Abstract
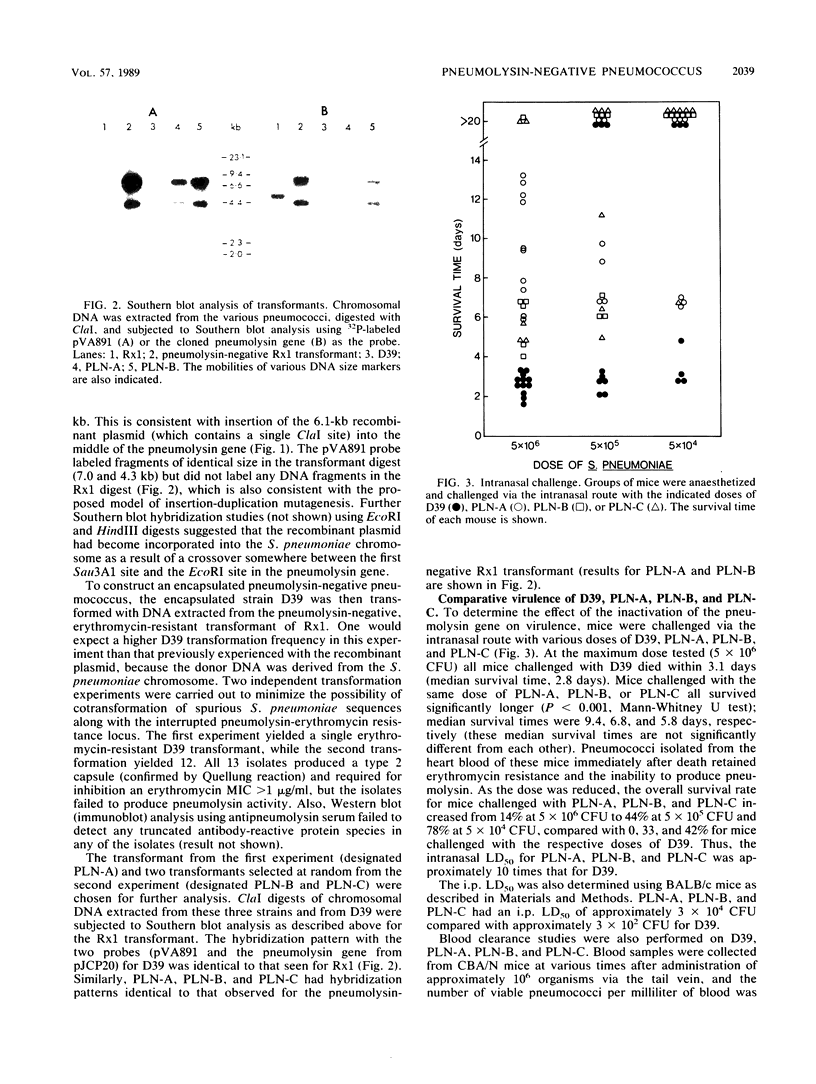
Insertion-duplication mutagenesis was used to construct a pneumolysin-negative derivative of Streptococcus pneumoniae. This was achieved by first transforming the nonencapsulated strain Rx1 with a derivative of the vector pVA891 carrying a 690-base-pair DNA fragment from the middle of the pneumolysin structural gene. DNA was extracted from the resultant erythromycin-resistant, pneumolysin-negative rough pneumococcus and used to transform S. pneumoniae D39, a virulent type 2 strain. Several erythromycin-resistant transformants were obtained from two independent experiments, and none of these produced pneumolysin. Southern blot analysis confirmed that the pneumolysin gene in these transformants had been interrupted by the plasmid-derived sequences. The pneumolysin-negative mutants showed reduced virulence for mice compared with D39, as judged by survival time after intranasal challenge, intraperitoneal 50% lethal dose, and blood clearance studies. Pneumolysin production was reinstated in one of the mutants by transformation with the cloned pneumolysin gene, with the concomitant loss of erythromycin resistance; the virulence in mice of this isolate was indistinguishable from that of D39. These results confirm the involvement of pneumolysin in pneumococcal pathogenesis.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berry A. M., Paton J. C., Glare E. M., Hansman D., Catcheside D. E. Cloning and expression of the pneumococcal neuraminidase gene in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1988 Nov 30;71(2):299–305. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90046-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briles D. E., Nahm M., Schroer K., Davie J., Baker P., Kearney J., Barletta R. Antiphosphocholine antibodies found in normal mouse serum are protective against intravenous infection with type 3 streptococcus pneumoniae. J Exp Med. 1981 Mar 1;153(3):694–705. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.3.694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chetty C., Kreger A. Characterization of pneumococcal purpura-producing principle. Infect Immun. 1980 Jul;29(1):158–164. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.1.158-164.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrante A., Rowan-Kelly B., Paton J. C. Inhibition of in vitro human lymphocyte response by the pneumococcal toxin pneumolysin. Infect Immun. 1984 Nov;46(2):585–589. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.2.585-589.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaillard J. L., Berche P., Sansonetti P. Transposon mutagenesis as a tool to study the role of hemolysin in the virulence of Listeria monocytogenes. Infect Immun. 1986 Apr;52(1):50–55. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.1.50-55.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lock R. A., Paton J. C., Hansman D. Comparative efficacy of pneumococcal neuraminidase and pneumolysin as immunogens protective against Streptococcus pneumoniae. Microb Pathog. 1988 Dec;5(6):461–467. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(88)90007-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lock R. A., Paton J. C., Hansman D. Purification and immunological characterization of neuraminidase produced by Streptococcus pneumoniae. Microb Pathog. 1988 Jan;4(1):33–43. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(88)90046-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macrina F. L., Evans R. P., Tobian J. A., Hartley D. L., Clewell D. B., Jones K. R. Novel shuttle plasmid vehicles for Escherichia-Streptococcus transgeneric cloning. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(1):145–150. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90176-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macrina F. L., Tobian J. A., Jones K. R., Evans R. P., Clewell D. B. A cloning vector able to replicate in Escherichia coli and Streptococcus sanguis. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):345–353. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90025-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDaniel L. S., Yother J., Vijayakumar M., McGarry L., Guild W. R., Briles D. E. Use of insertional inactivation to facilitate studies of biological properties of pneumococcal surface protein A (PspA). J Exp Med. 1987 Feb 1;165(2):381–394. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.2.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nandoskar M., Ferrante A., Bates E. J., Hurst N., Paton J. C. Inhibition of human monocyte respiratory burst, degranulation, phospholipid methylation and bactericidal activity by pneumolysin. Immunology. 1986 Dec;59(4):515–520. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paton J. C., Ferrante A. Inhibition of human polymorphonuclear leukocyte respiratory burst, bactericidal activity, and migration by pneumolysin. Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):1212–1216. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.1212-1216.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paton J. C., Lock R. A., Hansman D. J. Effect of immunization with pneumolysin on survival time of mice challenged with Streptococcus pneumoniae. Infect Immun. 1983 May;40(2):548–552. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.2.548-552.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paton J. C., Rowan-Kelly B., Ferrante A. Activation of human complement by the pneumococcal toxin pneumolysin. Infect Immun. 1984 Mar;43(3):1085–1087. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.3.1085-1087.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoemaker N. B., Guild W. R. Destruction of low efficiency markers is a slow process occurring at a heteroduplex stage of transformation. Mol Gen Genet. 1974;128(4):283–290. doi: 10.1007/BF00268516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. A., Allen R. L., Falmagne P., Johnson M. K., Boulnois G. J. Molecular cloning, characterization, and complete nucleotide sequence of the gene for pneumolysin, the sulfhydryl-activated toxin of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Infect Immun. 1987 May;55(5):1184–1189. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.5.1184-1189.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yother J., McDaniel L. S., Briles D. E. Transformation of encapsulated Streptococcus pneumoniae. J Bacteriol. 1986 Dec;168(3):1463–1465. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.3.1463-1465.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




