Abstract
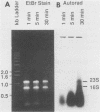
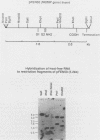
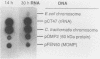
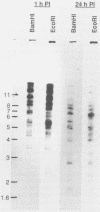
The incorporation of radiolabeled GTP into RNA in host-free Chlamydia trachomatis serovar L2 organisms was investigated. The incorporation was partially inhibited by rifampin and dactinomycin and hydrolyzed by RNase. RNA made by host-free chlamydiae consisted mainly of species of fewer than 800 bases in size, although 16S and 23S species were noted by agarose-gel electrophoresis. The hybridization of radiolabeled host-free RNA to restriction fragments of the gene encoding the major outer membrane protein was analyzed; all regions of the gene were transcribed. The relative intensity of hybridization of host-free RNA made by chlamydiae isolated during the middle and late stages of the developmental cycle to the DNA of clones encoding gene products known to be made at these times in vivo indicated that the temporal patterns of host-free and in vivo transcription were similar. Radiolabeled RNA from 1- and 24-h host-free Chlamydia psittaci 6BC organisms hybridized to many of the same EcoRI and BamHI restriction fragments of C. psittaci genomic DNA, although some differences could be noted. When these RNAs were used to screen a partial C. psittaci genomic library in lambda gt11, plaques were identified that reacted mainly either with 1-h RNA or with 24-h RNA. Because RNA synthesized by host-free chlamydiae appears to be developmental cycle stage specific, transcripts made by host-free chlamydiae may be convenient probes that can be used to clone developmental stage-specific chlamydial genes.
Full text
PDF

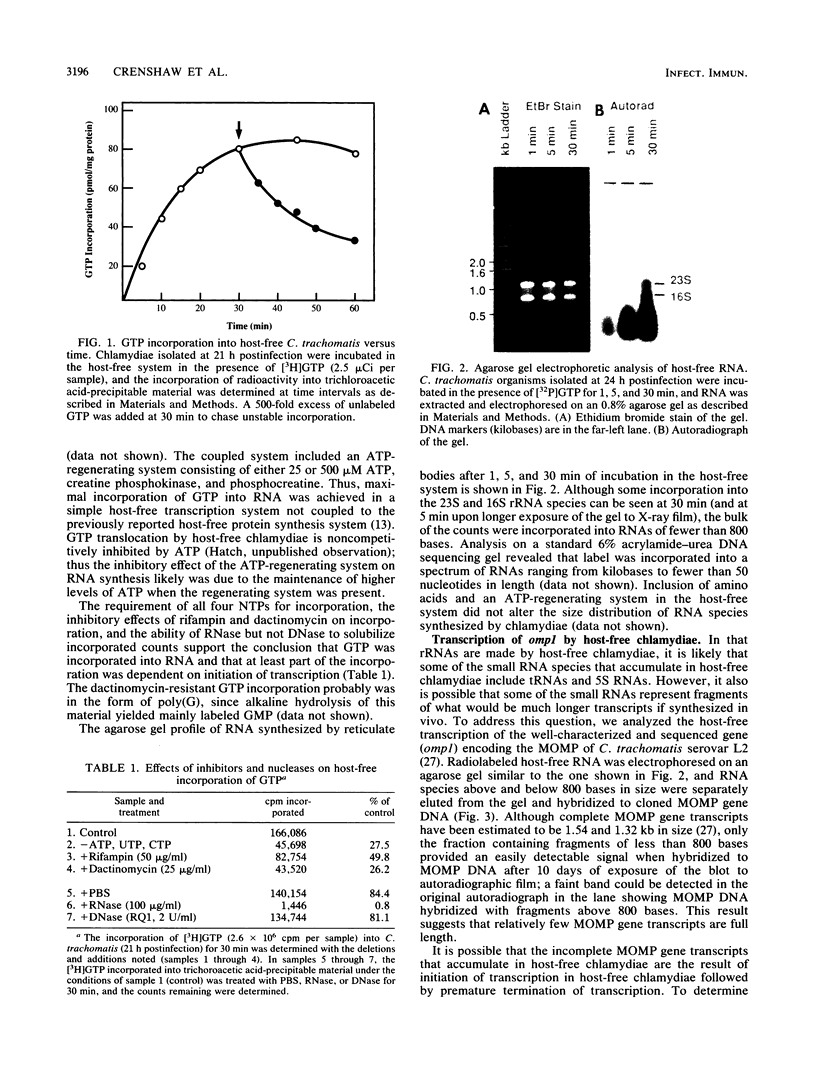





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen J. E., Stephens R. S. Identification by sequence analysis of two-site posttranslational processing of the cysteine-rich outer membrane protein 2 of Chlamydia trachomatis serovar L2. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jan;171(1):285–291. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.1.285-291.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baehr W., Zhang Y. X., Joseph T., Su H., Nano F. E., Everett K. D., Caldwell H. D. Mapping antigenic domains expressed by Chlamydia trachomatis major outer membrane protein genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):4000–4004. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.4000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birkelund S., Lundemose A. G., Christiansen G. Chemical cross-linking of Chlamydia trachomatis. Infect Immun. 1988 Mar;56(3):654–659. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.3.654-659.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birkelund S., Lundemose A. G., Christiansen G. The 75-kilodalton cytoplasmic Chlamydia trachomatis L2 polypeptide is a DnaK-like protein. Infect Immun. 1990 Jul;58(7):2098–2104. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.7.2098-2104.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke I. N., Ward M. E., Lambden P. R. Molecular cloning and sequence analysis of a developmentally regulated cysteine-rich outer membrane protein from Chlamydia trachomatis. Gene. 1988 Nov 30;71(2):307–314. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90047-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel J. N., Ganem D. Chlamydial rRNA operons: gene organization and identification of putative tandem promoters. J Bacteriol. 1987 Dec;169(12):5678–5685. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.12.5678-5685.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackstadt T., Todd W. J., Caldwell H. D. Disulfide-mediated interactions of the chlamydial major outer membrane protein: role in the differentiation of chlamydiae? J Bacteriol. 1985 Jan;161(1):25–31. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.1.25-31.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatch T. P., Al-Hossainy E., Silverman J. A. Adenine nucleotide and lysine transport in Chlamydia psittaci. J Bacteriol. 1982 May;150(2):662–670. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.2.662-670.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatch T. P., Allan I., Pearce J. H. Structural and polypeptide differences between envelopes of infective and reproductive life cycle forms of Chlamydia spp. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jan;157(1):13–20. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.1.13-20.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatch T. P., Miceli M., Silverman J. A. Synthesis of protein in host-free reticulate bodies of Chlamydia psittaci and Chlamydia trachomatis. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jun;162(3):938–942. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.3.938-942.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatch T. P., Miceli M., Sublett J. E. Synthesis of disulfide-bonded outer membrane proteins during the developmental cycle of Chlamydia psittaci and Chlamydia trachomatis. J Bacteriol. 1986 Feb;165(2):379–385. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.2.379-385.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatch T. P., Vance D. W., Jr, Al-Hossainy E. Identification of a major envelope protein in Chlamydia spp. J Bacteriol. 1981 Apr;146(1):426–429. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.1.426-429.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaul R., Roy K. L., Wenman W. M. Cloning, expression, and primary structure of a Chlamydia trachomatis binding protein. J Bacteriol. 1987 Nov;169(11):5152–5156. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.11.5152-5156.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambden P. R., Everson J. S., Ward M. E., Clarke I. N. Sulfur-rich proteins of Chlamydia trachomatis: developmentally regulated transcription of polycistronic mRNA from tandem promoters. Gene. 1990 Mar 1;87(1):105–112. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90500-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newhall W. J., 5th Biosynthesis and disulfide cross-linking of outer membrane components during the growth cycle of Chlamydia trachomatis. Infect Immun. 1987 Jan;55(1):162–168. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.1.162-168.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plaunt M. R., Hatch T. P. Protein synthesis early in the developmental cycle of Chlamydia psittaci. Infect Immun. 1988 Dec;56(12):3021–3025. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.12.3021-3025.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sardinia L. M., Engel J. N., Ganem D. Chlamydial gene encoding a 70-kilodalton antigen in Escherichia coli: analysis of expression signals and identification of the gene product. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jan;171(1):335–341. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.1.335-341.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sardinia L. M., Segal E., Ganem D. Developmental regulation of the cysteine-rich outer-membrane proteins of murine Chlamydia trachomatis. J Gen Microbiol. 1988 Apr;134(4):997–1004. doi: 10.1099/00221287-134-4-997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarov I., Becker Y. Deoxyribonucleic acid-dependent ribonucleic acid polymerase activity in purified trachoma elementary bodies: effect of sodium chloride on ribonucleic acid transcription. J Bacteriol. 1971 Sep;107(3):593–598. doi: 10.1128/jb.107.3.593-598.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. Gel electrophoresis of restriction fragments. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:152–176. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68011-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens R. S., Wagar E. A., Edman U. Developmental regulation of tandem promoters for the major outer membrane protein gene of Chlamydia trachomatis. J Bacteriol. 1988 Feb;170(2):744–750. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.2.744-750.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenman W. M., Meuser R. U. Chlamydia trachomatis elementary bodies possess proteins which bind to eucaryotic cell membranes. J Bacteriol. 1986 Feb;165(2):602–607. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.2.602-607.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler H. H. Protein and RNA synthesis by isolated Rickettsia prowazekii. Infect Immun. 1987 Sep;55(9):2032–2036. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.9.2032-2036.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Davis R. W. Efficient isolation of genes by using antibody probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1194–1198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuerner R. L., Thompson H. A. Protein synthesis by intact Coxiella burnetii cells. J Bacteriol. 1983 Oct;156(1):186–191. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.1.186-191.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]