Abstract
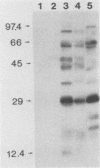
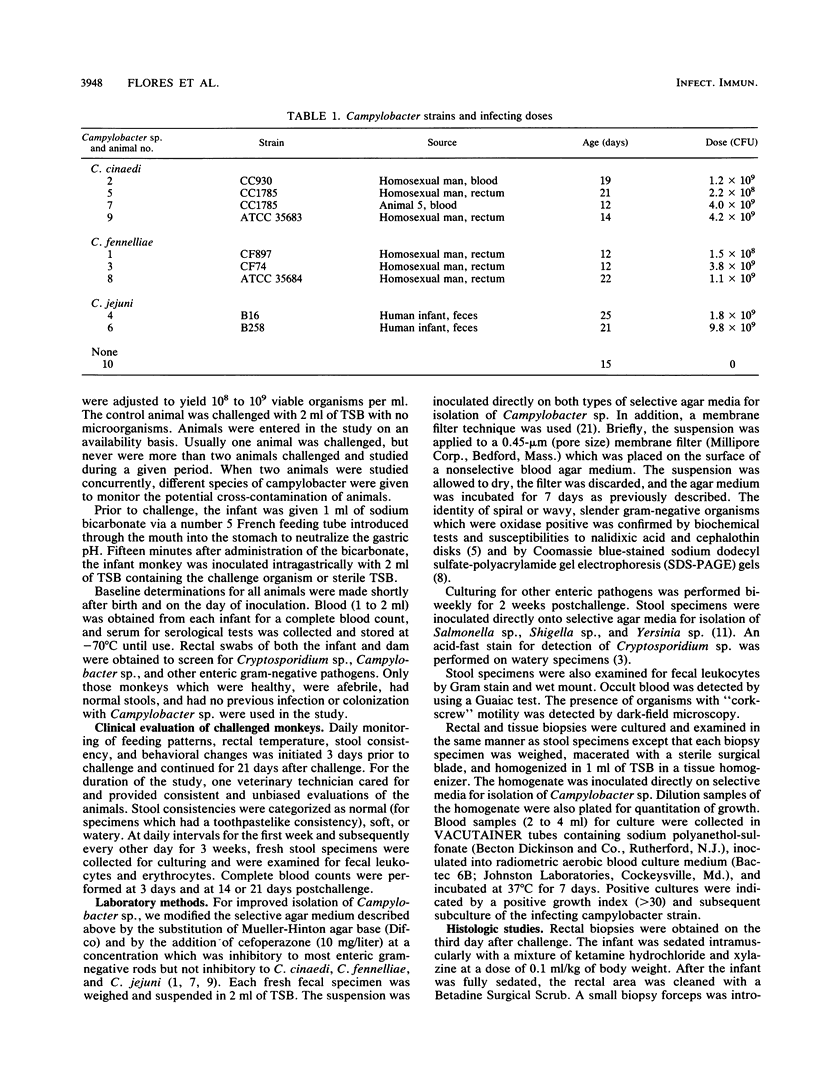
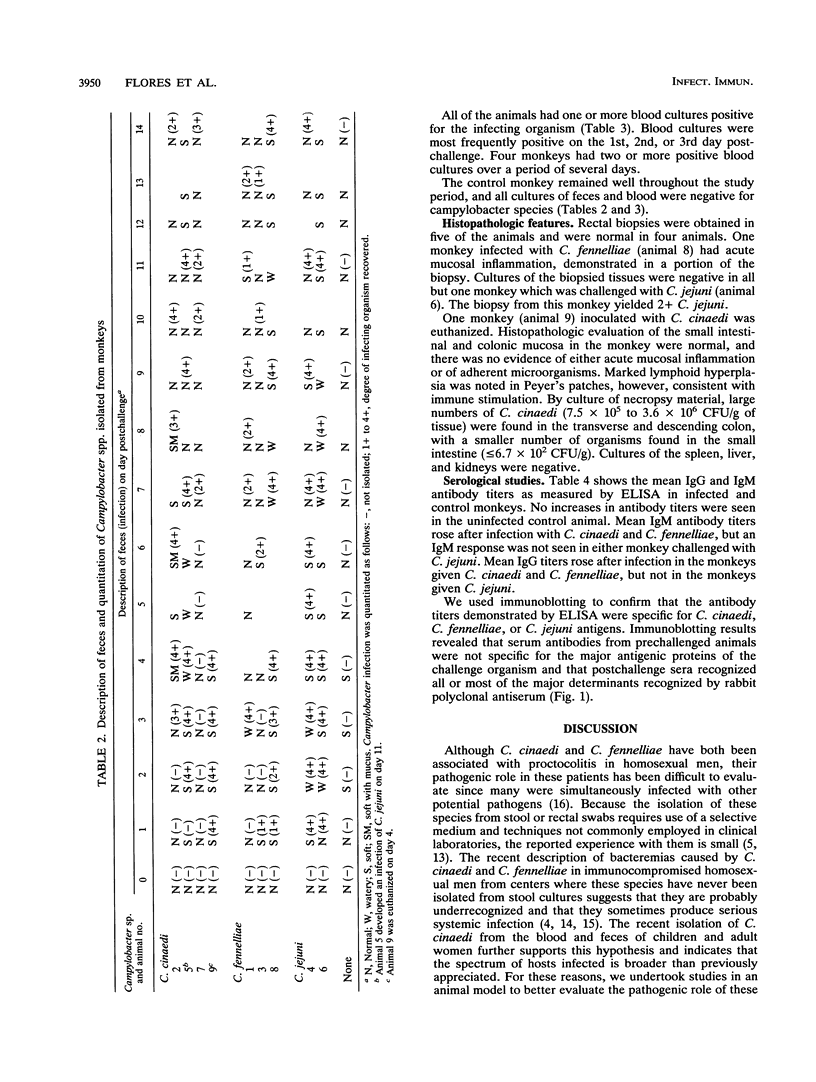
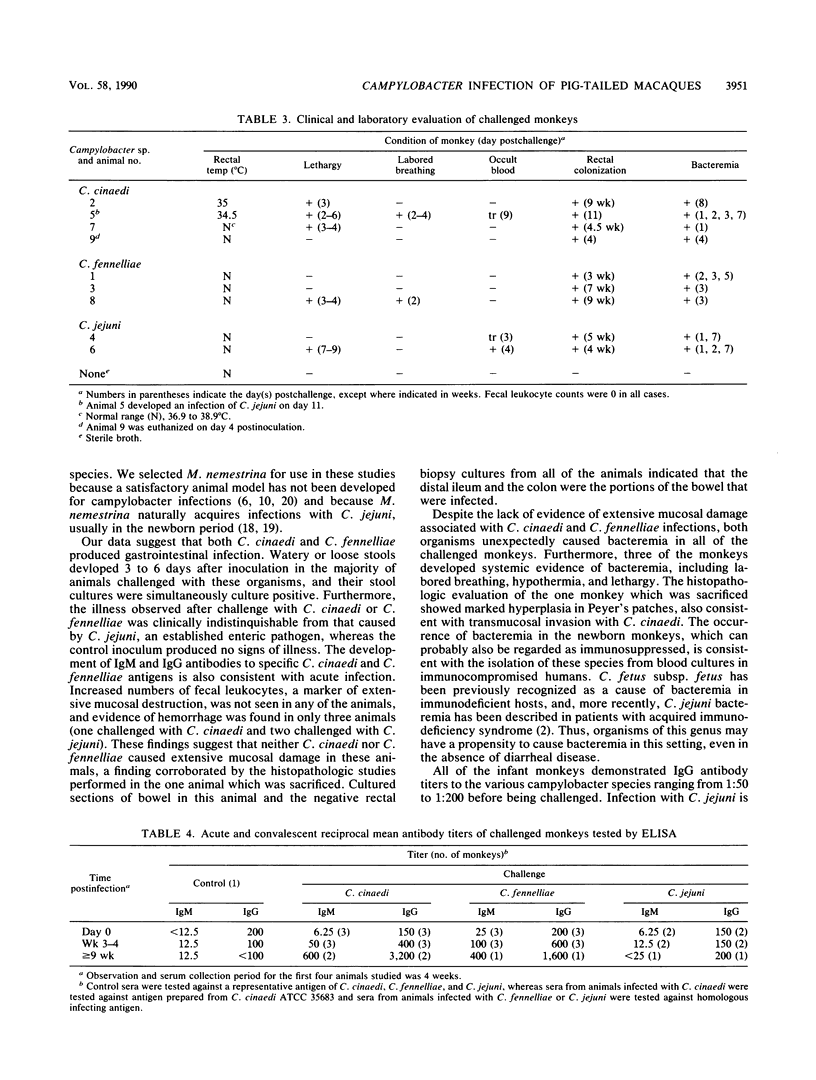
Campylobacter cinaedi and C. fennelliae have been associated with proctocolitis, bacteremia, and asymptomatic rectal infection, primarily in homosexual men. To more directly assess the pathogenic role of these organisms, we studied their disease-producing potential in 12- to 25-day-old pig-tailed macaques (Macaca nemestrina). Four infant monkeys were challenged with 10(8) to 10(9) C. cinaedi, three were challenged with C. fennelliae, two were challenged with C. jejuni, and one received no microorganisms. Watery or loose stools without associated fever or fecal leukocytes developed 3 to 7 days postinoculation in all of the animals given C. cinaedi, C. fennelliae, and C. jejuni, but not in the control animal. Stool cultures were simultaneously positive and remained so in the animals challenged with C. cinaedi or C. fennelliae for 3 weeks after inoculation despite the resolution of clinical illness. All of the animals challenged with C. cinaedi and C. fennelliae became bacteremic, and three had clinical evidence of septicemia. Histopathologic evaluation of rectal biopsies (five animals) and necropsy (one animal) showed no evidence of mucosal disruption. Specific immunoglobulin M and immunoglobulin G antibody responses occurred in all of the animals challenged with C. cinaedi and C. fennelliae, as determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and immunoblotting. We conclude that C. cinaedi and C. fennelliae consistently produce a diarrheal illness accompanied by bacteremia and followed by prolonged gastrointestinal colonization in M. nemestrina.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahonkhai V. I., Cherubin C. E., Sierra M. F., Bokkenheuser V. D., Shulman M. A., Mosenthal A. C. In vitro susceptibility of Campylobacter fetus subsp. jejuni to N-formimidoyl thienamycin, rosaramicin, cefoperazone, and other antimicrobial agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Dec;20(6):850–851. doi: 10.1128/aac.20.6.850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernard E., Roger P. M., Carles D., Bonaldi V., Fournier J. P., Dellamonica P. Diarrhea and Campylobacter infections in patients infected with the human immunodeficiency virus. J Infect Dis. 1989 Jan;159(1):143–144. doi: 10.1093/infdis/159.1.143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bronsdon M. A. Rapid dimethyl sulfoxide-modified acid-fast stain of Cryptosporidium oocysts in stool specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Jun;19(6):952–953. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.6.952-953.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cimolai N., Gill M. J., Jones A., Flores B., Stamm W. E., Laurie W., Madden B., Shahrabadi M. S. "Campylobacter cinaedi" bacteremia: case report and laboratory findings. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 May;25(5):942–943. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.5.942-943.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fennell C. L., Totten P. A., Quinn T. C., Patton D. L., Holmes K. K., Stamm W. E. Characterization of Campylobacter-like organisms isolated from homosexual men. J Infect Dis. 1984 Jan;149(1):58–66. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.1.58. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field L. H., Underwood J. L., Berry L. J. The role of gut flora and animal passage in the colonisation of adult mice with Campylobacter jejuni. J Med Microbiol. 1984 Feb;17(1):59–66. doi: 10.1099/00222615-17-1-59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores B. M., Fennell C. L., Holmes K. K., Stamm W. E. In vitro susceptibilities of Campylobacter-like organisms to twenty antimicrobial agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Aug;28(2):188–191. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.2.188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores B. M., Fennell C. L., Stamm W. E. Characterization of Campylobacter cinaedi and C. fennelliae antigens and analysis of the human immune response. J Infect Dis. 1989 Apr;159(4):635–640. doi: 10.1093/infdis/159.4.635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinkle A. M., LeBlanc B. M., Bodey G. P. In vitro evaluation of cefoperazone. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Mar;17(3):423–427. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.3.423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey C. D., Montag D. M., Pittman F. E. Experimental infection of hamsters with Campylobacter jejuni. J Infect Dis. 1985 Mar;151(3):485–493. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.3.485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laughon B. E., Vernon A. A., Druckman D. A., Fox R., Quinn T. C., Polk B. F., Bartlett J. G. Recovery of Campylobacter species from homosexual men. J Infect Dis. 1988 Aug;158(2):464–467. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.2.464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng V. L., Hadley W. K., Fennell C. L., Flores B. M., Stamm W. E. Successive bacteremias with "Campylobacter cinaedi" and "Campylobacter fennelliae" in a bisexual male. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Oct;25(10):2008–2009. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.10.2008-2009.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasternak J., Bolivar R., Hopfer R. L., Fainstein V., Mills K., Rios A., Bodey G. P., Fennell C. L., Totten P. A., Stamm W. E. Bacteremia caused by Campylobacter-like organisms in two male homosexuals. Ann Intern Med. 1984 Sep;101(3):339–341. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-101-3-339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn T. C., Goodell S. E., Fennell C., Wang S. P., Schuffler M. D., Holmes K. K., Stamm W. E. Infections with Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter-like organisms in homosexual men. Ann Intern Med. 1984 Aug;101(2):187–192. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-101-2-187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell R. G., Blaser M. J., Sarmiento J. I., Fox J. Experimental Campylobacter jejuni infection in Macaca nemestrina. Infect Immun. 1989 May;57(5):1438–1444. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.5.1438-1444.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell R. G., Krugner L., Tsai C. C., Ekstrom R. Prevalence of Campylobacter in infant, juvenile and adult laboratory primates. Lab Anim Sci. 1988 Dec;38(6):711–714. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell R. G., Rosenkranz S. L., Lee L. A., Howard H., DiGiacomo R. F., Bronsdon M. A., Blakley G. A., Tsai C. C., Morton W. R. Epidemiology and etiology of diarrhea in colony-born Macaca nemestrina. Lab Anim Sci. 1987 Jun;37(3):309–316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanyal S. C., Islam K. M., Neogy P. K., Islam M., Speelman P., Huq M. I. Campylobacter jejuni diarrhea model in infant chickens. Infect Immun. 1984 Mar;43(3):931–936. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.3.931-936.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steele T. W., McDermott S. N. The use of membrane filters applied directly to the surface of agar plates for the isolation of Campylobacter jejuni from feces. Pathology. 1984 Jul;16(3):263–265. doi: 10.3109/00313028409068535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tee W., Anderson B. N., Ross B. C., Dwyer B. Atypical campylobacters associated with gastroenteritis. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Jul;25(7):1248–1252. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.7.1248-1252.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Totten P. A., Fennell C. L., Tenover F. C., Wezenberg J. M., Perine P. L., Stamm W. E., Holmes K. K. Campylobacter cinaedi (sp. nov.) and Campylobacter fennelliae (sp. nov.): two new Campylobacter species associated with enteric disease in homosexual men. J Infect Dis. 1985 Jan;151(1):131–139. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.1.131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandamme P., Falsen E., Pot B., Kersters K., De Ley J. Identification of Campylobacter cinaedi isolated from blood and feces of children and adult females. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 May;28(5):1016–1020. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.5.1016-1020.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]