Abstract
Leprosy is a spectral disease in which clinical presentation is thought to be related to the host immune response. Previous investigations have suggested that selective unresponsiveness to Mycobacterium leprae in patients with lepromatous leprosy is due to the presence of M. leprae-specific T-suppressor cells. However, it has recently been suggested that CD2 modulation was the mechanism for the observed impaired immune response in lepromatous patients. Therefore, we studied the expression of CD2 and CD3 on lymphocytes in lepromatous skin lesions and peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC). Using immunohistochemical techniques, we found that virtually all of the CD3+ cells in leprosy skin lesions expressed CD2. In addition, indirect immunofluorescence flow cytometry demonstrated that most CD3+ cells in the peripheral blood possessed the CD2 marker, suggesting that CD2 expression of T-lymphocytes is normal. T-cell activation using paired anti-T11(2) and anti-T11(3) or anti-CD3 monoclonal antibodies demonstrated similar 3H-thymidine incorporation and gamma interferon production in the PBMC of lepromatous patients in comparison with the PBMC of their contacts and tuberculoid patients. However, lepromatous PBMC did not proliferate or produce gamma interferon in response to M. leprae. Our data suggest not only that CD2 expression is normal on T lymphocytes in lepromatous leprosy skin lesions but also that CD2 expression in peripheral blood lymphocytes is functional in T-cell activation. Defective CD2 modulation does not appear to be the mechanism for specific unresponsiveness in lepromatous leprosy.
Full text
PDF

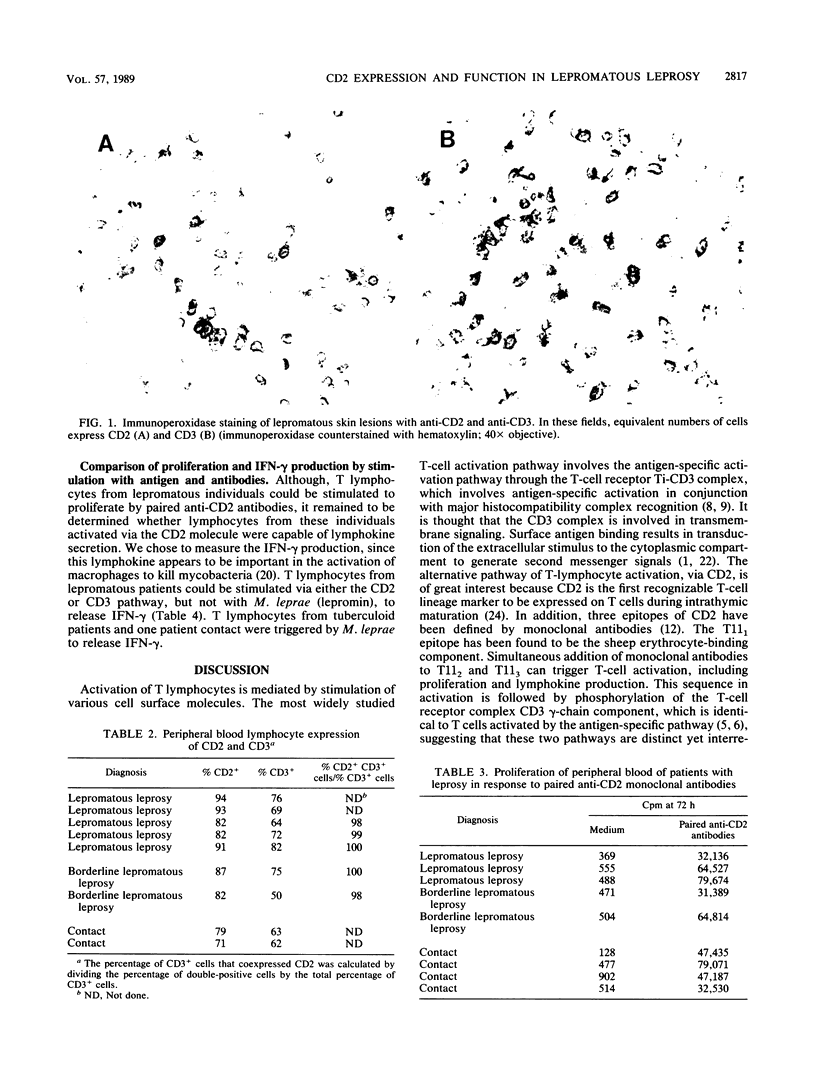

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alcover A., Ramarli D., Richardson N. E., Chang H. C., Reinherz E. L. Functional and molecular aspects of human T lymphocyte activation via T3-Ti and T11 pathways. Immunol Rev. 1987 Feb;95:5–36. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1987.tb00498.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bierer B. E., Peterson A., Barbosa J., Seed B., Burakoff S. J. Expression of the T-cell surface molecule CD2 and an epitope-loss CD2 mutant to define the role of lymphocyte function-associated antigen 3 (LFA-3) in T-cell activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(4):1194–1198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.4.1194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom B. R. In vitro approaches to the mechanism of cell-mediated immune reactions. Adv Immunol. 1971;13:101–208. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60184-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom B. R., Mehra V. Immunological unresponsiveness in leprosy. Immunol Rev. 1984 Aug;80:5–28. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1984.tb00493.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breitmeyer J. B., Daley J. F., Levine H. B., Schlossman S. F. The T11 (CD2) molecule is functionally linked to the T3/Ti T cell receptor in the majority of T cells. J Immunol. 1987 Nov 1;139(9):2899–2905. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantrell D., Davies A. A., Londei M., Feldman M., Crumpton M. J. Association of phosphorylation of the T3 antigen with immune activation of T lymphocytes. Nature. 1987 Feb 5;325(6104):540–542. doi: 10.1038/325540a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox D. A., Schlossman S. F., Reinherz E. L. Regulation of the alternative pathway of T cell activation by anti-T3 monoclonal antibody. J Immunol. 1986 Mar 15;136(6):1945–1950. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansburg D., Heber-Katz E., Fairwell T., Appella E. Major histocompatibility complex-controlled, antigen-presenting cell-expressed specificity of T cell antigen recognition. Identification of a site of interaction and its relationship to Ir genes. J Exp Med. 1983 Jul 1;158(1):25–39. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.1.25. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heber-Katz E., Schwartz R. H., Matis L. A., Hannum C., Fairwell T., Appella E., Hansburg D. Contribution of antigen-presenting cell major histocompatibility complex gene products to the specificity of antigen-induced T cell activation. J Exp Med. 1982 Apr 1;155(4):1086–1099. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.4.1086. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krensky A. M., Sanchez-Madrid F., Robbins E., Nagy J. A., Springer T. A., Burakoff S. J. The functional significance, distribution, and structure of LFA-1, LFA-2, and LFA-3: cell surface antigens associated with CTL-target interactions. J Immunol. 1983 Aug;131(2):611–616. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehra V., Mason L. H., Fields J. P., Bloom B. R. Lepromin-induced suppressor cells in patients with leprosy. J Immunol. 1979 Oct;123(4):1813–1817. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meuer S. C., Hussey R. E., Fabbi M., Fox D., Acuto O., Fitzgerald K. A., Hodgdon J. C., Protentis J. P., Schlossman S. F., Reinherz E. L. An alternative pathway of T-cell activation: a functional role for the 50 kd T11 sheep erythrocyte receptor protein. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):897–906. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90039-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modlin R. L., Brenner M. B., Krangel M. S., Duby A. D., Bloom B. R. T-cell receptors of human suppressor cells. Nature. 1987 Oct 8;329(6139):541–545. doi: 10.1038/329541a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modlin R. L., Hofman F. M., Horwitz D. A., Husmann L. A., Gillis S., Taylor C. R., Rea T. H. In situ identification of cells in human leprosy granulomas with monoclonal antibodies to interleukin 2 and its receptor. J Immunol. 1984 Jun;132(6):3085–3090. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modlin R. L., Kato H., Mehra V., Nelson E. E., Fan X. D., Rea T. H., Pattengale P. K., Bloom B. R. Genetically restricted suppressor T-cell clones derived from lepromatous leprosy lesions. 1986 Jul 31-Aug 6Nature. 322(6078):459–461. doi: 10.1038/322459a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modlin R. L., Mehra V., Wong L., Fujimiya Y., Chang W. C., Horwitz D. A., Bloom B. R., Rea T. H., Pattengale P. K. Suppressor T lymphocytes from lepromatous leprosy skin lesions. J Immunol. 1986 Nov 1;137(9):2831–2834. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muthukkaruppan V., Chakkalath H. R., James M. M. Immunologic unresponsiveness in leprosy is mediated by modulation of E-receptor. Immunol Lett. 1987 Jul;15(3):199–204. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(87)90025-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muthukkaruppan V., Chakkalath H. R., Malarkannan S. The classical and alternate pathways of T cell activation are impaired in leprosy. Immunol Lett. 1988 Sep;19(1):55–58. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(88)90119-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narayanan R. B., Girdhar B. K., Desikan K. V. OKT6+ epidermal Langerhans' cell numbers in DNCB reactions among leprosy patients. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1986 Sep;54(3):423–426. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F., Kaplan G., Levis W. R., Nusrat A., Witmer M. D., Sherwin S. A., Job C. K., Horowitz C. R., Steinman R. M., Cohn Z. A. Local and systemic effects of intradermal recombinant interferon-gamma in patients with lepromatous leprosy. N Engl J Med. 1986 Jul 3;315(1):6–15. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198607033150102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson E. E., Wong L., Uyemura K., Rea T. H., Modlin R. L. Lepromin-induced suppressor cells in lepromatous leprosy. Cell Immunol. 1987 Jan;104(1):99–104. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(87)90010-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oettgen H. C., Terhorst C. The T-cell receptor-T3 complex and T-lymphocyte activation. Hum Immunol. 1987 Mar;18(3):187–204. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(87)90084-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ottenhoff T. H., Elferink D. G., Klatser P. R., de Vries R. R. Cloned suppressor T cells from a lepromatous leprosy patient suppress Mycobacterium leprae reactive helper T cells. 1986 Jul 31-Aug 6Nature. 322(6078):462–464. doi: 10.1038/322462a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinherz E. L., Kung P. C., Goldstein G., Levey R. H., Schlossman S. F. Discrete stages of human intrathymic differentiation: analysis of normal thymocytes and leukemic lymphoblasts of T-cell lineage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1588–1592. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridley D. S. Histological classification and the immunological spectrum of leprosy. Bull World Health Organ. 1974;51(5):451–465. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridley D. S., Jopling W. H. Classification of leprosy according to immunity. A five-group system. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1966 Jul-Sep;34(3):255–273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selvaraj P., Plunkett M. L., Dustin M., Sanders M. E., Shaw S., Springer T. A. The T lymphocyte glycoprotein CD2 binds the cell surface ligand LFA-3. 1987 Mar 26-Apr 1Nature. 326(6111):400–403. doi: 10.1038/326400a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takai Y., Reed M. L., Burakoff S. J., Herrmann S. H. Direct evidence for a receptor-ligand interaction between the T-cell surface antigen CD2 and lymphocyte-function-associated antigen 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(19):6864–6868. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.19.6864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



