Abstract
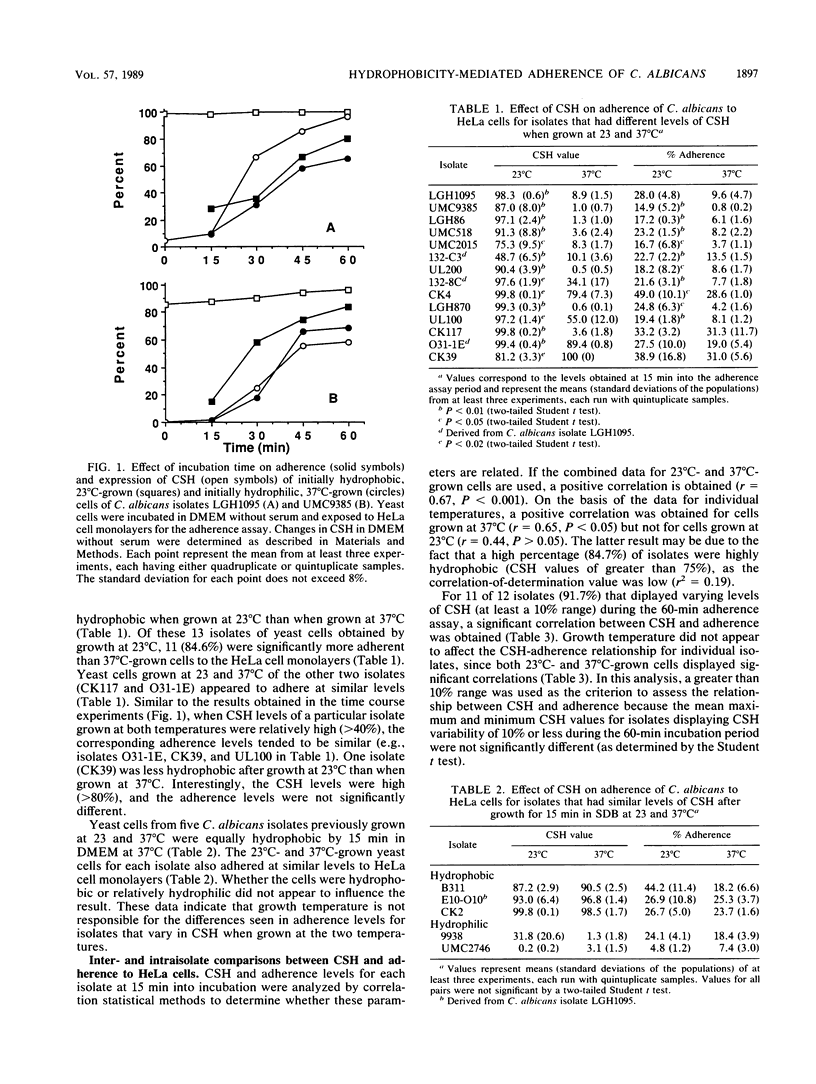
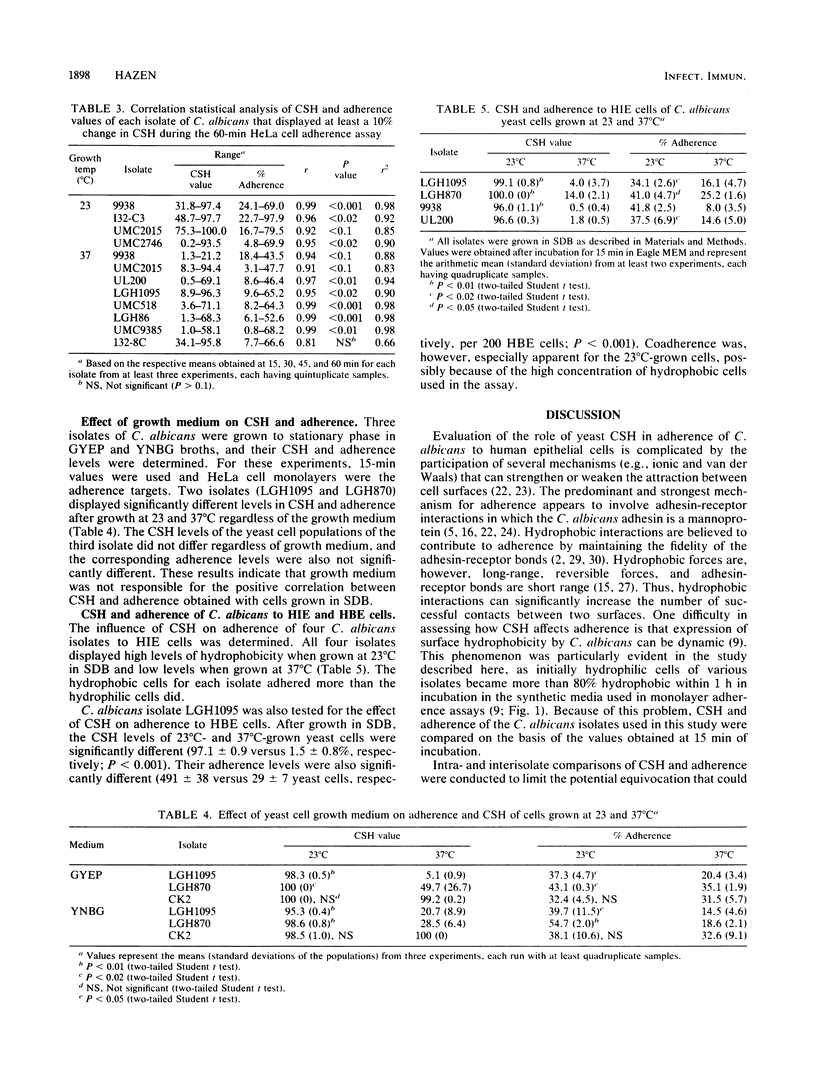
Recent studies have revealed that hydrophobic cells of the opportunistic pathogenic fungus Candida albicans are more virulent than hydrophilic cells. One critical step in the pathogenic process is adherence to host tissues. Adherence of C. albicans to epithelial tissues is mediated primarily by specific adhesin-receptor interactions, but whether cell surface hydrophobicity (CSH) of the yeast cells may also contribute has not been definitively demonstrated. Nineteen isolates of C. albicans were grown in Sabouraud dextrose broth at either 23 or 37 degrees C and tested for CSH by a polystyrene microsphere assay and for the ability to adhere to HeLa cells, a human cervical epithelioid carcinoma cell line. For 13 isolates, growth at 23 degrees C resulted in significantly higher levels of CSH than did growth at 37 degrees C. Three isolates were hydrophobic and two were hydrophilic regardless of growth temperature. One isolate was more hydrophobic after growth at 37 degrees C. Of the isolates that were more hydrophobic after growth at 23 degrees C, 86.5% (11 of 13) were also more adherent to HeLa cells. Growth temperature did not appear to determine adherence ability, as all isolates that did not differ in CSH after growth at either temperature also did not differ in ability to adhere. No correlation (r = 0.44) was obtained between CSH and adherence when the isolates grown at 23 degrees C were evaluated as a group. Higher correlation (r = 0.65) was obtained when the isolates were grown at 37 degrees C. Interestingly, a significantly positive correlation between CSH and adherence was obtained when individual isolates were analyzed. To accomplish this analysis, the isolates were allowed to vary in CSH over time in tissue culture medium without serum, and the corresponding adherence values determined. Only isolates that varied in CSH by greater than 10% were used. Correlation statistical analysis in which the coefficient of determination (r2) was calculated indicated that poor correlation between CSH and adherence for the isolates evaluated as a group was likely due to the fact that CSH had little effect on adherence once a moderately high level of CSH was attained. These results indicate that CSH is involved in adherence but is not the predominant mechanism and that the effect of CSH on adherence is isolate dependent.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antley P. P., Hazen K. C. Role of yeast cell growth temperature on Candida albicans virulence in mice. Infect Immun. 1988 Nov;56(11):2884–2890. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.11.2884-2890.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beachey E. H. Bacterial adherence: adhesin-receptor interactions mediating the attachment of bacteria to mucosal surface. J Infect Dis. 1981 Mar;143(3):325–345. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.3.325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Centeno A., Davis C. P., Cohen M. S., Warren M. M. Modulation of Candida albicans attachment to human epithelial cells by bacteria and carbohydrates. Infect Immun. 1983 Mar;39(3):1354–1360. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.3.1354-1360.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Critchley I. A., Douglas L. J. Isolation and partial characterization of an adhesin from Candida albicans. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Mar;133(3):629–636. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-3-629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cutler J. E. Chemotactic factor produced by Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1977 Dec;18(3):568–573. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.3.568-573.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garber N., Sharon N., Shohet D., Lam J. S., Doyle R. J. Contribution of hydrophobicity to hemagglutination reactions of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1985 Oct;50(1):336–337. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.1.336-337.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazen B. W., Hazen K. C. Dynamic expression of cell surface hydrophobicity during initial yeast cell growth and before germ tube formation of Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1988 Sep;56(9):2521–2525. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.9.2521-2525.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazen B. W., Hazen K. C. Isolation of hydrophobic and hydrophilic variants of Candida albicans. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1989 Jan 15;48(2):167–171. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1989.tb03293.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazen K. C., Hazen B. W. Temperature-modulated physiological characteristics of Candida albicans. Microbiol Immunol. 1987;31(6):497–508. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1987.tb03112.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazen K. C., Plotkin B. J., Klimas D. M. Influence of growth conditions on cell surface hydrophobicity of Candida albicans and Candida glabrata. Infect Immun. 1986 Oct;54(1):269–271. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.1.269-271.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israelachvili J. N., McGuiggan P. M. Forces between surfaces in liquids. Science. 1988 Aug 12;241(4867):795–800. doi: 10.1126/science.241.4867.795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy M. J. Adhesion and association mechanisms of Candida albicans. Curr Top Med Mycol. 1988;2:73–169. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4612-3730-3_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy M. J., Rogers A. L., Hanselmen L. R., Soll D. R., Yancey R. J., Jr Variation in adhesion and cell surface hydrophobicity in Candida albicans white and opaque phenotypes. Mycopathologia. 1988 Jun;102(3):149–156. doi: 10.1007/BF00437397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy M. J., Sandin R. L. Influence of growth conditions on Candida albicans adhesion, hydrophobicity and cell wall ultrastructure. J Med Vet Mycol. 1988 Apr;26(2):79–92. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy M. J., Volz P. A., Edwards C. A., Yancey R. J. Mechanisms of association of Candida albicans with intestinal mucosa. J Med Microbiol. 1987 Dec;24(4):333–341. doi: 10.1099/00222615-24-4-333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura L. H., Pearsall N. N. Relationship between germination of Candida albicans and increased adherence to human buccal epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1980 May;28(2):464–468. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.2.464-468.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King R. D., Lee J. C., Morris A. L. Adherence of Candida albicans and other Candida species to mucosal epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):667–674. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.667-674.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klotz S. A., Drutz D. J., Zajic J. E. Factors governing adherence of Candida species to plastic surfaces. Infect Immun. 1985 Oct;50(1):97–101. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.1.97-101.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. C., King R. D. Characterization of Candida albicans adherence to human vaginal epithelial cells in vitro. Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):1024–1030. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.1024-1030.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macura A. B. Hydrophobicity of Candida albicans related to their adherence to mucosal epithelial cells. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1987 Oct;266(3-4):491–496. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(87)80231-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murgui A., Elorza M. V., Sentandreu R. Tunicamycin and papulacandin B inhibit incorporation of specific mannoproteins into the wall of Candida albicans regenerating protoplasts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Dec 10;884(3):550–558. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(86)90207-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pashley R. M., McGuiggan P. M., Ninham B. W., Evans D. F. Attractive forces between uncharged hydrophobic surfaces: direct measurements in aqueous solution. Science. 1985 Sep 13;229(4718):1088–1089. doi: 10.1126/science.4035349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinhart H., Muller G., Sobel J. D. Specificity and mechanism of in vitro adherence of Candida albicans. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 1985 Sep-Oct;15(5):406–413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotrosen D., Calderone R. A., Edwards J. E., Jr Adherence of Candida species to host tissues and plastic surfaces. Rev Infect Dis. 1986 Jan-Feb;8(1):73–85. doi: 10.1093/clinids/8.1.73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotrosen D., Edwards J. E., Jr, Gibson T. R., Moore J. C., Cohen A. H., Green I. Adherence of Candida to cultured vascular endothelial cells: mechanisms of attachment and endothelial cell penetration. J Infect Dis. 1985 Dec;152(6):1264–1274. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.6.1264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samaranayake L. P., MacFarlane T. W. The adhesion of the yeast Candida albicans to epithelial cells of human origin in vitro. Arch Oral Biol. 1981;26(10):815–820. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(81)90178-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samaranayake L. P., MacFarlane T. W. The effect of dietary carbohydrates on the in-vitro adhesion of Candida albicans to epithelial cells. J Med Microbiol. 1982 Nov;15(4):511–517. doi: 10.1099/00222615-15-4-511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandin R. L., Rogers A. L., Patterson R. J., Beneke E. S. Evidence for mannose-mediated adherence of Candida albicans to human buccal cells in vitro. Infect Immun. 1982 Jan;35(1):79–85. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.1.79-85.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal E., Lehrer N., Ofek I. Adherence of Candida albicans to human vaginal epithelial cells: inhibition by amino sugars. Exp Cell Biol. 1982;50(1):13–17. doi: 10.1159/000163121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobel J. D., Muller G., Buckley H. R. Critical role of germ tube formation in the pathogenesis of candidal vaginitis. Infect Immun. 1984 Jun;44(3):576–580. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.3.576-580.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



