Abstract
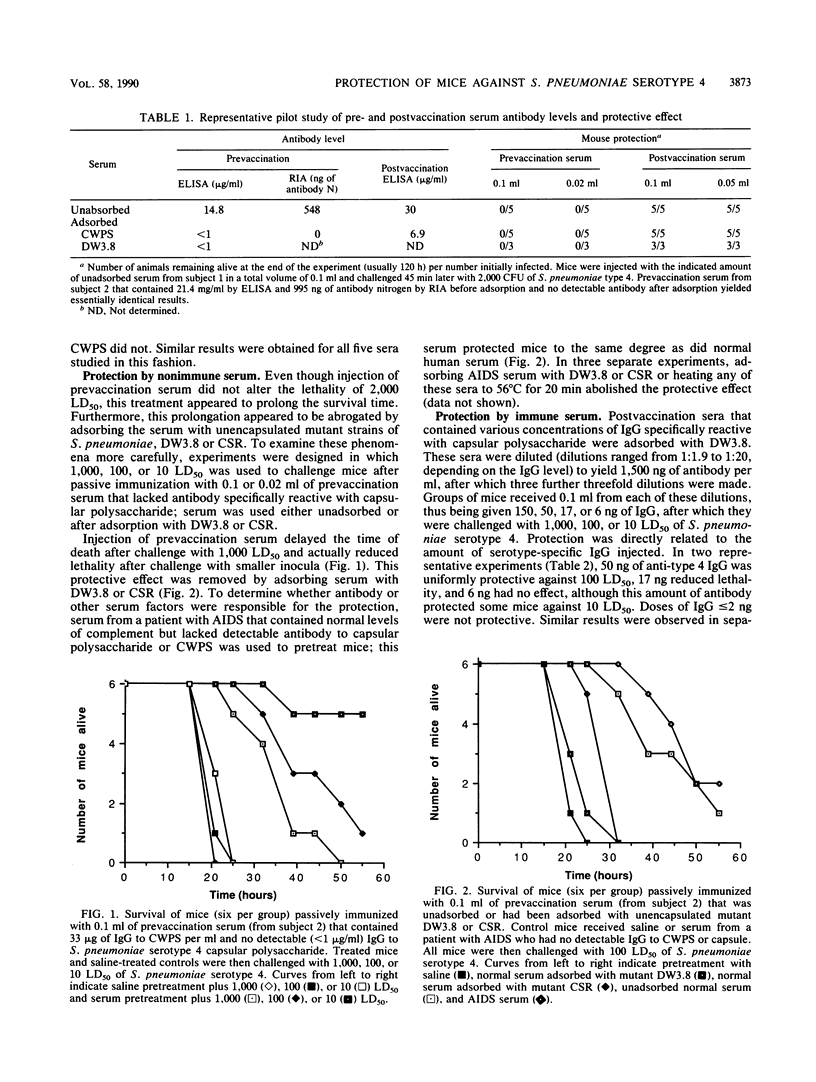
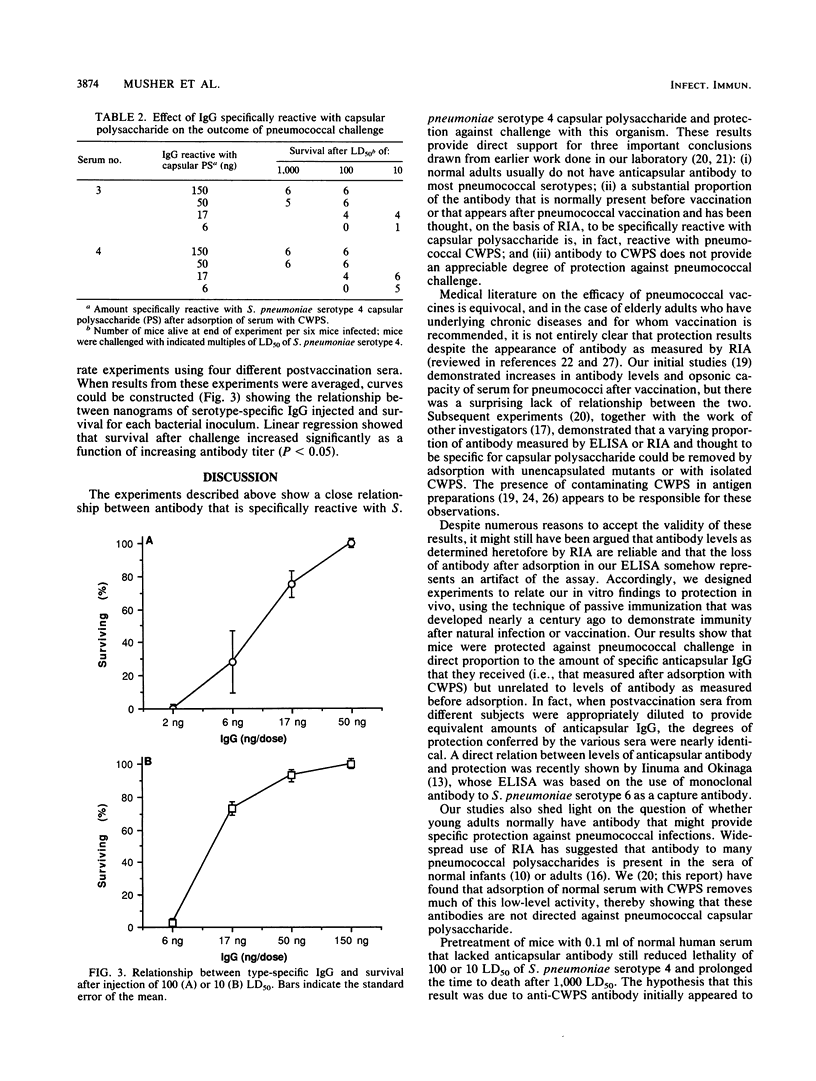
We have recently shown that a substantial proportion of antibody to pneumococcal polysaccharide as measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) or radioimmunoassay is removed by adsorption with pneumococcal cell wall polysaccharide (CWPS). The present study was undertaken to validate the hypothesis that only serotype-specific antibody that remains after adsorption with CWPS provides protection against pneumococcal infection. Serum samples were obtained from human subjects before and after they had been vaccinated with pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine. Antibody to Streptococcus pneumoniae serotype 4 was measured by ELISA without adsorption or after adsorption of serum with CWPS. Groups of mice were injected with graded doses of serum and then challenged intraperitoneally with 10, 100, or 1,000 50% lethal doses (LD50) of S. pneumoniae serotype 4. Without adsorption, prevaccination sera from five healthy adults appeared to contain up to 33 micrograms of antibody to S. pneumoniae serotype 4 antigen per ml; adsorption with CWPS removed all detectable antibody, and pretreating mice with up to 0.1 ml of these sera (less than or equal to 3.3 micrograms of antibody) failed to protect them against challenge with 100 LD50. In contrast, postvaccination sera contained 2.9 to 30 micrograms of antibody per ml that was not removed by adsorption. Diluting sera to administer desired amounts of serotype-specific immunoglobulin G showed a significant relationship between protection and antibody remaining after adsorption (P less than 0.05 by linear regression analysis); 150 ng was uniformly protective against 1,000 LD50, and 50 ng was protective against 100 LD50. These studies have, for the first time, quantitated the amount of serotype-specific antibody that protects mice against challenge with S. pneumoniae type 4. In light of these observations, it is necessary to reassess current concepts regarding the presence of antipneumococcal antibody in the unvaccinated population, responses to pneumococcal vaccination, and protective levels of immunoglobulin G.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Austrian R. Some observations on the pneumococcus and on the current status of pneumococcal disease and its prevention. Rev Infect Dis. 1981 Mar-Apr;3 (Suppl):S1–17. doi: 10.1093/clinids/3.supplement_1.s1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briles D. E., Nahm M., Schroer K., Davie J., Baker P., Kearney J., Barletta R. Antiphosphocholine antibodies found in normal mouse serum are protective against intravenous infection with type 3 streptococcus pneumoniae. J Exp Med. 1981 Mar 1;153(3):694–705. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.3.694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown E. J., Hosea S. W., Frank M. M. The role of antibody and complement in the reticuloendothelial clearance of pneumococci from the bloodstream. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Sep-Oct;5 (Suppl 4):S797–S805. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.supplement_4.s797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown E. J., Joiner K. A., Cole R. M., Berger M. Localization of complement component 3 on Streptococcus pneumoniae: anti-capsular antibody causes complement deposition on the pneumococcal capsule. Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):403–409. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.403-409.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finland M. Conference on the Pneumococcus: summary and comments. Rev Infect Dis. 1981 Mar-Apr;3(2):358–371. doi: 10.1093/clinids/3.2.358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray B. M., Dillon H. C., Jr Epidemiological studies of Streptococcus pneumoniae in infants: antibody to types 3, 6, 14, and 23 in the first two years of life. J Infect Dis. 1988 Nov;158(5):948–955. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.5.948. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holzer T. J., Edwards K. M., Gewurz H., Mold C. Binding of C-reactive protein to the pneumococcal capsule or cell wall results in differential localization of C3 and stimulation of phagocytosis. J Immunol. 1984 Sep;133(3):1424–1430. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iinuma H., Okinaga K. Prevention of pneumococcal bacteremia by immunization with type 6 pneumococcal capsular polysaccharide vaccine in splenectomized rats. J Infect Dis. 1989 Jul;160(1):66–75. doi: 10.1093/infdis/160.1.66. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein R. S., Selwyn P. A., Maude D., Pollard C., Freeman K., Schiffman G. Response to pneumococcal vaccine among asymptomatic heterosexual partners of persons with AIDS and intravenous drug users infected with human immunodeficiency virus. J Infect Dis. 1989 Nov;160(5):826–831. doi: 10.1093/infdis/160.5.826. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koskela M. Serum antibodies to pneumococcal C polysaccharide in children: response to acute pneumococcal otitis media or to vaccination. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1987 Jun;6(6):519–526. doi: 10.1097/00006454-198706000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDaniel L. S., Benjamin W. H., Jr, Forman C., Briles D. E. Blood clearance by anti-phosphocholine antibodies as a mechanism of protection in experimental pneumococcal bacteremia. J Immunol. 1984 Dec;133(6):3308–3312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musher D. M., Chapman A. J., Goree A., Jonsson S., Briles D., Baughn R. E. Natural and vaccine-related immunity to Streptococcus pneumoniae. J Infect Dis. 1986 Aug;154(2):245–256. doi: 10.1093/infdis/154.2.245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musher D. M., Luchi M. J., Watson D. A., Hamilton R., Baughn R. E. Pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine in young adults and older bronchitics: determination of IgG responses by ELISA and the effect of adsorption of serum with non-type-specific cell wall polysaccharide. J Infect Dis. 1990 Apr;161(4):728–735. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.4.728. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musher D. M., Watson D. A., Baughn R. E. Does naturally acquired IgG antibody to cell wall polysaccharide protect human subjects against pneumococcal infection? J Infect Dis. 1990 Apr;161(4):736–740. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.4.736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musher D. M., Watson D. A., Dominguez E. A. Pneumococcal vaccination: work to date and future prospects. Am J Med Sci. 1990 Jul;300(1):45–52. doi: 10.1097/00000441-199007000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiffman G., Douglas R. M., Bonner M. J., Robbins M., Austrian R. A radioimmunoassay for immunologic phenomena in pneumococcal disease and for the antibody response to pneumococcal vaccines. I. Method for the radioimmunoassay of anticapsular antibodies and comparison with other techniques. J Immunol Methods. 1980;33(2):133–144. doi: 10.1016/s0022-1759(80)80004-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siber G. R., Priehs C., Madore D. V. Standardization of antibody assays for measuring the response to pneumococcal infection and immunization. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1989 Jan;8(1 Suppl):S84–S91. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skov Sørensen U. B., Blom J., Birch-Andersen A., Henrichsen J. Ultrastructural localization of capsules, cell wall polysaccharide, cell wall proteins, and F antigen in pneumococci. Infect Immun. 1988 Aug;56(8):1890–1896. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.8.1890-1896.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szu S. C., Clarke S., Robbins J. B. Protection against pneumococcal infection in mice conferred by phosphocholine-binding antibodies: specificity of the phosphocholine binding and relation to several types. Infect Immun. 1983 Feb;39(2):993–999. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.2.993-999.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sørensen U. B., Henrichsen J. C-polysaccharide in a pneumococcal vaccine. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand C. 1984 Dec;92(6):351–356. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1984.tb00099.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiraby G., Fox M. S., Bernheimer H. Marker discrimination in deoxyribonucleic acid-mediated transformation of various Pneumococcus strains. J Bacteriol. 1975 Feb;121(2):608–618. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.2.608-618.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallick S., Claflin J. L., Briles D. E. Resistance to Streptococcus pneumoniae is induced by a phosphocholine-protein conjugate. J Immunol. 1983 Jun;130(6):2871–2875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson D. A., Musher D. M. Interruption of capsule production in Streptococcus pneumonia serotype 3 by insertion of transposon Tn916. Infect Immun. 1990 Sep;58(9):3135–3138. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.9.3135-3138.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



