Abstract
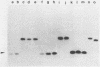
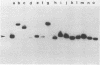
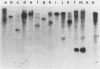
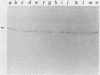
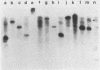
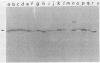
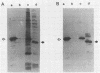
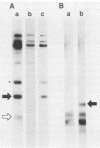
The mip gene of Legionella pneumophila serogroup 1 strain AA100 encodes a 24-kilodalton surface protein (Mip) and enhances the abilities of L. pneumophila to parasitize human macrophages and to cause pneumonia in experimental animals. To determine whether this virulence factor is conserved in the genus Legionella, a large panel of Legionella strains was examined by Southern hybridization and immunoblot analyses for the presence and expression of mip-related sequences. Strains representing all 14 serogroups of L. pneumophila contained a mip gene and expressed a 24-kilodalton Mip protein. Although the isolates of the 29 other Legionella species did not hybridize with mip DNA probes under high-stringency conditions, they did so at reduced stringency. In support of the notion that these strains possess mip-like genes, these species each expressed a protein (24 to 31 kilodaltons in size) that reacted with specific Mip antisera. Moreover, the cloned mip analog from Legionella micdadei encoded the cross-reactive protein. Thus, mip is conserved and specific to L. pneumophila, but mip-like genes are present throughout the genus, perhaps potentiating the intracellular infectivity of all Legionella species.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baine W. B. Cytolytic and phospholipase C activity in Legionella species. J Gen Microbiol. 1985 Jun;131(6):1383–1391. doi: 10.1099/00221287-131-6-1383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bangsborg J. M., Collins M. T., Høiby N., Hindersson P. Cloning and expression of the Legionella micdadei "common antigen" in Escherichia coli. APMIS. 1989 Jan;97(1):14–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bornstein N., Marmet D., Surgot M., Nowicki M., Meugnier H., Fleurette J., Ageron E., Grimont F., Grimont P. A., Thacker W. L. Legionella gratiana sp. nov. isolated from French spa water. Res Microbiol. 1989 Oct;140(8):541–552. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(89)90086-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bornstein N., Nowicki M., Fleurette J. Haemolytic activity in the genus Legionella. Ann Inst Pasteur Microbiol. 1988 May-Jun;139(3):325–329. doi: 10.1016/0769-2609(88)90024-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner D. J. Classification of the legionellae. Semin Respir Infect. 1987 Dec;2(4):190–205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cianciotto N. P., Eisenstein B. I., Mody C. H., Engleberg N. C. A mutation in the mip gene results in an attenuation of Legionella pneumophila virulence. J Infect Dis. 1990 Jul;162(1):121–126. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.1.121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cianciotto N. P., Eisenstein B. I., Mody C. H., Toews G. B., Engleberg N. C. A Legionella pneumophila gene encoding a species-specific surface protein potentiates initiation of intracellular infection. Infect Immun. 1989 Apr;57(4):1255–1262. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.4.1255-1262.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cianciotto N., Eisenstein B. I., Engleberg N. C., Shuman H. Genetics and molecular pathogenesis of Legionella pneumophila, an intracellular parasite of macrophages. Mol Biol Med. 1989 Oct;6(5):409–424. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciesielski C. A., Blaser M. J., Wang W. L. Serogroup specificity of Legionella pneumophila is related to lipopolysaccharide characteristics. Infect Immun. 1986 Feb;51(2):397–404. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.2.397-404.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennis P. J., Lee J. V. Differences in aerosol survival between pathogenic and non-pathogenic strains of Legionella pneumophila serogroup 1. J Appl Bacteriol. 1988 Aug;65(2):135–141. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1988.tb01501.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenstein B. I., Engleberg N. C. Applied molecular genetics: new tools for microbiologists and clinicians. J Infect Dis. 1986 Mar;153(3):416–430. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.3.416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engleberg N. C., Carter C., Weber D. R., Cianciotto N. P., Eisenstein B. I. DNA sequence of mip, a Legionella pneumophila gene associated with macrophage infectivity. Infect Immun. 1989 Apr;57(4):1263–1270. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.4.1263-1270.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engleberg N. C., Drutz D. J., Eisenstein B. I. Cloning and expression of Legionella pneumophila antigens in Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1984 May;44(2):222–227. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.2.222-227.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engleberg N. C., Pearlman E., Dixon D., Eisenstein B. I. Antibodies isolated by using cloned surface antigens recognize antigenically related components of Legionella pneumophila and other Legionella species. J Immunol. 1986 Feb 15;136(4):1415–1417. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fang G. D., Yu V. L., Vickers R. M. Disease due to the Legionellaceae (other than Legionella pneumophila). Historical, microbiological, clinical, and epidemiological review. Medicine (Baltimore) 1989 Mar;68(2):116–132. doi: 10.1097/00005792-198903000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fliermans C. B., Cherry W. B., Orrison L. H., Smith S. J., Tison D. L., Pope D. H. Ecological distribution of Legionella pneumophila. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Jan;41(1):9–16. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.1.9-16.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen E. B., Pedersen P. E., Schouls L. M., Severin E., van Embden J. D. Genetic characterization and partial sequence determination of a Treponema pallidum operon expressing two immunogenic membrane proteins in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jun;162(3):1227–1237. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.3.1227-1237.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohn B., Collins J. A small cosmid for efficient cloning of large DNA fragments. Gene. 1980 Nov;11(3-4):291–298. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90069-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi M. H., Pasculle A. W., Dowling J. N. Role of the alveolar macrophage in host defense and immunity to Legionella micdadei pneumonia in the guinea pig. Microb Pathog. 1987 Apr;2(4):269–282. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(87)90125-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearlman E., Engleberg N. C., Eisenstein B. I. Identification of protein antigens of Legionella pneumophila serogroup 1. Infect Immun. 1985 Jan;47(1):74–79. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.1.74-79.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pine L., Hoffman P. S., Malcolm G. B., Benson R. F., Keen M. G. Determination of catalase, peroxidase, and superoxide dismutase within the genus Legionella. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Sep;20(3):421–429. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.3.421-429.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plouffe J. F., Para M. F., Fuller K. A. Serum bactericidal activity against Legionella pneumophila. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Nov;22(5):863–864. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.5.863-864.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn F. D., Keen M. G., Tompkins L. S. Genetic, immunological, and cytotoxic comparisons of Legionella proteolytic activities. Infect Immun. 1989 Sep;57(9):2719–2725. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.9.2719-2725.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rechnitzer C., Blom J. Engulfment of the Philadelphia strain of Legionella pneumophila within pseudopod coils in human phagocytes. Comparison with other Legionella strains and species. APMIS. 1989 Feb;97(2):105–114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reingold A. L. Role of legionellae in acute infections of the lower respiratory tract. Rev Infect Dis. 1988 Sep-Oct;10(5):1018–1028. doi: 10.1093/clinids/10.5.1018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowbotham T. J. Current views on the relationships between amoebae, legionellae and man. Isr J Med Sci. 1986 Sep;22(9):678–689. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spratt B. G., Hedge P. J., te Heesen S., Edelman A., Broome-Smith J. K. Kanamycin-resistant vectors that are analogues of plasmids pUC8, pUC9, pEMBL8 and pEMBL9. Gene. 1986;41(2-3):337–342. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90117-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thacker W. L., Benson R. F., Schifman R. B., Pugh E., Steigerwalt A. G., Mayberry W. R., Brenner D. J., Wilkinson H. W. Legionella tucsonensis sp. nov. isolated from a renal transplant recipient. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Aug;27(8):1831–1834. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.8.1831-1834.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinbaum D. L., Benner R. R., Dowling J. N., Alpern A., Pasculle A. W., Donowitz G. R. Interaction of Legionella micdadei with human monocytes. Infect Immun. 1984 Oct;46(1):68–73. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.1.68-73.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson H. W., Drasar V., Thacker W. L., Benson R. F., Schindler J., Potuznikova B., Mayberry W. R., Brenner D. J. Legionella moravica sp. nov. and Legionella brunensis sp. nov. isolated from cooling-tower water. Ann Inst Pasteur Microbiol. 1988 Jul-Aug;139(4):393–402. doi: 10.1016/0769-2609(88)90102-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winn W. C., Jr Legionnaires disease: historical perspective. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1988 Jan;1(1):60–81. doi: 10.1128/cmr.1.1.60. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]