Abstract
Bilateral cochlear implant (BiCI) users gain an advantage in noisy situations from a second implant, but their bilateral performance falls short of normal hearing listeners. Channel interactions due to overlapping electrical fields between electrodes can impair speech perception, but its role in limiting binaural hearing performance has not been well characterized. To address the issue, binaural masking level differences (BMLD) for a 125 Hz tone in narrowband noise were measured using a pair of pitch-matched electrodes while simultaneously presenting the same masking noise to adjacent electrodes, representing a more realistic stimulation condition compared to prior studies that used only a single electrode pair. For five subjects, BMLDs averaged 8.9 ± 1.0 dB (mean ± s.e.) in single electrode pairs but dropped to 2.1 ± 0.4 dB when presenting noise on adjacent masking electrodes, demonstrating a negative impact of the additional maskers. Removing the masking noise from only the pitch-matched electrode pair not only lowered thresholds but also resulted in smaller BMLDs. The degree of channel interaction estimated from auditory nerve evoked potentials in three subjects was significantly and negatively correlated with BMLD. The data suggest that if the amount of channel interactions can be reduced, BiCI users may experience some performance improvements related to binaural hearing.
INTRODUCTION
Although bilateral cochlear implant (BiCI) users benefit from a second implant (e.g., Litovsky et al., 2009), not all aspects of bilateral hearing are comparable to normal hearing (NH) performance. An example is the binaural masking level difference (BMLD), a measure of how well sounds from the left and right ears are integrated to improve signal detection in noise (Hirsh, 1948). When masked by diotic (N0) noise, dichotic signals (out-of-phase, Sπ) are better detected compared to diotic signals (in-phase, S0). The improved detection threshold is due in part to computations such as equalization-cancellation (Durlach, 1963). In addition, interaural correlation may serve as a cue since the signal in N0Sπ is interaurally decorrelated but correlated in N0S0 (Gabriel and Colburn, 1981; Goupell and Hartmann, 2007). For NH listeners, BMLDs were reported to be about 15–20 dB using transposed tones (van de Par and Kohlrausch, 1997) in comparison to 4–9 dB for BiCI users tested with single pairs of electrodes (Long et al., 2006; Van Deun et al., 2009; Lu et al., 2010). While interaural level difference (ILD) cues are generally well perceived, BiCI users show a wide range of sensitivities to interaural timing differences (ITD) that at best are still poorer than NH listeners (van Hoesel et al., 1993; van Hoesel and Clark, 1997; van Hoesel, 2007; Laback and Majdak, 2008; van Hoesel, 2008; van Hoesel et al., 2009; Aronoff et al., 2010; Litovsky et al., 2010). Consequently, cues that rely on ITDs provide a smaller benefit for BiCI users than for NH listeners, and poor ITD sensitivity may be a significant factor in lower levels of BMLDs for speech in BiCI users, particularly at headwidth delays of 700 μs or less (van Hoesel et al., 2008).
Complex sounds such as speech, in combination with background and environmental noises, activate a wide range of electrodes. Potentially, different ITD cues on distinct electrode pairs can interfere with each other through channel interactions (Jones et al., 2009) that result from the electrical field spread of neighboring electrodes that stimulate overlapping populations of auditory nerve fibers (Shannon, 1983; Tong and Clark, 1986; Lim et al., 1989; Chatterjee and Shannon, 1998; Abbas et al., 2004; Nelson et al., 2008). In unilateral CI usage, it is known that channel interactions detrimentally affect performance on a number of perceptual tasks (McKay et al., 1996; Fu et al., 1998; Pfingst et al., 2001; Middlebrooks, 2004; Stickney et al., 2006) and limit the usefulness of additional electrodes for speech perception (Fishman et al., 1997; Friesen et al., 2001). The role of channel interactions may be significant, but it has not been well characterized in the context of binaural hearing. The limited number of BiCI studies on BMLD have been based on either single electrode pairs (Long et al., 2006; Van Deun et al., 2009; Lu et al., 2010) or speech presented acoustically through clinical and research processors (van Hoesel and Tyler, 2003; Laszig et al., 2004; Schleich et al., 2004; Buss et al., 2008; van Hoesel et al., 2008). With the former, there are no channel interactions, while the latter does not provide direct control over electrode selection to control the amount of channel interaction.
The main hypothesis of this study proposes that channel interactions are detrimental to binaural hearing by reducing the effect of binaural unmasking. The experiments in this study are designed to (1) obtain BMLDs under varying levels of channel interactions controlled by different masking electrode configurations, (2) assess BMLDs when masking noise is exclusively off-channel, and (3) provide an objective measure of channel interaction using evoked potentials that correlates with the behavioral measures of BMLD.
The first objective was to experimentally verify that BiCI users can still take advantage of BMLD in the presence of channel interactions. The alternative is that the cue for BMLD is not robust to masking noise from neighboring electrodes, and it becomes an insignificant effect under such conditions. Using parameters for N0S0 and N0Sπ (125 Hz tone in ±25 Hz narrowband noise) that produce large BMLDs with single electrode pairs (the target electrode pair), the effects of channel interactions can be studied by manipulating the number, proximity, and apical vs basal location of adjacent electrodes which output masking noise. Both larger numbers of masking electrodes and their closer proximity to the target electrode pair would increase the amount of channel interaction due to spread of the electric field, which is greatest near the stimulation electrode and decays over distance (e.g., Cohen et al., 2003). Since the electric field spread determines which populations of auditory neurons are activated, increasing the number of masking electrodes would increase the likelihood that auditory neurons normally activated by the target pair are also activated by noise from the masking electrodes. The same reasoning applies with the distance the masking electrodes are to the target electrodes. The apical and basal location of the masking electrode may have an effect if there are dead regions in the neural survival pattern. From these manipulations, it is expected that binaural masking level differences would be proportionally reduced by the contribution of electric fields emanating from adjacent masking electrodes.
Second, since signal and noise may be output on separate electrodes under realistic stimulation conditions, this study asks whether BMLD is still a significant effect if masking noise is introduced solely through channel interactions, e.g., a spectrally notched masker. In NH listeners, widening the spectral-notch of a noise masker lead to a decrease in BMLD (Hall et al., 1983; Nitschmann et al., 2009; 2010). Similarly, it is expected that notched masking would reduce BMLD in CI users. In addition, by using a notched masker, it is possible to better isolate and study the effect of adjacent masking electrodes on N0S0/N0Sπ thresholds and BMLD.
The third question was if any reduction in the behavioral measure of BMLD is correlated with an objective physiological estimate of channel interaction. These neural data would complement the behaviorally acquired BMLD data to positively identify channel interactions as a source of reduction in BMLD. The degree and sensitivity of the correlation between the two can shed some light onto the mechanisms by which channel interactions affect BMLD. A high correlation would point to a largely peripheral mechanism at the auditory periphery. Lower correlations would imply additional mechanisms that occur more centrally since channel interactions would not be able to explain any trends in the behavioral data.
By taking an intermediate approach with multiple masking electrodes, this study will help fill the knowledge gap between BMLDs obtained with single electrode pairs and those obtained using speech. The results may provide some insight to further improving binaural hearing in bilateral CI users.
METHODS
Subjects
All experimental protocols were approved by the University of California Irvine Institutional Review Board. Five bilateral CI subjects with Nucleus 24 or Freedom implants provided informed consent and were paid for their participation (Table TABLE I.). All had high levels of speech understanding with their implants, and one subject, CI8, had fewer than 2 years of bilateral experience at the time of testing. Two of the subjects, CI1 and CI5, participated in a prior study on BMLDs (Lu et al., 2010).
Table 1.
Subject information.
| Subject | Gender/age | Etiology | Age at hearing loss | Years of CI use (L/R) | Electrode pair used (L/R)a | HINT speech scores (quiet, noise) (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CI1 | F/62 | Ototoxicity | 26 | 7/19 | 12/12a | L: 83, 32 R: 95, 65 Bi: N/A |
| CI5 | M/68 | Progressive | 34 | 7/7 | 14/12a | L: 98, 39 R: 98, 55 Bi: 100, 58 |
| CI6 | F/58 | Genetic | 39 | 2/4 | 12a/14 | L: N/A R: 100, N/A Bi: N/A |
| CI7 | F/64 | Unknown | 5 | 13/6 | 10ab/12 | L: N/A, 90 R: N/A, 74 Bi: N/A, 96 |
| CI8 | M/48 | Genetic | Birth | 0.5/1.5 | 13/12a | L: 99, 81 R: 95, 77 Bi: N/A |
“Better ear.”
Electrodes
Thresholds and maximal comfort levels were mapped using the Spear3 research interface and Seed-Speak (Hearworks, Ltd, Melbourne, Australia). Stimuli were 500 ms long, 1000 pps pulse train in with 25 μs phases, and monopolar stimulation mode, MP1+2. A bilateral pair of pitch-matched electrodes was selected in the middle of the electrode arrays. Four pairs of immediately adjacent electrodes were used to present masking noise. All electrodes were balanced for loudness within and between ears near maximum comfortable level. For subject CI5, the electrode pair judged to be pitch-matched was different from the pair used in a previous study (Lu et al., 2010). CI5 described the matches between the two pairs as very similar but felt the newer pair matched better at the time of testing. The difference was one electrode position and changes in pitch perception over time have been reported in CI users (Reiss et al., 2007).
Stimuli
All stimuli were generated digitally at 44.1 kHz sampling rate using matlab (Mathworks, Natick, MA) and output through a personal computer sound card directly to the line-in jack on the Spear3 research interface. Signal and noise parameters were chosen to have the same values as those used in previous studies (Long et al., 2006; Van Deun et al., 2009; Lu et al., 2010). The signal to be detected was a 300 ms sinusoid at 125 Hz. Masking sounds were 400 ms bandpassed noise with bandwidths of ±25 Hz, centered at 125 Hz. Bandpass filters were fourth-order Butterworth with −24 dB/octave rolloff. Masker onset preceded the signal onset by 50 ms. Onset/offset were linear 5 ms ramps. Overall root mean squared (rms) sound levels were scaled to a reference tone at 125 Hz such that the peaks in stimulation output to the tone corresponded to about 95% of the subject’s dynamic range. The signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) was calculated as ratio of the power of the signal to the masking noise. The stimuli were generated separately with the signal on the left channel, masking noise on the right channel, and their relative amplitudes scaled to the desired SNR. The signals and noise were then mixed in real-time by the Spear3 running a custom program. N0S0 denotes diotic (0° phase difference) masking noise, N0, and diotic signal, S0. N0Sπ denotes diotic masking noise but dichotic (180° phase difference) signals, Sπ.
Spear3 implementation
The Spear3 research processor ran a custom program [Fig. 1A] based on a continuous interleaved sampling algorithm (Wilson et al., 1991). Audio signals were digitized by the Spear3 at 14.4 kHz. The stimuli from the left and right channels were mixed according to the test condition, half-wave rectified, and low-passed filtered at 500 Hz using a 4-pole Butterworth filter. A standard loudness growth map was used to compress the amplitude of the signal (Long et al. 2006, Lu et al. 2010). Because of the limited electric dynamic range in the hardware, a small amount of amplitude clipping at the signal input to the Spear3 was unavoidable, particularly at low SNR (e.g., −10 dB) that have high noise levels. The loudness growth map would have reduced this effect since higher amplitude levels were more compressed. This applied equally to both N0S0 and N0Sπ stimuli. The resulting signal was used to amplitude modulate a 1000 pps pulse train on each electrode using monopolar stimulation mode (MP1+2, ball and plate extracochlear electrodes), 25 μs per phase, 8 μs interpulse gap, and 8 μs interframe gap. With these pulse parameters, interleaving the stimulation on multiple electrodes resulted in a channel delay of 66 μs, measured from the first rising edges of the biphasic pulses. The output delay from the first pulse to the last for five stimulating electrodes is 264 μs. These delays were confirmed via electrodogram produced by IF5/PCI and RFStatsNT (Hearworks, Ltd). The high pulse rate relative to the signal and noise frequencies in addition to the 500 Hz low-pass filtering eliminated the possibility of the listeners using subsampled cues. Output pulses were delivered through one or more electrodes, appropriately scaled for threshold and maximal comfort levels. The timing of left and right pulse outputs of the Spear3 were set to have an interaural time difference of 0 μs and was verified by oscilloscope and “Implant-in–a-Box” (Cochlear, Ltd., Lane Cove, Australia) to be synchronized to within 1 μs.
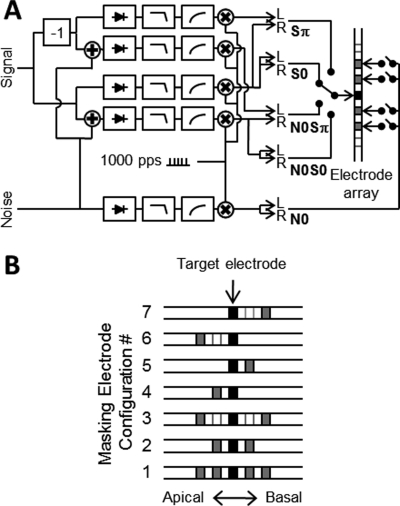
Figure 1.
(A) Block diagram of custom signal processing on-board the Spear3 research interface. Signal and noise were mixed, half-wave rectified, low-pass filtered, and compressed. The outputs were used to modulate a pulse train scaled to threshold and comfort levels for each electrode. The switches indicate specific stimulus conditions and masking electrodes that could be enabled and disabled. (B) Tested configurations of masking electrodes. For masking electrode configurations (MEC) #1–7, referred to as “full masking,” both signal and masking noise, N0S0 and N0Sπ were delivered to the target electrode pair. For each experimental condition, the same MEC was used bilaterally, with the pitch-matched electrode pair at the center. The target electrode pair, indicated in black, was the only pair to which the signal was delivered. Active masking electrodes, indicated in gray, always contained masking noise. Inactive electrodes are indicated in white. The second parallel set of conditions with noise removed from the target electrode (MEC #1n–7n) are referred to as “notched masking” and have the same masking electrode configurations as MEC #1–7.
The tested masking electrode configurations (MEC) of signal and masking electrodes are shown in Fig. 1B. The signal to be detected was always presented bilaterally with the middle pair of pitch-matched electrodes, referred to as the “target electrode pair.” Masking noise from a single source, N0, was routed to adjacent electrodes pairs, called “masking electrodes.” For MEC #1–7, N0S0 and N0Sπ were delivered with the target electrode pair. Conditions where N0 was presented to all active electrodes including the target electrode pair are referred to as “full masking.” In the second set of conditions, referred to as “notched masking” (MEC #1n–7n), N0 was presented with all active masking electrode except the target electrode pair which only had S0 and Sπ. Otherwise, the second set had the same permutations of MEC as in #1–7. A single electrode pair condition using the target electrodes for both signal and noise was also tested. This condition is the same as that used in previous studies (Long et al., 2006,Van Deun et al., 2009; Lu et al., 2010).
The stimulation levels for the target electrodes were balanced pairwise across ears. On each ear, stimulation levels for each of masking electrodes were adjusted to match the level for the target electrode. The stimuli were swept across the set of target and masking electrodes, and the subject was asked to indicate if any stimuli sounded louder or softer than the others. Any deviations in loudness were adjusted as necessary. Although the stimulations levels among electrodes were pairwise loudness balanced, no additional normalization was performed to equalize loudness among the 14 MECs. These masking electrodes were not required to be pitch-matched but always had the same MEC between ears.
The amount of channel interaction by adjacent masking electrodes on the target electrodes were varied by changing several factors: the number of masking electrodes, proximity of masking electrodes, and apical vs basal location. For example, comparisons can be made between MEC #1 and 2, and between #1 and 3 for the effect of number of masking electrodes. The increase in the number of masking electrodes would decrease the overall SNR ratio and make detection of the signal more difficult. Since electric fields decay over distance, moving noise farther away from the signal would reduce the amount of interaction with the signal on the target electrode. This was tested with different numbers of masking electrodes. The basal–apical location of masking electrodes is also important to account for any possible asymmetry in the electric field spread or differences in neural survival patterns.
Psychophysical procedure
All subjects were tested using a three-interval, three-alternative forced choice adaptive procedure (Levitt, 1971) with a graphical testing interface implemented in matlab. All three intervals contained N0 on adjacent masking electrodes. The signal, S0, was randomly assigned to a single interval and presented only through the target pair. The subjects were instructed to listen for the target tone and to identify which one of the three intervals contained the signal. Two correct successive responses resulted in decreased SNR on the next trial, while one incorrect response resulted in increased SNR on the next trial. Each change in direction of SNR (decreasing to increasing or vice versa) counted as a reversal. Testing was terminated after five reversals, and the last four reversal points were averaged to produce one SNR threshold. Smaller SNRs indicate better detection of the signal in noise compared to larger SNRs.
As an example for the full-masking condition, the target electrode pair would present N0, N0, and N0S0 for the three intervals. Under notched-masking condition the same example on the target electrode pair would be [quiet], [quiet], and S0. The adjacent masking electrodes would present N0, N0, and N0 for both full- and notched-masking conditions.
In order to help familiarize the subjects with the procedure and maximize performance, MECs with the fewest electrodes carrying masking noise were tested first (i.e., #7n and 6n), followed by MECs with increased masking, determined by number and proximity of the masking electrodes to the target electrode. Each run had a randomly chosen stimulus phase, contained two tracks, and was repeated two (CI5, CI7, and CI8) or three times (CI1 and CI6) to produce four or six threshold values, respectively, before testing the other phase condition. The average threshold values were then used in subsequent statistical analyses.
Although learning effects were not assessed over the testing period, any significant learning would have tended to reduce the masking effect, being been stronger for the first easier runs and less effective toward the end. This would have resulted in underestimating the threshold difference between MECs with more masker electrodes compared to those with only one masking electrode pair. Any fatigue would have been unlikely to have an effect on the later and more difficult conditions as testing occurred over multiple days.
Neural response telemetry (NRT)
Evoked compound action potentials were recorded in three subjects (CI1, CI6, and CI7) using the NRT feature of the Nucleus cochlear implant along with clinical software and equipment (Custom Sound EP 2.0, Cochlear, Ltd.). These three were a subset of the five assessed for BMLD. Adequate responses for CI5 would have required uncomfortable levels, and CI8 was not tested due to time constraint.
The stimuli used here were different from those used to obtain the behavioral data. Spread of excitation was measured using probe and masker pulses in a forward masking paradigm (e.g., Cohen et al., 2003; Abbas et al., 2004) for the five electrode pairs from the psychophysical testing. Both probe and masker pulses used MP1 stimulation mode (ball electrode), pulse width of 25 μs with a 25 μs interphase gap. Masker–probe interval was 400 μs. Maximum comfort levels for probe and masker combinations were established by increasing the stimulation levels relative to threshold. Masker level was set the same as probe level. Stimulation rate was low at 40 Hz to allow time the neural response, and the evoked potential data were averaged over 100 sweeps. Recording electrode was ±2 offset in MP2 mode. Two measurements were taken for each probe electrode using recording electrodes spaced +2 and −2 away from the probe.
Data analysis
Thresholds and BMLDs are reported as means with the standard error (mean ± s.e.). The error bars in Figs. 2–5 represent s.e. over MECs for each subject. For group means, data were first averaged over subjects before averaging over MEC. Statistical tests included paired and unpaired t-tests and repeated-measures analysis of variance (r.m. ANOVA). With small sample sizes, the likelihood of a type I error (false positive) may be increased and this limitation is acknowledged. Signal detection thresholds were analyzed with a three-way r.m. ANOVA to test for effects of signal phase, full vs notched masking, and electrode configuration. For paired t-tests, pairing was done according to MEC, unless otherwise noted.
Figure 2.
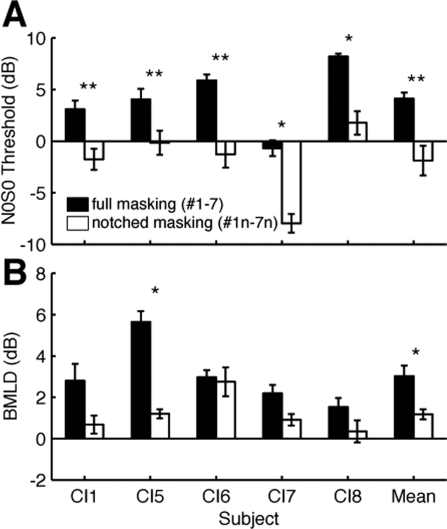
Single electrode pair masking level thresholds for N0S0 and N0Sπ. Significantly different N0S0 (black) and N0Sπ (white) thresholds are indicated with *(unpaired t-test, p < 0.05) or **(p < 0.001). The mean group thresholds are labeled as “Mean,” and its associated error bars indicate standard error from five subjects. For group average the statistical test compared average paired N0S0 and N0Sπ thresholds from each subject. (paired t-test, p = 0.0009).
Figure 5.
Full vs notched masking. (A) N0S0 thresholds are represented on the y-axis. Subjects and group average are listed on the x-axis. (B) BMLD. Data are grouped by subject and averaged over electrode configuration. Black bars represent conditions where noise was presented on the target electrode (MEC #1–7). White bars indicate conditions where masking noise was only presented on electrodes adjacent to the target electrode (MEC #1n–7n). Error bars are standard errors. Statistically significant differences between the two conditions are marked with *(paired t-test, p < 0.05). Mean and the associated error bars indicate average data and standard error. Data were averaged over subject first and then over MEC.
RESULTS
Binaural unmasking with single electrode pairs
In order to assess the effect of channel interaction on BMLD, baseline data were first obtained using single pairs of pitch-matched electrodes (Fig. 2). Single pair data of CI1 were from Lu et al. (2010). Despite some intersubject variability, every subject exhibited sensitivity to the binaural phase difference in the target signal. All subjects had positive SNR values for thresholds in the N0S0 condition and negative SNR values for N0Sπ, indicating that they could detect the target signal even when its amplitude was smaller than the noise. Individual N0S0 and N0Sπ thresholds were significantly different (p < 0.05, unpaired t-test) in each subject. Stimulus phase had a statistically significant effect on mean thresholds [N0S0: 3.9 ± 2.5 dB (mean ± s.e.); N0Sπ: −55.0 ± 1.9 dB; r.m. ANOVA, F1,4 = 77.163, p = 0.001]. An average BMLD of 8.9 ± 1.0 dB was calculated from the mean threshold difference between phase conditions, N0S0 − N0Sπ (in decibels).
Binaural unmasking with multiple masking electrodes
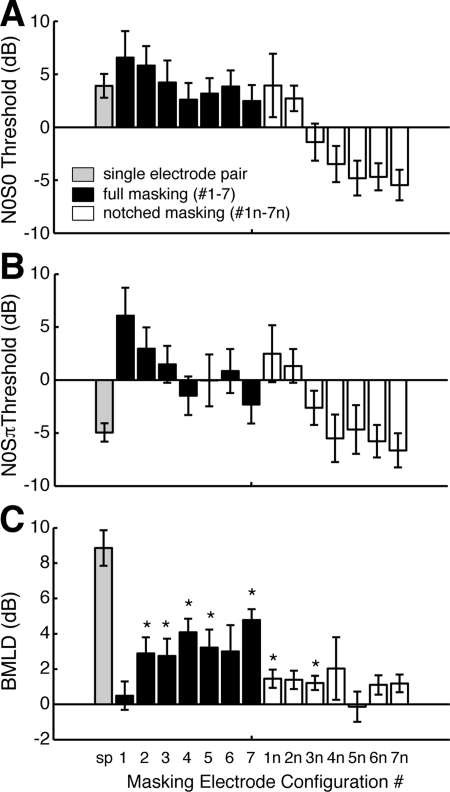
With BMLD levels established for each subject, masking noise waspresented on electrodes adjacent to the target electrode pair to introduce channel interaction. N0S0 thresholds varied widely depending on MEC and ranged from −5.5 to 6.6 dB [Fig. 3A]. The highest average N0S0 threshold was seen in the configuration with all adjacent masking electrode pairs active and full masking present (#1). Lowest mean thresholds were observed in some cases with notched masking and only one pair of masking electrodes spaced two away (#7n). N0Sπ thresholds ranged from −6.6 to 6.1 dB and appeared to follow a similar trend as for N0S0 thresholds [Fig. 3B].
Figure 3.
Masking electrode configurations (MEC). (A) N0S0 thresholds averaged across the five subjects, plotted according to electrode configuration [shown in Fig. 1B]. Error bars represent standard error for the five subjects. (B) N0Sπ thresholds. (C) BMLDs averaged across subjects for each electrode configuration. Significantly different N0S0 and N0Sπ thresholds, paired by subject, are indicated with *(paired t-test, p < 0.05). For reference, thresholds and BMLDs obtained from single electrode pairs are shown.
BMLDs ranged from −0.1 to 4.8 dB and were significant (p < 0.05, t-test paired by subject) for half of the conditions tested [indicated by *, Fig. 3C]. Although nearly half of these configurations did not have significant BMLDs, for nearly all MECs, N0Sπ thresholds were lower than N0S0, indicated by positive BMLD values.
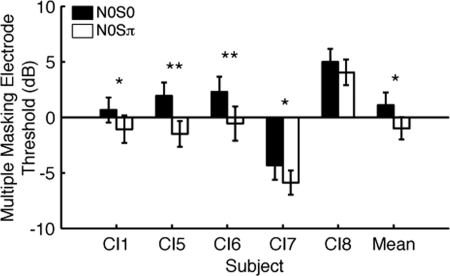
Thresholds averaged across all tested MECs are shown in Fig. 4. These values reflect the average level of masking that could be expected from a more complex stimulation condition where multiple electrodes are activated, rather than limiting considerations to a single set and/or configuration of electrodes. The data were analyzed with a three-way r.m. ANOVA to test for effect of phase, full vs notched masking, and electrode configuration. Thresholds for N0S0 (1.1 ± 1.1 dB) were higher than N0Sπ (−1.0 ± 1.0 dB). The mean difference, i.e., the BMLD (2.1 ± 0.4 dB) was statistically significant (three-way r.m. ANOVA; F1,4 = 21.475, p = 0.010) relative to the null hypothesis of a BMLD of 0 dB. Average BMLD under multielectrode masking was significantly lower than that observed for single electrode pairs, 2.1 vs 8.9 dB, respectively (p = 0.002, t-test paired by subject). Consideration of the data by subject showed that phase had a significant effect over all electrode configurations in four of five subjects (p < 0.05, t-test, paired by MEC), excluding subject CI8 (p = 0.081). This may be related to the fact that CI8 also had the shortest duration of BiCI experience compared to the other subjects (Table TABLE I.).
Figure 4.
BMLD for multiple masking electrodes. Masking level thresholds for N0S0 and N0Sπ averaged over all electrode configurations. Format is similar to Fig. 2. *indicate statistically significant difference (paired t-test, p < 0.05) between N0S0 and N0Sπ conditions paired by electrode configuration. For the group mean, the thresholds were averaged over subject first, and then by MEC. The difference between average N0S0 and N0Sπ was significant when paired by subject (paired t-test, p = 0.010).
Full vs notched masking
One of the most significant factors on thresholds was the removal of masking noise from the target electrode pair (MEC #1n–7n). Overall thresholds (pooled N0S0 and N0Sπ) decreased from 2.6 ± 1.6 dB to −2.5 ± 1.7 dB (three-way r.m. ANOVA; F1,4 = 28.144, p = 0.006). No significant interaction between phase and full/notched masking was observed (three-way r.m. ANOVA; F1,4 = 6.681, p = 0.061).
Mean threshold for just the N0S0 condition [Fig. 5A] showed a clear decrease due to notched masking, from 4.1 ± 0.6 dB to −1.9 ± 1.4 dB (p < 0.001, paired t-test). Mean N0Sπ threshold also decreased from 1.1 ± 1.1 dB to −3.1 ± 1.4 dB (data not shown; p < 0.001, paired t-test). These threshold drops were expected since removing masking noise from the target electrode pair improved overall SNR.
With full/notched masking and phase as the only factors, the effect of phase was still significant using a two-way r.m. ANOVA (BMLD: 2.1 ± 0.4 dB; F1,4 = 21.537, p = 0.010). As can be seen in Fig. 5B, along with the decrease in overall N0S0 threshold, mean BMLDs decreased significantly with notched masking from 3.0 ± 0.5 dB to 1.2 ± 0.3 dB (p = 0.017, paired t-test). The smaller BMLD was due more to changes in N0S0 thresholds than N0Sπ. It is important to note that despite the drop in BMLD, the mean N0S0 threshold with notched masking (−1.9 dB) was significantly lower than N0Sπ with full masking (1.1 dB, p = 0.005, paired t-test), meaning that for signal detection with these stimuli, binaural unmasking was less effective than simply moving masking noise off the target electrode.
Correlations with physiological measures of channel interaction
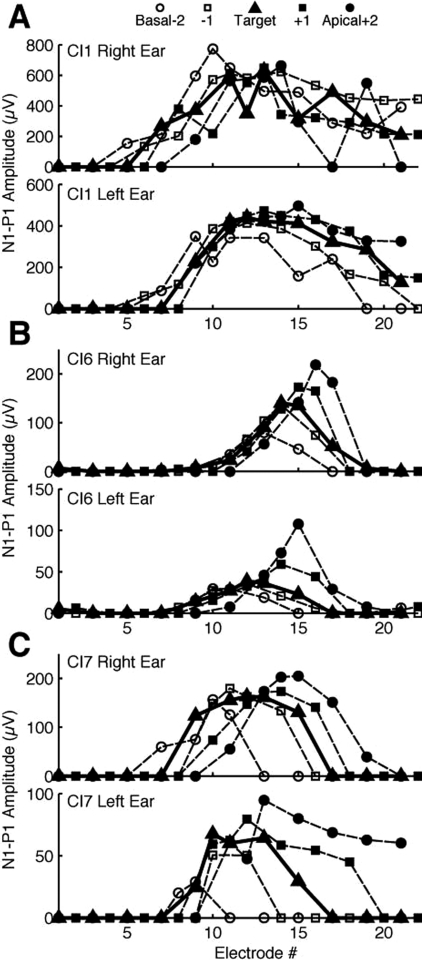
In order to gain some insight into the neural mechanismsunderlying the effects of MEC on thresholds and BMLD, electrically evoked compound action potentials were recorded from three subjects using NRT (Fig. 6). N1-P1 amplitudes indicate the amount of neural activation over the electrode array in response to a single place of electrical stimulation. Due to variations in neural survival, electrode array positioning, and other factors, such as subjective comfort levels, the absolute amplitudes can be different from subject to subject and ear to ear. A large amount of overlap between NRT curves can be seen, and they reflect the potential for channel interactions. The area of overlap between masking electrodes and the target electrode were quantified into a channel interaction index (ChII).
Figure 6.
Spread of excitation measured through evoked potentials. (A) Subject CI1. (B) CI6. (C) CI7. In each panel, the upper and lower plots are data from the right and left ears, respectively. The y-axis indicates the magnitude of recorded neural activity. The x-axis indicates the masker active electrode. Symbol legend in (A) indicates the active electrode.
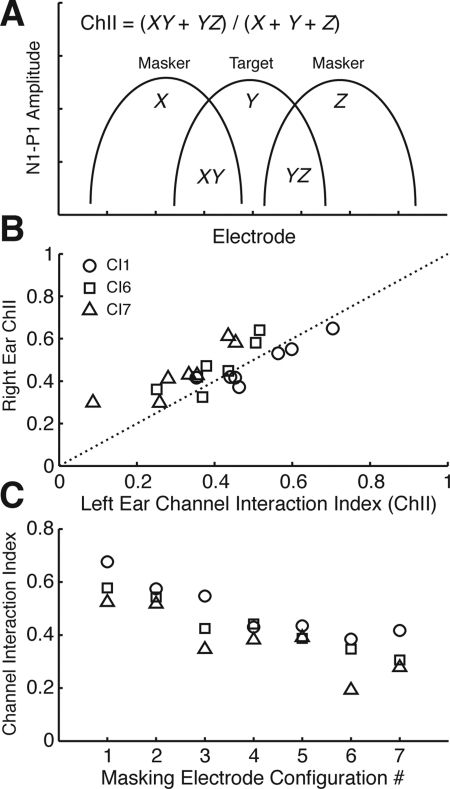
Data from the NRT measurements were analyzed in matlab. For each electrode, the area under the curve from the spread of excitation measurement was estimated using a rectangular integration method and normalized electrode distances, e.g., electrodes 12 and 13 have a separation of 1 unit. Then for each MEC, a ChII was calculated as follows [Fig. 7A]. The areas of masking electrodes that overlapped the target electrode were summed and then normalized by the total cumulative areas of masking and target electrodes. A ChII of 0 would indicate that no overlap in neural response existed between any of the masking electrodes and target electrodes. Greater amounts of overlap between channels result in higher ChII values. Since masking noises on the target electrode pair do not contribute to this calculation, ChII values for notched-masking conditions (MEC #1n–7n) are the same as their equivalent configuration in full masking (#1–7).
Figure 7.
Channel interaction index (ChII). (A) Schematic of ChII calculation. Curves represent evoked potential data shown in Fig. 6. X,Y, and Z are the areas under each curve, XY and YZ are the intersected area. Y represents the target electrode. X and Z represent masker electrodes. (B) Right ChII plotted as a function of left ChII for masking electrode configurations #1–7 [see Fig. 1B]. Symbols represent different subjects. (C) ChII plotted against MEC #1–7. MEC #1n–7n have the same ChII values as their equivalent in #1–7 and are not shown. Left and right ears were averaged to produce a single ChII value for each MEC.
ChII determined by MEC
Fig. 7B shows ChII of the right ear plotted against the left ear for MEC #1–7. Mean ChII value was higher and statistically different for the right ear compared to the left (R: 0.46 ± 0.02; L: 0.41 ± 0.03; paired t-test, p = 0.012). Within each subject, ChII points appeared above or below the y = x line, depending on whether ChII was smaller for the left ear (CI6 and CI7) or right ear (CI1), respectively, matching with their self-reported ear preference (e.g., for telephone listening, marked by “a” in Table TABLE I.). For the subsequent analyses, the left and right ChII were averaged since they were highly correlated (p < 0.001, Spearman’s rho = 0.721, N = 21, two-tailed).
Since each MEC had different electrode numbers and spacing, it follows that ChII should reflect this variation [7C]. Some configurations with more masking electrodes such as MEC #1 and 2 had higher ChIIs. The average ChII over the three subjects and MECs were 0.59 ± 0.05 (n = 3) for the condition with four masking electrodes pairs (MEC #1), 0.49 ± 0.04 (n = 6) for two pairs (MEC #2 and 3), and 0.37 ± 0.02 (n = 12) for one pair (MEC #4–7). There was a significant difference in ChII between the four vs one masker pairs (p = 0.012, Mann-Whitney U, with Bonferroni correction) but not for two vs four (p = 0.498) and one vs two (p = 0.072).
Regarding subjects, CI7 (triangles) consistently had the lowest ChIIs while CI1 had the highest. ChIIs were significantly different between subjects (CI1: 0.49 ± 0.03; CI6: 0.43 ± 0.03; CI7: 0.38 ± 0.04; one-way ANOVA, F2,39 = 3.701, p = 0.034). Post hoc comparison showed a significant difference between CI1 and CI7 (p = 0.029, t-test with Bonferroni correction) but not between CI6 and the others (p > 0.05).
Thresholds and BMLDs are correlated with ChII
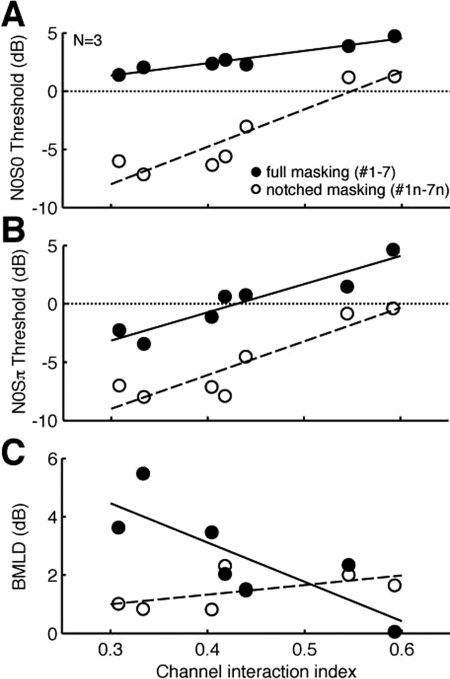
With each MEC reduced to a single ChII value, the physiologically derived measure of channel interaction and behaviorally acquired BMLDs were plotted against each other (Fig. 8). The correlations between N0S0/N0Sπ/ BMLD and ChII were considered separately for full (MEC #1–7) and notched-masking (MEC #1n–7n) conditions.
Figure 8.
Behavioral correlations with average ChII. Each data point represents the mean threshold or BMLD from the 3 subjects shown in Figs. 67. (A) N0S0 thresholds plotted against ChII for full masking (MECs #1–7; filled circles) and notched masking (#1n–7n, open circles). (B) N0Sπ thresholds vs ChII. (C) BMLD plotted against ChII. Regression equations and statistics are listed in Table TABLE II..
Decreasing SNR by increasing the amount of channel interactions should increase detection thresholds, and this was observed for all conditions [Fig. 8A]. Linear regression analyses of each correlation showed statistically significant linear fits (Table TABLE II.). Thus reducing channel interactions had only a small effect on N0S0 in the presence on-target noise in full masking.
Table 2.
Linear regression analysis.
| Condition | Equation | R2 | Statistics (ANOVA) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N0S0 | Full masking (MEC #1–7) | y = 10.68*x − 1.88 | 0.93 | F1,5 = 71.278, p < 0.001 |
| Notched masking (MEC #1n–7n) | y = 32.27*x − 17.65 | 0.87 | F1,5 = 34.459, p = 0.002 | |
| N0Sπ | Full masking | y = 24.19*x − 10.40 | 0.88 | F1,5 = 35.622, p = 0.002 |
| Notched masking | y = 28.87*x − 17.66 | 0.83 | F1,5 = 24.193, p = 0.004 | |
| BMLD | Full masking | y = −13.49*x + 8.51 | 0.65 | F1,5 = 9.313, p = 0.028 |
| Notched masking | y = 3.30*x + 0.01 | 0.35 | F1,5 = 2.637, p = 0.165 |
N0Sπ showed increasing thresholds with increasing amount of channel interaction [8B]. In this case, while full masking increased thresholds, the slopes between full and notched-masking conditions were nearly the same. Thresholds were shifted by almost a constant amount over the range of ChII shown. This means that reducing the amount of channel interaction would produce the same drop in N0Sπ threshold regardless of whether the masking noise was full or notched.
In the presence of full masking, there was an increase in BMLD with lower ChII [Fig. 8C]. Since there was only a small drop in N0S0 thresholds with smaller ChII, most of the improvement appears to come from N0Sπ at lower ChII values. With notched masking, N0S0 and N0Sπ slopes were nearly the same, and thus BMLD showed a slight but not significant decrease with smaller ChII.
It should be noted that the BMLD regression equation for full masking had a y-intercept of 8.5 dB. This is comparable to the single electrode pair condition with ChII = 0, and the value was almost the same as the actual average BMLD of 8.6 dB for these three subjects using single electrode pairs. The same analysis underestimated average N0S0 and N0Sπ thresholds by 4–5 dB. Individually, the extrapolation was not as accurate as BMLD intercepts were 12.8, 8.1, and 4.4 dB for CI1, CI6, and CI7 compared to their actual values of 11.3, 6.4, and 8.0 dB, respectively.
DISCUSSION
Despite the presence of channel interactions resulting from masking noise on neighboring electrodes, the data in this study from BiCI users showed that BMLD can be observed under controlled stimulation conditions. BMLDs obtained from single electrode pairs are consistent with existing CI data, which show reduced performance at <9 dB compared to <20 dB for NH listeners under similar conditions using transposed tones (van de Par and Kohlrausch, 1997) or acoustic CI simulation (Lu et al. 2010). This lower baseline performance of CI users indicates that even under idealized laboratory conditions, binaural processing in CI is not at normal hearing levels. Clinically bilateral CI users are not able to take full advantage of BMLD under real world conditions even when presented with fine timing information (van Hoesel et al., 2008). The factors that might contribute to this finding include lack of synchronization at the level of individual pairs of electrodes, poor ITD sensitivity in many BiCI users, compressed dynamic range, and channel interaction. The latter factor could be a significant complication to consider and was therefore of interest in the current investigation.
Generally, the addition of masking electrodes raised thresholds and reduced BMLD. The data showed that the MECs that would have potential for higher channel interactions typically showed lower BMLDs [Fig. 3C]. For CI users, adding more electrodes was similar to widening the masking noise bandwidth in NH listeners. NH listeners showed that when the spectrum level (decibel/hertz) of the masking noise was kept constant, N0Sπ thresholds increased at narrow bandwidths while N0S0 thresholds showed more subject-dependent variability (Zurek and Durlach, 1987). BMLD has typically been found to decrease in NH listeners with wider masking bandwidth (Hall and Fernandes, 1983; Zurek and Durlach, 1987; van de Par and Kohlrausch, 1999), which is consistent with the findings in the present study.
The notched-masking condition in this study is similar to the spectrally notched noise for NH listeners, keeping in mind that the mechanisms of auditory nerve stimulation between NH and CI are different. With notched noise, BMLDs in NH listeners have been found to decrease with widening of the notch width, from roughly 15 to 5 dB (Hall et al., 1983; Nitschmann et al., 2009; 2010). For bandpassed noise, BMLD decreased with a widening of bandwidth (Hall et al., 1983; Zurek and Durlach, 1987; Staffel et al., 1990; van de Par and Kohlrausch, 1999). This is consistent with the observation in this study that BMLD decreased with increased amount of masking [Fig. 8C, full masking condition].
Full versus notched masking
The main reason that BMLDs were reduced as channel interaction was increased appeared to be due to higher sensitivity of N0Sπ thresholds under full masking compared to N0S0 (Fig. 8). One explanation could be that for N0S0, the contribution of off-target masking noise was much less than that resulting from on-target noise. These adjacent maskers had a larger effect on N0Sπ thresholds. This suggested that perhaps on-target noise contributed less to the N0Sπ thresholds.
An interesting finding is that the sensitivity (or slope) of N0S0 thresholds to ChII was affected by the type of masking while the sensitivity of N0Sπ thresholds did not appear to change [Fig. 8A, 8B]. N0S0 thresholds had lower sensitivity under the full masking condition, presumably since the presence of on-target masking noise had a larger contribution to N0S0 thresholds than off-target noise. Once the masking noise was notched, N0S0 threshold sensitivity became similar to that for N0Sπ, as evidenced by roughly similar slopes in their regression equation (Table TABLE II.). An interpretation is that for the N0Sπ stimuli with full masking, binaural computations (e.g., equalization-cancellation) effectively resulted in notched masking at the neural level. The higher thresholds for N0Sπ with full masking compared to N0S0 with notched masking could be due to less than ideal equalization-cancellation of the on-target masking noise.
Physiological measures of channel interaction
In order to show the influence of channel interactions on BMLD, ChII was calculated for each MEC and compared with the behavioral measures. Not surprisingly, higher N0S0 and N0Sπ thresholds were significantly correlated with larger ChII. Other studies have similarly shown that the amount of channel interaction is correlated with behavioral measures (Shannon, 1983; Cohen et al., 2003; Hughes and Abbas, 2006; Stickney et al., 2006; Hughes, 2008). It should be noted that in this study the ear with lower average ChII was self-reported as the “better ear” and had higher HINT scores (Table TABLE I.). No clinical testing on speech was performed for CI6 due to already high scores on the right. CI6 also preferred the left ear despite being implanted later.
In absence of channel interactions, ChII would be 0, and BMLD would be dependent only on the signal and noise on the target pair, essentially the single electrode pair condition. Extrapolating the data for full masking using the linear regression predicted the actual BMLDs for the single-electrode case, despite being outside the range of data. The average BMLD value of the three subjects for single electrode pairs was 8.6 dB, which is almost the same as the y-intercept value, 8.5 dB of the regression calculated on the data, for the full masking condition (Table TABLE II.).
With notched masking, the intercept was 0.01 dB, keeping in mind that this fit was not statistically significant. In the absence of full masking, thresholds would be largely based on detecting signal energy in the target pair, with minimal contribution from interaural differences. Although BMLDs were small (1–2 dB), the shallow rise in slope with increased ChII suggests that BiCI users can take advantage of binaural cues when noise is introduced through spread of excitation from adjacent masking electrodes to overlap with the target electrode pair.
Individual differences
The average trends for BMLD generally followed what was observed in NH listeners, but there were a few noteworthy points concerning individual subjects. CI5 was tested in Lu et al. (2010). His single-electrode BMLD (11.3 ± 2.1 s.e. dB) was nearly the same as his previously recorded value (11.2 ± 1.1 dB) using a middle pair of electrodes, with the caveat that the electrode pairs were different. The similarity of the BMLD values between data collected about 1 year apart showed consistent performance in this subject, who had been using his implant for over 6 years. His plateau below NH levels of 15-20 dB suggested an impaired ability of the auditory system to make full use of binaural cues. This impairment was further supported by data showing NH listeners using a vocoder to acoustically simulate CI performed better than actual CI users on the N0Sπ detection task, while N0S0 thresholds were roughly the same (Lu et al., 2010). Auditory deprivation may be a factor as abnormal physiological function has been observed in neonatally and congenitally deafened animal models in response to electrical stimulation (Shepherd et al., 1999; Vollmer et al., 2007; Kral et al., 2009; Tillein et al., 2009).
A third subject (CI8) had less experience than the others with his implants but had used hearing aids extensively prior to implantation. At the time of testing, he had only used his second implant for about 6 months, but his BMLD for a single electrode pair was consistent with the other subjects (Fig. 2). The shorter duration of CI use could explain his lower scores in the presence of multielectrode masking (Fig. 4).
Subject CI7 had BMLDs comparable to the other subjects, but N0S0 and N0Sπ thresholds were much lower compared to the other subjects tested under the multiple masking channel condition (e.g., Fig. 4). A possible explanation is that the subject was able to discriminate between electrodes fairly well and thus was able to better attend to the signal channel despite masking noises on other channels. The NRT data are consistent with this notion, since CI7 had the lowest values of ChII, and lower thresholds were correlated with lower ChII (Fig. 8A, 8B].
Limitations of this study
There are some considerations to make in interpreting these data. First, this study changed the amount of channel interaction by altering the number and proximity of masking electrodes and not through narrowing of the electric field (e.g., using bipolar stimulation mode). It is unknown how BMLDs compare between monopolar and bipolar configurations using a single electrode pair. Second, the noise applied to neighboring electrode pairs was always diotic and generated from the same source. It is expected that having independent noise sources on each masking electrode would further erode binaural cues in the target electrode in terms of absolute threshold and BMLD. Third, overall masker levels were not normalized, and doing so would further confound the data. Standardizing the overall sound level by adjusting levels in each channel may affect the pitch-match quality. A fixed adjustment increment in stimulation level on one electrode may produce a perceptual increment of different sizes due to factors such as pattern of nerve survival and intracochlear electrode positioning. The comparison with NRT data is facilitated since overall stimulation levels were not adjusted with MEC.
Since both the NRT and behavioral data were gathered at maximal comfort level for different stimulation rates, stimulation levels would be higher at the lower rate. Consequently, the spread of excitation may be wider than what occurs during the behavioral tests. However, since the ChIIs extracted from the NRT data are normalized measures, the relative amount of ChII due to MEC should not change. Finally, the NRT data only included three subjects, limiting statistical power.
Implications for speech
Measures of BMLD are thought to be important for understanding how speech is perceived in complex listening situations, such as when target speech is presented from one location and maskers co-occur from different spatial locations. To the extent that binaural mechanisms are successful at producing release from masking in the presence of spatial cues may depend on listeners’ sensitivity to binaural cues. With BiCI users, poor ITD sensitivity (van Hoesel and Clark, 1997; van Hoesel, 2007; Laback and Majdak, 2008; van Hoesel et al., 2009; Litovsky et al., 2010) appear to contribute to low BMLD levels (van Hoesel et al., 2008). Because the small speech BMLDs in the study by van Hoesel et al. (2008) were obtained using a 700 μs ITD while the studies with 125 Hz tones that used 4 ms ITD (π-phase) found BMLDs around 4–9 dB (Long et al., 2006; Van Deun et al., 2009; Lu et al., 2010), the comparison of BMLD between these studies is not so clear. Although Long et al. (2006) did use a 600 μs delay using single electrode pairs and 125 Hz tone, that specific condition did not include compression and resulted in BMLD of 15 dB. It was noted in the discussion section of van Hoesel et al. (2008) that their own informal testing showed smaller BMLD for a 125 Hz tone with a 1 ms phase shift compared to 4 ms. In contrast, BMLDs around 9 dB were observed in two subjects for signal frequencies of 500 Hz (Lu et al., 2010). This would correspond to a 1 ms phase shift for the N0Sπ condition. Additional experiments may be warranted to clarify the effect of stimulus ITD on BMLDs for tones and speech.
Data in this study demonstrated that adjacent masking electrodes lower BMLD levels to below that obtained with single electrode pairs. This is a finding that needs to be carefully examined, since speech understanding can rarely be achieved with single-channel stimulation. The across-frequency distribution of information in speech may serve to increase the saliency of binaural cues. This study only tested the specific condition of a single target electrode pair with noise adjacent maskers. In order to advance the understanding of factors that affect binaural hearing and its impact on spatial unmasking in CI users, further experiments in parametrically controlling signal and noise presentations would need to be carried out, including presenting both tone and noise to multiple electrodes.
The predictability of BMLD from measures of electric field spread suggests a significant role of channel interactions at the auditory periphery. In contrast, limitations of BMLD due to poor ITD sensitivity as seen in van Hoesel et al. (2008) may be an issue with central auditory processing since auditory nerve fibers have been shown to have a very high degree of synchronized responses to electrical stimulation (Hartmann et al., 1984). Thus both peripheral and central auditory mechanisms will need to be addressed in restoring binaural hearing.
Clinically, monopolar stimulation is desirable due to lowered thresholds and power consumption. In fact, despite greater electric field spread in monopolar stimulation, speech recognition has been reported to be at least as good or better than with bipolar stimulation in which smaller electric field spread occurs (Pfingst et al., 1997; Pfingst et al., 2001). Some attempts have been made to reduce channel interactions in BiCI by reducing the number of electrodes used, but the input frequency bands were interleaved such that any pitch-matched electrodes would have received different information (Perreau et al., 2010; Tyler et al., 2010). It remains to be seen whether stimulation modes such as bipolar and and tripolar (i.e., quadrupolar), both of which reduce electric field spread (Jolly et al., 1996; Kral et al., 1998; Briaire and Frijns, 2000), can provide a clinical advantage for BiCI users in binaurally relevant tasks.
Summary
The main findings of this study are (1) BMLDs were 8.9 dB for single electrode pairs and 2.1 dB with multiple electrode maskers, (2) notched masking not only reduced thresholds compared to full masking but also decreased BMLD, and (3) thresholds and BMLD values were significantly correlated with ChII. These results demonstrate that noise from adjacent electrodes can lower BMLDs in BiCI users and that the effect was mainly due to channel interactions at the auditory periphery. Further gains in BiCI binaural hearing may be realized by narrowing the electric field spread and by developing stimulation algorithms that minimize channel interactions.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This research was supported by National Institutes of Health Grant Nos. 5 R01 DC003083 (R.L.) and P30 DC008369 (F.-G.Z.).
References
- Abbas, P. J., Hughes, M. L., Brown, C. J., Miller, C. A., and South, H. (2004). “Channel interaction in cochlear implant users evaluated using the electrically evoked compound action potential,” Audiol. Neuro-Otol. 9, 203–213. 10.1159/000078390 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aronoff, J. M., Yoon, Y. S., Freed, D. J., Vermiglio, A. J., Pal, I., and Soli, S. D. (2010). “The use of interaural time and level difference cues by bilateral cochlear implant users,” J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 127, EL87–EL92. 10.1121/1.3298451 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briaire, J. J., and Frijns, J. H. (2000). “Field patterns in a 3D tapered spiral model of the electrically stimulated cochlea,” Hear. Res. 148, 18–30. 10.1016/S0378-5955(00)00104-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buss, E., Pillsbury, H. C., Buchman, C. A., Pillsbury, C. H., Clark, M. S., Haynes, D. S., Labadie, R. F., Amberg, S., Roland, P. S., Kruger, P., Novak, M. A., Wirth, J. A., Black, J. M., Peters, R., Lake, J., Wackym, P. A., Firszt, J. B., Wilson, B. S., Lawson, D. T., Schatzer, R., D’Haese, P. S., and Barco, A. L. (2008). “Multicenter U.S. bilateral MED-EL cochlear implantation study: Speech perception over the first year of use,” Ear Hear. 29, 20–32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee, M., and Shannon, R. V. (1998). “Forward masked excitation patterns in multielectrode electrical stimulation,” J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 103, 2565–2572. 10.1121/1.422777 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, L. T., Richardson, L. M., Saunders, E., and Cowan, R. S. (2003). “Spatial spread of neural excitation in cochlear implant recipients: Comparison of improved ECAP method and psychophysical forward masking,” Hear. Res. 179, 72–87. 10.1016/S0378-5955(03)00096-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durlach, N. I. (1963). “Equalization and cancellation theory of binaural masking-level differences,” J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 35, 1206–1218. 10.1121/1.1918675 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Fishman, K. E., Shannon, R. V., and Slattery, W. H. (1997). “Speech recognition as a function of the number of electrodes used in the SPEAK cochlear implant speech processor,” J. Speech Lang. Hear Res. 40, 1201–1215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friesen, L. M., Shannon, R. V., Baskent, D., and Wang, X. (2001). “Speech recognition in noise as a function of the number of spectral channels: Comparison of acoustic hearing and cochlear implants,” J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 110, 1150–1163. 10.1121/1.1381538 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Q. J., Shannon, R. V., and Wang, X. (1998). “Effects of noise and spectral resolution on vowel and consonant recognition: Acoustic and electric hearing,” J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 104, 3586–3596. 10.1121/1.423941 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabriel, K. J., and Colburn, H. S. (1981). “Interaural correlation discrimination: I. Bandwidth and level dependence,” J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 69, 1394–1401. 10.1121/1.385821 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goupell, M. J., and Hartmann, W. M. (2007). “Interaural fluctuations and the detection of interaural incoherence. III. Narrowband experiments and binaural models,” J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 122, 1029–1045. 10.1121/1.2734489 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall, J. W., and Fernandes, M. A. (1983). “Monaural and binaural intensity discrimination in normal and cochlear-impaired listeners,” Audiology 22, 364–371. 10.3109/00206098309072796 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall, J. W., Tyler, R. S., and Fernandes, M. A. (1983). “Monaural and binaural auditory frequency resolution measured using bandlimited noise and notched-noise masking,” J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 73, 894–898. 10.1121/1.389013 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann, R., Topp, G., and Klinke, R. (1984). “Discharge patterns of cat primary auditory fibers with electrical stimulation of the cochlea,” Hear. Res. 13, 47–62. 10.1016/0378-5955(84)90094-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsh, I. J. (1948). “Binaural summation and interaural inhibition as a function of the level of masking noise,” Am. J. Psychol. 61, 205–213. 10.2307/1416966 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes, M. L. (2008). “A re-evaluation of the relation between physiological channel interaction and electrode pitch ranking in cochlear implants,” J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 124, 2711–2714. 10.1121/1.2990710 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes, M. L., and Abbas, P. J. (2006). “The relation between electrophysiologic channel interaction and electrode pitch ranking in cochlear implant recipients,” J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 119, 1527–1537. 10.1121/1.2163273 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jolly, C. N., Spelman, F. A., and Clopton, B. M. (1996). “Quadrupolar stimulation for cochlear prostheses: Modeling and experimental data,” IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 43, 857–865. 10.1109/10.508549 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones, G. L., Litovsky, R. Y., and van Hoesel, R. (2009). “Relationship of monaural and binaural channel interaction effects in bilateral cochlear implant users (abstract),” in Conference on Implantable Auditory Prostheses (Lake Tahoe, CA: ).
- Kral, A., Hartmann, R., Mortazavi, D., and Klinke, R. (1998). “Spatial resolution of cochlear implants: The electrical field and excitation of auditory afferents,” Hear. Res. 121, 11–28. 10.1016/S0378-5955(98)00061-6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kral, A., Tillein, J., Hubka, P., Schiemann, D., Heid, S., Hartmann, R., and Engel, A. K. (2009). “Spatiotemporal patterns of cortical activity with bilateral cochlear implants in congenital deafness,” J. Neurosci. 29, 811–827. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2424-08.2009 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laback, B., and Majdak, P. (2008). “Binaural jitter improves interaural time-difference sensitivity of cochlear implantees at high pulse rates,” Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 105, 814–817. 10.1073/pnas.0709199105 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laszig, R., Aschendorff, A., Stecker, M., Muller-Deile, J., Maune, S., Dillier, N., Weber, B., Hey, M., Begall, K., Lenarz, T., Battmer, R. D., Bohm, M., Steffens, T., Strutz, J., Linder, T., Probst, R., Allum, J., Westhofen, M., and Doering, W. (2004). “Benefits of bilateral electrical stimulation with the nucleus cochlear implant in adults: 6-month postoperative results,” Otol. Neurotol. 25, 958–968. 10.1097/00129492-200411000-00016 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitt, H. (1971). “Transformed up-down methods in psychoacoustics,” J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 49(2), 467–477. 10.1121/1.1912375 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim, H. H., Tong, Y. C., and Clark, G. M. (1989). “Forward masking patterns produced by intracochlear electrical stimulation of one and two electrode pairs in the human cochlea,” J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 86, 971–980. 10.1121/1.398732 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litovsky, R. Y., Jones, G. L., Agrawal, S., and van Hoesel, R. (2010). “Effect of age at onset of deafness on binaural sensitivity in electric hearing in humans,” J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 127, 400–414. 10.1121/1.3257546 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litovsky, R. Y., Parkinson, A., and Arcaroli, J. (2009). “Spatial hearing and speech intelligibility in bilateral cochlear implant users,” Ear Hear. 30, 419–431. 10.1097/AUD.0b013e3181a165be [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long, C. J., Carlyon, R. P., Litovsky, R. Y., and Downs, D. H. (2006). “Binaural unmasking with bilateral cochlear implants,” J. Assoc. Res. Otolaryngol. 7, 352–360. 10.1007/s10162-006-0049-4 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu, T., Litovsky, R., and Zeng, F. G. (2010). “Binaural masking level differences in actual and simulated bilateral cochlear implant listeners,” J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 127, 1479–1490. 10.1121/1.3290994 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay, C. M., McDermott, H. J., and Clark, G. M. (1996). “The perceptual dimensions of single-electrode and nonsimultaneous dual-electrode stimuli in cochlear implantees,” J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 99, 1079–1090. 10.1121/1.414594 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middlebrooks, J. C. (2004). “Effects of cochlear-implant pulse rate and inter-channel timing on channel interactions and thresholds,” J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 116, 452–468. 10.1121/1.1760795 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, D. A., Donaldson, G. S., and Kreft, H. (2008). “Forward-masked spatial tuning curves in cochlear implant users,” J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 123, 1522–1543. 10.1121/1.2836786 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nitschmann, M., Verhey, J. L., and Kollmeier, B. (2009). “The role of across-frequency processes in dichotic listening conditions,” J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 126, 3188–3198. 10.1121/1.3243307 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nitschmann, M., Verhey, J. L., and Kollmeier, B. (2010). “Monaural and binaural frequency selectivity in hearing-impaired subjects,” Int. J. Audiol. 49, 357–367. 10.3109/14992020903470775 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perreau, A., Tyler, R. S., and Witt, S. A. (2010). “The effect of reducing the number of electrodes on spatial hearing tasks for bilateral cochlear implant recipients,” J. Am. Acad. Audiol. 21, 110–120. 10.3766/jaaa.21.2.5 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfingst, B. E., Franck, K. H., Xu, L., Bauer, E. M., and Zwolan, T. A. (2001). “Effects of electrode configuration and place of stimulation on speech perception with cochlear prostheses,” J. Assoc. Res. Otolaryngol. 2, 87–103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfingst, B. E., Zwolan, T. A., and Holloway, L. A. (1997). “Effects of stimulus configuration on psychophysical operating levels and on speech recognition with cochlear implants,” Hear. Res. 112, 247–260. 10.1016/S0378-5955(97)00122-6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiss, L. A., Turner, C. W., Erenberg, S. R., and Gantz, B. J. (2007). “Changes in pitch with a cochlear implant over time,” J. Assoc. Res. Otolaryngol. 8, 241–257. 10.1007/s10162-007-0077-8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleich, P., Nopp, P., and D’Haese, P. (2004). “Head shadow, squelch, and summation effects in bilateral users of the MED-EL COMBI 40/40+ cochlear implant,” Ear Hear. 25, 197–204. 10.1097/01.AUD.0000130792.43315.97 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shannon, R. V. (1983). “Multichannel electrical stimulation of the auditory nerve in man. II. Channel interaction,” Hear. Res. 12, 1–16. 10.1016/0378-5955(83)90115-6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd, R. K., Baxi, J. H., and Hardie, N. A. (1999). “Response of inferior colliculus neurons to electrical stimulation of the auditory nerve in neonatally deafened cats,” J. Neurophysiol. 82, 1363–1380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staffel, J. G., Hall, J. W. III, Grose, J. H., and Pillsbury, H. C. (1990). “NoSo and NoS pi detection as a function of masker bandwidth in normal-hearing and cochlear-impaired listeners,” J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 87, 1720–1727. 10.1121/1.399420 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stickney, G. S., Loizou, P. C., Mishra, L. N., Assmann, P. F., Shannon, R. V., and Opie, J. M. (2006). “Effects of electrode design and configuration on channel interactions,” Hear. Res. 211, 33–45. 10.1016/j.heares.2005.08.008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tillein, J., Hubka, P., Syed, E., Hartmann, R., Engel, A. K., and Kral, A. (2009). “Cortical representation of interaural time difference in congenital deafness,” Cereb. Cortex 20, 492–506. 10.1093/cercor/bhp222 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tong, Y. C., and Clark, G. M. (1986). “Loudness summation, masking, and temporal interaction for sensations produced by electric stimulation of two sites in the human cochlea,” J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 79, 1958–1966. 10.1121/1.393203 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyler, R. S., Witt S. A., Dunn, C. C., Perreau, A., Parkinson, A. J., and Wilson, B. S. (2010). “An attempt to improve bilateral cochlear implants by increasing the distance between electrodes and providing complementary information to the two ears,” J. Am. Acad. Audiol. 21, 52–65. 10.3766/jaaa.21.1.7 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Par, S., and Kohlrausch, A. (1997). “A new approach to comparing binaural masking level differences at low and high frequencies,” J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 101, 1671–1680. 10.1121/1.418151 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Par, S., and Kohlrausch, A. (1999). “Dependence of binaural masking level differences on center frequency, masker bandwidth, and interaural parameters,” J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 106, 1940–1947. 10.1121/1.427942 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Deun, L., van Wieringen, A., Francart, T., Scherf, F., Dhooge, I. J., Deggouj, N., Desloovere, C., Van de Heyning, P. H., Offeciers, F. E., De Raeve, L., and Wouters, J. (2009). “Bilateral cochlear implants in children: Binaural unmasking,” Audiol. Neuro-Otol. 14, 240–247. 10.1159/000190402 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Hoesel, R., Bohm, M., Pesch, J., Vandali, A., Battmer, R. D., and Lenarz, T. (2008). “Binaural speech unmasking and localization in noise with bilateral cochlear implants using envelope and fine-timing based strategies,” J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 123, 2249–2263. 10.1121/1.2875229 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Hoesel, R. J. (2007). “Sensitivity to binaural timing in bilateral cochlear implant users,” J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 121, 2192–2206. 10.1121/1.2537300 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Hoesel, R. J. (2008). “Observer weighting of level and timing cues in bilateral cochlear implant users,” J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 124, 3861–3872. 10.1121/1.2998974 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Hoesel, R. J., and Clark, G. M. (1997). “Psychophysical studies with two binaural cochlear implant subjects,” J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 102, 495–507. 10.1121/1.419611 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Hoesel, R. J., Jones, G. L., and Litovsky, R. Y. (2009). “Interaural time-delay sensitivity in bilateral cochlear implant users: Effects of pulse rate, modulation rate, and place of stimulation,” J. Assoc. Res. Otolaryngol. 10, 557–567. 10.1007/s10162-009-0175-x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Hoesel, R. J., Tong, Y. C., Hollow, R. D., and Clark, G. M. (1993). “Psychophysical and speech perception studies: A case report on a binaural cochlear implant subject,” J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 94, 3178–3189. 10.1121/1.407223 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Hoesel, R. J., and Tyler, R. S. (2003). “Speech perception, localization, and lateralization with bilateral cochlear implants,” J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 113, 1617–1630. 10.1121/1.1539520 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vollmer, M. Beitel, R. E., Snyder, R. L., and Leake, P. A. (2007). “Spatial selectivity to intracochlear electrical stimulation in the inferior colliculus is degraded after long-term deafness in cats,” J. Neurophysiol. 98, 2588–2603. 10.1152/jn.00011.2007 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, B. S., Finley, C. C., Lawson, D. T., Wolford, R. D., Eddington, D. K., and Rabinowitz, W. M. (1991). “Better speech recognition with cochlear implants,” Nature (London) 352, 236–238. 10.1038/352236a0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zurek, P. M., and Durlach, N. I. (1987). “Masker-bandwidth dependence in homophasic and antiphasic tone detection,” J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 81, 459–464. 10.1121/1.394911 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]