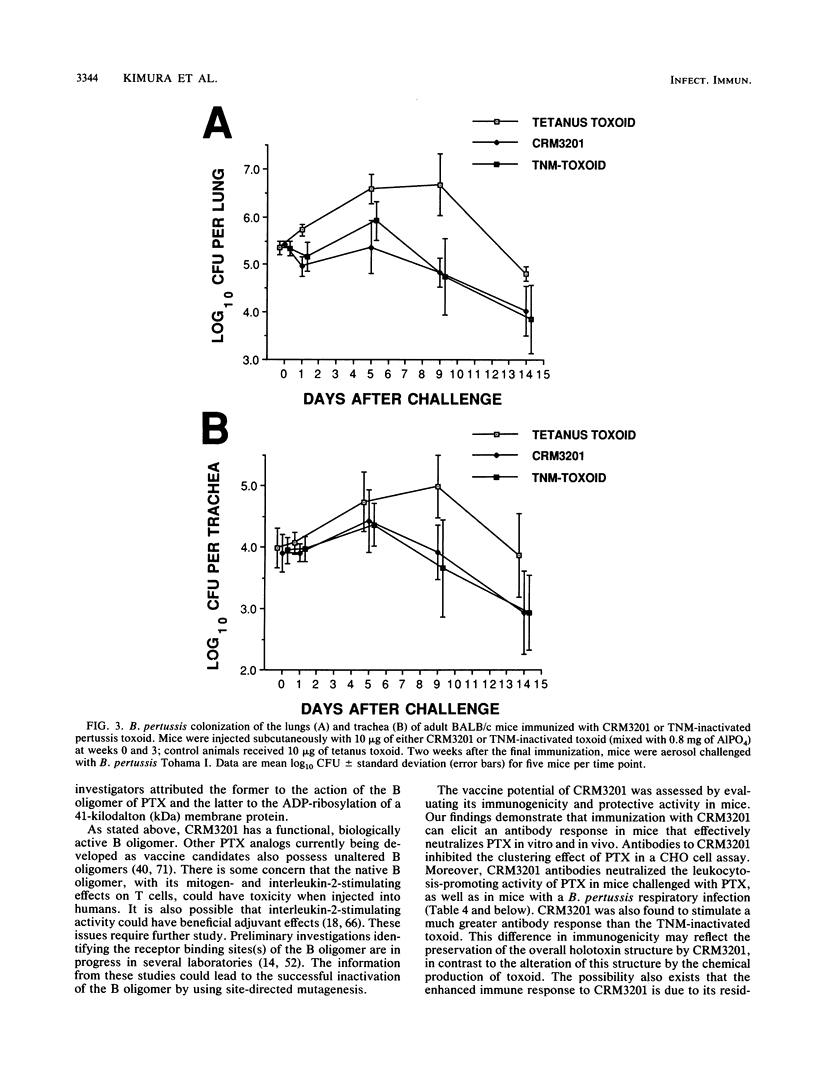
Abstract
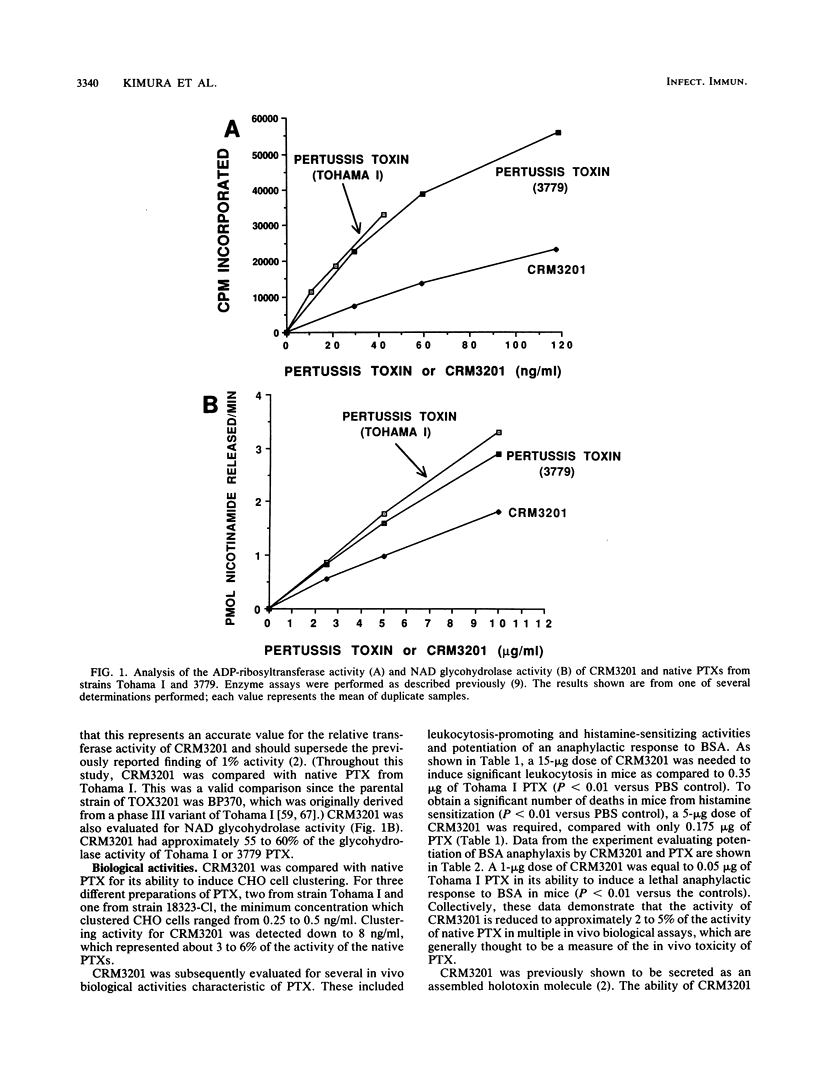
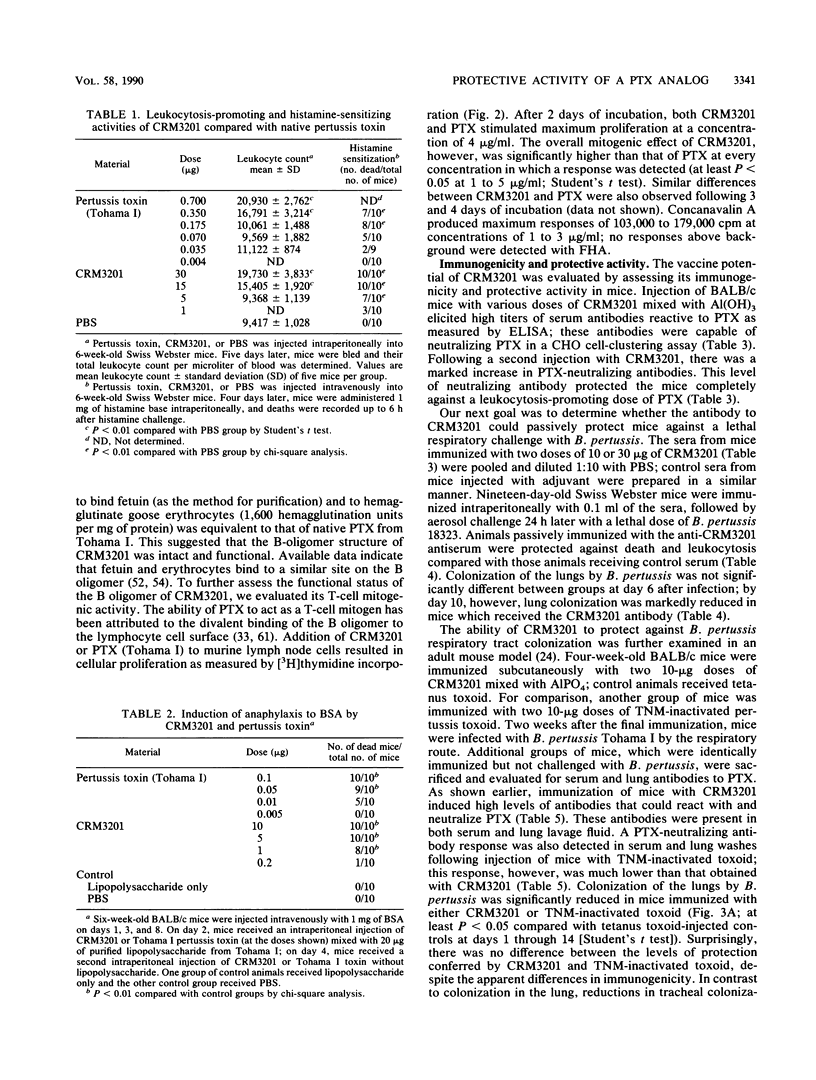
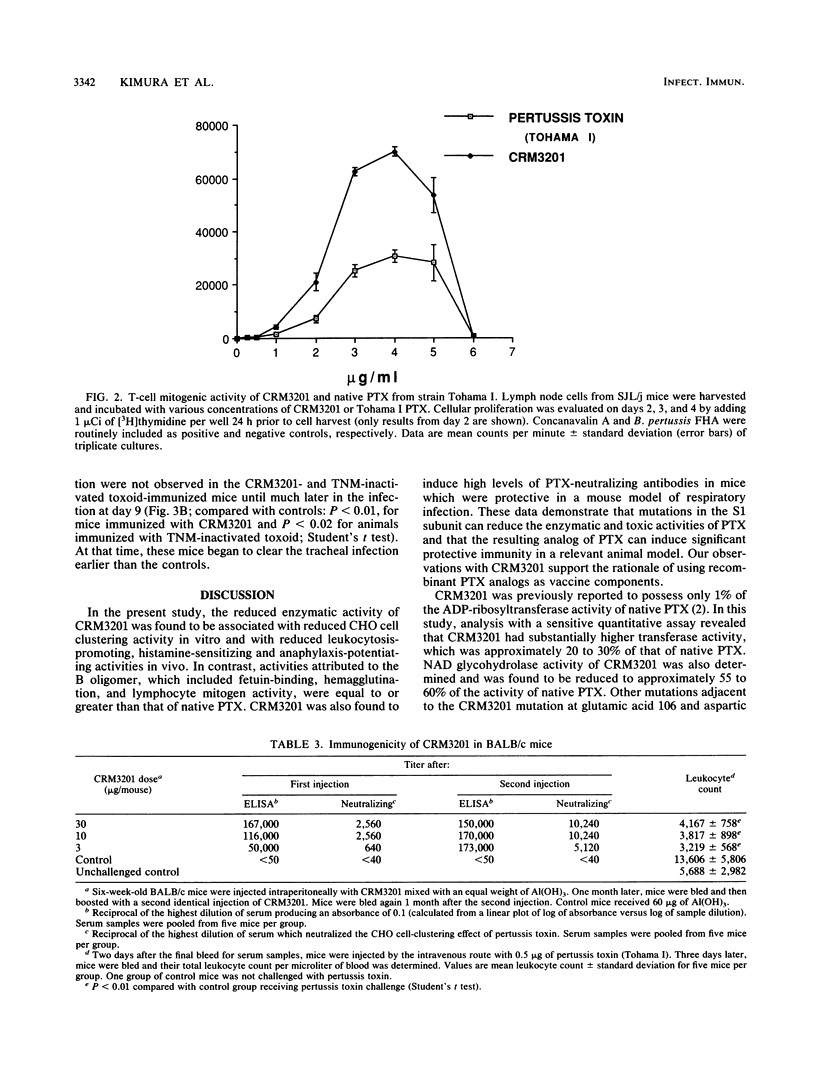
Bordetella pertussis TOX3201 has a 12-base-pair insertion in the S1 subunit gene of pertussis toxin (PTX), which encodes for a 4-amino-acid insertion between residues 107 and 108 of the mature S1 subunit (Black et al., Science 240:656-659, 1988). This mutant strain has been shown to secrete a holotoxin analog of PTX, designated CRM3201, with reduced ADP-ribosyltransferase activity. In the present study, we evaluated the biochemical, biological, and immunoprotective activities of purified CRM3201. Assay of enzymatic activities showed that CRM3201 had 20 to 30% of the ADP-ribosyltransferase activity and 55 to 60% of the NAD glycohydrolase activity of native PTX. CRM3201, however, had only 2 to 6% of the activity of PTX in clustering CHO cells, promoting leukocytosis, inducing histamine sensitization, and potentiating an anaphylactic response to bovine serum albumin. In contrast, activities associated with the B oligomer (binding to fetuin, hemagglutination of goose erythrocytes, and lymphocyte mitogen activity) were comparable to those of native PTX. Injection of BALB/c mice with CRM3201 mixed with Al(OH)3 elicited high titers of antibody to PTX (as measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay), which neutralized a leukocytosis-promoting dose of PTX in these mice and neutralized PTX in a CHO cell assay. Passive transfer of the anti-CRM3201 antibody protected 20-day-old Swiss-Webster mice against a lethal aerosol challenge with B. pertussis 18323. Active immunization with CRM3201 significantly reduced lung colonization in adult BALB/c mice with a B. pertussis respiratory infection. These results demonstrate (i) that the reduced ADP-ribosyltransferase activity of CRM3201 is associated with reductions in certain biological and toxic activities of PTX (the enzymatic and biological activities are not, however, totally concordant); (ii) that CRM3201 possesses a functional B oligomer; and (iii) that CRM3201 can induce toxin-neutralizing antibodies which protect mice against a respiratory challenge with B. pertussis. Our studies with CRM3201 show that recombinant analogs of PTX have the potential to be developed into safe, protective immunogens for use in new acellular pertussis vaccines.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Black W. J., Munoz J. J., Peacock M. G., Schad P. A., Cowell J. L., Burchall J. J., Lim M., Kent A., Steinman L., Falkow S. ADP-ribosyltransferase activity of pertussis toxin and immunomodulation by Bordetella pertussis. Science. 1988 Apr 29;240(4852):656–659. doi: 10.1126/science.2896387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bokoch G. M., Katada T., Northup J. K., Hewlett E. L., Gilman A. G. Identification of the predominant substrate for ADP-ribosylation by islet activating protein. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2072–2075. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N., Cieplak W., Mar V. L., Kaljot K. T., Sato H., Keith J. M. Pertussis toxin S1 mutant with reduced enzyme activity and a conserved protective epitope. Science. 1988 Oct 7;242(4875):72–74. doi: 10.1126/science.2459776. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chedid M., Shirakawa F., Naylor P., Mizel S. B. Signal transduction pathway for IL-1. Involvement of a pertussis toxin-sensitive GTP-binding protein in the activation of adenylate cyclase. J Immunol. 1989 Jun 15;142(12):4301–4306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheers C., Gray D. F. Macrophage behaviour during the complaisant phase of murine pertussis. Immunology. 1969 Dec;17(6):875–887. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherry J. D. The epidemiology of pertussis and pertussis immunization in the United Kingdom and the United States: a comparative study. Curr Probl Pediatr. 1984 Feb;14(2):1–78. doi: 10.1016/0045-9380(84)90016-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cieplak W., Burnette W. N., Mar V. L., Kaljot K. T., Morris C. F., Chen K. K., Sato H., Keith J. M. Identification of a region in the S1 subunit of pertussis toxin that is required for enzymatic activity and that contributes to the formation of a neutralizing antigenic determinant. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(13):4667–4671. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.13.4667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cody C. L., Baraff L. J., Cherry J. D., Marcy S. M., Manclark C. R. Nature and rates of adverse reactions associated with DTP and DT immunizations in infants and children. Pediatrics. 1981 Nov;68(5):650–660. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eidels L., Proia R. L., Hart D. A. Membrane receptors for bacterial toxins. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Dec;47(4):596–620. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.4.596-620.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fine P. E., Clarkson J. A. Reflections on the efficacy of pertussis vaccines. Rev Infect Dis. 1987 Sep-Oct;9(5):866–883. doi: 10.1093/clinids/9.5.866. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fish F., Cowell J. L., Manclark C. R. Proliferative response of immune mouse T-lymphocytes to the lymphocytosis-promoting factor of Bordetella pertussis. Infect Immun. 1984 Apr;44(1):1–6. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.1.1-6.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillenius P., Jätmaa E., Askelöf P., Granström M., Tiru M. The standardization of an assay for pertussis toxin and antitoxin in microplate culture of Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Biol Stand. 1985 Jan;13(1):61–66. doi: 10.1016/s0092-1157(85)80034-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore W., Weiner L. P. The effects of pertussis toxin and cholera toxin on mitogen-induced interleukin-2 production: evidence for G protein involvement in signal transduction. Cell Immunol. 1988 May;113(2):235–250. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(88)90023-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold R. Pertussis and pertussis vaccine. Can Med Assoc J. 1985 May 1;132(9):1043–1044. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Good M. F., Pombo D., Lunde M. N., Maloy W. L., Halenbeck R., Koths K., Miller L. H., Berzofsky J. A. Recombinant human IL-2 overcomes genetic nonresponsiveness to malaria sporozoite peptides. Correlation of effect with biologic activity of IL-2. J Immunol. 1988 Aug 1;141(3):972–977. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray L. S., Huber K. S., Gray M. C., Hewlett E. L., Engelhard V. H. Pertussis toxin effects on T lymphocytes are mediated through CD3 and not by pertussis toxin catalyzed modification of a G protein. J Immunol. 1989 Mar 1;142(5):1631–1638. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewlett E. L., Cowell J. L. Evaluation of the mouse model for study of encephalopathy in pertussis vaccine recipients. Infect Immun. 1989 Mar;57(3):661–663. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.3.661-663.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewlett E. L., Sauer K. T., Myers G. A., Cowell J. L., Guerrant R. L. Induction of a novel morphological response in Chinese hamster ovary cells by pertussis toxin. Infect Immun. 1983 Jun;40(3):1198–1203. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.3.1198-1203.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson K. G., Perry M. B. Improved techniques for the preparation of bacterial lipopolysaccharides. Can J Microbiol. 1976 Jan;22(1):29–34. doi: 10.1139/m76-004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katada T., Ui M. Direct modification of the membrane adenylate cyclase system by islet-activating protein due to ADP-ribosylation of a membrane protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(10):3129–3133. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.10.3129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura A., Mountzouros K. T., Relman D. A., Falkow S., Cowell J. L. Bordetella pertussis filamentous hemagglutinin: evaluation as a protective antigen and colonization factor in a mouse respiratory infection model. Infect Immun. 1990 Jan;58(1):7–16. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.1.7-16.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Locht C., Capiau C., Feron C. Identification of amino acid residues essential for the enzymatic activities of pertussis toxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(9):3075–3079. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.9.3075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meade B. D., Kind P. D., Ewell J. B., McGrath P. P., Manclark C. R. In vitro inhibition of murine macrophage migration by Bordetella pertussis lymphocytosis-promoting factor. Infect Immun. 1984 Sep;45(3):718–725. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.3.718-725.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meade B. D., Kind P. D., Manclark C. R. Lymphocytosis-promoting factor of Bordetella pertussis alters mononuclear phagocyte circulation and response to inflammation. Infect Immun. 1984 Dec;46(3):733–739. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.3.733-739.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller D. L., Ross E. M., Alderslade R., Bellman M. H., Rawson N. S. Pertussis immunisation and serious acute neurological illness in children. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1981 May 16;282(6276):1595–1599. doi: 10.1136/bmj.282.6276.1595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizel S. B. The interleukins. FASEB J. 1989 Oct;3(12):2379–2388. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.3.12.2676681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munoz J. J., Arai H., Bergman R. K., Sadowski P. L. Biological activities of crystalline pertussigen from Bordetella pertussis. Infect Immun. 1981 Sep;33(3):820–826. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.3.820-826.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munoz J. J., Arai H., Cole R. L. Mouse-protecting and histamine-sensitizing activities of pertussigen and fimbrial hemagglutinin from Bordetella pertussis. Infect Immun. 1981 Apr;32(1):243–250. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.1.243-250.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munoz J. J., Peacock M. G. Role of pertussigen (pertussis toxin) on the mouse protective activity of vaccines made from Bordetella species. Microbiol Immunol. 1989;33(4):341–355. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1989.tb01982.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nogimori K., Tamura M., Yajima M., Hashimura N., Ishii S., Ui M. Structure-function relationship of islet-activating protein, pertussis toxin: biological activities of hybrid toxins reconstituted from native and methylated subunits. Biochemistry. 1986 Mar 25;25(6):1355–1363. doi: 10.1021/bi00354a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nogimori K., Tamura M., Yajima M., Ito K., Nakamura T., Kajikawa N., Maruyama Y., Ui M. Dual mechanisms involved in development of diverse biological activities of islet-activating protein, pertussis toxin, as revealed by chemical modification of lysine residues in the toxin molecule. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Sep 28;801(2):232–243. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(84)90072-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oda M., Cowell J. L., Burstyn D. G., Manclark C. R. Protective activities of the filamentous hemagglutinin and the lymphocytosis-promoting factor of Bordetella pertussis in mice. J Infect Dis. 1984 Dec;150(6):823–833. doi: 10.1093/infdis/150.6.823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olin P., Storsaeter J., Romanus V. The efficacy of acellular pertussis vaccine. JAMA. 1989 Jan 27;261(4):560–560. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson G. L. A simplification of the protein assay method of Lowry et al. which is more generally applicable. Anal Biochem. 1977 Dec;83(2):346–356. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittman M. The concept of pertussis as a toxin-mediated disease. Pediatr Infect Dis. 1984 Sep-Oct;3(5):467–486. doi: 10.1097/00006454-198409000-00019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pizza M., Bartoloni A., Prugnola A., Silvestri S., Rappuoli R. Subunit S1 of pertussis toxin: mapping of the regions essential for ADP-ribosyltransferase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(20):7521–7525. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.20.7521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quentin-Millet M. J., Arminjon F., Danve B., Cadoz M., Armand J. Acellular pertussis vaccines: evaluation of reversion in a nude mouse model. J Biol Stand. 1988 Apr;16(2):99–108. doi: 10.1016/0092-1157(88)90037-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redhead K., Robinson A., Ashworth L. A., Melville-Smith M. The activity of purified Bordetella pertussis components in murine encephalopathy. J Biol Stand. 1987 Oct;15(4):341–351. doi: 10.1016/s0092-1157(87)80007-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson A., Ashworth L. A., Baskerville A., Irons L. I. Protection against intranasal infection of mice with Bordetella pertussis. Dev Biol Stand. 1985;61:165–172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson A., Irons L. I., Ashworth L. A. Pertussis vaccine: present status and future prospects. Vaccine. 1985 Mar;3(1):11–22. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(85)90004-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson A., Irons L. I. Synergistic effect of Bordetella pertussis lymphocytosis-promoting factor on protective activities of isolated Bordetella antigens in mice. Infect Immun. 1983 May;40(2):523–528. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.2.523-528.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato H., Sato Y. Bordetella pertussis infection in mice: correlation of specific antibodies against two antigens, pertussis toxin, and filamentous hemagglutinin with mouse protectivity in an intracerebral or aerosol challenge system. Infect Immun. 1984 Nov;46(2):415–421. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.2.415-421.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato Y., Cowell J. L., Sato H., Burstyn D. G., Manclark C. R. Separation and purification of the hemagglutinins from Bordetella pertussis. Infect Immun. 1983 Jul;41(1):313–320. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.1.313-320.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato Y., Izumiya K., Sato H., Cowell J. L., Manclark C. R. Aerosol infection of mice with Bordetella pertussis. Infect Immun. 1980 Jul;29(1):261–266. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.1.261-266.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato Y., Izumiya K., Sato H., Cowell J. L., Manclark C. R. Role of antibody to leukocytosis-promoting factor hemagglutinin and to filamentous hemagglutinin in immunity to pertussis. Infect Immun. 1981 Mar;31(3):1223–1231. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.3.1223-1231.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato Y., Kimura M., Fukumi H. Development of a pertussis component vaccine in Japan. Lancet. 1984 Jan 21;1(8369):122–126. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)90061-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt M. A., Schmidt W. Inhibition of pertussis toxin binding to model receptors by antipeptide antibodies directed at an antigenic domain of the S2 subunit. Infect Immun. 1989 Dec;57(12):3828–3833. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.12.3828-3833.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekura R. D., Fish F., Manclark C. R., Meade B., Zhang Y. L. Pertussis toxin. Affinity purification of a new ADP-ribosyltransferase. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 10;258(23):14647–14651. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shahin R. D., Brennan M. J., Li Z. M., Meade B. D., Manclark C. R. Characterization of the protective capacity and immunogenicity of the 69-kD outer membrane protein of Bordetella pertussis. J Exp Med. 1990 Jan 1;171(1):63–73. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.1.63. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. K., Krohn R. I., Hermanson G. T., Mallia A. K., Gartner F. H., Provenzano M. D., Fujimoto E. K., Goeke N. M., Olson B. J., Klenk D. C. Measurement of protein using bicinchoninic acid. Anal Biochem. 1985 Oct;150(1):76–85. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90442-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spangrude G. J., Braaten B. A., Daynes R. A. Molecular mechanisms of lymphocyte extravasation. I. Studies of two selective inhibitors of lymphocyte recirculation. J Immunol. 1984 Jan;132(1):354–362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stibitz S., Black W., Falkow S. The construction of a cloning vector designed for gene replacement in Bordetella pertussis. Gene. 1986;50(1-3):133–140. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90318-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storsaeter J., Olin P., Renemar B., Lagergård T., Norberg R., Romanus V., Tiru M. Mortality and morbidity from invasive bacterial infections during a clinical trial of acellular pertussis vaccines in Sweden. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1988 Sep;7(9):637–645. doi: 10.1097/00006454-198809000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura M., Nogimori K., Yajima M., Ase K., Ui M. A role of the B-oligomer moiety of islet-activating protein, pertussis toxin, in development of the biological effects on intact cells. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 10;258(11):6756–6761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trollfors B., Rabo E. Whooping cough in adults. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1981 Sep 12;283(6293):696–697. doi: 10.1136/bmj.283.6293.696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuomanen E., Weiss A. Characterization of two adhesins of Bordetella pertussis for human ciliated respiratory-epithelial cells. J Infect Dis. 1985 Jul;152(1):118–125. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.1.118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuomanen E., Weiss A., Rich R., Zak F., Zak O. Filamentous hemagglutinin and pertussis toxin promote adherence of Bordetella pertussis to cilia. Dev Biol Stand. 1985;61:197–204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg A., Merigan T. C. Recombinant interleukin 2 as an adjuvant for vaccine-induced protection. Immunization of guinea pigs with herpes simplex virus subunit vaccines. J Immunol. 1988 Jan 1;140(1):294–299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A. A., Falkow S. Genetic analysis of phase change in Bordetella pertussis. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):263–269. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.263-269.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A. A., Goodwin M. S. Lethal infection by Bordetella pertussis mutants in the infant mouse model. Infect Immun. 1989 Dec;57(12):3757–3764. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.12.3757-3764.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A. A., Hewlett E. L., Myers G. A., Falkow S. Pertussis toxin and extracytoplasmic adenylate cyclase as virulence factors of Bordetella pertussis. J Infect Dis. 1984 Aug;150(2):219–222. doi: 10.1093/infdis/150.2.219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A. A., Hewlett E. L. Virulence factors of Bordetella pertussis. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1986;40:661–686. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.40.100186.003305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



