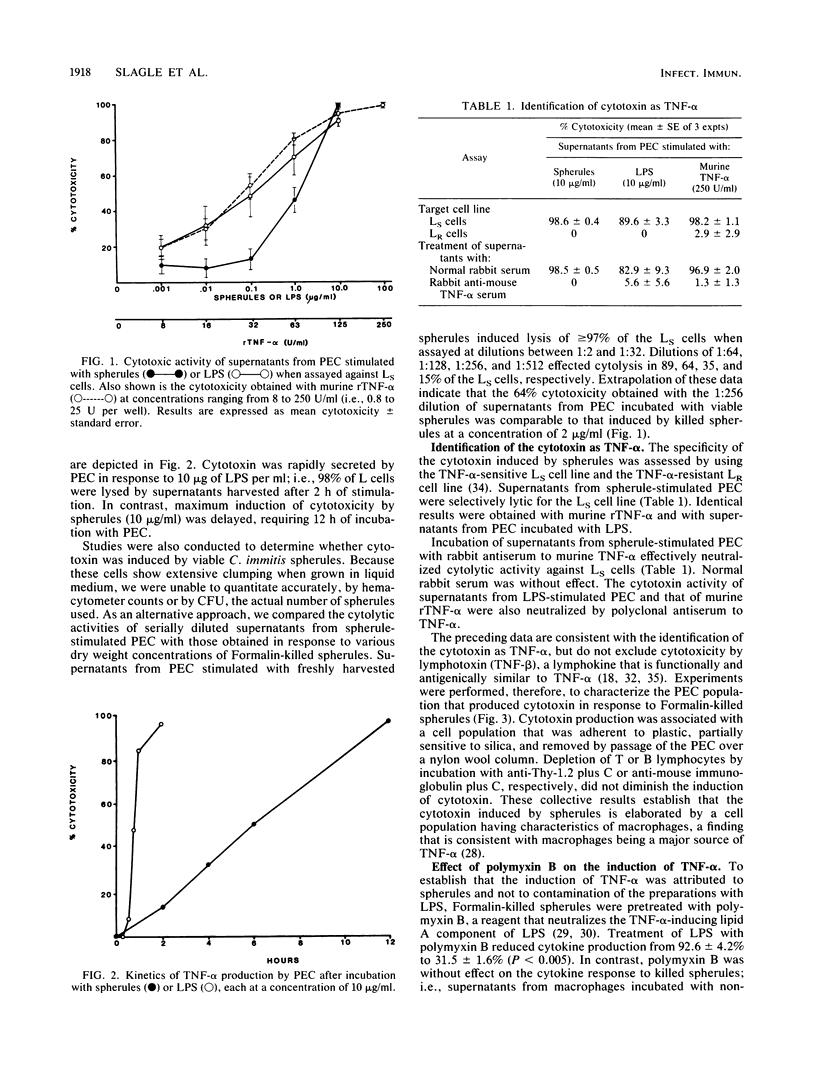
Abstract
The cytokine tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) functions as an immunomodulatory protein and as a mediator of cachexia. We report that viable or Formalin-killed spherules of Coccidioides immitis induced the secretion of TNF-alpha by peritoneal-exudate cells from BALB/c mice. The identification of the cytokine as TNF-alpha was based on its lytic activity against the TNF-alpha-sensitive LS murine fibrosarcoma cell line but not the TNF-alpha-resistant LR cell line, its neutralization by rabbit anti-TNF-alpha, and its secretion by peritoneal cells having characteristics of macrophages. The induction of TNF-alpha was to spherules and not to contaminating lipopolysaccharide (endotoxin), as evidenced by the finding that polymyxin B, a reagent that blocks the TNF-alpha-inducing component of lipopolysaccharide, did not negate the production of TNF-alpha in response to spherules, whereas pretreatment of spherules with hyperimmune goat antiserum to spherulin neutralized the induction of TNF-alpha by these cells. The demonstration that C. immitis activates macrophages to secrete TNF-alpha in vitro is a new finding and warrants studies to determine whether this cytokine is produced during active coccidioidomycosis.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aderka D., Holtmann H., Toker L., Hahn T., Wallach D. Tumor necrosis factor induction by Sendai virus. J Immunol. 1986 Apr 15;136(8):2938–2942. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bate C. A., Taverne J., Playfair J. H. Malarial parasites induce TNF production by macrophages. Immunology. 1988 Jun;64(2):227–231. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bermudez L. E., Young L. S. Tumor necrosis factor, alone or in combination with IL-2, but not IFN-gamma, is associated with macrophage killing of Mycobacterium avium complex. J Immunol. 1988 May 1;140(9):3006–3013. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Greenwald D., Hulmes J. D., Chang M., Pan Y. C., Mathison J., Ulevitch R., Cerami A. Identity of tumour necrosis factor and the macrophage-secreted factor cachectin. Nature. 1985 Aug 8;316(6028):552–554. doi: 10.1038/316552a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Milsark I. W., Cerami A. C. Passive immunization against cachectin/tumor necrosis factor protects mice from lethal effect of endotoxin. Science. 1985 Aug 30;229(4716):869–871. doi: 10.1126/science.3895437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanchard D. K., Djeu J. Y., Klein T. W., Friedman H., Stewart W. E., 2nd Induction of tumor necrosis factor by Legionella pneumophila. Infect Immun. 1987 Feb;55(2):433–437. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.2.433-437.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanchard D. K., Djeu J. Y., Klein T. W., Friedman H., Stewart W. E., 2nd Protective effects of tumor necrosis factor in experimental Legionella pneumophila infections of mice via activation of PMN function. J Leukoc Biol. 1988 May;43(5):429–435. doi: 10.1002/jlb.43.5.429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caput D., Beutler B., Hartog K., Thayer R., Brown-Shimer S., Cerami A. Identification of a common nucleotide sequence in the 3'-untranslated region of mRNA molecules specifying inflammatory mediators. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1670–1674. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carswell E. A., Old L. J., Kassel R. L., Green S., Fiore N., Williamson B. An endotoxin-induced serum factor that causes necrosis of tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3666–3670. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark I. A., Hunt N. H., Butcher G. A., Cowden W. B. Inhibition of murine malaria (Plasmodium chabaudi) in vivo by recombinant interferon-gamma or tumor necrosis factor, and its enhancement by butylated hydroxyanisole. J Immunol. 1987 Nov 15;139(10):3493–3496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox R. A., Britt L. A. Antigenic identity of biologically active antigens in coccidioidin and spherulin. Infect Immun. 1987 Nov;55(11):2590–2596. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.11.2590-2596.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox R. A., Kennell W. Suppression of T-lymphocyte response by Coccidioides immitis antigen. Infect Immun. 1988 Jun;56(6):1424–1429. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.6.1424-1429.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damonneville M., Wietzerbin J., Pancré V., Joseph M., Delanoye A., Capron A., Auriault C. Recombinant tumor necrosis factors mediate platelet cytotoxicity to Schistosoma mansoni larvae. J Immunol. 1988 Jun 1;140(11):3962–3965. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Titto E. H., Catterall J. R., Remington J. S. Activity of recombinant tumor necrosis factor on Toxoplasma gondii and Trypanosoma cruzi. J Immunol. 1986 Aug 15;137(4):1342–1345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Djeu J. Y., Blanchard D. K., Halkias D., Friedman H. Growth inhibition of Candida albicans by human polymorphonuclear neutrophils: activation by interferon-gamma and tumor necrosis factor. J Immunol. 1986 Nov 1;137(9):2980–2984. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Djeu J. Y., Blanchard D. K., Richards A. L., Friedman H. Tumor necrosis factor induction by Candida albicans from human natural killer cells and monocytes. J Immunol. 1988 Dec 1;141(11):4047–4052. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray P. W., Aggarwal B. B., Benton C. V., Bringman T. S., Henzel W. J., Jarrett J. A., Leung D. W., Moffat B., Ng P., Svedersky L. P. Cloning and expression of cDNA for human lymphotoxin, a lymphokine with tumour necrosis activity. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):721–724. doi: 10.1038/312721a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haidaris C. G., Haynes J. D., Meltzer M. S., Allison A. C. Serum containing tumor necrosis factor is cytotoxic for the human malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum. Infect Immun. 1983 Oct;42(1):385–393. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.1.385-393.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havell E. A. Production of tumor necrosis factor during murine listeriosis. J Immunol. 1987 Dec 15;139(12):4225–4231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izumi S., Hirai O., Hayashi K., Konishi Y., Okuhara M., Kohsaka M., Aoki H., Yamamura Y. Induction of a tumor necrosis factor-like activity by Nocardia rubra cell wall skeleton. Cancer Res. 1987 Apr 1;47(7):1785–1792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julius M. H., Simpson E., Herzenberg L. A. A rapid method for the isolation of functional thymus-derived murine lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1973 Oct;3(10):645–649. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830031011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jupin C., Anderson S., Damais C., Alouf J. E., Parant M. Toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 as an inducer of human tumor necrosis factors and gamma interferon. J Exp Med. 1988 Mar 1;167(3):752–761. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.3.752. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagan E., Hartmann D. P. Elimination of macrophages with silica and asbestos. Methods Enzymol. 1984;108:325–335. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(84)08099-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawakami M., Cerami A. Studies of endotoxin-induced decrease in lipoprotein lipase activity. J Exp Med. 1981 Sep 1;154(3):631–639. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.3.631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le J., Vilcek J. Tumor necrosis factor and interleukin 1: cytokines with multiple overlapping biological activities. Lab Invest. 1987 Mar;56(3):234–248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leist T. P., Frei K., Kam-Hansen S., Zinkernagel R. M., Fontana A. Tumor necrosis factor alpha in cerebrospinal fluid during bacterial, but not viral, meningitis. Evaluation in murine model infections and in patients. J Exp Med. 1988 May 1;167(5):1743–1748. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.5.1743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. C., Jacobs D. M. Binding of polymyxin B to the lipid A portion of bacterial lipopolysaccharides. Immunochemistry. 1976 Oct;13(10):813–818. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(76)90181-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Männel D. N., Moore R. N., Mergenhagen S. E. Macrophages as a source of tumoricidal activity (tumor-necrotizing factor). Infect Immun. 1980 Nov;30(2):523–530. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.2.523-530.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishijima M., Amano F., Akamatsu Y., Akagawa K., Tokunaga T., Raetz C. R. Macrophage activation by monosaccharide precursors of Escherichia coli lipid A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):282–286. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAPPAGIANIS D., MILLER R. L., SMITH C. E., KOBAYASHI G. S. Response of monkeys to respiratory challenge following subcutaneous inoculation with Coccidioides immitis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1960 Aug;82:244–250. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1960.82.2.244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennica D., Nedwin G. E., Hayflick J. S., Seeburg P. H., Derynck R., Palladino M. A., Kohr W. J., Aggarwal B. B., Goeddel D. V. Human tumour necrosis factor: precursor structure, expression and homology to lymphotoxin. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):724–729. doi: 10.1038/312724a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Repo H., Jättelä M., Leirisalo-Repo M., Hurme M. Production of tumour necrosis factor and interleukin 1 by monocytes of patients with previous Yersinia arthritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1988 Jun;72(3):410–414. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin B. Y., Anderson S. L., Sullivan S. A., Williamson B. D., Carswell E. A., Old L. J. Nonhematopoietic cells selected for resistance to tumor necrosis factor produce tumor necrosis factor. J Exp Med. 1986 Oct 1;164(4):1350–1355. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.4.1350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruddle N. H., Powell M. B., Conta B. S. Lymphotoxin, a biologically relevant model lymphokine. Lymphokine Res. 1983;2(1):23–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scuderi P., Sterling K. E., Lam K. S., Finley P. R., Ryan K. J., Ray C. G., Petersen E., Slymen D. J., Salmon S. E. Raised serum levels of tumour necrosis factor in parasitic infections. Lancet. 1986 Dec 13;2(8520):1364–1365. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)92007-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherry B., Cerami A. Cachectin/tumor necrosis factor exerts endocrine, paracrine, and autocrine control of inflammatory responses. J Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;107(4):1269–1277. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.4.1269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taverne J., Tavernier J., Fiers W., Playfair J. H. Recombinant tumour necrosis factor inhibits malaria parasites in vivo but not in vitro. Clin Exp Immunol. 1987 Jan;67(1):1–4. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracey K. J., Beutler B., Lowry S. F., Merryweather J., Wolpe S., Milsark I. W., Hariri R. J., Fahey T. J., 3rd, Zentella A., Albert J. D. Shock and tissue injury induced by recombinant human cachectin. Science. 1986 Oct 24;234(4775):470–474. doi: 10.1126/science.3764421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracey K. J., Wei H., Manogue K. R., Fong Y., Hesse D. G., Nguyen H. T., Kuo G. C., Beutler B., Cotran R. S., Cerami A. Cachectin/tumor necrosis factor induces cachexia, anemia, and inflammation. J Exp Med. 1988 Mar 1;167(3):1211–1227. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.3.1211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vacheron F., Smets P., Nauciel C., Guenounou M. Immunological activities of RU-41740, a glycoproteic extract from Klebsiella pneumoniae. II.--Activation of macrophage cytotoxicity against tumour cells and production of a cytotoxic factor. Ann Inst Pasteur Immunol. 1987 Jul-Aug;138(4):571–584. doi: 10.1016/s0769-2625(87)80127-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valone S. E., Rich E. A., Wallis R. S., Ellner J. J. Expression of tumor necrosis factor in vitro by human mononuclear phagocytes stimulated with whole Mycobacterium bovis BCG and mycobacterial antigens. Infect Immun. 1988 Dec;56(12):3313–3315. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.12.3313-3315.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wirth J. J., Kierszenbaum F. Recombinant tumor necrosis factor enhances macrophage destruction of Trypanosoma cruzi in the presence of bacterial endotoxin. J Immunol. 1988 Jul 1;141(1):286–288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto A., Nagamuta M., Usami H., Sugawara Y., Watanabe N., Niitsu Y., Urushizaki I. Release of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) into mouse peritoneal fluids by OK-432, a streptococcal preparation. Immunopharmacology. 1986 Apr;11(2):79–86. doi: 10.1016/0162-3109(86)90027-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto A., Usami H., Nagamuta M., Sugawara Y., Hamada S., Yamamoto T., Kato K., Kokeguchi S., Kotani S. The use of lipoteichoic acid (LTA) from Streptococcus pyogenes to induce a serum factor causing tumour necrosis. Br J Cancer. 1985 May;51(5):739–742. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1985.112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



