Abstract
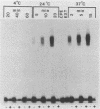
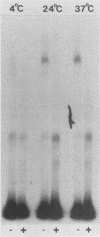
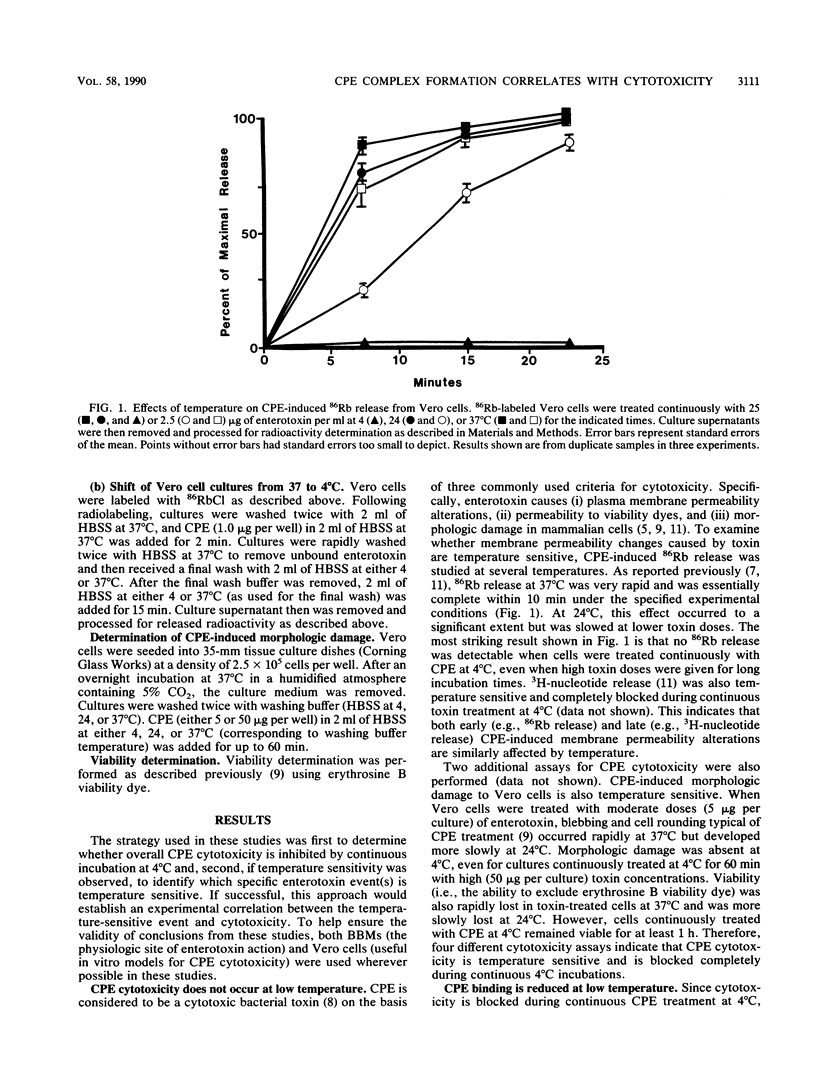
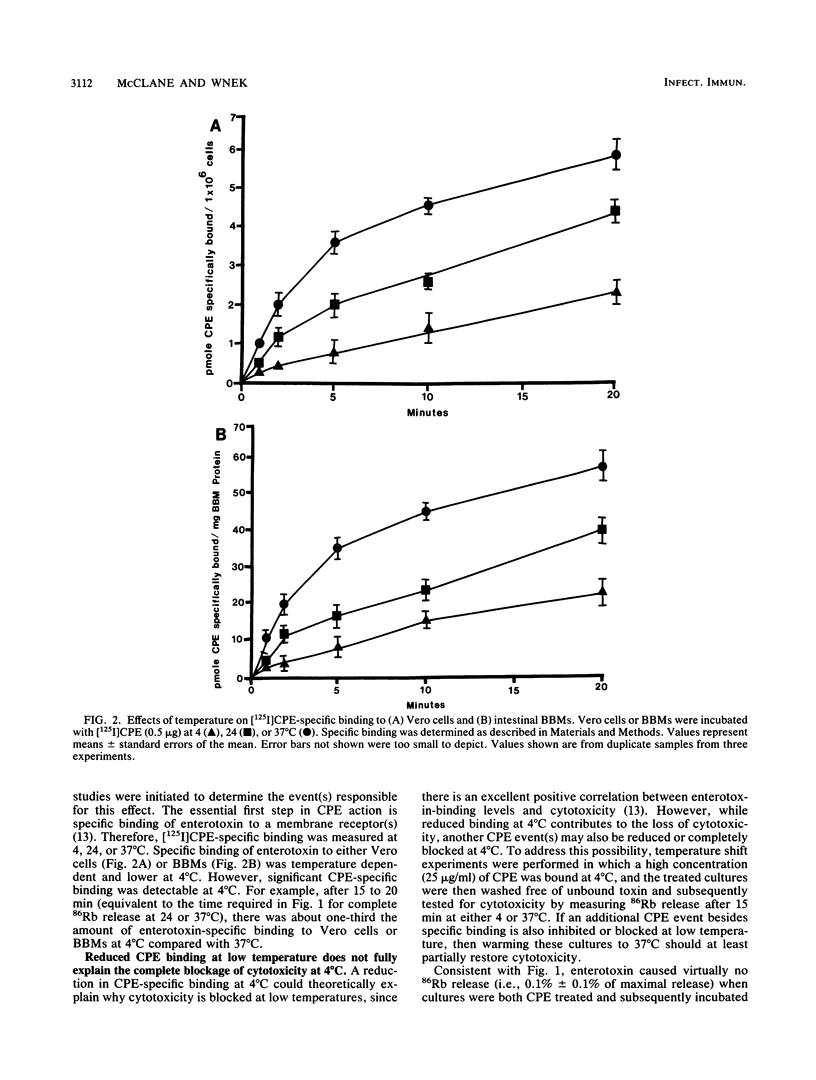
The cytotoxicity of Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin (CPE) was completely blocked in Vero cells continuously CPE treated at 4 degrees C. [125I]CPE-specific binding to either Vero cells or isolated rabbit intestinal brush border membranes (BBMs) was lower at 4 degrees C than at 24 or 37 degrees C, but reduced enterotoxin binding could not totally explain the loss of cytotoxicity at low temperature. Insertion of enterotoxin into Vero cell membranes or BBMs was temperature independent. However, CPE complex formation (A. P. Wnek and B. A. McClane, Infect. Immun. 57:574-581, 1989) in BBMs and Vero cells was blocked at 4 degrees C. When Vero cells were CPE treated at 4 degrees C, washed to remove unbound toxin, and then shifted to 37 degrees C, complex formation and cytotoxicity were rapidly detected. When CPE binding and complex formation were permitted for 2 min at 37 degrees C, and the Vero cells were then shifted to 4 degrees C, cytotoxicity was detectable at 4 degrees C. These results are consistent with complex formation, rather than complex activity, being the temperature-sensitive step in CPE action which is blocked at 4 degrees C. These studies demonstrate a strong correlation between complex formation and cytotoxicity and are consistent with complex involvement in CPE cytotoxicity. These studies also strongly suggest that CPE insertion precedes both complex formation and induction of small-molecule permeability changes.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Farahbakhsh Z. T., Wisnieski B. J. The acid-triggered entry pathway of Pseudomonas exotoxin A. Biochemistry. 1989 Jan 24;28(2):580–585. doi: 10.1021/bi00428a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horiguchi Y., Uemura T., Kozaki S., Sakaguchi G. Effects of Ca2+ and other cations on the action of Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Oct 31;889(1):65–71. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(86)90009-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hulkower K. I., Wnek A. P., McClane B. A. Evidence that alterations in small molecule permeability are involved in the Clostridium perfringens type A enterotoxin-induced inhibition of macromolecular synthesis in Vero cells. J Cell Physiol. 1989 Sep;140(3):498–504. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041400314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda M., Ozutsumi K., Iwahashi H., Sugimoto N. Primary action of Clostridium perfringens type A enterotoxin on HeLa and Vero cells in the absence of extracellular calcium: rapid and characteristic changes in membrane permeability. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Dec 15;141(2):704–710. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80229-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClane B. A., Hanna P. C., Wnek A. P. Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin. Microb Pathog. 1988 May;4(5):317–323. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(88)90059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClane B. A., McDonel J. L. Characterization of membrane permeability alterations induced in Vero cells by Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Aug 14;600(3):974–985. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90499-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClane B. A., McDonel J. L. The effects of Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin on morphology, viability, and macromolecular synthesis in Vero cells. J Cell Physiol. 1979 May;99(2):191–200. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040990205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClane B. A. Osmotic stabilizers differentially inhibit permeability alterations induced in Vero cells by Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Oct 17;777(1):99–106. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(84)90501-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClane B. A., Wnek A. P., Hulkower K. I., Hanna P. C. Divalent cation involvement in the action of Clostridium perfringens type A enterotoxin. Early events in enterotoxin action are divalent cation-independent. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 15;263(5):2423–2435. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonel J. L. Binding of Clostridium perfringens [125I]enterotoxin to rabbit intestinal cells. Biochemistry. 1980 Oct 14;19(21):4801–4807. doi: 10.1021/bi00562a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonel J. L., McClane B. A. Binding versus biological activity of Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin in Vero cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Mar 30;87(2):497–504. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91823-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonel J. L., McClane B. A. Production, purification, and assay of Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin. Methods Enzymol. 1988;165:94–103. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(88)65018-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrie H. T., McDonel J. L., Schlegel R. A. Intracellular antibody against Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin fails to counteract toxin-induced damage. Cell Biol Int Rep. 1982 Jul;6(7):705–711. doi: 10.1016/0309-1651(82)90140-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandvig K., Olsnes S., Brown J. E., Petersen O. W., van Deurs B. Endocytosis from coated pits of Shiga toxin: a glycolipid-binding protein from Shigella dysenteriae 1. J Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;108(4):1331–1343. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.4.1331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigrist H., Ronner P., Semenza G. A hydrophobic form of the small-intestinal sucrase-isomaltase complex. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Oct 17;406(3):433–446. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90022-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugimoto N., Ozutsumi K., Matsuda M. Morphological alterations and changes in cellular cations induced by Clostridium perfringens type A enterotoxin in tissue culture cells. Eur J Epidemiol. 1985 Dec;1(4):264–273. doi: 10.1007/BF00237101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thelestam M., Möllby R. Sensitive assay for detection of toxin-induced damage to the cytoplasmic membrane of human diploid fibroblasts. Infect Immun. 1975 Aug;12(2):225–232. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.2.225-232.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tolleshaug H., Skjelkvåle R., Berg T. Quantitation of binding and subcellular distribution of Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin in rat liver cells. Infect Immun. 1982 Aug;37(2):486–491. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.2.486-491.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wnek A. P., McClane B. A. Comparison of receptors for Clostridium perfringens type A and cholera enterotoxins in isolated rabbit intestinal brush border membranes. Microb Pathog. 1986 Feb;1(1):89–100. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(86)90035-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wnek A. P., McClane B. A. Identification of a 50,000 Mr protein from rabbit brush border membranes that binds Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 May 16;112(3):1099–1105. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91731-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wnek A. P., McClane B. A. Preliminary evidence that Clostridium perfringens type A enterotoxin is present in a 160,000-Mr complex in mammalian membranes. Infect Immun. 1989 Feb;57(2):574–581. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.2.574-581.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wnek A. P., Strouse R. J., McClane B. A. Production and characterization of monoclonal antibodies against Clostridium perfringens type A enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1985 Nov;50(2):442–448. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.2.442-448.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zalman L. S., Wisnieski B. J. Characterization of the insertion of Pseudomonas exotoxin A into membranes. Infect Immun. 1985 Dec;50(3):630–635. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.3.630-635.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]