Abstract
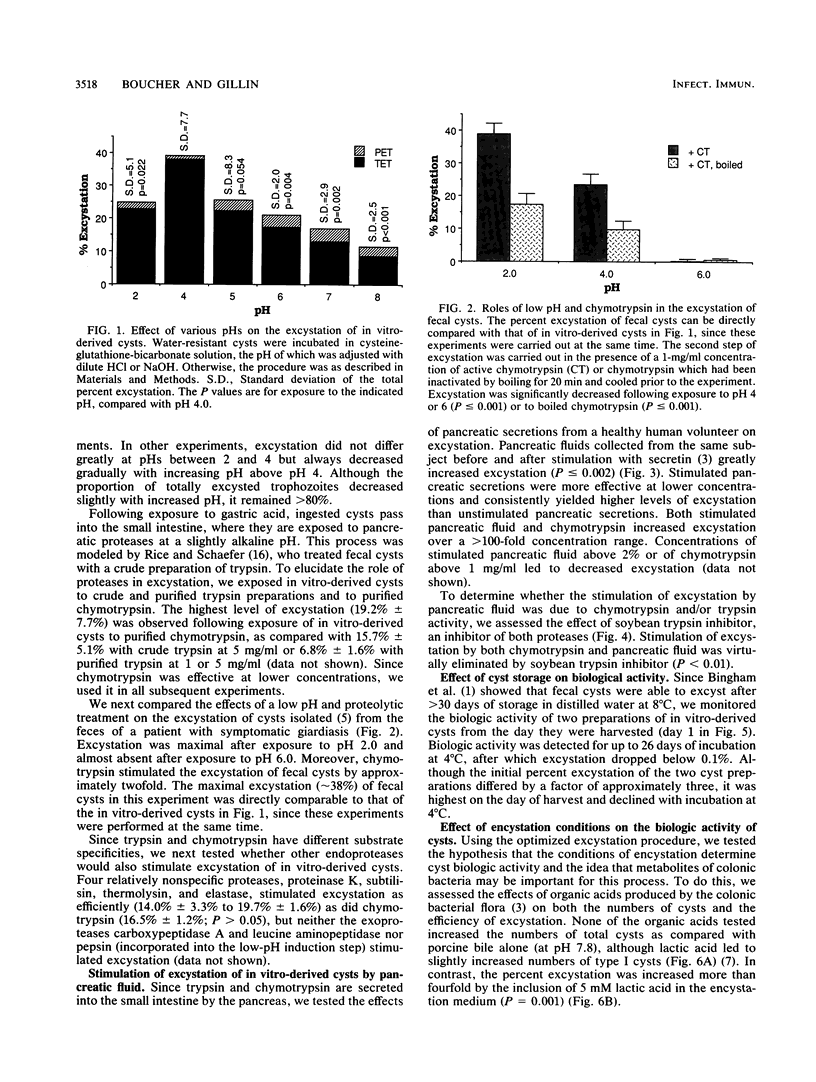
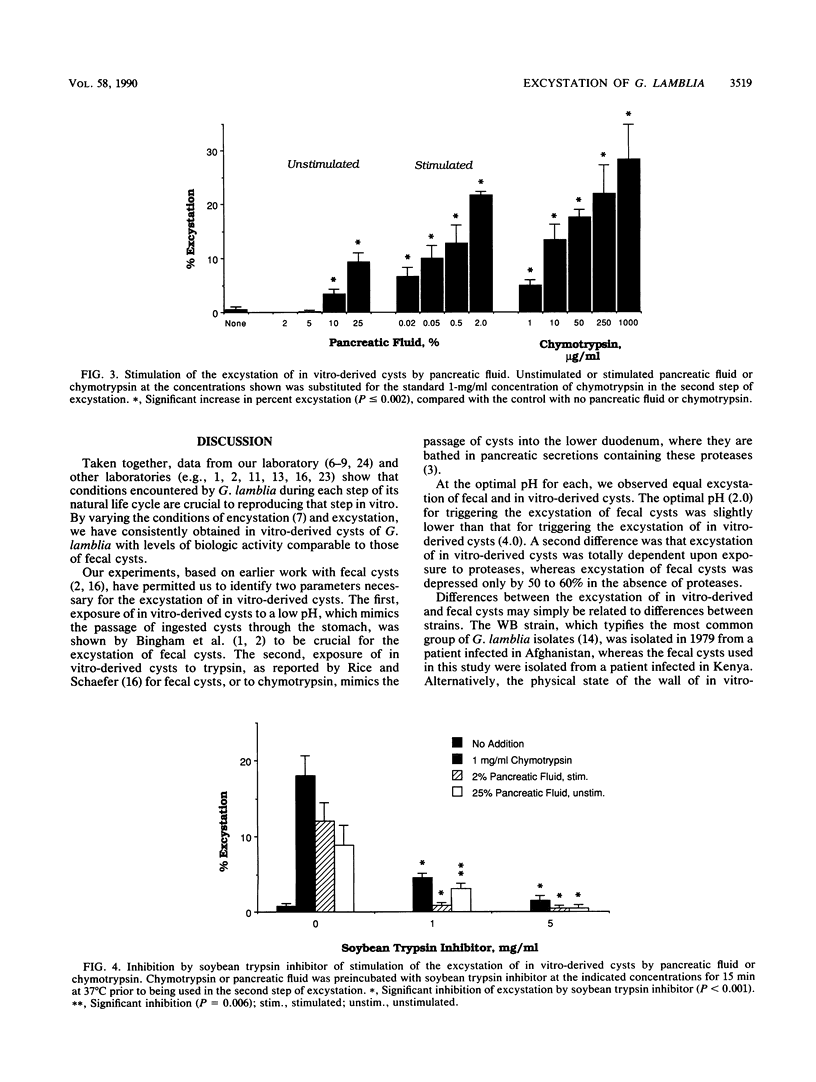
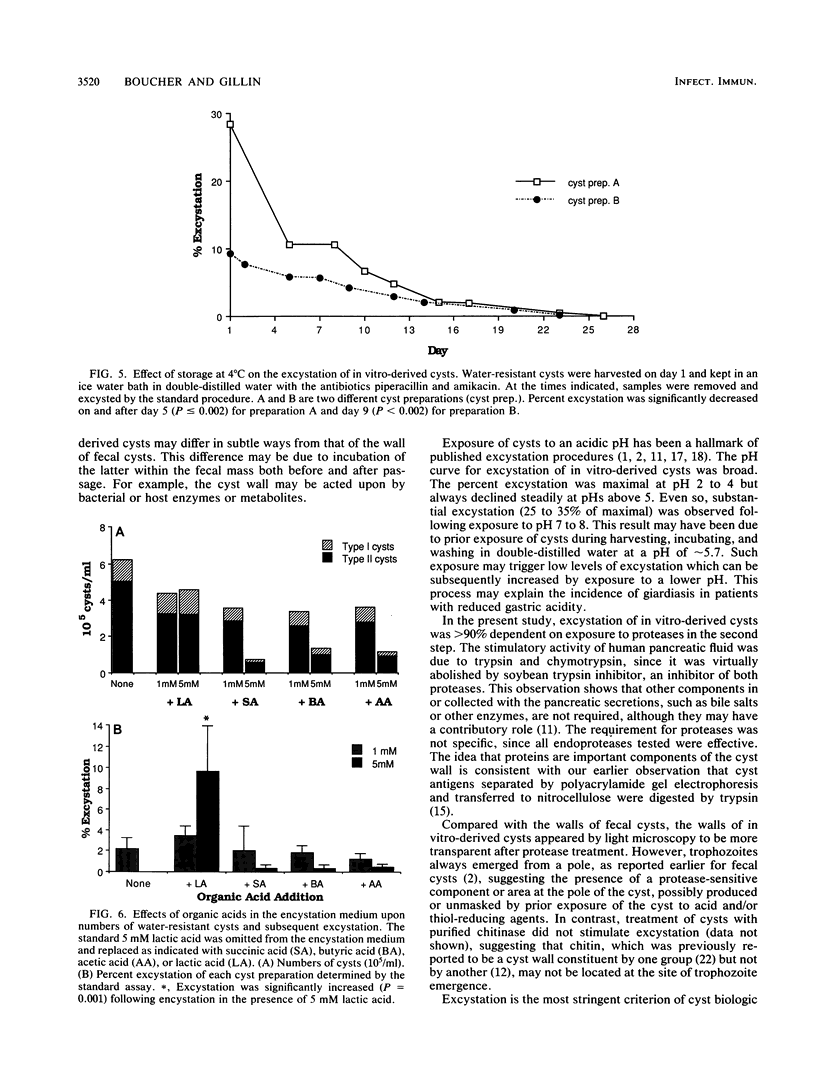
This is the first in-depth analysis of the excystation of Giardia lamblia cysts prepared in vitro. Its goals were both to achieve efficient excystation and to gain insights into this crucial but poorly understood process. To identify the critical elements of excystation, we tested the sequential low-pH induction and protease treatments which had been reported to be important for excystation of fecal cysts. The optimal pH for induction of excystation was 4.0. Emergence was greatly (approximately 10-fold) stimulated by subsequent exposure of in vitro-derived cysts to chymotrypsin, trypsin, or human pancreatic fluid. The stimulatory activity of each was abolished by soybean trypsin inhibitor, demonstrating that the activity of pancreatic fluid was due to these proteases. Excystation of in vitro-derived cysts was approximately 10 to 38%. Although the walls of in vitro-derived cysts were partially digested by protease treatment, trophozoites emerged only from one pole, as observed with fecal cysts. The conditions of encystation also determined the efficiency of excystation. Specifically, encystation in the presence of lactic acid, a major metabolite of colonic bacteria, stimulated excystation approximately fourfold, although it did not increase the total numbers of cysts. These experiments have shown that excystation of in vitro-derived cysts reflects that of cysts purified from human feces in that it is dependent upon conditions which simulate the passage of cysts through the human stomach (low pH) and into the small intestine (pancreatic proteases).
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bingham A. K., Jarroll E. L., Jr, Meyer E. A., Radulescu S. Giardia sp.: physical factors of excystation in vitro, and excystation vs eosin exclusion as determinants of viability. Exp Parasitol. 1979 Apr;47(2):284–291. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(79)90080-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bingham A. K., Meyer E. A. Giardia excystation can be induced in vitro in acidic solutions. Nature. 1979 Jan 25;277(5694):301–302. doi: 10.1038/277301a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond L. S., Harlow D. R., Cunnick C. C. A new medium for the axenic cultivation of Entamoeba histolytica and other Entamoeba. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1978;72(4):431–432. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(78)90144-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas H., Reiner D. S., Gillin F. D. A new method for purification of Giardia lamblia cysts. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1987;81(2):315–316. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(87)90250-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillin F. D., Boucher S. E., Rossi S. S., Reiner D. S. Giardia lamblia: the roles of bile, lactic acid, and pH in the completion of the life cycle in vitro. Exp Parasitol. 1989 Aug;69(2):164–174. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(89)90185-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillin F. D., Reiner D. S., Boucher S. E. Small-intestinal factors promote encystation of Giardia lamblia in vitro. Infect Immun. 1988 Mar;56(3):705–707. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.3.705-707.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillin F. D., Reiner D. S., Gault M. J., Douglas H., Das S., Wunderlich A., Sauch J. F. Encystation and expression of cyst antigens by Giardia lamblia in vitro. Science. 1987 Feb 27;235(4792):1040–1043. doi: 10.1126/science.3547646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann A. F., Roda A. Physicochemical properties of bile acids and their relationship to biological properties: an overview of the problem. J Lipid Res. 1984 Dec 15;25(13):1477–1489. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaac-Renton J., Proctor E. M., Prameya R., Wong Q. A method of excystation and culture of Giardia lamblia. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1986;80(6):989–990. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(86)90281-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarroll E. L., Manning P., Lindmark D. G., Coggins J. R., Erlandsen S. L. Giardia cyst wall-specific carbohydrate: evidence for the presence of galactosamine. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1989 Jan 15;32(2-3):121–131. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(89)90063-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keister D. B. Axenic culture of Giardia lamblia in TYI-S-33 medium supplemented with bile. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1983;77(4):487–488. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(83)90120-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash T. E., McCutchan T., Keister D., Dame J. B., Conrad J. D., Gillin F. D. Restriction-endonuclease analysis of DNA from 15 Giardia isolates obtained from humans and animals. J Infect Dis. 1985 Jul;152(1):64–73. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.1.64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiner D. S., Douglas H., Gillin F. D. Identification and localization of cyst-specific antigens of Giardia lamblia. Infect Immun. 1989 Mar;57(3):963–968. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.3.963-968.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice E. W., Schaefer F. W., 3rd Improved in vitro excystation procedure for Giardia lamblia cysts. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Dec;14(6):709–710. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.6.709-710.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schupp D. G., Erlandsen S. L. A new method to determine Giardia cyst viability: correlation of fluorescein diacetate and propidium iodide staining with animal infectivity. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Apr;53(4):704–707. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.4.704-707.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schupp D. G., Januschka M. M., Sherlock L. A., Stibbs H. H., Meyer E. A., Bemrick W. J., Erlandsen S. L. Production of viable Giardia cysts in vitro: determination by fluorogenic dye staining, excystation, and animal infectivity in the mouse and Mongolian gerbil. Gastroenterology. 1988 Jul;95(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(88)90283-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward H. D., Alroy J., Lev B. I., Keusch G. T., Pereira M. E. Identification of chitin as a structural component of Giardia cysts. Infect Immun. 1985 Sep;49(3):629–634. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.3.629-634.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward H. D., Lev B. I., Kane A. V., Keusch G. T., Pereira M. E. Identification and characterization of taglin, a mannose 6-phosphate binding, trypsin-activated lectin from Giardia lamblia. Biochemistry. 1987 Dec 29;26(26):8669–8675. doi: 10.1021/bi00400a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zenian A., Gillin F. D. Interactions of Giardia lamblia with human intestinal mucus: enhancement of trophozoite attachment to glass. J Protozool. 1985 Nov;32(4):664–668. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1985.tb03098.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



