Abstract
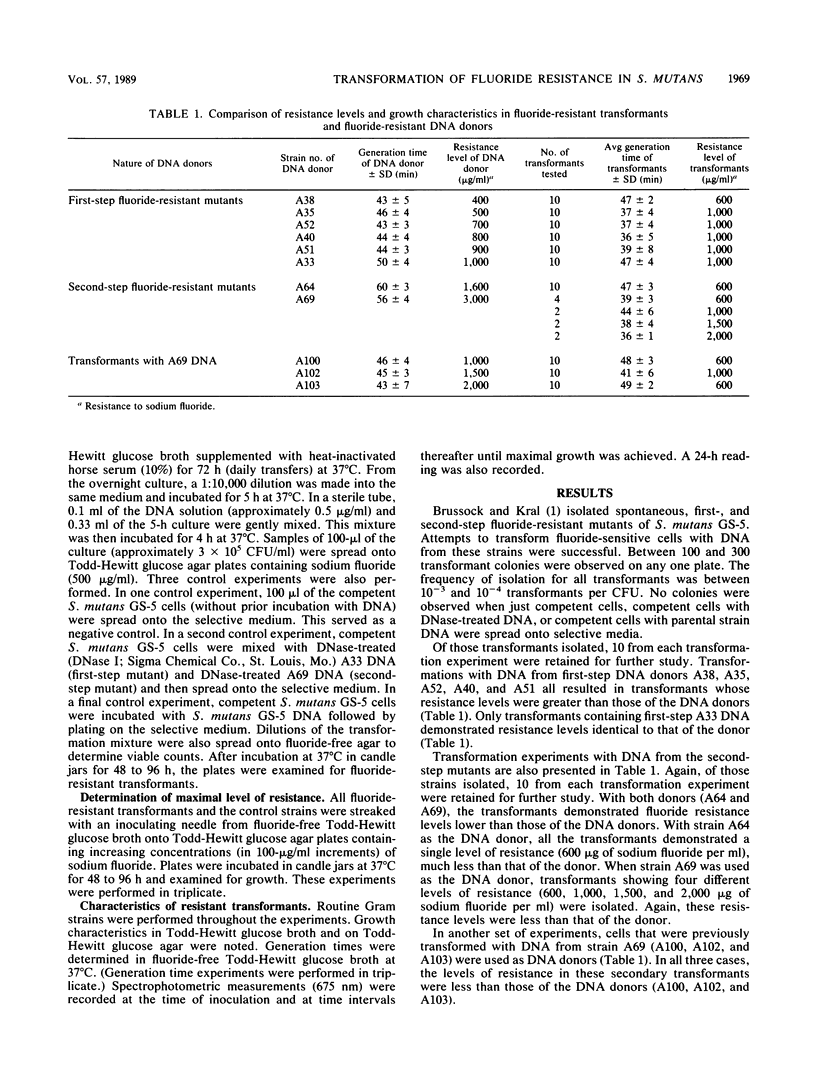
To study the nature of fluoride resistance in Streptococcus mutans, we transformed DNA extracted from fluoride-resistant mutants of S. mutans GS-5 into fluoride-sensitive cells of the same strain. Transformation with DNA from first-step mutants produced transformants with resistance to either 600 or 1,000 micrograms of sodium fluoride per ml, both of which are within the first-step resistance range (400 to 1,000 micrograms/ml). In five of six of these transformation experiments, however, the transformant resistance levels were greater than those of their respective DNA donors. Transformation with DNA from a second-step mutant resistant to 1,600 micrograms/ml resulted in transformants resistant to 600 micrograms/ml, similar to some transformants receiving DNA from first-step mutants. When a second-step mutant resistant to 3,000 micrograms/ml was used as a DNA donor, four different levels of resistance were seen in the transformants (600, 1,000, 1,500, and 2,000 micrograms/ml). In many cases, the growth rates of the transformants (first and second step) were faster than those of the DNA donors. Additionally, many of the transformants demonstrated abrupt shifts in growth rates at relatively low culture densities.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bunick F. J., Kashket S. Enolases from fluoride-sensitive and fluoride-resistant streptococci. Infect Immun. 1981 Dec;34(3):856–863. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.3.856-863.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry D., Kuramitsu H. K. Genetic transformation of Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1981 Jun;32(3):1295–1297. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.3.1295-1297.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



