Abstract
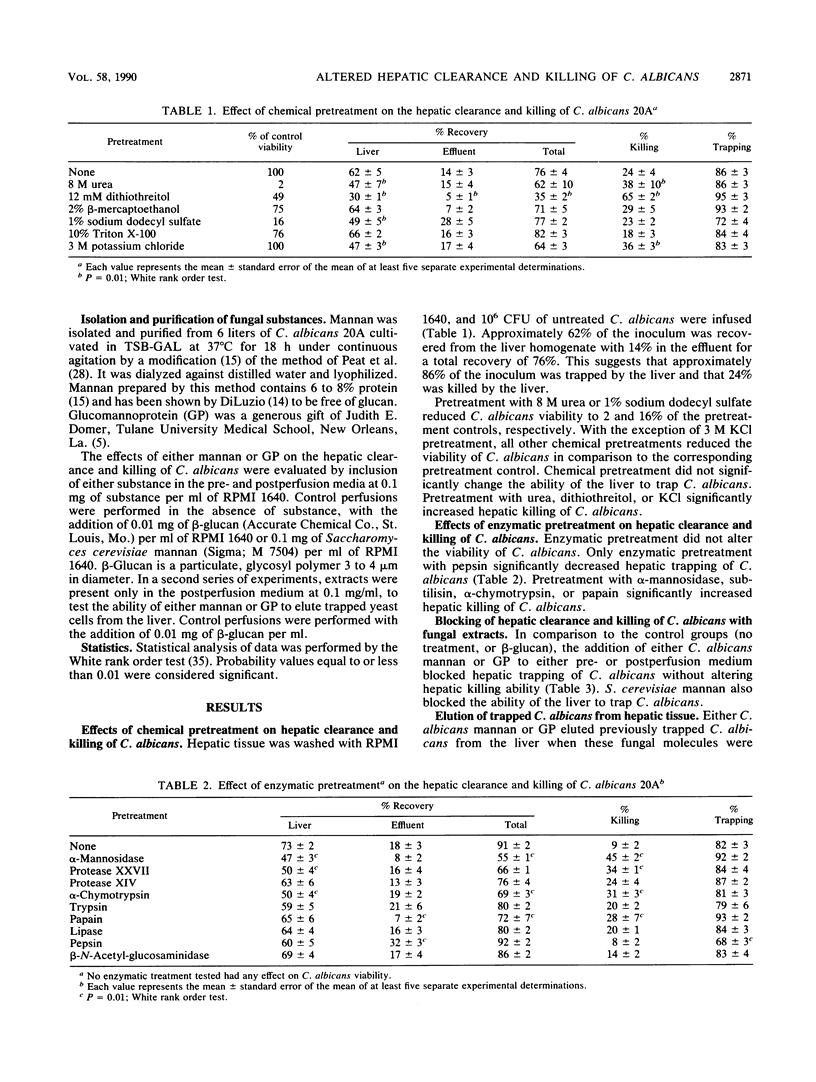
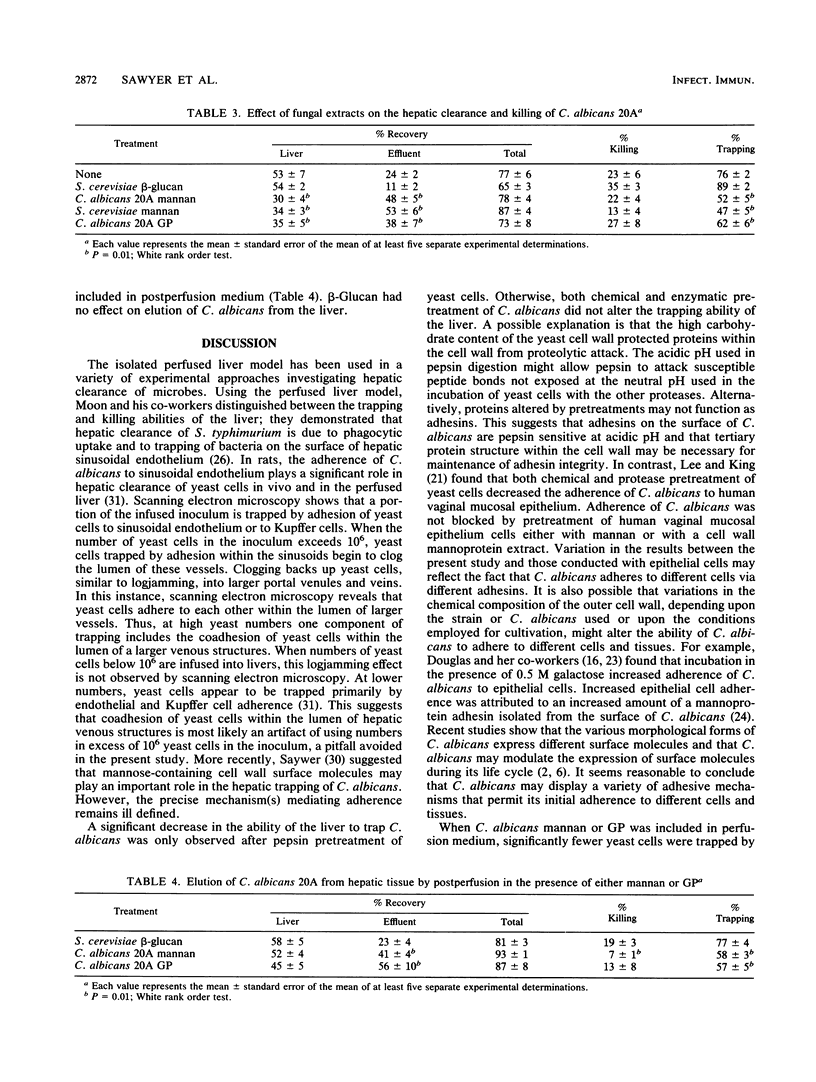
The adherence of Candida albicans was studied in situ by using the perfused mouse liver model. After exhaustive washing, 10(6) C. albicans were infused into mouse livers. At the time of recovery, 62 +/- 5% (mean +/- standard error of the mean) of the infused C. albicans were recovered from the liver and 14 +/- 3% were recovered from the effluent for a total recovery of 76 +/- 4%. This indicates that 86 +/- 3% of the original inoculum was trapped by the liver and that 24 +/- 4% was killed within the liver. Chemical pretreatment of C. albicans with 8 M urea, 12 mM dithiothreitol, 2% beta-mercaptoethanol, 1% sodium dodecyl sulfate, 10% Triton X-100, or 3 M potassium chloride or enzyme pretreatment with alpha-mannosidase, alpha-chymotrypsin, subtilisin, beta-N-acetyl-glucosaminidase, pronase, trypsin, papain, or lipase did not alter adherence of C. albicans to hepatic tissue. By contrast, pepsin pretreatment significantly decreased hepatic trapping. Simultaneous perfusion with either 100 mg of C. albicans glycoprotein per liter or 100 mg of C. albicans mannan per liter also decreased trapping. Furthermore, both substances eluted previously trapped C. albicans from hepatic tissue. Chemical pretreatment with 8 M urea, 12 mM dithiothreitol, or 3 M KCI or enzymatic pretreatment with alpha-mannosidase, subtilisin, alpha-chymotrypsin, or papain increased killing of C. albicans three- to fivefold within hepatic tissue. The data suggest that mannose-containing structures on the surface of C. albicans, for example. mannans or glucomannoproteins, mediate adherence of C. albicans within the liver. Indirectly, chemical and enzymatic pretreatment renders C. albicans more susceptible to hepatic killing.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bouchara J. P., Tronchin G., Annaix V., Robert R., Senet J. M. Laminin receptors on Candida albicans germ tubes. Infect Immun. 1990 Jan;58(1):48–54. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.1.48-54.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brawner D. L., Cutler J. E., Beatty W. L. Caveats in the investigation of form-specific molecules of Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1990 Feb;58(2):378–383. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.2.378-383.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullock W. E., Wright S. D. Role of the adherence-promoting receptors, CR3, LFA-1, and p150,95, in binding of Histoplasma capsulatum by human macrophages. J Exp Med. 1987 Jan 1;165(1):195–210. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.1.195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnie J. P., Odds F. C., Lee W., Webster C., Williams J. D. Outbreak of systemic Candida albicans in intensive care unit caused by cross infection. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1985 Mar 9;290(6470):746–748. doi: 10.1136/bmj.290.6470.746. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrow E. W., Domer J. E. Immunoregulation in experimental murine candidiasis: specific suppression induced by Candida albicans cell wall glycoprotein. Infect Immun. 1985 Jul;49(1):172–181. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.1.172-181.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaffin W. L., Skudlarek J., Morrow K. J. Variable expression of a surface determinant during proliferation of Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1988 Feb;56(2):302–309. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.2.302-309.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cutler J. E., Brawner D. L., Hazen K. C., Jutila M. A. Characteristics of Candida albicans adherence to mouse tissues. Infect Immun. 1990 Jun;58(6):1902–1908. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.6.1902-1908.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daimond R. D., Krzesicki R. Mechanisms of attachment of neutrophils to Candida albicans pseudohyphae in the absence of serum, and of subsequent damage to pseudohyphae by microbicidal processes of neutrophils in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1978 Feb;61(2):360–369. doi: 10.1172/JCI108946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond R. D. Fungal surfaces: effects of interactions with phagocytic cells. Rev Infect Dis. 1988 Jul-Aug;10 (Suppl 2):S428–S431. doi: 10.1093/cid/10.supplement_2.s428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond R. D., Oppenheim F., Nakagawa Y., Krzesicki R., Haudenschild C. C. Properties of a product of Candida albicans hyphae and pseudohyphae that inhibits contact between the fungi and human neutrophils in vitro. J Immunol. 1980 Dec;125(6):2797–2804. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domer J. E., Garner R. E., Befidi-Mengue R. N. Mannan as an antigen in cell-mediated immunity (CMI) assays and as a modulator of mannan-specific CMI. Infect Immun. 1989 Mar;57(3):693–700. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.3.693-700.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans E. G. The incidence of pathogenic yeasts among open-heart surgery patients-the value of prophylaxis. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1975 Sep;70(3):466–470. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ezdinli E. Z., O'Sullivan D. D., Wasser L. P., Kim U., Stutzman L. Oral amphotericin for candidiasis in patients with hematologic neoplasms. An autopsy study. JAMA. 1979 Jul 20;242(3):258–260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houston J. G., Douglas L. J. Interaction of Candida albicans with neutrophils: effect of phenotypic changes in yeast cell-surface composition. J Gen Microbiol. 1989 Jul;135(7):1885–1893. doi: 10.1099/00221287-135-7-1885. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krause W., Matheis H., Wulf K. Fungaemia and funguria after oral administration of Candida albicans. Lancet. 1969 Mar 22;1(7595):598–599. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)91534-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. C., King R. D. Characterization of Candida albicans adherence to human vaginal epithelial cells in vitro. Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):1024–1030. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.1024-1030.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lew M. A., Siber G. R., Donahue D. M., Maiorca F. Enhanced detection with an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay of candida mannan in antibody-containing serum after heat extraction. J Infect Dis. 1982 Jan;145(1):45–56. doi: 10.1093/infdis/145.1.45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCourtie J., Douglas L. J. Extracellular polymer of Candida albicans: isolation, analysis and role in adhesion. J Gen Microbiol. 1985 Mar;131(3):495–503. doi: 10.1099/00221287-131-3-495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCourtie J., Douglas L. J. Relationship between cell surface composition of Candida albicans and adherence to acrylic after growth on different carbon sources. Infect Immun. 1981 Jun;32(3):1234–1241. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.3.1234-1241.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meckstroth K. L., Reiss E., Keller J. W., Kaufman L. Detection of antibodies and antigenemia in leukemic patients with candidiasis by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Infect Dis. 1981 Jul;144(1):24–32. doi: 10.1093/infdis/144.1.24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moon R. J., Vrable R. A., Broka J. A. In situ separation of bacterial trapping and killing functions of the perfused liver. Infect Immun. 1975 Aug;12(2):411–418. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.2.411-418.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myerowitz R. L., Pazin G. J., Allen C. M. Disseminated candidiasis. Changes in incidence, underlying diseases, and pathology. Am J Clin Pathol. 1977 Jul;68(1):29–38. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/68.1.29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotrosen D., Calderone R. A., Edwards J. E., Jr Adherence of Candida species to host tissues and plastic surfaces. Rev Infect Dis. 1986 Jan-Feb;8(1):73–85. doi: 10.1093/clinids/8.1.73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawyer R. T., Moon R. J., Beneke E. S. Hepatic clearance of Candida albicans in rats. Infect Immun. 1976 Dec;14(6):1348–1355. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.6.1348-1355.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawyer R. T., Moon R. J., Beneke E. S. Trapping and killing of Candida albicans by Corynebacterium parvum-activated livers. Infect Immun. 1981 May;32(2):945–950. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.2.945-950.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawyer R. T. The effect of monosaccharides on in situ hepatic trapping of Candida albicans. Mycopathologia. 1988 Nov;104(2):81–85. doi: 10.1007/BF00436931. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxena A., Calderone R. Purification and characterization of the extracellular C3d-binding protein of Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1990 Feb;58(2):309–314. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.2.309-314.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tronchin G., Bouchara J. P., Robert R., Senet J. M. Adherence of Candida albicans germ tubes to plastic: ultrastructural and molecular studies of fibrillar adhesins. Infect Immun. 1988 Aug;56(8):1987–1993. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.8.1987-1993.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Repentigny L., Kuykendall R. J., Chandler F. W., Broderson J. R., Reiss E. Comparison of serum mannan, arabinitol, and mannose in experimental disseminated candidiasis. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Jun;19(6):804–812. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.6.804-812.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Repentigny L., Reiss E. Current trends in immunodiagnosis of candidiasis and aspergillosis. Rev Infect Dis. 1984 May-Jun;6(3):301–312. doi: 10.1093/clinids/6.3.301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


