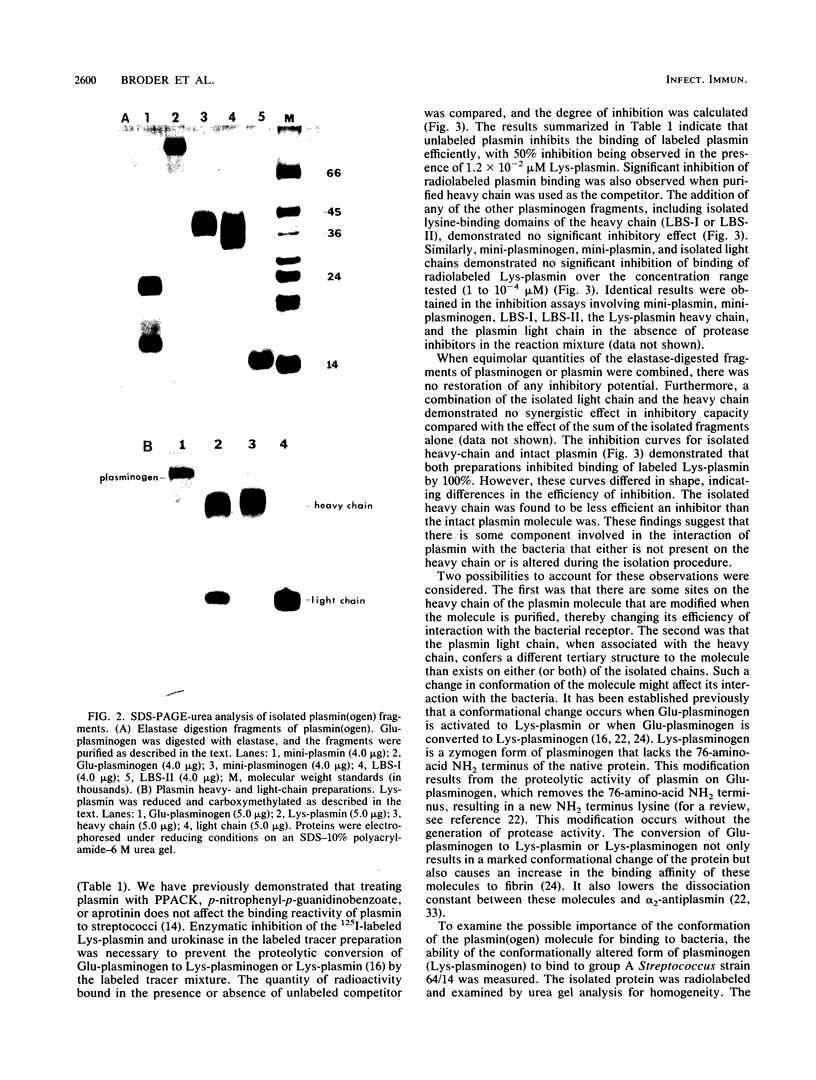
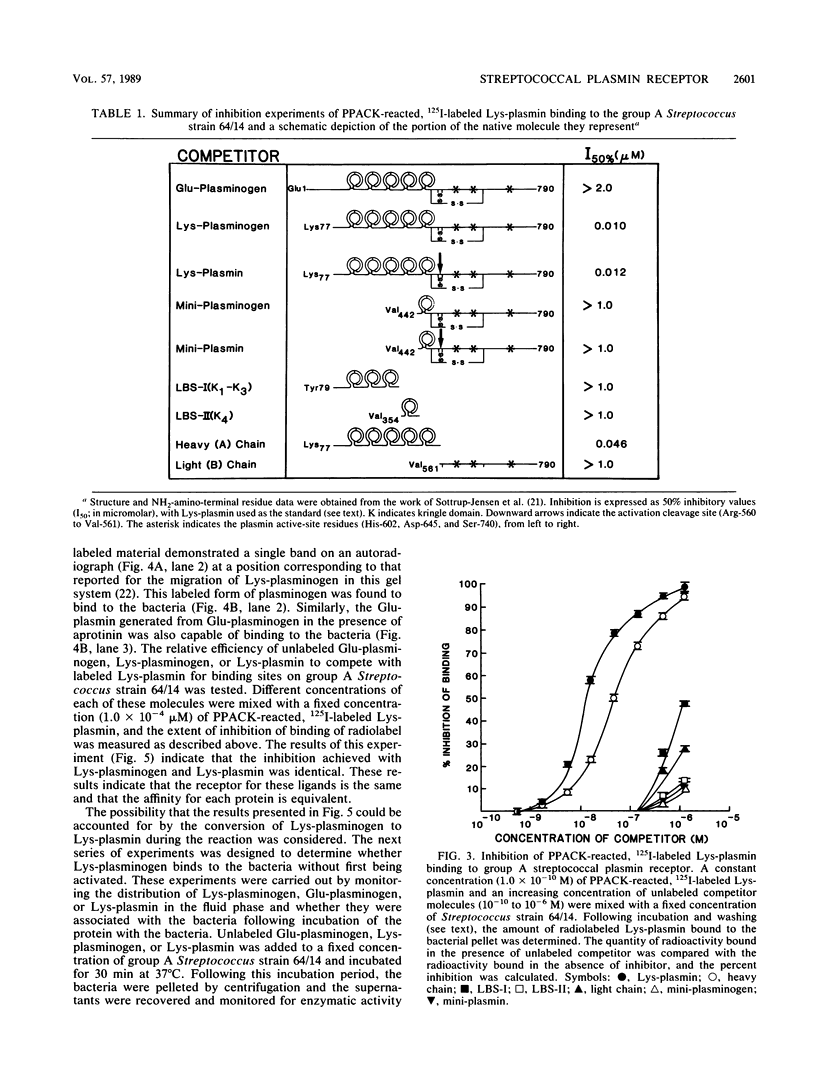
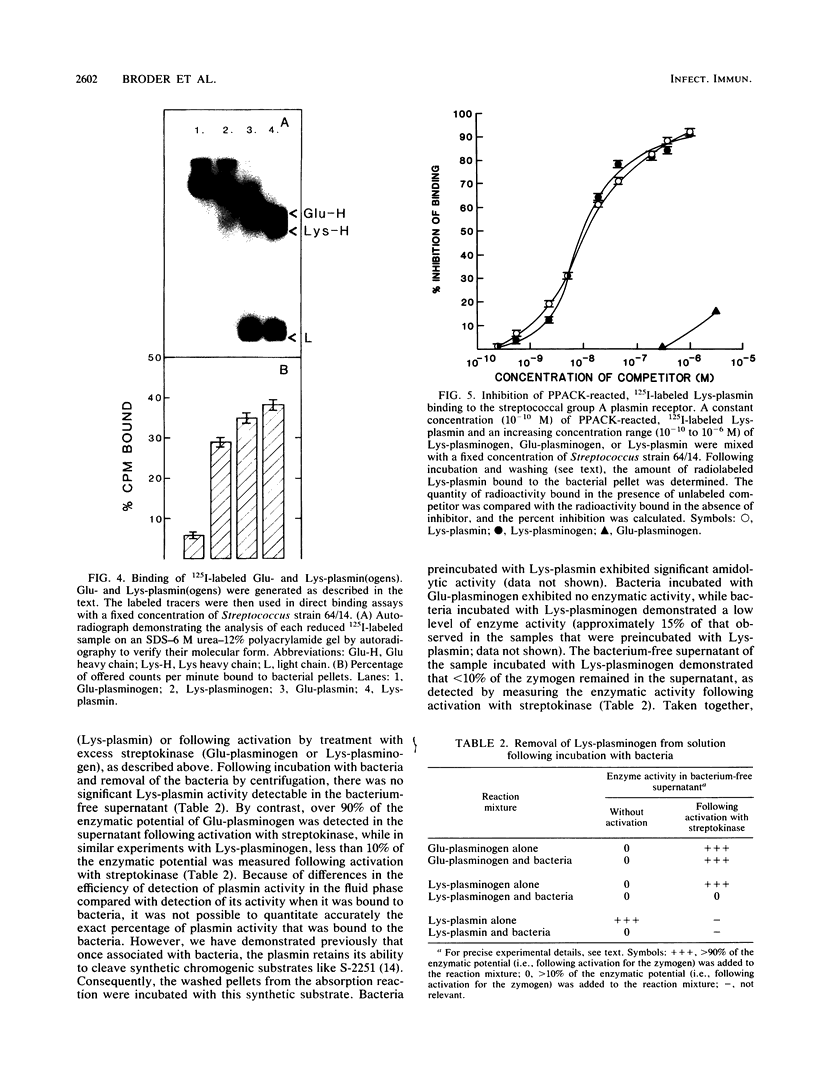
A high-affinity surface receptor for human plasmin has been reported on certain group A streptococci. To map the region of the plasmin molecule that binds to the bacterial receptor, isolated domains of plasmin were tested for their ability to inhibit the binding of intact radiolabeled plasmin to receptor-positive bacteria. Complete inhibition of binding of labeled plasmin to bacteria by isolated heavy chains was achieved, but this inhibition was not as efficient on a molar basis when compared with that of unlabeled plasmin. By contrast, a conformationally altered form of native plasminogen was found to bind to bacteria and was as efficient a competitive inhibitor as intact plasmin was. The results of this study indicate that the selective binding of human plasmin to a group A streptococcus is dependent on structures present in the conformationally altered form of native plasminogen or plasmin that are not found on the native zymogen, the plasminogen with NH2-terminal glutamic acid.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bok R. A., Mangel W. F. Quantitative characterization of the binding of plasminogen to intact fibrin clots, lysine-sepharose, and fibrin cleaved by plasmin. Biochemistry. 1985 Jun 18;24(13):3279–3286. doi: 10.1021/bi00334a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broeseker T. A., Boyle M. D., Lottenberg R. Characterization of the interaction of human plasmin with its specific receptor on a group A streptococcus. Microb Pathog. 1988 Jul;5(1):19–27. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(88)90077-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cederholm-Williams S. A., De Cock F., Lijnen H. R., Collen D. Kinetics of the reactions between streptokinase, plasmin and alpha 2-antiplasmin. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Oct;100(1):125–132. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb02040.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cederholm-Williams S. A. The binding of plasminogen (mol. wt. 84,000) and plasmin to fibrin. Thromb Res. 1977 Sep;11(3):421–423. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(77)90193-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collen D. On the regulation and control of fibrinolysis. Edward Kowalski Memorial Lecture. Thromb Haemost. 1980 Jun 18;43(2):77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haupt H., Heimburger N. Humanserumproteine mit hoher Affinität zu Carboxymethylcellulose. I. Isolierung von Lysozym, C1q und bisher unbekannten -Globulinen. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1972 Jul;353(7):1125–1132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holvoet P., Lijnen H. R., Collen D. A monoclonal antibody specific for Lys-plasminogen. Application to the study of the activation pathways of plasminogen in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 5;260(22):12106–12111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurell C. B. Quantitative estimation of proteins by electrophoresis in agarose gel containing antibodies. Anal Biochem. 1966 Apr;15(1):45–52. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(66)90246-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerch P. G., Rickli E. E., Lergier W., Gillessen D. Localization of individual lysine-binding regions in human plasminogen and investigations on their complex-forming properties. Eur J Biochem. 1980;107(1):7–13. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04617.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung L. L., Nachman R. L., Harpel P. C. Complex formation of platelet thrombospondin with histidine-rich glycoprotein. J Clin Invest. 1984 Jan;73(1):5–12. doi: 10.1172/JCI111206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lijnen H. R., Hoylaerts M., Collen D. Isolation and characterization of a human plasma protein with affinity for the lysine binding sites in plasminogen. Role in the regulation of fibrinolysis and identification as histidine-rich glycoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 10;255(21):10214–10222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lottenberg R., Broder C. C., Boyle M. D. Identification of a specific receptor for plasmin on a group A streptococcus. Infect Immun. 1987 Aug;55(8):1914–1918. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.8.1914-1918.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markus G., DePasquale J. L., Wissler F. C. Quantitative determination of the binding of epsilon-aminocaproic acid to native plasminogen. J Biol Chem. 1978 Feb 10;253(3):727–732. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markus G., Evers J. L., Hobika G. H. Comparison of some properties of native (Glu) and modified (Lys) human plasminogen. J Biol Chem. 1978 Feb 10;253(3):733–739. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
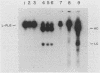
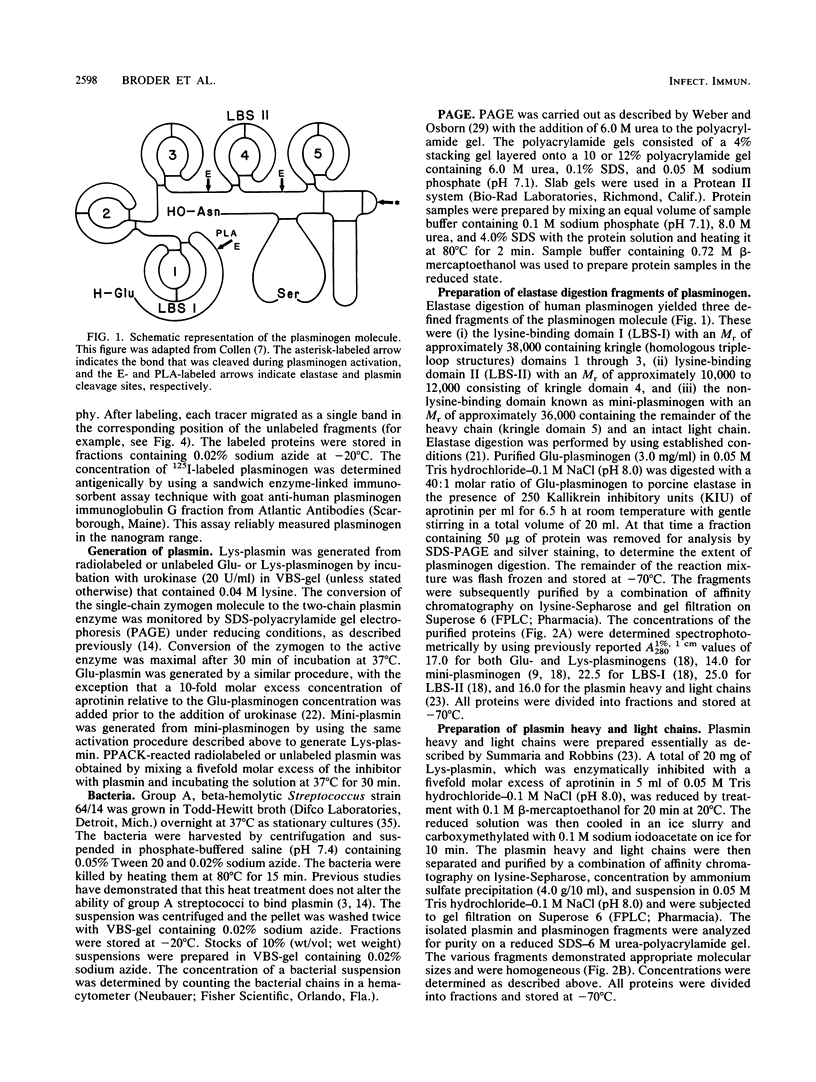
- Markwell M. A. A new solid-state reagent to iodinate proteins. I. Conditions for the efficient labeling of antiserum. Anal Biochem. 1982 Sep 15;125(2):427–432. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90025-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson T., Sjöholm I., Wiman B. Circular dichroism studies on alpha 2-antiplasmin and its interactions with plasmin and plasminogen. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Jul 26;705(2):264–270. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(82)90187-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan T. J. Photoaffinity labeling of human plasmin and plasminogen. Pharmacol Ther. 1987;34(2):335–348. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(87)90017-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suenson E., Thorsen S. Secondary-site binding of Glu-plasmin, Lys-plasmin and miniplasmin to fibrin. Biochem J. 1981 Sep 1;197(3):619–628. doi: 10.1042/bj1970619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
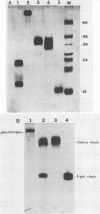
- Summaria L., Robbins K. C. Isolation of a human plasmin-derived, functionally active, light (B) chain capable of forming with streptokinase an equimolar light (B) chain-streptokinase complex with plasminogen activator activity. J Biol Chem. 1976 Sep 25;251(18):5810–5813. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorsen S., Clemmensen I., Sottrup-Jensen L., Magnusson S. Adsorption to fibrin of native fragments of known primary structure from human plasminogen. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 May 29;668(3):377–387. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(81)90171-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorsen S. Differences in the binding to fibrin of native plasminogen and plasminogen modified by proteolytic degradation. Influence of omega-aminocarboxylic acids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 May 30;393(1):55–65. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(75)90216-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Violand B. N., Sodetz J. M., Castellino F. J. The effect of epsilon-amino caproic acid on the gross conformation of plasminogen and plasmin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1975 Sep;170(1):300–305. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(75)90121-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walz D. A., Bacon-Baguley T., Kendra-Franczak S., DePoli P. Binding of thrombospondin to immobilized ligands: specific interaction with fibrinogen, plasminogen, histidine-rich glycoprotein, and fibronectin. Semin Thromb Hemost. 1987 Jul;13(3):317–325. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1003507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiman B., Lijnen H. R., Collen D. On the specific interaction between the lysine-binding sites in plasmin and complementary sites in alpha2-antiplasmin and in fibrinogen. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Jul 25;579(1):142–154. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(79)90094-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiman B. Primary structure of peptides released during activation of human plasminogen by urokinase. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Nov 1;39(1):1–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb03096.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiman B. Primary structure of the B-chain of human plasmin. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Jun 1;76(1):129–137. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11578.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winn E. S., Hu S. P., Hochschwender S. M., Laursen R. A. Studies on the lysine-binding sites of human plasminogen. The effect of ligand structure on the binding of lysine analogs to plasminogen. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Mar;104(2):579–586. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04461.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarnall M., Boyle M. D. Isolation and partial characterization of a type II Fc receptor from a group A streptococcus. Mol Cell Biochem. 1986 Apr;70(1):57–66. doi: 10.1007/BF00233803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]