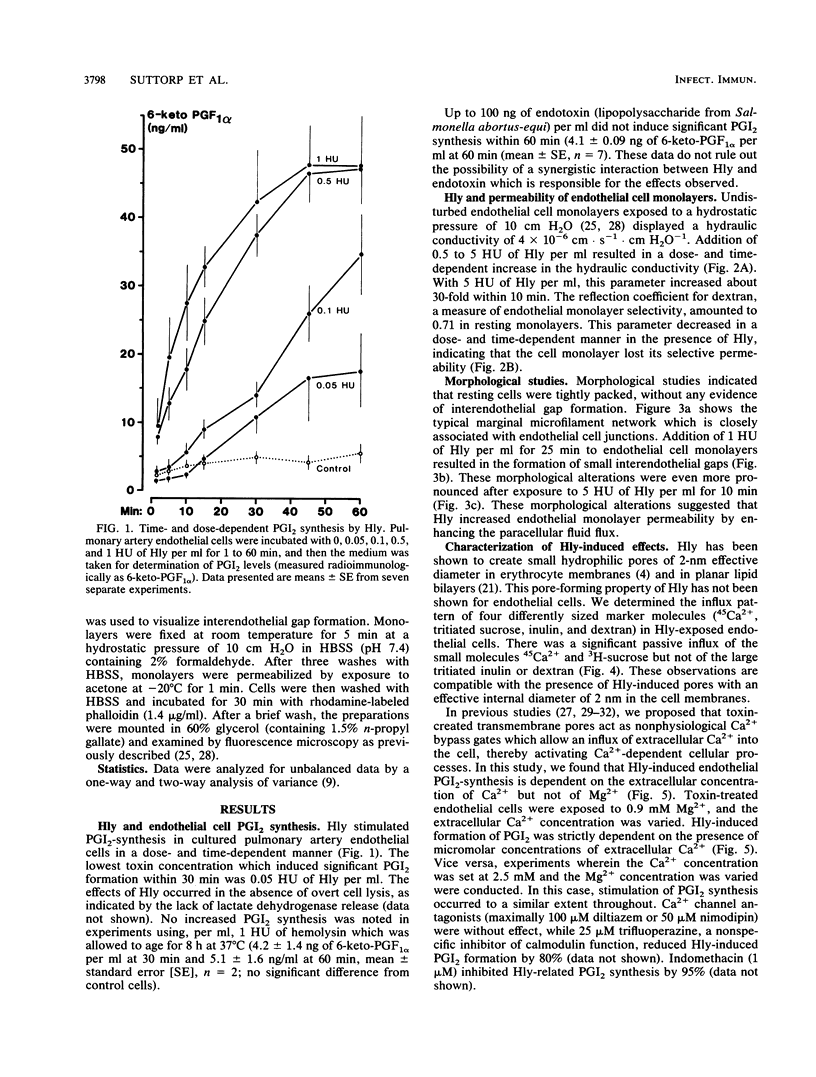
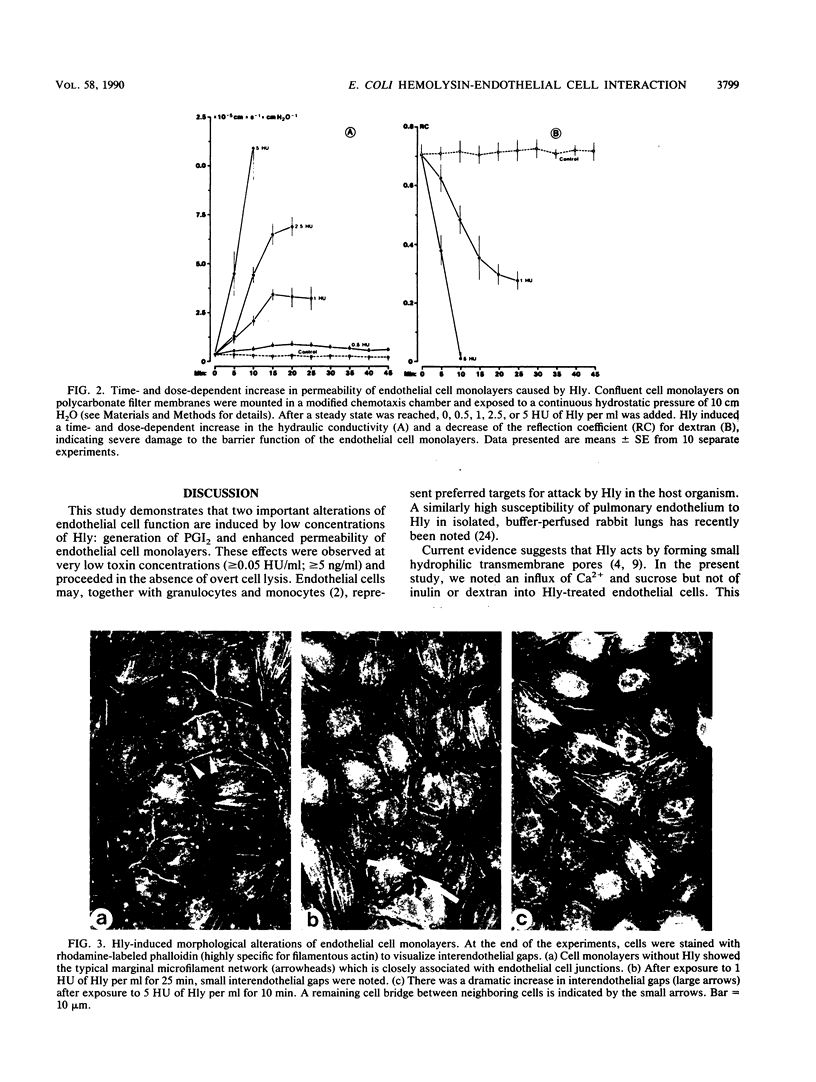
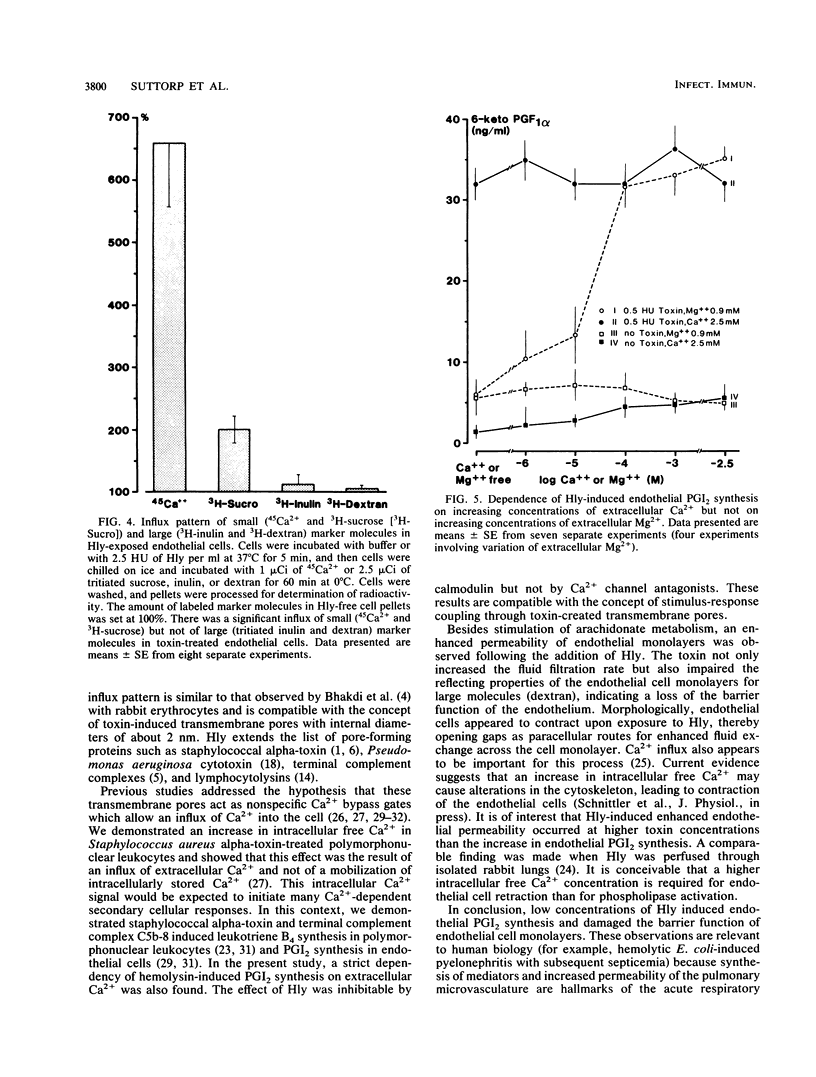
Abstract
Escherichia coli hemolysin is considered an important virulence factor in extraintestinal E. coli infections. The present study demonstrates that cultured pulmonary artery endothelial cells are susceptible to attack by low concentrations of E. coli hemolysin (greater than or equal to 0.05 hemolytic units/ml; greater than or equal to 5 ng/ml). Sublytic amounts of hemolysin increased the permeability of endothelial cell monolayers in a time- and dose-dependent manner. The hydraulic conductivity increased approximately 30-fold and the reflection coefficient for large molecules dropped from 0.71 to less than 0.05, indicating a toxin-induced loss of endothelial barrier function. The alterations of endothelial monolayer permeability were accompanied by cell retraction and interendothelial gap formation. In addition, E. coli hemolysin stimulated prostacyclin synthesis in endothelial cells. This effect was strictly dependent on the presence of extracellular Ca2+ but not of Mg2+. An enhanced passive influx of 45Ca2+ and 3H-sucrose but not of tritiated inulin and dextran was noted in toxin-treated cells, indicating that small transmembrane pores comparable to those detected in rabbit erythrocytes had been generated in endothelial cell membranes. These pores may act as nonphysiologic Ca2+ gates, thereby initiating different Ca2+-dependent cellular processes. We conclude that endothelial cells are highly susceptible to E. coli hemolysin and that two major endothelial cell functions are altered by very low concentrations of hemolysin.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bhakdi S., Füssle R., Tranum-Jensen J. Staphylococcal alpha-toxin: oligomerization of hydrophilic monomers to form amphiphilic hexamers induced through contact with deoxycholate detergent micelles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5475–5479. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Greulich S., Muhly M., Eberspächer B., Becker H., Thiele A., Hugo F. Potent leukocidal action of Escherichia coli hemolysin mediated by permeabilization of target cell membranes. J Exp Med. 1989 Mar 1;169(3):737–754. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.3.737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Mackman N., Menestrina G., Gray L., Hugo F., Seeger W., Holland I. B. The hemolysin of Escherichia coli. Eur J Epidemiol. 1988 Jun;4(2):135–143. doi: 10.1007/BF00144740. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Mackman N., Nicaud J. M., Holland I. B. Escherichia coli hemolysin may damage target cell membranes by generating transmembrane pores. Infect Immun. 1986 Apr;52(1):63–69. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.1.63-69.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Tranum-Jensen J. Damage to mammalian cells by proteins that form transmembrane pores. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1987;107:147–223. doi: 10.1007/BFb0027646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Tranum-Jensen J. Mechanism of complement cytolysis and the concept of channel-forming proteins. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1984 Sep 6;306(1129):311–324. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1984.0092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brigham K. L., Meyrick B. Endotoxin and lung injury. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1986 May;133(5):913–927. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavalieri S. J., Bohach G. A., Snyder I. S. Escherichia coli alpha-hemolysin: characteristics and probable role in pathogenicity. Microbiol Rev. 1984 Dec;48(4):326–343. doi: 10.1128/mr.48.4.326-343.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eberspächer B., Hugo F., Bhakdi S. Quantitative study of the binding and hemolytic efficiency of Escherichia coli hemolysin. Infect Immun. 1989 Mar;57(3):983–988. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.3.983-988.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felmlee T., Pellett S., Welch R. A. Nucleotide sequence of an Escherichia coli chromosomal hemolysin. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jul;163(1):94–105. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.1.94-105.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friberger P., Knös M., Mellstam L. A quantitative endotoxin assay utilizing LAL and a chromogenic substrate. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1982;93:195–206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hacker J., Hughes C., Hof H., Goebel W. Cloned hemolysin genes from Escherichia coli that cause urinary tract infection determine different levels of toxicity in mice. Infect Immun. 1983 Oct;42(1):57–63. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.1.57-63.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henkart P. A. Mechanism of lymphocyte-mediated cytotoxicity. Annu Rev Immunol. 1985;3:31–58. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.03.040185.000335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koronakis V., Cross M., Senior B., Koronakis E., Hughes C. The secreted hemolysins of Proteus mirabilis, Proteus vulgaris, and Morganella morganii are genetically related to each other and to the alpha-hemolysin of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1987 Apr;169(4):1509–1515. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.4.1509-1515.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- König B., König W., Scheffer J., Hacker J., Goebel W. Role of Escherichia coli alpha-hemolysin and bacterial adherence in infection: requirement for release of inflammatory mediators from granulocytes and mast cells. Infect Immun. 1986 Dec;54(3):886–892. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.3.886-892.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lo R. Y., Strathdee C. A., Shewen P. E. Nucleotide sequence of the leukotoxin genes of Pasteurella haemolytica A1. Infect Immun. 1987 Sep;55(9):1987–1996. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.9.1987-1996.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lutz F., Maurer M., Failing K. Cytotoxic protein from Pseudomonas aeruginosa: formation of hydrophilic pores in Ehrlich ascites tumor cells and effect on cell viability. Toxicon. 1987;25(3):293–305. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(87)90258-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackman N., Holland I. B. Functional characterization of a cloned haemolysin determinant from E. coli of human origin, encoding information for the secretion of a 107K polypeptide. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;196(1):129–134. doi: 10.1007/BF00334104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackman N., Nicaud J. M., Gray L., Holland I. B. Secretion of haemolysin by Escherichia coli. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1986;125:159–181. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-71251-7_10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menestrina G., Mackman N., Holland I. B., Bhakdi S. Escherichia coli haemolysin forms voltage-dependent ion channels in lipid membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Nov 27;905(1):109–117. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(87)90014-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinaldo J. E., Rogers R. M. Adult respiratory distress syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1986 Aug 28;315(9):578–580. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198608283150909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeger W., Suttorp N., Hellwig A., Bhakdi S. Noncytolytic terminal complement complexes may serve as calcium gates to elicit leukotriene B4 generation in human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Immunol. 1986 Aug 15;137(4):1286–1293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeger W., Walter H., Suttorp N., Muhly M., Bhakdi S. Thromboxane-mediated hypertension and vascular leakage evoked by low doses of Escherichia coli hemolysin in rabbit lungs. J Clin Invest. 1989 Jul;84(1):220–227. doi: 10.1172/JCI114144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suttorp N., Fuchs T., Seeger W., Wilke A., Drenckhahn D. Role of Ca2+ and Mg2+ for endothelial permeability of water and albumin in vitro. Lab Invest. 1989 Aug;61(2):183–191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suttorp N., Galanos C., Neuhof H. Endotoxin alters arachidonate metabolism in pulmonary endothelial cells. Am J Physiol. 1987 Sep;253(3 Pt 1):C384–C390. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1987.253.3.C384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suttorp N., Habben E. Effect of staphylococcal alpha-toxin on intracellular Ca2+ in polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1988 Sep;56(9):2228–2234. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.9.2228-2234.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suttorp N., Hessz T., Seeger W., Wilke A., Koob R., Lutz F., Drenckhahn D. Bacterial exotoxins and endothelial permeability for water and albumin in vitro. Am J Physiol. 1988 Sep;255(3 Pt 1):C368–C376. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1988.255.3.C368. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suttorp N., Seeger W., Dewein E., Bhakdi S., Roka L. Staphylococcal alpha-toxin-induced PGI2 production in endothelial cells: role of calcium. Am J Physiol. 1985 Jan;248(1 Pt 1):C127–C134. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1985.248.1.C127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suttorp N., Seeger W., Uhl J., Lutz F., Roka L. Pseudomonas aeruginosa cytotoxin stimulates prostacyclin production in cultured pulmonary artery endothelial cells: membrane attack and calcium influx. J Cell Physiol. 1985 Apr;123(1):64–72. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041230111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suttorp N., Seeger W., Zinsky S., Bhakdi S. Complement complex C5b-8 induces PGI2 formation in cultured endothelial cells. Am J Physiol. 1987 Jul;253(1 Pt 1):C13–C21. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1987.253.1.C13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suttorp N., Seeger W., Zucker-Reimann J., Roka L., Bhakdi S. Mechanism of leukotriene generation in polymorphonuclear leukocytes by staphylococcal alpha-toxin. Infect Immun. 1987 Jan;55(1):104–110. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.1.104-110.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suttorp N., Toepfer W., Roka L. Antioxidant defense mechanisms of endothelial cells: glutathione redox cycle versus catalase. Am J Physiol. 1986 Nov;251(5 Pt 1):C671–C680. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1986.251.5.C671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch R. A., Dellinger E. P., Minshew B., Falkow S. Haemolysin contributes to virulence of extra-intestinal E. coli infections. Nature. 1981 Dec 17;294(5842):665–667. doi: 10.1038/294665a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch R. A. Identification of two different hemolysin determinants in uropathogenic Proteus isolates. Infect Immun. 1987 Sep;55(9):2183–2190. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.9.2183-2190.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]