Abstract
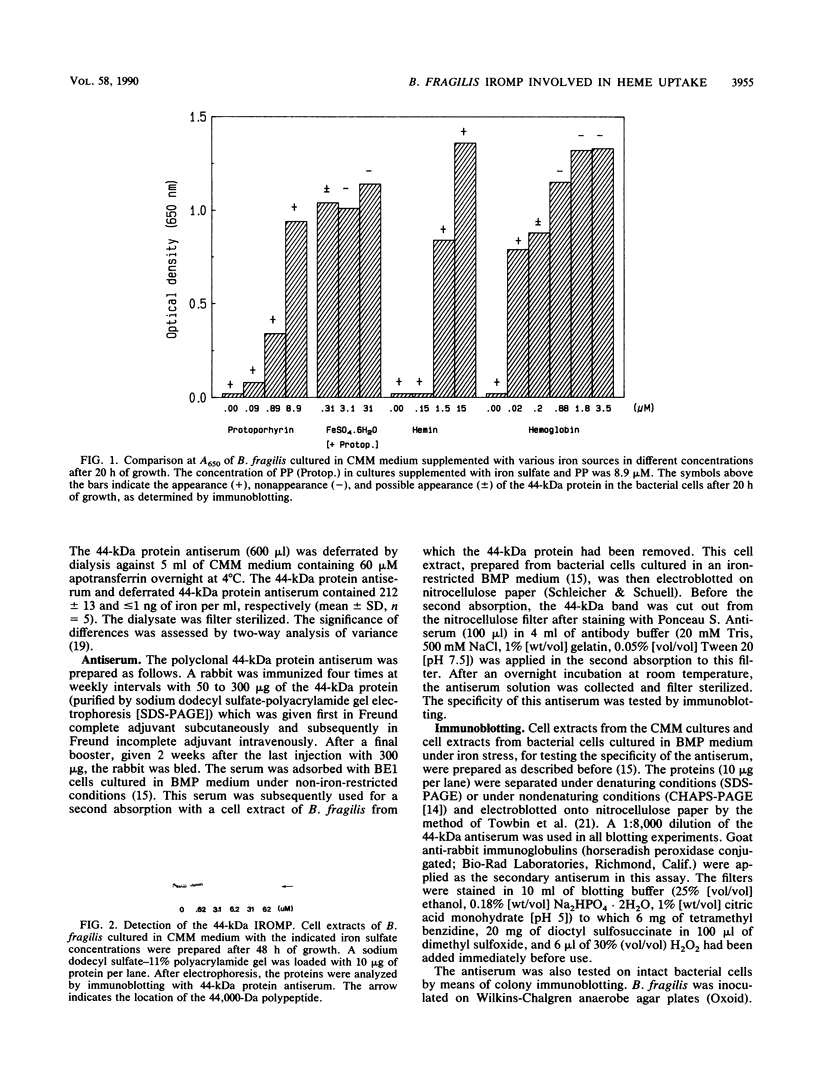
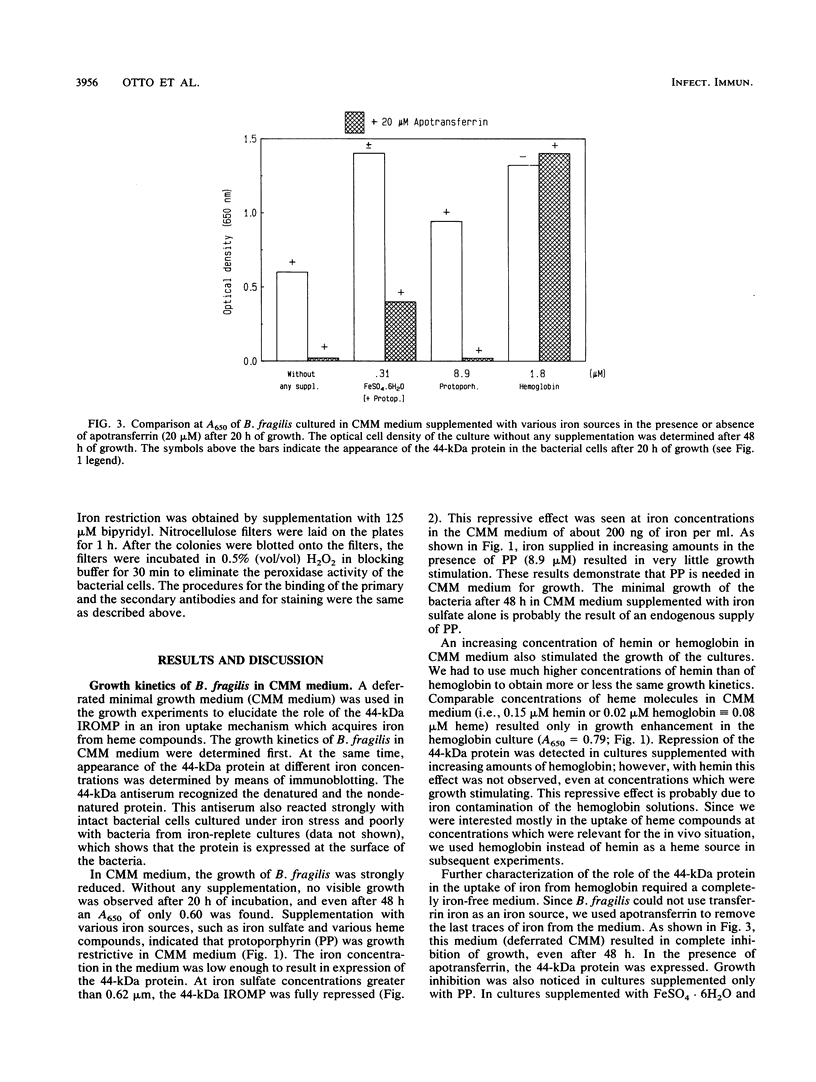
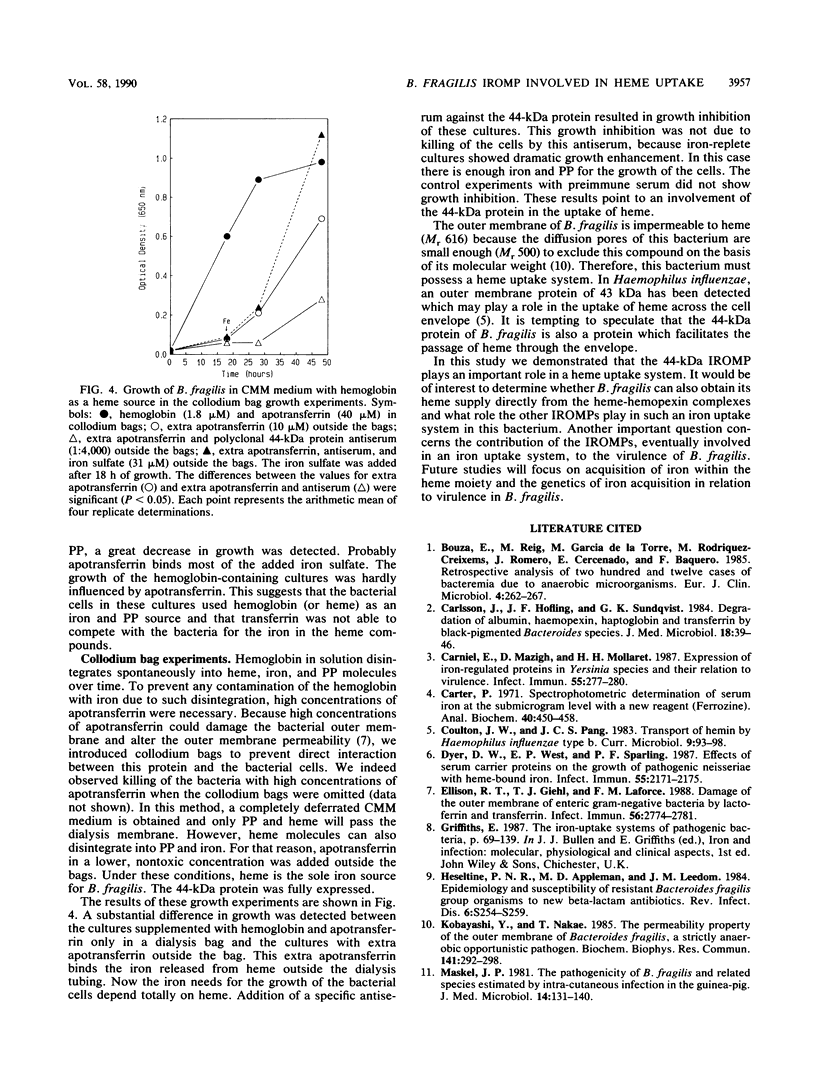
Under iron starvation, Bacteroides fragilis expresses various iron-regulated outer membrane proteins. In this study, a deferrated minimal medium was used in growth experiments, and the role of one of these iron-regulated outer membrane proteins (a 44-kDa protein) in an iron uptake mechanism which acquires iron from heme compounds was elucidated. When a specific 44-kDa protein antiserum was used in a medium with heme as the only iron source, growth inhibition was observed. These results demonstrate that the 44-kDa outer membrane protein plays an important role in the uptake of heme in B. fragilis.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bouza E., Reig M., Garcia de la Torre M., Rodríguez-Créixems M., Romero J., Cercenado E., Baquero F. Retrospective analysis of two hundred and twelve cases of bacteremia due to anaerobic microorganisms. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jun;4(3):262–267. doi: 10.1007/BF02013649. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson J., Höfling J. F., Sundqvist G. K. Degradation of albumin, haemopexin, haptoglobin and transferrin, by black-pigmented Bacteroides species. J Med Microbiol. 1984 Aug;18(1):39–46. doi: 10.1099/00222615-18-1-39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carniel E., Mazigh D., Mollaret H. H. Expression of iron-regulated proteins in Yersinia species and their relation to virulence. Infect Immun. 1987 Jan;55(1):277–280. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.1.277-280.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter P. Spectrophotometric determination of serum iron at the submicrogram level with a new reagent (ferrozine). Anal Biochem. 1971 Apr;40(2):450–458. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90405-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyer D. W., West E. P., Sparling P. F. Effects of serum carrier proteins on the growth of pathogenic neisseriae with heme-bound iron. Infect Immun. 1987 Sep;55(9):2171–2175. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.9.2171-2175.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellison R. T., 3rd, Giehl T. J., LaForce F. M. Damage of the outer membrane of enteric gram-negative bacteria by lactoferrin and transferrin. Infect Immun. 1988 Nov;56(11):2774–2781. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.11.2774-2781.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heseltine P. N., Appleman M. D., Leedom J. M. Epidemiology and susceptibility of resistant Bacteroides fragilis group organisms to new beta-lactam antibiotics. Rev Infect Dis. 1984 Mar-Apr;6 (Suppl 1):S254–S259. doi: 10.1093/clinids/6.supplement_1.s254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi Y., Nakae T. The permeability property of the outer membrane of Bacteroides fragilis, a strictly anaerobic opportunistic pathogen. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Nov 26;141(1):292–298. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80367-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maskell J. P. The pathogenicity of Bacteroides fragilis and related species estimated by intracutaneous infection in the guinea-pig. J Med Microbiol. 1981 Feb;14(1):131–140. doi: 10.1099/00222615-14-1-131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse S. A., Chen C. Y., LeFaou A., Mietzner T. A. A potential role for the major iron-regulated protein expressed by pathogenic Neisseria species. Rev Infect Dis. 1988 Jul-Aug;10 (Suppl 2):S306–S310. doi: 10.1093/cid/10.supplement_2.s306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neilands J. B., Bindereif A., Montgomerie J. Z. Genetic basis of iron assimilation in pathogenic Escherichia coli. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1985;118:179–195. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-70586-1_10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otto B. R., Verweij-Van Vught A. M., Maclaren D. M. Purification and partial characterization of an iron regulated outer membrane protein of B. fragilis under non-denaturing conditions. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1990 Jan 1;54(1-3):285–290. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(90)90298-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otto B. R., Verweij-van Vught A. M., van Doorn J., Maclaren D. M. Outer membrane proteins of Bacteroides fragilis and Bacteroides vulgatus in relation to iron uptake and virulence. Microb Pathog. 1988 Apr;4(4):279–287. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(88)90088-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne S. M. Iron and virulence in Shigella. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Sep;3(9):1301–1306. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00281.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pidcock K. A., Wooten J. A., Daley B. A., Stull T. L. Iron acquisition by Haemophilus influenzae. Infect Immun. 1988 Apr;56(4):721–725. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.4.721-725.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigel S. P., Payne S. M. Effect of iron limitation on growth, siderophore production, and expression of outer membrane proteins of Vibrio cholerae. J Bacteriol. 1982 Apr;150(1):148–155. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.1.148-155.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoebner J. A., Payne S. M. Iron-regulated hemolysin production and utilization of heme and hemoglobin by Vibrio cholerae. Infect Immun. 1988 Nov;56(11):2891–2895. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.11.2891-2895.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verweij-van Vught A. M., Namavar F., Vel W. A., Sparrius M., MacLaren D. M. Pathogenic synergy between Escherichia coli and Bacteroides fragilis or B. vulgatus in experimental infections: a non-specific phenomenon. J Med Microbiol. 1986 Feb;21(1):43–47. doi: 10.1099/00222615-21-1-43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




