Abstract
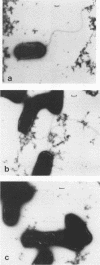
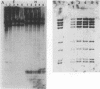
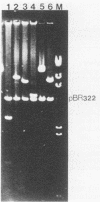
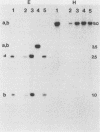
The species Vibrio cholerae contains within it two biotypes, classical and El Tor, both of which are motile. Phenotypic expression of motility was unaffected by type of growth medium, salt concentration, pH, or temperature of incubation. However, seven strains of classical V. cholerae produced spontaneous nonmotile mutants at an unusually high frequency (ca. 10(-4)), while no mutants were detected for all three El Tor strains examined. No revertants of these nonmotile mutants were detected. Four independent mutants of classical strain 395 were isolated to characterize this phenomenon. By transmission electron microscopy, one of the nonmotile mutants was found to be flagellated, while the other three were found to be aflagellate. Chromosomal DNA from the mutants and parental wild-type strain 395 was examined by Southern blot analysis with, as probes, V. cholerae mutagenic prophages VcA-1 and VcA-2 and six cloned motility gene regions isolated from transposon insertion motility mutants of strains 395 and N16961 (El Tor, Inaba). The parental wild-type strain and all of the mutants exhibited the same pattern of bands when probed with VcA-1 and VcA-2 DNAs. Four of the cloned motility gene regions hybridized to the same fragments of DNA in both the wild-type and mutant isolates. However, two other probes detected a new fragment for a single aflagellate mutant. The observations that spontaneous nonmotile mutants occurred at a high frequency and that these mutants did not revert at a detectable frequency suggested that a genetic event is involved. The phenomenon appears to be limited to classical V. cholerae and may explain why classical V. cholerae is only sporadically associated with disease in the current pandemic.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baselski V., Briggs R., Parker C. Intestinal fluid accumulation induced by oral challenge with Vibrio cholerae or cholera toxin in infant mice. Infect Immun. 1977 Mar;15(3):704–712. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.3.704-712.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell M. B., Guerry P., Lee E. C., Burans J. P., Walker R. I. Reversible expression of flagella in Campylobacter jejuni. Infect Immun. 1985 Dec;50(3):941–943. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.3.941-943.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook W. L., Wachsmuth K., Johnson S. R., Birkness K. A., Samadi A. R. Persistence of plasmids, cholera toxin genes, and prophage DNA in classical Vibrio cholerae O1. Infect Immun. 1984 Jul;45(1):222–226. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.1.222-226.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg S., Murphy J. R. Molecular epidemiological studies of United States Gulf Coast Vibrio cholerae strains: integration site of mutator vibriophage VcA-3. Infect Immun. 1983 Oct;42(1):224–230. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.1.224-230.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guentzel M. N., Berry L. J. Motility as a virulence factor for Vibrio cholerae. Infect Immun. 1975 May;11(5):890–897. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.5.890-897.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guidolin A., Manning P. A. Genetics of Vibrio cholerae and its bacteriophages. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Jun;51(2):285–298. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.2.285-298.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoopes B. C., McClure W. R. Studies on the selectivity of DNA precipitation by spermine. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Oct 24;9(20):5493–5504. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.20.5493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Kaper J. B., Herrington D., Losonsky G., Morris J. G., Clements M. L., Black R. E., Tall B., Hall R. Volunteer studies of deletion mutants of Vibrio cholerae O1 prepared by recombinant techniques. Infect Immun. 1988 Jan;56(1):161–167. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.1.161-167.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mekalanos J. J. Duplication and amplification of toxin genes in Vibrio cholerae. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):253–263. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90228-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mekalanos J. J., Moseley S. L., Murphy J. R., Falkow S. Isolation of enterotoxin structural gene deletion mutations in Vibrio cholerae induced by two mutagenic vibriophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(1):151–155. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.1.151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson K., Nixon L., Mostow P., Kaper J. B., Michalski J. Transposon-induced non-motile mutants of Vibrio cholerae. J Gen Microbiol. 1990 Apr;136(4):717–725. doi: 10.1099/00221287-136-4-717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sporecke I., Castro D., Mekalanos J. J. Genetic mapping of Vibrio cholerae enterotoxin structural genes. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jan;157(1):253–261. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.1.253-261.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stibitz S., Aaronson W., Monack D., Falkow S. Phase variation in Bordetella pertussis by frameshift mutation in a gene for a novel two-component system. Nature. 1989 Mar 16;338(6212):266–269. doi: 10.1038/338266a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Way J. C., Davis M. A., Morisato D., Roberts D. E., Kleckner N. New Tn10 derivatives for transposon mutagenesis and for construction of lacZ operon fusions by transposition. Gene. 1984 Dec;32(3):369–379. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90012-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A. A., Falkow S. Genetic analysis of phase change in Bordetella pertussis. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):263–269. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.263-269.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yancey R. J., Willis D. L., Berry L. J. Role of motility in experimental cholera in adult rabbits. Infect Immun. 1978 Nov;22(2):387–392. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.2.387-392.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]