Abstract
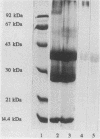
A panel of monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) to seven Brucella outer membrane proteins were characterized. These antibodies were obtained by immunizing mice with sodium dodecyl sulfate-insoluble (SDS-I) fractions, cell walls, or whole bacterial cells of Brucella abortus or B. melitensis. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays were used to screen the hybridoma supernatants and to determine their binding at the surface of rough and smooth B. abortus and B. melitensis cells. The outer membrane proteins (OMPs) recognized by these antibodies were the proteins with molecular masses of 25 to 27 kDa and 36 to 38 kDa (porin) (major proteins) and the proteins with molecular masses of 10, 16.5, 19, 31 to 34, and 89 kDa (minor proteins). Surface exposure of these OMPs was visualized by electron microscopy by using the MAbs and immunogold labeling. Binding of the MAbs on whole rough bacterial cells indicates that the 10-, 16.5-, 19-, 25- to 27-, 31- to 34-, 36- to 38-, and 89-kDa OMPs are exposed at the cell surface. However, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay results indicate a much better binding of the anti-OMP MAbs on rough strains than on the corresponding smooth strains except for the anti-19-kDa MAb. Immunoelectron microscopy showed that on smooth B. abortus cells only the 89- and 31- to 34-kDa OMPs were not accessible to the MAbs tested. Binding of the anti-31- to 34-kDa MAb at the cell surface was observed for the rough B. abortus cells and for the rough and smooth B. melitensis cells. These results indicate the importance of steric hindrance due to the presence of the long lipopolysaccharide O side chains in the accessibility of OMPs on smooth Brucella strains and should be considered when undertaking vaccine development.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bascoul S., Cannat A., Huguet M. F., Serre A. Studies on the immune protection to murine experimental brucellosis conferred by Brucella fractions. I. Positive role of immune serum. Immunology. 1978 Aug;35(2):213–221. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentley A. T., Klebba P. E. Effect of lipopolysaccharide structure on reactivity of antiporin monoclonal antibodies with the bacterial cell surface. J Bacteriol. 1988 Mar;170(3):1063–1068. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.3.1063-1068.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun V. Covalent lipoprotein from the outer membrane of Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Oct 31;415(3):335–377. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(75)90013-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas J. T., Rosenberg E. Y., Nikaido H., Verstreate D. R., Winter A. J. Porins of Brucella species. Infect Immun. 1984 Apr;44(1):16–21. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.1.16-21.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubray G., Bézard G. Isolation of three Brucella abortus cell-wall antigens protective in murine experimental brucellosis. Ann Rech Vet. 1980;11(4):367–373. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubray G., Charriaut C. Evidence of three major polypeptide species and two major polysaccharide species in the Brucella outer membrane. Ann Rech Vet. 1983;14(3):311–318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubray G., Limet J. Evidence of heterogeneity of lipopolysaccharides among Brucella biovars in relation to A and M specificities. Ann Inst Pasteur Microbiol. 1987 Jan-Feb;138(1):27–37. doi: 10.1016/0769-2609(87)90051-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubray G., Plommet M. Structure et constituants des Brucella. Caractérisation des fractions et propriétés biologiques. Dev Biol Stand. 1976;31:68–91. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubray G. Protective antigens in brucellosis. Ann Inst Pasteur Microbiol. 1987 Jan-Feb;138(1):84–87. doi: 10.1016/0769-2609(87)90080-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill J., Stellwag E., Dworkin M. Monoclonal antibodies against cell-surface antigens of developing cells of Myxococcus xanthus. Ann Inst Pasteur Microbiol. 1985 Jan-Feb;136A(1):11–18. doi: 10.1016/s0769-2609(85)80015-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gómez-Miguel M. J., Moriyón I. Demonstration of a peptidoglycan-linked lipoprotein and characterization of its trypsin fragment in the outer membrane of Brucella spp. Infect Immun. 1986 Sep;53(3):678–684. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.3.678-684.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackstadt T. Steric hindrance of antibody binding to surface proteins of Coxiella burnetti by phase I lipopolysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1988 Apr;56(4):802–807. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.4.802-807.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leong D., Diaz R., Milner K., Rudbach J., Wilson J. B. Some structural and biological properties of Brucella endotoxin. Infect Immun. 1970 Feb;1(2):174–182. doi: 10.1128/iai.1.2.174-182.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Limet J. N., Berbinschi A., Cloeckaert A., Cambiaso C. L., Masson P. L. Longitudinal study of brucellosis in mice by immunoassay of lipopolysaccharide-related antigens in blood and urine. J Med Microbiol. 1988 May;26(1):37–45. doi: 10.1099/00222615-26-1-37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Limet J., Plommet A. M., Dubray G., Plommet M. Immunity conferred upon mice by anti-LPS monoclonal antibodies in murine brucellosis. Ann Inst Pasteur Immunol. 1987 May-Jun;138(3):417–424. doi: 10.1016/s0769-2625(87)80052-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez-Merino A., Asselineau J., Serre A., Roux J., Bascoul S., Lacave C. Immunization by an insoluble fraction extracted from Brucella melitensis: immunological and chemical characterization of the active substances. Infect Immun. 1976 Feb;13(2):311–321. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.2.311-321.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madraso E. D., Cheers C. Polyadenylic acid-polyuridylic acid (poly A : U) and experimental murine brucellosis. II. Macrophages as target cells of poly A : U in experimental brucellosis. Immunology. 1978 Jul;35(1):77–84. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montaraz J. A., Winter A. J. Comparison of living and nonliving vaccines for Brucella abortus in BALB/c mice. Infect Immun. 1986 Aug;53(2):245–251. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.2.245-251.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montaraz J. A., Winter A. J., Hunter D. M., Sowa B. A., Wu A. M., Adams L. G. Protection against Brucella abortus in mice with O-polysaccharide-specific monoclonal antibodies. Infect Immun. 1986 Mar;51(3):961–963. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.3.961-963.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moriyon I., Berman D. T. Isolation, purification, and partial characterization of Brucella abortus matrix protein. Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):394–402. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.394-402.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakane P. K., Kawaoi A. Peroxidase-labeled antibody. A new method of conjugation. J Histochem Cytochem. 1974 Dec;22(12):1084–1091. doi: 10.1177/22.12.1084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardon P. Resistance against a subcutaneous Brucella challenge of mice immunized with living or dead Brucella or by transfer of immune serum. Ann Immunol (Paris) 1977 Nov-Dec;128(6):1025–1037. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavlov H., Hogarth M., McKenzie I. F., Cheers C. In vivo and in vitro effects of monoclonal antibody to Ly antigens on immunity to infection. Cell Immunol. 1982 Jul 15;71(1):127–138. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(82)90502-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plommet M. Brucellosis and immunity: humoral and cellular components in mice. Ann Inst Pasteur Microbiol. 1987 Jan-Feb;138(1):105–110. doi: 10.1016/0769-2609(87)90086-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plommet M., Plommet A. M. Anti-Brucella cell-mediated immunity in mice vaccinated with a cell-wall fraction. Ann Rech Vet. 1987;18(4):429–437. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plommet M., Plommet A. M. Immune serum-mediated effects on brucellosis evolution in mice. Infect Immun. 1983 Jul;41(1):97–105. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.1.97-105.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plommet M., Serre A., Fensterbank R. Vaccines, vaccination in brucellosis. Ann Inst Pasteur Microbiol. 1987 Jan-Feb;138(1):117–121. doi: 10.1016/0769-2609(87)90089-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pâques M., Teppema J. S., Beuvery E. C., Abdillahi H., Poolman J. T., Verkleij A. J. Accessibility of gonococcal and meningococcal surface antigens: immunogold labeling for quantitative electron microscopy. Infect Immun. 1989 Feb;57(2):582–589. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.2.582-589.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasooly G., Olitzki A. L., Sulitzeanu D. Immunization against Brucella with killed vaccines. Immunizing activity in mice of Brucella cell walls and of fractions derived from them. Isr J Med Sci. 1966 Sep-Oct;2(5):569–584. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SULITZEANU D., JONES L., STABLEFORTH A. W. Protective action of monospecific anti-Brucella sera in mice. Nature. 1955 Jun 11;175(4467):1040–1041. doi: 10.1038/1751040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santos J. M., Verstreate D. R., Perera V. Y., Winter A. J. Outer membrane proteins from rough strains of four Brucella species. Infect Immun. 1984 Oct;46(1):188–194. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.1.188-194.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shafer W. M. Lipopolysaccharide masking of gonococcal outer-membrane proteins modulates binding of bacterial cathepsin G to gonococci. J Gen Microbiol. 1988 Mar;134(3):539–545. doi: 10.1099/00221287-134-3-539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer W. R., Barondes S. H. Monoclonal antibodies block cell-cell adhesion in Dictyostelium discoideum. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 25;258(8):4698–4701. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verstreate D. R., Creasy M. T., Caveney N. T., Baldwin C. L., Blab M. W., Winter A. J. Outer membrane proteins of Brucella abortus: isolation and characterization. Infect Immun. 1982 Mar;35(3):979–989. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.3.979-989.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verstreate D. R., Winter A. J. Comparison of sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis profiles and antigenic relatedness among outer membrane proteins of 49 Brucella abortus strains. Infect Immun. 1984 Oct;46(1):182–187. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.1.182-187.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voorhout W. F., Leunissen-Bijvelt J. J., Leunissen J. L., Verkleij A. J. Steric hindrance in immunolabelling. J Microsc. 1986 Mar;141(Pt 3):303–310. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1986.tb02724.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winter A. J., Rowe G. E., Duncan J. R., Eis M. J., Widom J., Ganem B., Morein B. Effectiveness of natural and synthetic complexes of porin and O polysaccharide as vaccines against Brucella abortus in mice. Infect Immun. 1988 Nov;56(11):2808–2817. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.11.2808-2817.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Ley P., Kuipers O., Tommassen J., Lugtenberg B. O-antigenic chains of lipopolysaccharide prevent binding of antibody molecules to an outer membrane pore protein in Enterobacteriaceae. Microb Pathog. 1986 Feb;1(1):43–49. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(86)90030-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]