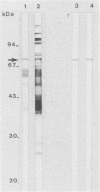
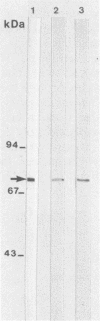
Abstract
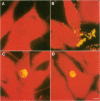
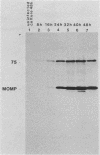
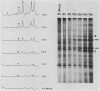
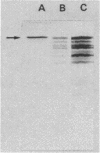
A 75-kilodalton (kDa) immunogen from Chlamydia trachomatis serovar L2 was characterized. The 75-kDa protein was localized in the cytoplasm of chlamydiae and was shown to be a protein synthesized early in the developmental cycle of chlamydiae. A gene library was made by the recombinant DNA technique, using the expression vectors pEX1, pEX2, and pEX3. From this library one clone was found which reacted with a monoclonal antibody against the 75-kDa immunogen of C. trachomatis. The 75-kDa protein produced by the recombinant Escherichia coli was expressed independently of the promoter for the hybrid protein cro-betagalactosidase. Thus it is not produced as a fusion protein. Epitope mapping of the 75-kDa protein from C. trachomatis L2 and from the recombinant E. coli performed by Staphylococcus aureus V8 protease digestion showed that the two proteins are identical. Furthermore, patient sera reacted with both proteins.
Full text
PDF


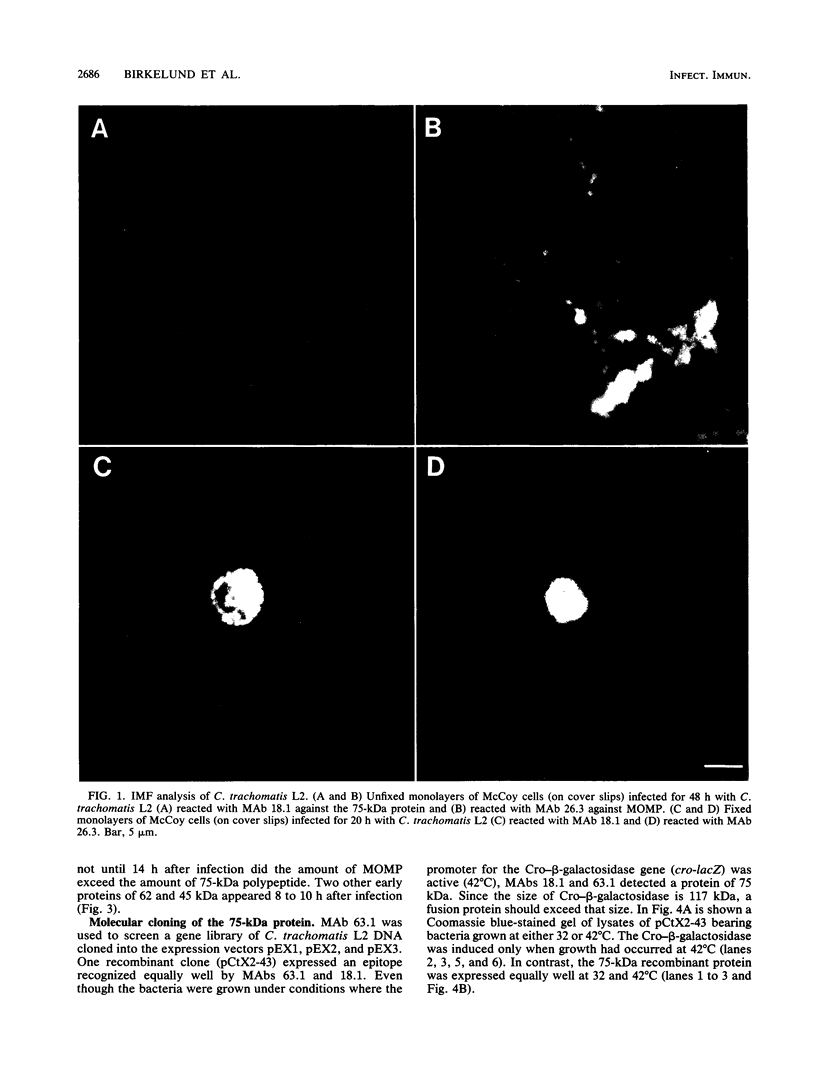
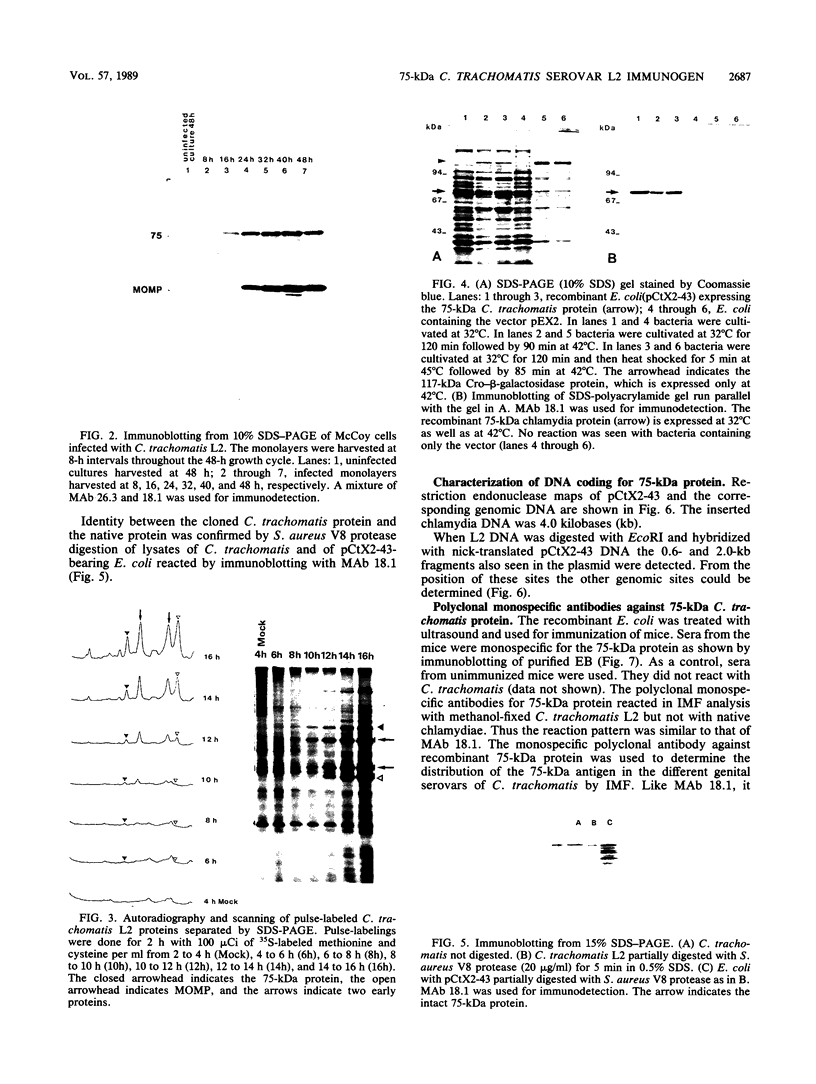



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bernard H. U., Remaut E., Hershfield M. V., Das H. K., Helinski D. R., Yanofsky C., Franklin N. Construction of plasmid cloning vehicles that promote gene expression from the bacteriophage lambda pL promoter. Gene. 1979 Jan;5(1):59–76. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(79)90092-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birkelund S., Lundemose A. G., Christiansen G. Chemical cross-linking of Chlamydia trachomatis. Infect Immun. 1988 Mar;56(3):654–659. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.3.654-659.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bordier C. Phase separation of integral membrane proteins in Triton X-114 solution. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 25;256(4):1604–1607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunham R. C., Peeling R., Maclean I., McDowell J., Persson K., Osser S. Postabortal Chlamydia trachomatis salpingitis: correlating risk with antigen-specific serological responses and with neutralization. J Infect Dis. 1987 Apr;155(4):749–755. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.4.749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklin F. C., Bagdasarian M., Bagdasarian M. M., Timmis K. N. Molecular and functional analysis of the TOL plasmid pWWO from Pseudomonas putida and cloning of genes for the entire regulated aromatic ring meta cleavage pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7458–7462. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyypiä T., Jalava A., Larsen S. H., Terho P., Hukkanen V. Detection of Chlamydia trachomatis in clinical specimens by nucleic acid spot hybridization. J Gen Microbiol. 1985 Apr;131(4):975–978. doi: 10.1099/00221287-131-4-975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaul R., Roy K. L., Wenman W. M. Cloning, expression, and primary structure of a Chlamydia trachomatis binding protein. J Bacteriol. 1987 Nov;169(11):5152–5156. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.11.5152-5156.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClenaghan M., Herring A. J., Aitken I. D. Comparison of Chlamydia psittaci isolates by DNA restriction endonuclease analysis. Infect Immun. 1984 Aug;45(2):384–389. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.2.384-389.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newhall W. J., 5th Biosynthesis and disulfide cross-linking of outer membrane components during the growth cycle of Chlamydia trachomatis. Infect Immun. 1987 Jan;55(1):162–168. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.1.162-168.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newhall W. J., Batteiger B., Jones R. B. Analysis of the human serological response to proteins of Chlamydia trachomatis. Infect Immun. 1982 Dec;38(3):1181–1189. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.3.1181-1189.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plaunt M. R., Hatch T. P. Protein synthesis early in the developmental cycle of Chlamydia psittaci. Infect Immun. 1988 Dec;56(12):3021–3025. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.12.3021-3025.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ripa K. T. Biological principles of the culture of Chlamydia trachomatis in cell monolayers. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 1982;32:25–29. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schachter J. The intracellular life of Chlamydia. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1988;138:109–139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley K. K., Luzio J. P. Construction of a new family of high efficiency bacterial expression vectors: identification of cDNA clones coding for human liver proteins. EMBO J. 1984 Jun;3(6):1429–1434. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01988.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley K. K. Solubilization and immune-detection of beta-galactosidase hybrid proteins carrying foreign antigenic determinants. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jun 25;11(12):4077–4092. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.12.4077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang S. P., Grayston J. T. Human serology in Chlamydia trachomatis infection with microimmunofluorescence. J Infect Dis. 1974 Oct;130(4):388–397. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.4.388. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang S. P., Kuo C. C., Grayston J. T. A simplified method for immunological typing of trachoma-inclusion conjunctivitis-lymphogranuloma venereum organisms. Infect Immun. 1973 Mar;7(3):356–360. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.3.356-360.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenman W. M., Lovett M. A. Expression in E. coli of Chlamydia trachomatis antigen recognized during human infection. Nature. 1982 Mar 4;296(5852):68–70. doi: 10.1038/296068a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenman W. M., Meuser R. U. Chlamydia trachomatis elementary bodies possess proteins which bind to eucaryotic cell membranes. J Bacteriol. 1986 Feb;165(2):602–607. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.2.602-607.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise K. S., Kim M. F. Identification of intrinsic and extrinsic membrane proteins bearing surface epitopes of Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae. Isr J Med Sci. 1987 May;23(5):469–473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]