Abstract
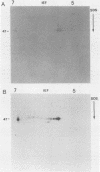
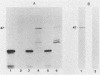
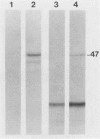
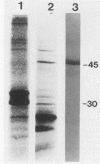
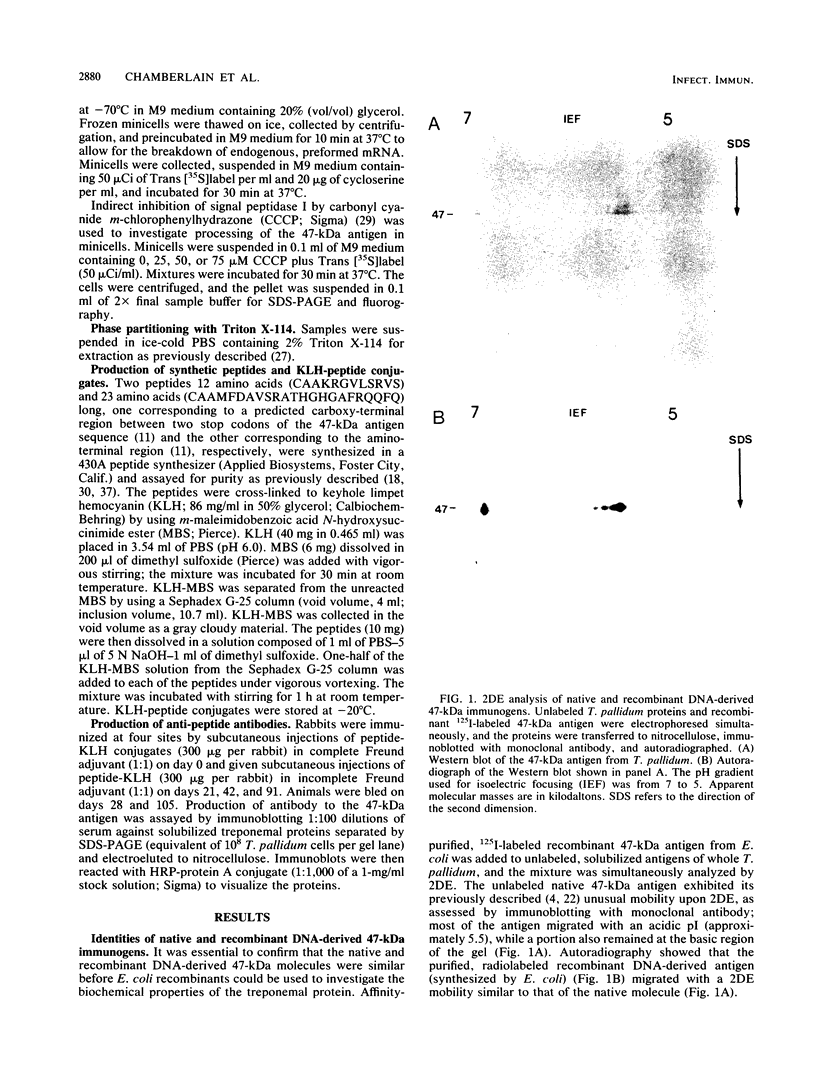
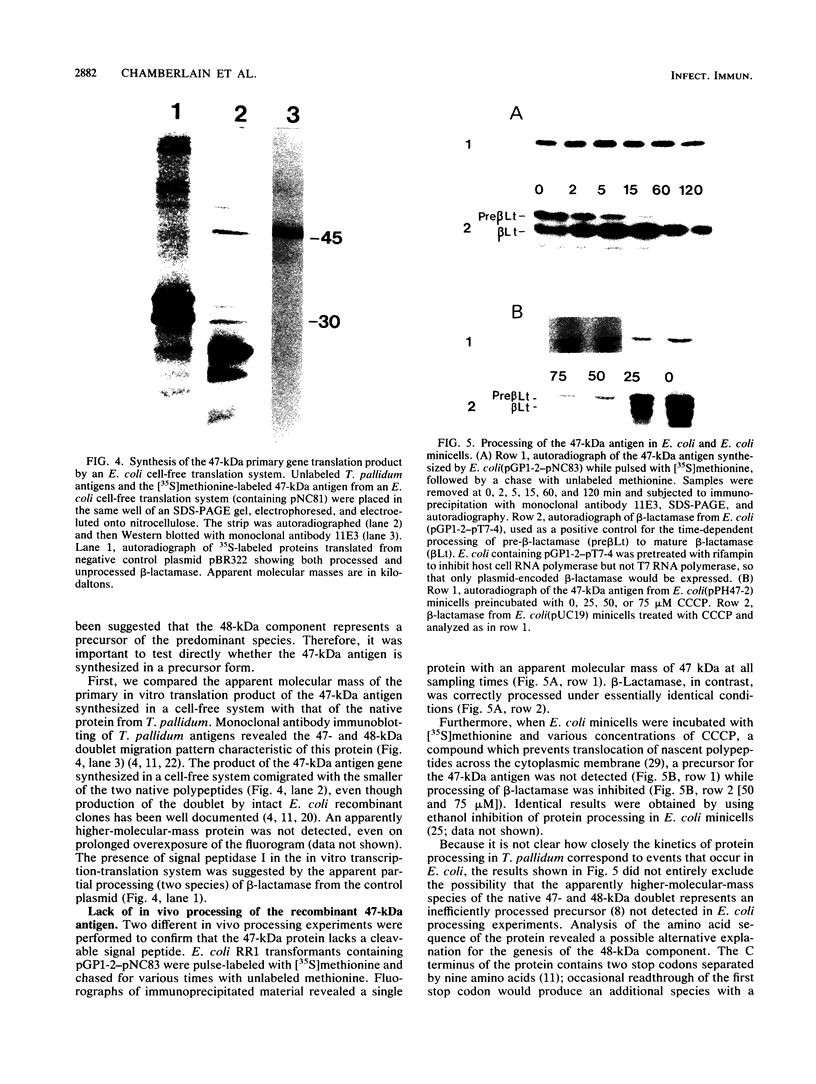
The 47-kilodalton (kDa) major integral membrane immunogen of Treponema pallidum was recently found to be a proteolipid. Similar two-dimensional electrophoretic mobilities and common hydrophobic properties displayed by the native (T. pallidum) and recombinant (Escherichia coli) 47-kDa antigens suggested that the recombinant antigen also possesses covalently bound lipid. Both intact E. coli and E. coli minicells acylated the 47-kDa antigen; immunoprecipitation with a monoclonal antibody specific for the 47-kDa immunogen supported the contention that the acylated product of E. coli corresponds to the cloned T. pallidum antigen. Triton X-114 phase partitioning was used to compare the relative hydrophobicities of 47-kDa molecules synthesized by in vitro and in vivo protein translation systems. The products synthesized by T. pallidum, intact E. coli, or E. coli minicells were hydrophobic, while the protein synthesized in an E. coli cell-free translation system was hydrophilic. Processing experiments with E. coli suggested that the primary gene translation product of the protein is not synthesized in a precursor form, unlike other bacterial proteolipids. These results indicate that the hydrophobicity of the 47-kDa integral membrane protein is conferred substantially by the covalently attached lipid(s). The biochemical similarities between the native and recombinant 47-kDa proteolipids will provide a foundation for future investigations into the structure and immunogenicity of this integral membrane protein of T. pallidum.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler H. I., Fisher W. D., Cohen A., Hardigree A. A. MINIATURE escherichia coli CELLS DEFICIENT IN DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Feb;57(2):321–326. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.2.321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlain J. P. Fluorographic detection of radioactivity in polyacrylamide gels with the water-soluble fluor, sodium salicylate. Anal Biochem. 1979 Sep 15;98(1):132–135. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90716-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlain N. R., Brandt M. E., Erwin A. L., Radolf J. D., Norgard M. V. Major integral membrane protein immunogens of Treponema pallidum are proteolipids. Infect Immun. 1989 Sep;57(9):2872–2877. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.9.2872-2877.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlain N. R., Radolf J. D., Hsu P. L., Sell S., Norgard M. V. Genetic and physicochemical characterization of the recombinant DNA-derived 47-kilodalton surface immunogen of Treponema pallidum subsp. pallidum. Infect Immun. 1988 Jan;56(1):71–78. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.1.71-78.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham T. M., Walker E. M., Miller J. N., Lovett M. A. Selective release of the Treponema pallidum outer membrane and associated polypeptides with Triton X-114. J Bacteriol. 1988 Dec;170(12):5789–5796. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.12.5789-5796.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dallas W. S., Ray P. H., Leong J., Benedict C. D., Stamm L. V., Bassford P. J., Jr Identification and purification of a recombinant Treponema pallidum basic membrane protein antigen expressed in Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1987 May;55(5):1106–1115. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.5.1106-1115.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frazer A. C., Curtiss R., 3rd Production, properties and utility of bacterial minicells. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1975;69:1–84. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-50112-8_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu P. L., Chamberlain N. R., Orth K., Moomaw C. R., Zhang L. Q., Slaughter C. A., Radolf J. D., Sell S., Norgard M. V. Sequence analysis of the 47-kilodalton major integral membrane immunogen of Treponema pallidum. Infect Immun. 1989 Jan;57(1):196–203. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.1.196-203.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones S. A., Marchitto K. S., Miller J. N., Norgard M. V. Monoclonal antibody with hemagglutination, immobilization, and neutralization activities defines an immunodominant, 47,000 mol wt, surface-exposed immunogen of Treponema pallidum (Nichols). J Exp Med. 1984 Nov 1;160(5):1404–1420. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.5.1404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAGNUSON H. J., THOMAS E. W., OLANSKY S., KAPLAN B. I., DE MELLO L., CUTLER J. C. Inoculation syphilis in human volunteers. Medicine (Baltimore) 1956 Feb;35(1):33–82. doi: 10.1097/00005792-195602000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maher P. A., Singer S. J. Anomalous interaction of the acetylcholine receptor protein with the nonionic detergent Triton X-114. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):958–962. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchitto K. S., Jones S. A., Schell R. F., Holmans P. L., Norgard M. V. Monoclonal antibody analysis of specific antigenic similarities among pathogenic Treponema pallidum subspecies. Infect Immun. 1984 Sep;45(3):660–666. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.3.660-666.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchitto K. S., Selland-Grossling C. K., Norgard M. V. Molecular specificities of monoclonal antibodies directed against virulent Treponema pallidum. Infect Immun. 1986 Jan;51(1):168–176. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.1.168-176.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido H., Vaara M. Molecular basis of bacterial outer membrane permeability. Microbiol Rev. 1985 Mar;49(1):1–32. doi: 10.1128/mr.49.1.1-32.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norgard M. V., Chamberlain N. R., Swancutt M. A., Goldberg M. S. Cloning and expression of the major 47-kilodalton surface immunogen of Treponema pallidum in Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1986 Nov;54(2):500–506. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.2.500-506.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norgard M. V., Miller J. N. Cloning and expression of Treponema pallidum (Nichols) antigen genes in Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1983 Nov;42(2):435–445. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.2.435-445.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orndorff P. E., Falkow S. Organization and expression of genes responsible for type 1 piliation in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1984 Aug;159(2):736–744. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.2.736-744.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palva E. T., Hirst T. R., Hardy S. J., Holmgren J., Randall L. Synthesis of a precursor to the B subunit of heat-labile enterotoxin in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1981 Apr;146(1):325–330. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.1.325-330.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pillai S., Baltimore D. Myristoylation and the post-translational acquisition of hydrophobicity by the membrane immunoglobulin heavy-chain polypeptide in B lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7654–7658. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7654. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radolf J. D., Chamberlain N. R., Clausell A., Norgard M. V. Identification and localization of integral membrane proteins of virulent Treponema pallidum subsp. pallidum by phase partitioning with the nonionic detergent triton X-114. Infect Immun. 1988 Feb;56(2):490–498. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.2.490-498.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson S. M., Kettman J. R., Miller J. N., Norgard M. V. Murine monoclonal antibodies specific for virulent Treponema pallidum (Nichols). Infect Immun. 1982 Jun;36(3):1076–1085. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.3.1076-1085.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russel M., Model P. Filamentous phage pre-coat is an integral membrane protein: analysis by a new method of membrane preparation. Cell. 1982 Jan;28(1):177–184. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90387-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarin V. K., Kent S. B., Tam J. P., Merrifield R. B. Quantitative monitoring of solid-phase peptide synthesis by the ninhydrin reaction. Anal Biochem. 1981 Oct;117(1):147–157. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90704-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sefton B. M., Buss J. E. The covalent modification of eukaryotic proteins with lipid. J Cell Biol. 1987 Jun;104(6):1449–1453. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.6.1449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sell S., Norris S. J. The biology, pathology, and immunology of syphilis. Int Rev Exp Pathol. 1983;24:203–276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamm L. V., Bassford P. J., Jr Cellular and extracellular protein antigens of Treponema pallidum synthesized during in vitro incubation of freshly extracted organisms. Infect Immun. 1985 Mar;47(3):799–807. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.3.799-807.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamm L. V., Dallas W. S., Ray P. H., Bassford P. J., Jr Identification, cloning, and purification of protein antigens of Treponema pallidum. Rev Infect Dis. 1988 Jul-Aug;10 (Suppl 2):S403–S407. doi: 10.1093/cid/10.supplement_2.s403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swancutt M. A., Twehous D. A., Norgard M. V. Monoclonal antibody selection and analysis of a recombinant DNA-derived surface immunogen of Treponema pallidum expressed in Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1986 Apr;52(1):110–119. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.1.110-119.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. A bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase/promoter system for controlled exclusive expression of specific genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1074–1078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tam J. P. Synthesis of biologically active transforming growth factor alpha. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1987 Mar;29(3):421–431. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1987.tb02269.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu H. C., Tokunaga M. Biogenesis of lipoproteins in bacteria. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1986;125:127–157. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-71251-7_9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]