Abstract
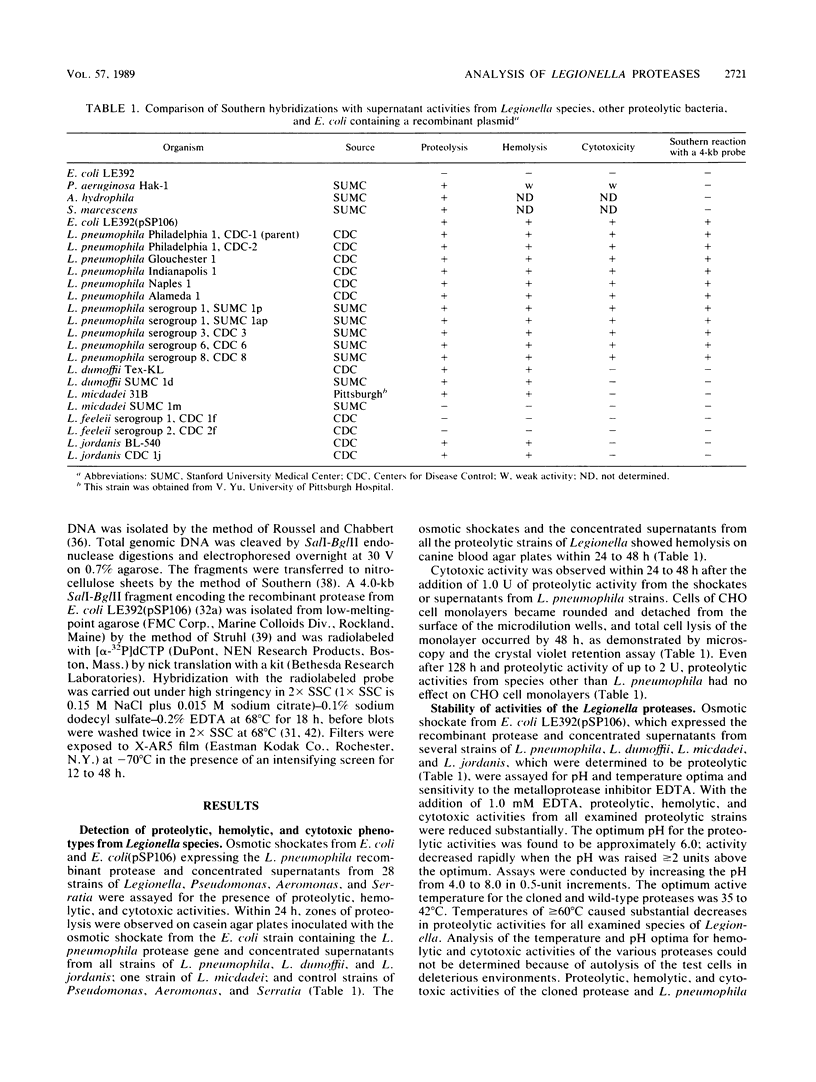
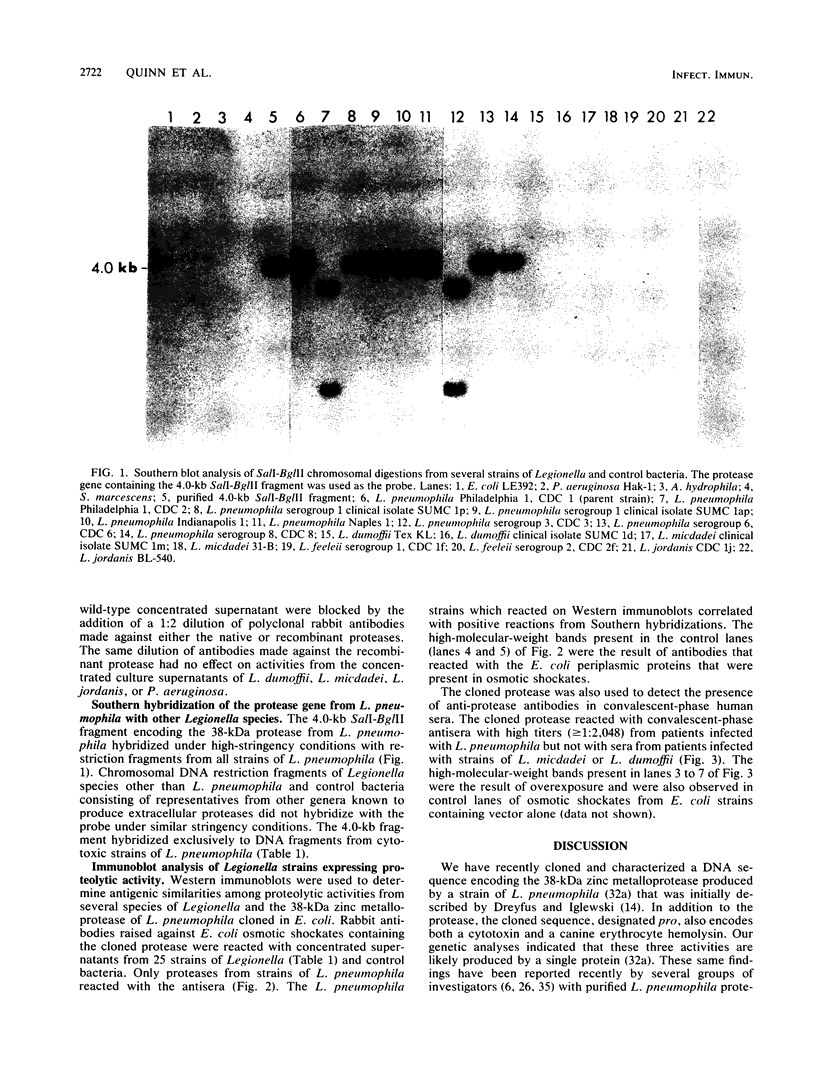
Several strains of Legionella pneumophila and other species of Legionella with proteolytic activities were compared by assays, including Southern hybridizations and Western immunoblots, to determine their proteolytic, hemolytic, and cytotoxic activities. Only proteases from strains of L. pneumophila were both hemolytic and cytotoxic, and proteolytic activities extracted from other species of Legionella possessed only hemolytic activity. A 4.0-kilobase DNA sequence encoding the 38-kilodalton metalloprotease from L. pneumophila Philadelphia 1 that we showed previously was responsible for the observed hemolytic and cytotoxic phenotypes (F. D. Quinn and L. S. Tompkins, Mol. Microbiol., 3:797-805, 1989) was used in Southern hybridizations to probe chromosomal DNA from several strains of L. pneumophila and other Legionella species. The probe hybridized to the chromosomal DNA of all serogroups of L. pneumophila but not to any strains of L. dumoffii, L. micdadei, L. feeleii, or L. jordanis that we examined. Additionally, Western immunoblots done with rabbit antisera made to the cloned L. pneumophila protease demonstrated cross-reactions among 38-kilodalton proteins from strains of L. pneumophila, but no reactions were observed with proteins from other species of Legionella. Similarly, the cloned protease from L. pneumophila reacted with convalescent-phase sera from patients infected with L. pneumophila, but not with antisera isolated from patients infected with other Legionella species. Thus, despite some similarities among the proteolytic activities of members of the genus Legionella, including proteolytic and hemolytic phenotypes, metal requirements for zinc or iron, sensitivity to EDTA, and temperature and pH optima, we documented distinct genetic, immunological, and cytotoxicity differences among the proteolytic activities produced by Legionella species.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnow P. M., Chou T., Weil D., Shapiro E. N., Kretzschmar C. Nosocomial Legionnaires' disease caused by aerosolized tap water from respiratory devices. J Infect Dis. 1982 Oct;146(4):460–467. doi: 10.1093/infdis/146.4.460. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baine W. B. Cytolytic and phospholipase C activity in Legionella species. J Gen Microbiol. 1985 Jun;131(6):1383–1391. doi: 10.1099/00221287-131-6-1383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barer M. R., Millership S. E., Tabaqchali S. Relationship of toxin production to species in the genus Aeromonas. J Med Microbiol. 1986 Dec;22(4):303–309. doi: 10.1099/00222615-22-4-303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baskerville A., Conlan J. W., Ashworth L. A., Dowsett A. B. Pulmonary damage caused by a protease from Legionella pneumophila. Br J Exp Pathol. 1986 Aug;67(4):527–536. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berdal B. P., Fossum K. Occurrence and immunogenicity of proteinases from Legionella species. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Feb;1(1):7–11. doi: 10.1007/BF02014133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berdal B. P., Hushovd O., Olsvik O., odegård O. R., Bergan T. Demonstration of extracellular proteolytic enzymes from Legionella species strains by using synthetic chromogenic peptide substrates. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand B. 1982 Apr;90(2):119–123. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1982.tb00092.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackmon J. A., Chandler F. W., Cherry W. B., England A. C., 3rd, Feeley J. C., Hicklin M. D., McKinney R. M., Wilkinson H. W. Legionellosis. Am J Pathol. 1981 Jun;103(3):429–465. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blander S. J., Horwitz M. A. Vaccination with the major secretory protein of Legionella pneumophila induces cell-mediated and protective immunity in a guinea pig model of Legionnaires' disease. J Exp Med. 1989 Mar 1;169(3):691–705. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.3.691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bornstein N., Nowicki M., Fleurette J. Haemolytic activity in the genus Legionella. Ann Inst Pasteur Microbiol. 1988 May-Jun;139(3):325–329. doi: 10.1016/0769-2609(88)90024-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conlan J. W., Baskerville A., Ashworth L. A. Separation of Legionella pneumophila proteases and purification of a protease which produces lesions like those of Legionnaires' disease in guinea pig lung. J Gen Microbiol. 1986 Jun;132(6):1565–1574. doi: 10.1099/00221287-132-6-1565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyfus L. A., Iglewski B. H. Purification and characterization of an extracellular protease of Legionella pneumophila. Infect Immun. 1986 Mar;51(3):736–743. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.3.736-743.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- England A. C., 3rd, Fraser D. W., Plikaytis B. D., Tsai T. F., Storch G., Broome C. V. Sporadic legionellosis in the United States: the first thousand cases. Ann Intern Med. 1981 Feb;94(2):164–170. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-94-2-164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- England A. C., 3rd, Fraser D. W. Sporadic and epidemic nosocomial legionellosis in the United States. Epidemiologic features. Am J Med. 1981 Mar;70(3):707–711. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(81)90601-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser D. W. Potable water as a source for legionellosis. Environ Health Perspect. 1985 Oct;62:337–341. doi: 10.1289/ehp.8562337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman R. L., Iglewski B. H., Miller R. D. Identification of a cytotoxin produced by Legionella pneumophila. Infect Immun. 1980 Jul;29(1):271–274. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.1.271-274.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frisch C. F., Baine W. B. Production of extracellular hemolytic cytotoxin by Legionella bozemanii. Microbiol Immunol. 1984;28(11):1267–1272. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1984.tb00784.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentry M. K., Dalrymple J. M. Quantitative microtiter cytotoxicity assay for Shigella toxin. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Sep;12(3):361–366. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.3.361-366.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg D. J., Wrench J. G., Collier P. W., Emslie J. A., Fallon R. J., Forbes G. I., McKay T. M., Macpherson A. C., Markwick T. A., Reid D. Lochgoilhead fever: outbreak of non-pneumonic legionellosis due to Legionella micdadei. Lancet. 1989 Feb 11;1(8633):316–318. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)91319-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray L. D., Kreger A. S. Purification and characterization of an extracellular cytolysin produced by Vibrio vulnificus. Infect Immun. 1985 Apr;48(1):62–72. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.1.62-72.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gul'nik S. V., Yusupova M. P., Lavrenova G. I., Tartakovsky I. S., Prozorovsky S. V., Stepanov V. M. Proteinases of Legionella: phenylalanineaminopeptidase of L. pneumophila. J Gen Microbiol. 1986 Feb;132(2):387–392. doi: 10.1099/00221287-132-2-387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herwaldt L. A., Gorman G. W., McGrath T., Toma S., Brake B., Hightower A. W., Jones J., Reingold A. L., Boxer P. A., Tang P. W. A new Legionella species, Legionella feeleii species nova, causes Pontiac fever in an automobile plant. Ann Intern Med. 1984 Mar;100(3):333–338. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-100-3-333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homma J. Y., Abe C., Tanamoto K., Hirao Y., Morihara K., Tsuzuki H., Yanagawa R., Honda E., Aoi Y., Fujimoto Y. Effectiveness of immunization with single and multi-component vaccines prepared from a common antigen (OEP), protease and elastase toxoids of Pseudomonas aeruginosa on protection against hemorrhagic pneumonia in mink due to P. aeruginosa. Jpn J Exp Med. 1978 Apr;48(2):111–133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keen M. G., Hoffman P. S. Characterization of a Legionella pneumophila extracellular protease exhibiting hemolytic and cytotoxic activities. Infect Immun. 1989 Mar;57(3):732–738. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.3.732-738.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyerly D. M., Kreger A. S. Importance of serratia protease in the pathogenesis of experimental Serratia marcescens pneumonia. Infect Immun. 1983 Apr;40(1):113–119. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.1.113-119.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda H., Molla A., Oda T., Katsuki T. Internalization of serratial protease into cells as an enzyme-inhibitor complex with alpha 2-macroglobulin and regeneration of protease activity and cytotoxicity. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 15;262(23):10946–10950. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangione E. J., Remis R. S., Tait K. A., McGee H. B., Gorman G. W., Wentworth B. B., Baron P. A., Hightower A. W., Barbaree J. M., Broome C. V. An outbreak of Pontiac fever related to whirlpool use, Michigan 1982. JAMA. 1985 Jan 25;253(4):535–539. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver J. D., Wear J. E., Thomas M. B., Warner M., Linder K. Production of extracellular enzymes and cytotoxicity by Vibrio vulnificus. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1986 Jul;5(2):99–111. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(86)90112-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn F. D., Tompkins L. S. Analysis of a cloned sequence of Legionella pneumophila encoding a 38 kD metalloprotease possessing haemolytic and cytotoxic activities. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Jun;3(6):797–805. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00228.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reingold A. L., Thomason B. M., Brake B. J., Thacker L., Wilkinson H. W., Kuritsky J. N. Legionella pneumonia in the United States: the distribution of serogroups and species causing human illness. J Infect Dis. 1984 May;149(5):819–819. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.5.819. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roussel A. F., Chabbert Y. A. Taxonomy and epidemiology of gram-negative bacterial plasmids studied by DNA-DNA filter hybridization in formamide. J Gen Microbiol. 1978 Feb;104(2):269–276. doi: 10.1099/00221287-104-2-269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solymossy M., Nagy Z., Antoni F. Cytotoxic material released from Staphylococcus epidermidis. I. Effects on [3H]thymidine incorporation of human lymphocytes. Acta Microbiol Acad Sci Hung. 1982;29(1):27–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K. Direct selection for gene replacement events in yeast. Gene. 1983 Dec;26(2-3):231–241. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90193-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tartakovskii I. S., Belyi Iu F., Vertiev Iu V., Nagaev I. G., Prozorovskii S. V. Tsitolizin kak immunoserologicheskii marker Legionella pneumophila. Zh Mikrobiol Epidemiol Immunobiol. 1988 May;(5):58–61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tompkins L. S., Roessler B. J., Redd S. C., Markowitz L. E., Cohen M. L. Legionella prosthetic-valve endocarditis. N Engl J Med. 1988 Mar 3;318(9):530–535. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198803033180902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tompkins L. S., Troup N., Labigne-Roussel A., Cohen M. L. Cloned, random chromosomal sequences as probes to identify Salmonella species. J Infect Dis. 1986 Jul;154(1):156–162. doi: 10.1093/infdis/154.1.156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vesey G., Dennis P. J., Lee J. V., West A. A. Further development of simple tests to differentiate the legionellas. J Appl Bacteriol. 1988 Oct;65(4):339–345. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1988.tb01900.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams A., Baskerville A., Dowsett A. B., Conlan J. W. Immunocytochemical demonstration of the association between Legionella pneumophila, its tissue-destructive protease, and pulmonary lesions in experimental legionnaires' disease. J Pathol. 1987 Nov;153(3):257–264. doi: 10.1002/path.1711530310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winn W. C., Jr, Glavin F. L., Perl D. P., Keller J. L., Andres T. L., Brown T. M., Coffin C. M., Sensecqua J. E., Roman L. N., Craighead J. E. The pathology of Legionnaires' disease. Fourteen fatal cases from the 1977 outbreak in Vermont. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1978 Jul;102(7):344–350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]