Abstract
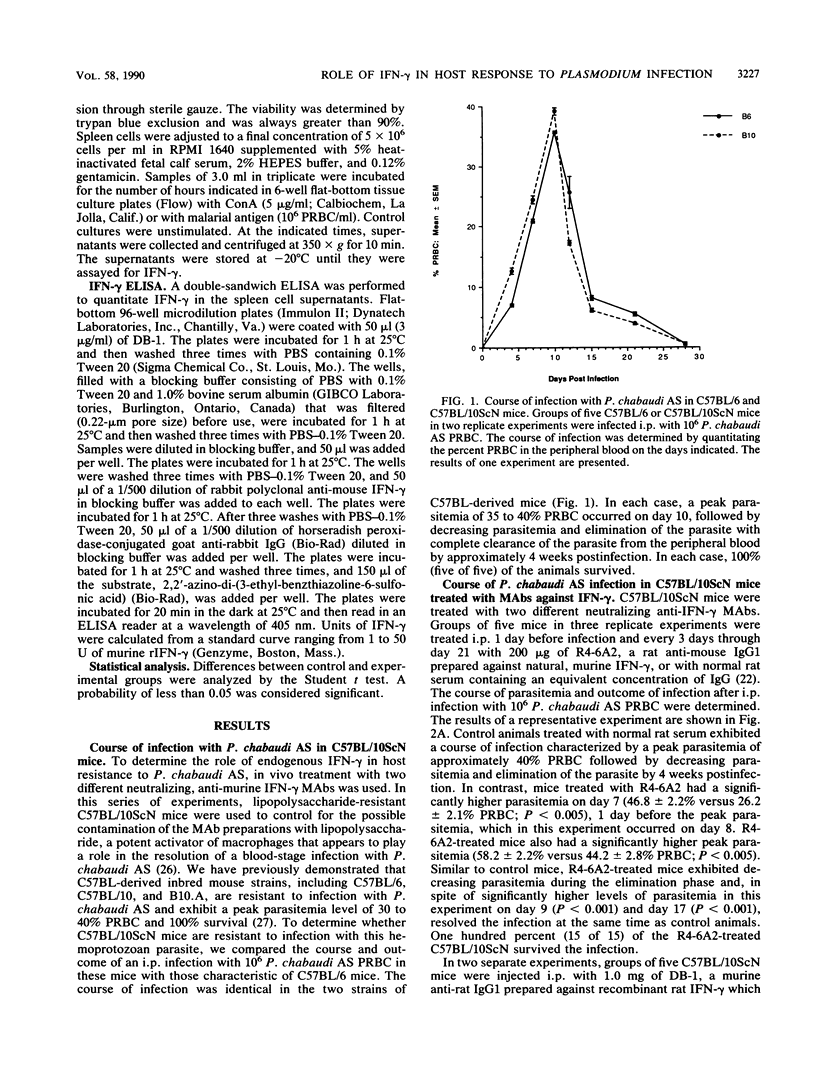
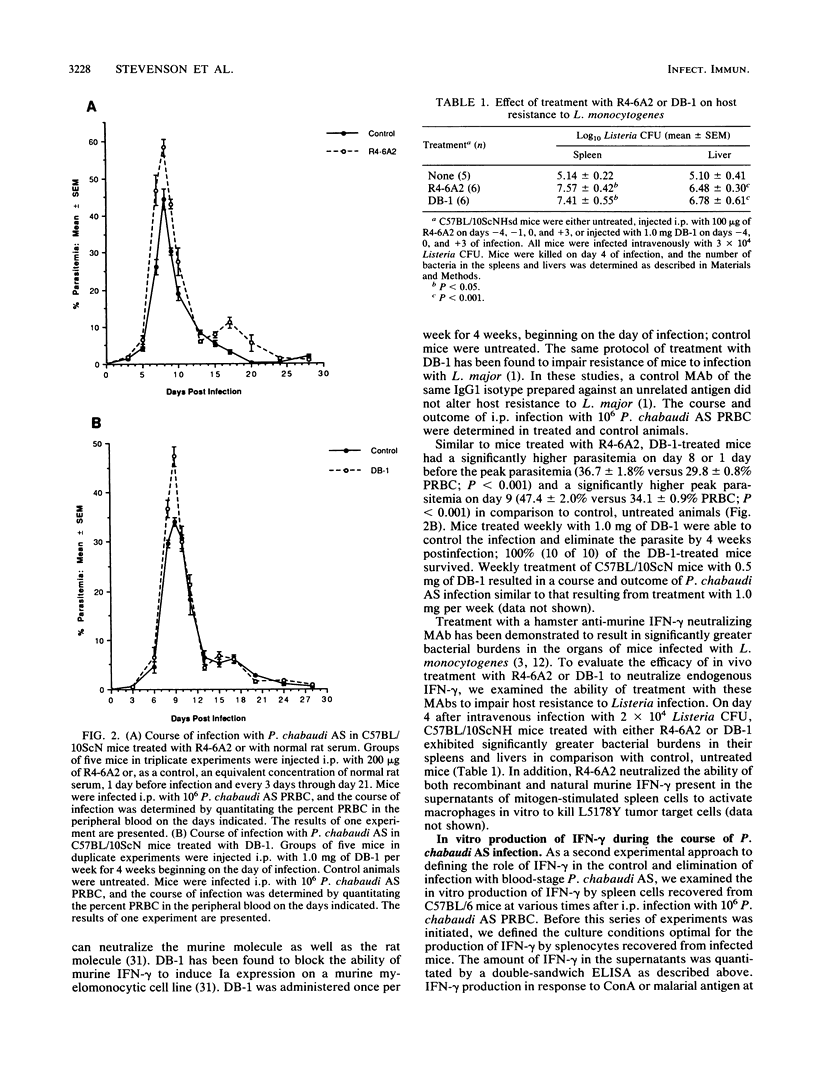
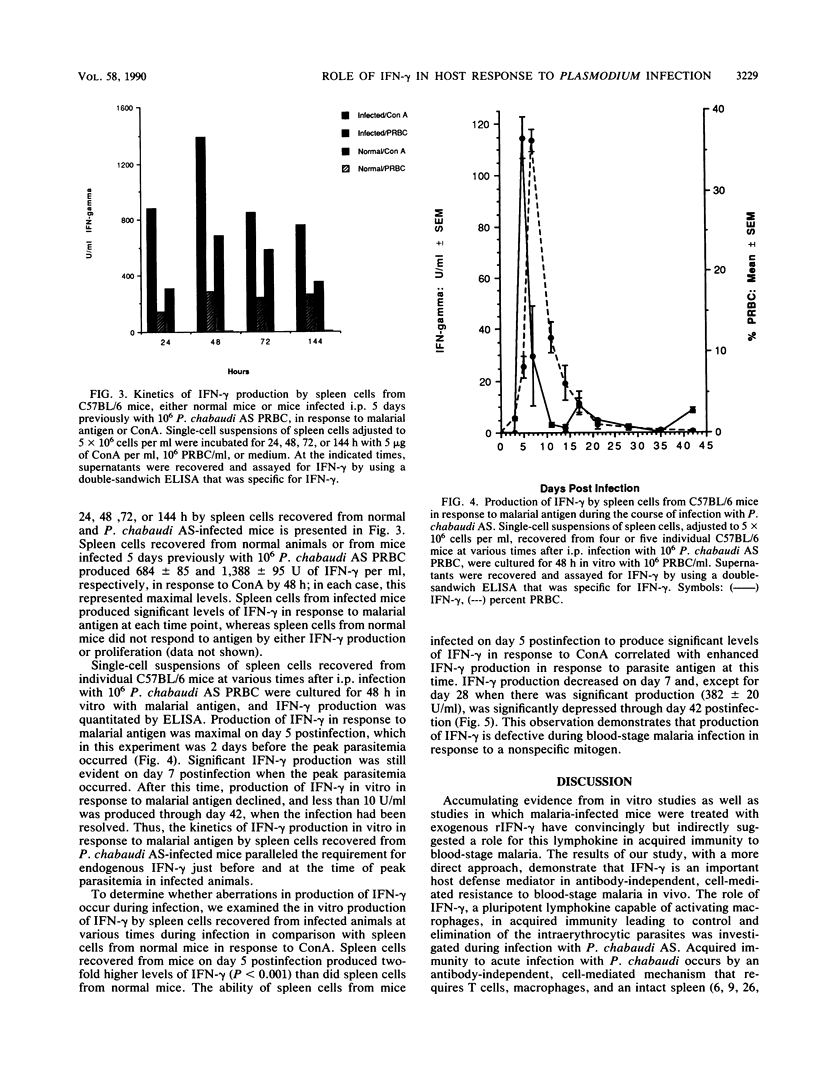
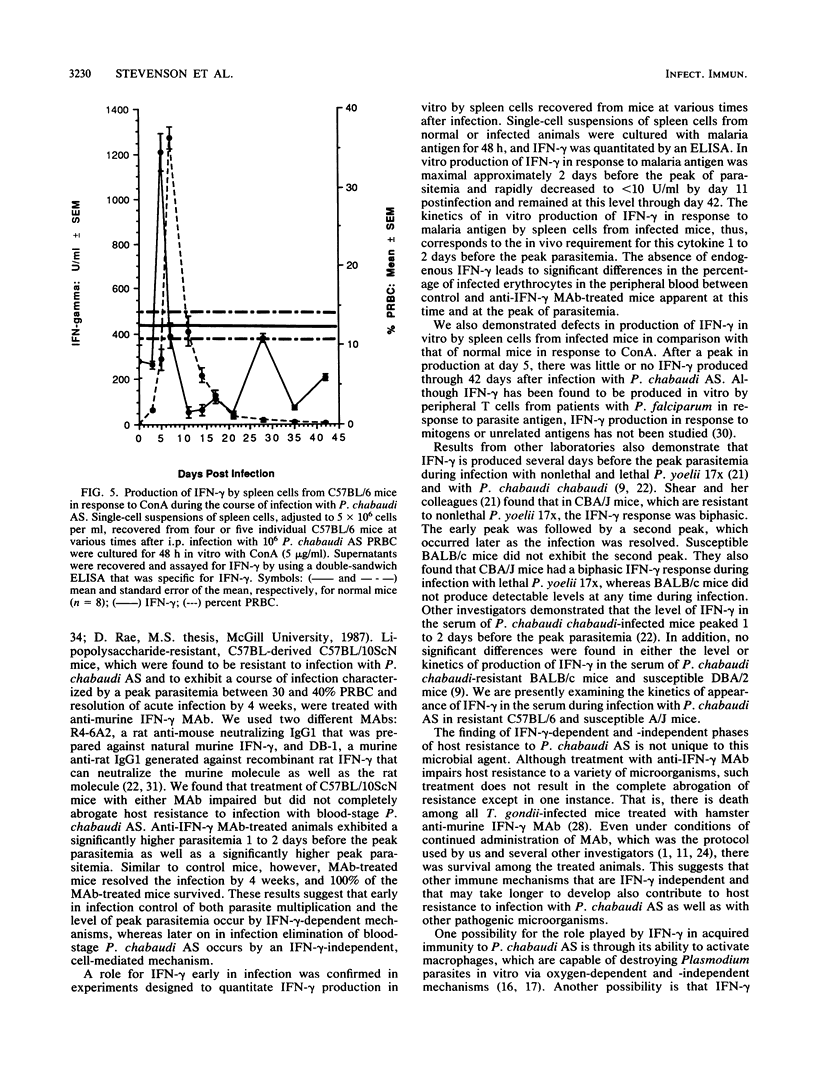
The role of gamma interferon (IFN-gamma), a pluripotent lymphokine capable of activating macrophages, in acquired immunity to blood-stage malaria was investigated. C57BL-derived, lipopolysaccharide-resistant C57BL/10ScN mice, which were found to be resistant to intraperitoneal (i.p.) infection with 10(6) Plasmodium chabaudi AS parasitized erythrocytes, were treated with monoclonal anti-IFN-gamma antibody (MAb). Two MAbs were used: R4-6A2, a rat anti-mouse, neutralizing immunoglobulin G1, which was prepared against natural murine IFN-gamma, and DB-1, a murine anti-rat immunoglobulin G1 prepared against recombinant rat IFN-gamma, which can neutralize the murine molecule as well as the rat molecule. C57BL/10ScNH mice were injected i.p. with 200 micrograms of R4-6A2 1 day before infection and every 3 days through day 21. Control mice were treated with normal rat serum. In separate experiments, DB-1 (1.0 mg per week for 4 weeks) was administered i.p. to C57BL/10ScNH mice beginning on the day of infection; control mice were untreated. Control and MAb-treated mice were infected i.p. with 10(6) P. chabaudi AS parasitized erythrocytes, and the course and outcome of infection were determined. Control mice exhibited a course of infection that was characterized by a peak parasitemia between 30 and 40% parasitized erythrocytes and elimination of the parasite by 4 weeks. MAb-treated mice exhibited a significantly greater parasitemia 1 to 2 days before the peak parasitemia as well as a significantly greater peak parasitemia but also completely cleared the infection by 4 weeks. Thus, these results suggest that treatment with anti-IFN-gamma MAb impairs but does not completely abrogate host resistance to P. chabaudi AS. We also examined the kinetics of IFN-gamma production by spleen cells cultured in vitro with malaria antigen or concanavalin A. Spleen cells were recovered from individual C57BL/6 mice at various times after i.p. infection with 10(6) P. chabaudi AS parasitized erythrocytes. The amount of IFN-gamma produced was quantitated by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. In each case, the peak of IFN-gamma production occurred just before the peak parasitemia, followed by a decrease to little or no IFN-gamma production through 42 days postinfection. There was thus a parallel between the kinetics of production of IFN-gamma in vitro by spleen cells from infected animals and the requirement in vivo for the endogenous molecule just before and at the time of peak parasitemia. In conclusion, these results suggest that IFN-gamma-dependent and -independent mechanisms contribute to host resistance to P. chabaudi AS.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Belosevic M., Finbloom D. S., Van Der Meide P. H., Slayter M. V., Nacy C. A. Administration of monoclonal anti-IFN-gamma antibodies in vivo abrogates natural resistance of C3H/HeN mice to infection with Leishmania major. J Immunol. 1989 Jul 1;143(1):266–274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Cerami A. Cachectin: more than a tumor necrosis factor. N Engl J Med. 1987 Feb 12;316(7):379–385. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198702123160705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchmeier N. A., Schreiber R. D. Requirement of endogenous interferon-gamma production for resolution of Listeria monocytogenes infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(21):7404–7408. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.21.7404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavacini L. A., Guidotti M., Parke L. A., Melancon-Kaplan J., Weidanz W. P. Reassessment of the role of splenic leukocyte oxidative activity and macrophage activation in expression of immunity to malaria. Infect Immun. 1989 Dec;57(12):3677–3682. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.12.3677-3682.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark I. A., Hunt N. H., Butcher G. A., Cowden W. B. Inhibition of murine malaria (Plasmodium chabaudi) in vivo by recombinant interferon-gamma or tumor necrosis factor, and its enhancement by butylated hydroxyanisole. J Immunol. 1987 Nov 15;139(10):3493–3496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Titto E. H., Catterall J. R., Remington J. S. Activity of recombinant tumor necrosis factor on Toxoplasma gondii and Trypanosoma cruzi. J Immunol. 1986 Aug 15;137(4):1342–1345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grun J. L., Weidanz W. P. Immunity to Plasmodium chabaudi adami in the B-cell-deficient mouse. Nature. 1981 Mar 12;290(5802):143–145. doi: 10.1038/290143a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havell E. A. Production of tumor necrosis factor during murine listeriosis. J Immunol. 1987 Dec 15;139(12):4225–4231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kindler V., Sappino A. P., Grau G. E., Piguet P. F., Vassalli P. The inducing role of tumor necrosis factor in the development of bactericidal granulomas during BCG infection. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):731–740. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90676-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langhorne J., Meding S. J., Eichmann K., Gillard S. S. The response of CD4+ T cells to Plasmodium chabaudi chabaudi. Immunol Rev. 1989 Dec;112:71–94. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1989.tb00553.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le J., Vilcek J. Tumor necrosis factor and interleukin 1: cytokines with multiple overlapping biological activities. Lab Invest. 1987 Mar;56(3):234–248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li H., Jerrells T. R., Spitalny G. L., Walker D. H. Gamma interferon as a crucial host defense against Rickettsia conorii in vivo. Infect Immun. 1987 May;55(5):1252–1255. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.5.1252-1255.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magee D. M., Wing E. J. Secretion of colony-stimulating factors by T cell clones. Role in adoptive protection against Listeria monocytogenes. J Immunol. 1989 Oct 1;143(7):2336–2341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray H. W. Interferon-gamma, the activated macrophage, and host defense against microbial challenge. Ann Intern Med. 1988 Apr;108(4):595–608. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-108-4-595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nacy C. A., Fortier A. H., Meltzer M. S., Buchmeier N. A., Schreiber R. D. Macrophage activation to kill Leishmania major: activation of macrophages for intracellular destruction of amastigotes can be induced by both recombinant interferon-gamma and non-interferon lymphokines. J Immunol. 1985 Nov;135(5):3505–3511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakane A., Minagawa T., Kato K. Endogenous tumor necrosis factor (cachectin) is essential to host resistance against Listeria monocytogenes infection. Infect Immun. 1988 Oct;56(10):2563–2569. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.10.2563-2569.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ockenhouse C. F., Schulman S., Shear H. L. Induction of crisis forms in the human malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum by gamma-interferon-activated, monocyte-derived macrophages. J Immunol. 1984 Sep;133(3):1601–1608. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ockenhouse C. F., Shear H. L. Oxidative killing of the intraerythrocytic malaria parasite Plasmodium yoelii by activated macrophages. J Immunol. 1984 Jan;132(1):424–431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parke L. M., Long C. A., Weidanz W. P. A method for freeing murine plasmodia of contaminating lactate dehydrogenase elevating virus. J Parasitol. 1986 Dec;72(6):956–958. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed S. G., Nathan C. F., Pihl D. L., Rodricks P., Shanebeck K., Conlon P. J., Grabstein K. H. Recombinant granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor activates macrophages to inhibit Trypanosoma cruzi and release hydrogen peroxide. Comparison with interferon gamma. J Exp Med. 1987 Dec 1;166(6):1734–1746. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.6.1734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadick M. D., Heinzel F. P., Holaday B. J., Pu R. T., Dawkins R. S., Locksley R. M. Cure of murine leishmaniasis with anti-interleukin 4 monoclonal antibody. Evidence for a T cell-dependent, interferon gamma-independent mechanism. J Exp Med. 1990 Jan 1;171(1):115–127. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.1.115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shear H. L., Srinivasan R., Nolan T., Ng C. Role of IFN-gamma in lethal and nonlethal malaria in susceptible and resistant murine hosts. J Immunol. 1989 Sep 15;143(6):2038–2044. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slade S. J., Langhorne J. Production of interferon-gamma during infection of mice with Plasmodium chabaudi chabaudi. Immunobiology. 1989 Oct;179(4-5):353–365. doi: 10.1016/S0171-2985(89)80041-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spitalny G. L., Havell E. A. Monoclonal antibody to murine gamma interferon inhibits lymphokine-induced antiviral and macrophage tumoricidal activities. J Exp Med. 1984 May 1;159(5):1560–1565. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.5.1560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squires K. E., Schreiber R. D., McElrath M. J., Rubin B. Y., Anderson S. L., Murray H. W. Experimental visceral leishmaniasis: role of endogenous IFN-gamma in host defense and tissue granulomatous response. J Immunol. 1989 Dec 15;143(12):4244–4249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson M. M., Ghadirian E. Human recombinant tumor necrosis factor alpha protects susceptible A/J mice against lethal Plasmodium chabaudi AS infection. Infect Immun. 1989 Dec;57(12):3936–3939. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.12.3936-3939.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson M. M., Ghadirian E., Phillips N. C., Rae D., Podoba J. E. Role of mononuclear phagocytes in elimination of Plasmodium chabaudi AS infection. Parasite Immunol. 1989 Sep;11(5):529–544. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1989.tb00687.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson M. M., Lyanga J. J., Skamene E. Murine malaria: genetic control of resistance to Plasmodium chabaudi. Infect Immun. 1982 Oct;38(1):80–88. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.1.80-88.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki Y., Orellana M. A., Schreiber R. D., Remington J. S. Interferon-gamma: the major mediator of resistance against Toxoplasma gondii. Science. 1988 Apr 22;240(4851):516–518. doi: 10.1126/science.3128869. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Troye-Blomberg M., Andersson G., Stoczkowska M., Shabo R., Romero P., Patarroyo M. E., Wigzell H., Perlmann P. Production of IL 2 and IFN-gamma by T cells from malaria patients in response to Plasmodium falciparum or erythrocyte antigens in vitro. J Immunol. 1985 Nov;135(5):3498–3504. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unanue E. R. Antigen-presenting function of the macrophage. Annu Rev Immunol. 1984;2:395–428. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.02.040184.002143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Rooijen N. The liposome-mediated macrophage 'suicide' technique. J Immunol Methods. 1989 Nov 13;124(1):1–6. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(89)90178-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weidanz W. P., Long C. A. The role of T cells in immunity to malaria. Prog Allergy. 1988;41:215–252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyler D. J., Beller D. I., Sypek J. P. Macrophage activation for antileishmanial defense by an apparently novel mechanism. J Immunol. 1987 Feb 15;138(4):1246–1249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhong G. M., Peterson E. M., Czarniecki C. W., Schreiber R. D., de la Maza L. M. Role of endogenous gamma interferon in host defense against Chlamydia trachomatis infections. Infect Immun. 1989 Jan;57(1):152–157. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.1.152-157.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Meide P. H., Dubbeld M., Vijverberg K., Kos T., Schellekens H. The purification and characterization of rat gamma interferon by use of two monoclonal antibodies. J Gen Virol. 1986 Jun;67(Pt 6):1059–1071. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-6-1059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



