Abstract
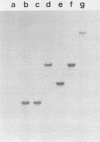
One hundred fifty Tn5 IS50L::phoA (TnphoA) mutants of a mouse-virulent, nalidixic acid-resistant (Nalr), prototrophic Salmonella typhimurium strain, C5 Nalr, were isolated. None of the mutants were auxotrophs. Groups of 8 to 10 BALB/c mice were infected orally with each of 95 mutants with a dose equivalent to 20-fold the 50% lethal dose of the wild-type C5 Nalr strain, and deaths were counted over the next 28 days. Fifteen of the mutants failed to kill any mice, whereas all mice died following challenge with the other mutants. Nine of the 15 attenuated mutants exhibited a defect in lipopolysaccharide biosynthesis. The remaining six mutants were smooth. The TnphoA transposon of each of the smooth attenuated mutants was moved, using P22-mediated transduction, into a fresh C5 background, and all retransductants were still attenuated. Analysis of the membrane proteins of the attenuated mutants failed to reveal any alterations in detectable major outer membrane proteins, although colonies of two of the mutants exhibited a mucoid phenotype following growth on L-agar plates. Individual attenuated mutants differed in their abilities to translocate to livers and spleens of mice following oral infection. All of the smooth TnphoA mutants exhibited increased 50% lethal doses with respect to the wild type following intravenous infection of BALB/c mice. Southern analysis of DNA prepared from each of the mutants suggested that TnphoA had inserted into a number of different sites in the S. typhimurium genome. None of the TnphoA mutants had inserts in the virulence-associated plasmid.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baird G. D., Manning E. J., Jones P. W. Evidence for related virulence sequences in plasmids of Salmonella dublin and Salmonella typhimurium. J Gen Microbiol. 1985 Jul;131(7):1815–1823. doi: 10.1099/00221287-131-7-1815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benjamin W. H., Jr, Turnbough C. L., Jr, Goguen J. D., Posey B. S., Briles D. E. Genetic mapping of novel virulence determinants of Salmonella typhimurium to the region between trpD and supD. Microb Pathog. 1986 Apr;1(2):115–124. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(86)90014-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements J. D., El-Morshidy S. Construction of a potential live oral bivalent vaccine for typhoid fever and cholera-Escherichia coli-related diarrheas. Infect Immun. 1984 Nov;46(2):564–569. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.2.564-569.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M. Vaccines and cell-mediated immunity. Bacteriol Rev. 1974 Dec;38(4):371–402. doi: 10.1128/br.38.4.371-402.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtiss R., 3rd, Kelly S. M. Salmonella typhimurium deletion mutants lacking adenylate cyclase and cyclic AMP receptor protein are avirulent and immunogenic. Infect Immun. 1987 Dec;55(12):3035–3043. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.12.3035-3043.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dougan G., Dowd G., Kehoe M. Organization of K88ac-encoded polypeptides in the Escherichia coli cell envelope: use of minicells and outer membrane protein mutants for studying assembly of pili. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):364–370. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.364-370.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dougan G., Sherratt D. The transposon Tn1 as a probe for studying ColE1 structure and function. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Mar 7;151(2):151–160. doi: 10.1007/BF00338689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duguid J. P., Darekar M. R., Wheater D. W. Fimbriae and infectivity in Salmonella typhimurium. J Med Microbiol. 1976 Nov;9(4):459–473. doi: 10.1099/00222615-9-4-459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields P. I., Swanson R. V., Haidaris C. G., Heffron F. Mutants of Salmonella typhimurium that cannot survive within the macrophage are avirulent. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5189–5193. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay B. B., Gumbiner B., Falkow S. Penetration of Salmonella through a polarized Madin-Darby canine kidney epithelial cell monolayer. J Cell Biol. 1988 Jul;107(1):221–230. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.1.221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay B. B., Starnbach M. N., Francis C. L., Stocker B. A., Chatfield S., Dougan G., Falkow S. Identification and characterization of TnphoA mutants of Salmonella that are unable to pass through a polarized MDCK epithelial cell monolayer. Mol Microbiol. 1988 Nov;2(6):757–766. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1988.tb00087.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germanier R., Füer E. Isolation and characterization of Gal E mutant Ty 21a of Salmonella typhi: a candidate strain for a live, oral typhoid vaccine. J Infect Dis. 1975 May;131(5):553–558. doi: 10.1093/infdis/131.5.553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giannella R. A., Washington O., Gemski P., Formal S. B. Invasion of HeLa cells by Salmonella typhimurium: a model for study of invasiveness of Salmonella. J Infect Dis. 1973 Jul;128(1):69–75. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.1.69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gulig P. A., Curtiss R., 3rd Plasmid-associated virulence of Salmonella typhimurium. Infect Immun. 1987 Dec;55(12):2891–2901. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.12.2891-2901.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackett J., Kotlarski I., Mathan V., Francki K., Rowley D. The colonization of Peyer's patches by a strain of Salmonella typhimurium cured of the cryptic plasmid. J Infect Dis. 1986 Jun;153(6):1119–1125. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.6.1119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrington K. A., Hormaeche C. E. Expression of the innate resistance gene Ity in mouse Kupffer cells infected with Salmonella typhimurium in vitro. Microb Pathog. 1986 Jun;1(3):269–274. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(86)90051-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heffernan E. J., Fierer J., Chikami G., Guiney D. Natural history of oral Salmonella dublin infection in BALB/c mice: effect of an 80-kilobase-pair plasmid on virulence. J Infect Dis. 1987 Jun;155(6):1254–1259. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.6.1254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrington D. A., Hall R. H., Losonsky G., Mekalanos J. J., Taylor R. K., Levine M. M. Toxin, toxin-coregulated pili, and the toxR regulon are essential for Vibrio cholerae pathogenesis in humans. J Exp Med. 1988 Oct 1;168(4):1487–1492. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.4.1487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoiseth S. K., Stocker B. A. Aromatic-dependent Salmonella typhimurium are non-virulent and effective as live vaccines. Nature. 1981 May 21;291(5812):238–239. doi: 10.1038/291238a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hormaeche C. E. Natural resistance to Salmonella typhimurium in different inbred mouse strains. Immunology. 1979 Jun;37(2):311–318. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones G. W., Rabert D. K., Svinarich D. M., Whitfield H. J. Association of adhesive, invasive, and virulent phenotypes of Salmonella typhimurium with autonomous 60-megadalton plasmids. Infect Immun. 1982 Nov;38(2):476–486. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.2.476-486.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kehoe M., Sellwood R., Shipley P., Dougan G. Genetic analysis of K88-mediated adhesion of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Nature. 1981 May 14;291(5811):122–126. doi: 10.1038/291122a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Killar L. M., Eisenstein T. K. Immunity to Salmonella typhimurium infection in C3H/HeJ and C3H/HeNCrlBR mice: studies with an aromatic-dependent live S. typhimurium strain as a vaccine. Infect Immun. 1985 Mar;47(3):605–612. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.3.605-612.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manoil C., Beckwith J. TnphoA: a transposon probe for protein export signals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):8129–8133. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.8129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maskell D. J., Sweeney K. J., O'Callaghan D., Hormaeche C. E., Liew F. Y., Dougan G. Salmonella typhimurium aroA mutants as carriers of the Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin B subunit to the murine secretory and systemic immune systems. Microb Pathog. 1987 Mar;2(3):211–221. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(87)90022-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrissey P. M., Dougan G. Expression of a cloned 987P adhesion-antigen fimbrial determinant in Escherichia coli K-12 strain HB101. Gene. 1986;43(1-2):79–84. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90010-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien A. D., Metcalf E. S. Control of early Salmonella typhimurium growth in innately Salmonella-resistant mice does not require functional T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1982 Oct;129(4):1349–1351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Callaghan D., Maskell D., Liew F. Y., Easmon C. S., Dougan G. Characterization of aromatic- and purine-dependent Salmonella typhimurium: attention, persistence, and ability to induce protective immunity in BALB/c mice. Infect Immun. 1988 Feb;56(2):419–423. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.2.419-423.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plant J., Glynn A. A. Genetics of resistance to infection with Salmonella typhimurium in mice. J Infect Dis. 1976 Jan;133(1):72–78. doi: 10.1093/infdis/133.1.72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roantree R. J. Salmonella O antigens and virulence. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1967;21:443–466. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.21.100167.002303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmieger H. Phage P22-mutants with increased or decreased transduction abilities. Mol Gen Genet. 1972;119(1):75–88. doi: 10.1007/BF00270447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson R. N., O'Brien A. D. Genetic control of the innate resistance of mice to Salmonella typhimurium: Ity gene is expressed in vivo by 24 hours after infection. J Immunol. 1983 Dec;131(6):3014–3020. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tannock G. W., Blumershine R. V., Savage D. C. Association of Salmonella typhimurium with, and its invasion of, the ileal mucosa in mice. Infect Immun. 1975 Feb;11(2):365–370. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.2.365-370.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor R. K., Miller V. L., Furlong D. B., Mekalanos J. J. Use of phoA gene fusions to identify a pilus colonization factor coordinately regulated with cholera toxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):2833–2837. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.2833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tite J. P., Russell S. M., Dougan G., O'Callaghan D., Jones I., Brownlee G., Liew F. Y. Antiviral immunity induced by recombinant nucleoprotein of influenza A virus. I. Characteristics and cross-reactivity of T cell responses. J Immunol. 1988 Dec 1;141(11):3980–3987. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. M., Frasch C. E. A sensitive silver stain for detecting lipopolysaccharides in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 1;119(1):115–119. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90673-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A. A., Hewlett E. L., Myers G. A., Falkow S. Tn5-induced mutations affecting virulence factors of Bordetella pertussis. Infect Immun. 1983 Oct;42(1):33–41. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.1.33-41.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson C. M., Baird G. D., Manning E. J. A common virulence region on plasmids from eleven serotypes of Salmonella. J Gen Microbiol. 1988 Apr;134(4):975–982. doi: 10.1099/00221287-134-4-975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yancey R. J., Breeding S. A., Lankford C. E. Enterochelin (enterobactin): virulence factor for Salmonella typhimurium. Infect Immun. 1979 Apr;24(1):174–180. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.1.174-180.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]