Abstract
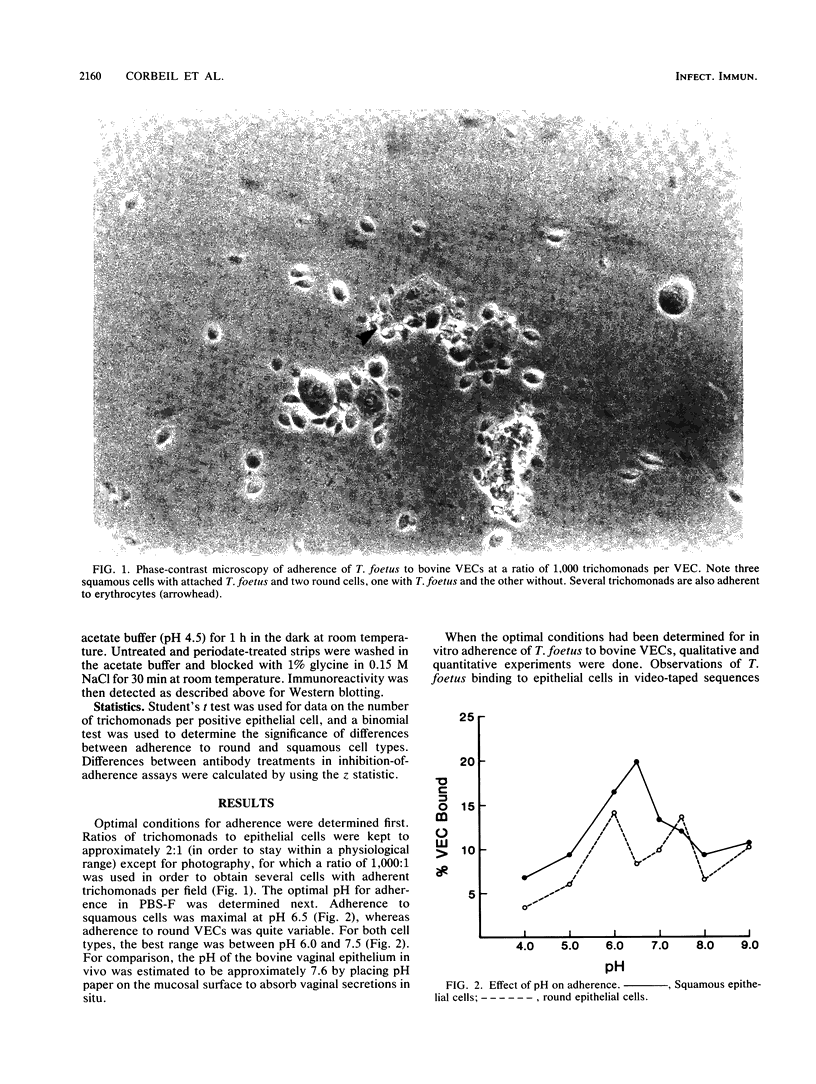
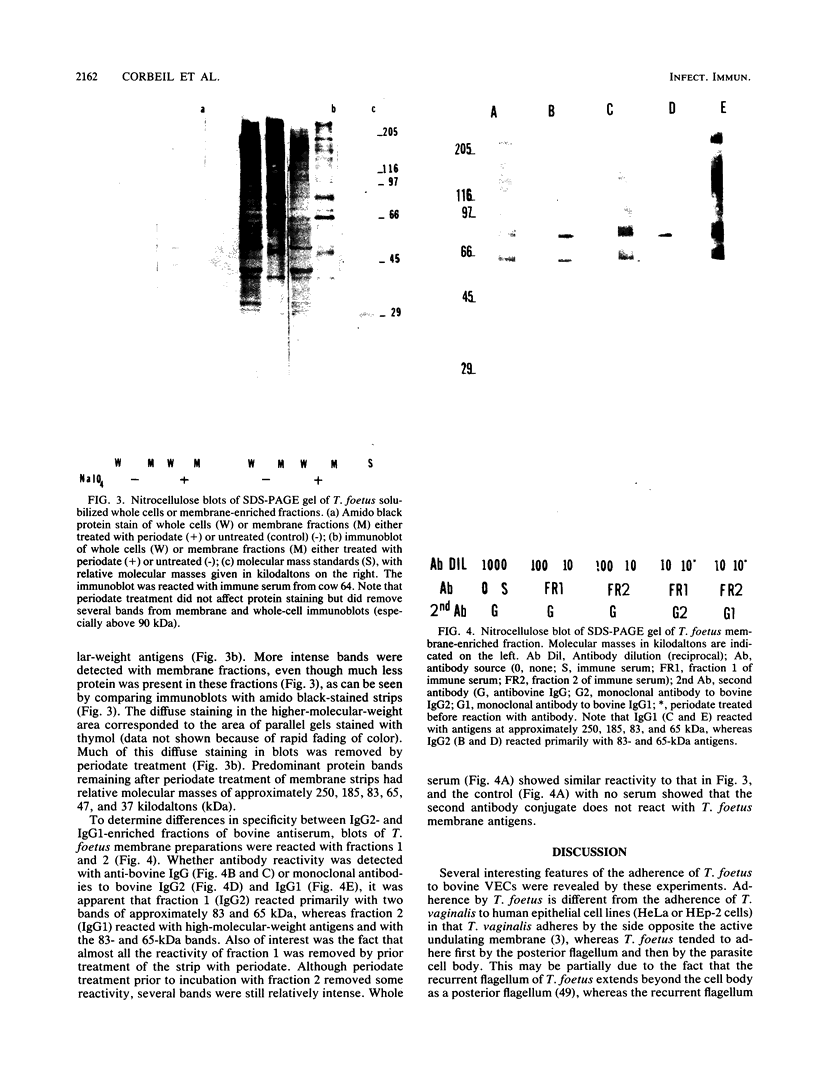
Adherence of Tritrichomonas foetus to bovine vaginal epithelial cells (VECs) in vitro was investigated with fresh washed bovine VECs and log-phase cultures of T. foetus. Observation under phase-contrast microscopy showed that T. foetus usually adhered first by the posterior flagellum and later by the body. Significantly more keratinized squamous epithelial cells were detected with attached parasites than nonkeratinized round epithelial cells. The optimal pH range for attachment was 6.0 to 7.5, with peak attachment at pH 6.5 for squamous VECs. Surface-reactive bovine antiserum to T. foetus prevented adherence to bovine squamous VECs. Inhibition of adherence occurred at nonagglutinating, nonimmobilizing serum dilutions. Antiserum fractions enriched for immunoglobulin G1 inhibited adherence, but fractions enriched for immunoglobulin G2 did not. The inhibitory antiserum was specific for several medium- to high-molecular-weight membrane antigens as detected in Western blots (immunoblots). The ability of surface-reactive antibodies to prevent adherence and to agglutinate and immobilize T. foetus indicates that they may be protective.
Full text
PDF





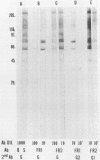
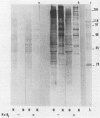
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alderete J. F., Demeś P., Gombosova A., Valent M., Fabusová M., Jánoska A., Stefanovic J., Arroyo R. Specific parasitism of purified vaginal epithelial cells by Trichomonas vaginalis. Infect Immun. 1988 Oct;56(10):2558–2562. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.10.2558-2562.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alderete J. F., Garza G. E. Identification and properties of Trichomonas vaginalis proteins involved in cytadherence. Infect Immun. 1988 Jan;56(1):28–33. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.1.28-33.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alderete J. F., Garza G. E. Specific nature of Trichomonas vaginalis parasitism of host cell surfaces. Infect Immun. 1985 Dec;50(3):701–708. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.3.701-708.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alderete J. F., Garza G., Smith J., Spence M. Trichomonas vaginalis: electrophoretic analysis and heterogeneity among isolates due to high-molecular-weight trichomonad proteins. Exp Parasitol. 1986 Apr;61(2):244–251. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(86)90158-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alderete J. F., Kasmala L., Metcalfe E., Garza G. E. Phenotypic variation and diversity among Trichomonas vaginalis isolates and correlation of phenotype with trichomonal virulence determinants. Infect Immun. 1986 Aug;53(2):285–293. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.2.285-293.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alderete J. F., Kasmala L. Monoclonal antibody to a major glycoprotein immunogen mediates differential complement-independent lysis of Trichomonas vaginalis. Infect Immun. 1986 Sep;53(3):697–699. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.3.697-699.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alderete J. F., Pearlman E. Pathogenic Trichomonas vaginalis cytotoxicity to cell culture monolayers. Br J Vener Dis. 1984 Apr;60(2):99–105. doi: 10.1136/sti.60.2.99. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alderete J. F., Suprun-Brown L., Kasmala L. Monoclonal antibody to a major surface glycoprotein immunogen differentiates isolates and subpopulations of Trichomonas vaginalis. Infect Immun. 1986 Apr;52(1):70–75. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.1.70-75.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benchimol M., Elias C. A., de Souza W. Tritrichomonas foetus: fine structure of freeze-fractured membranes. J Protozool. 1982 Aug;29(3):348–353. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1982.tb05413.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benchimol M., Pereira M. E., Elias C. A., de Souza W. Cell surface carbohydrates in Tritrichomonas foetus. J Protozool. 1981 Aug;28(3):337–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1981.tb02861.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg R. L., Firehammer B. D., Border M., Myers L. L. Effects of passively and actively acquired antibody on bovine campylobacteriosis (vibriosis). Am J Vet Res. 1979 Jan;40(1):21–25. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Border M. M., Firehammer B. D. Antigens of Campylobacter fetus subsp fetus eliciting vaccinal immunity in heifers. Am J Vet Res. 1980 May;41(5):746–750. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess D. E. Clonal and geographic distribution of a surface antigen of Tritrichomonas foetus. J Protozool. 1988 Feb;35(1):119–122. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1988.tb04090.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess D. E. Tritrichomonas foetus: preparation of monoclonal antibodies with effector function. Exp Parasitol. 1986 Oct;62(2):266–274. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(86)90031-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler J. E. Biochemistry and biology of ruminant immunoglobulins. Prog Vet Microbiol Immunol. 1986;2:1–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark B. L., Dufty J. H., Parsonson I. M. The effect of Tritrichomonas foetus infection on calving rates in beef cattle. Aust Vet J. 1983 Mar;60(3):71–74. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-0813.1983.tb05873.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark B. L., Emery D. L., Dufty J. H. Therapeutic immunisation of bulls with the membranes and glycoproteins of Tritrichomonas foetus var. brisbane. Aust Vet J. 1984 Feb;61(2):65–66. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-0813.1984.tb07197.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connelly R. J., Torian B. E., Stibbs H. H. Identification of a surface antigen of Trichomonas vaginalis. Infect Immun. 1985 Aug;49(2):270–274. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.2.270-274.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbeil L. B. Criteria for development of animal models of diseases of the reproductive system. Am J Pathol. 1980 Dec;101(3 Suppl):S241–S253. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbeil L. B., Duncan J. R., Schurig G. G., Hall C. E., Winter A. J. Bovine venereal vibriosis: variations in immunoglobulin class of antibodies in genital secretions and serum. Infect Immun. 1974 Nov;10(5):1084–1090. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.5.1084-1090.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbeil L. B., Schurig G. G., Bier P. J., Winter A. J. Bovine veneral vibriosis: antigenic variation of the bacterium during infection. Infect Immun. 1975 Feb;11(2):240–244. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.2.240-244.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbeil L. B., Schurig G. G., Duncan J. R., Wilkie B. N., Winter A. J. Immunity in the female bovine reproductive tract based on the response to "Campylobacter fetus". Adv Exp Med Biol. 1981;137:729–743. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan J. R., Wilkie B. N., Hiestand F., Winter A. J. The serum and secretory immunoglobulins of cattle: characterization and quantitation. J Immunol. 1972 Apr;108(4):965–976. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gander J. E. Gel protein stains: glycoproteins. Methods Enzymol. 1984;104:447–451. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(84)04112-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garber G. E., Proctor E. M., Bowie W. R. Immunogenic proteins of Trichomonas vaginalis as demonstrated by the immunoblot technique. Infect Immun. 1986 Jan;51(1):250–253. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.1.250-253.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garber N., Sharon N., Shohet D., Lam J. S., Doyle R. J. Contribution of hydrophobicity to hemagglutination reactions of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1985 Oct;50(1):336–337. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.1.336-337.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodger W. J., Skirrow S. Z. Epidemiologic and economic analyses of an unusually long epizootic of trichomoniasis in a large California dairy herd. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1986 Oct 1;189(7):772–776. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall M. R., Huang J. C., Ota R., Redelman D., Hanks D., Taylor R. E. Characterization of Tritrichomonas foetus antigens, using bovine antiserum. Am J Vet Res. 1986 Dec;47(12):2549–2553. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimsey P. B., Darien B. J., Kendrick J. W., Franti C. E. Bovine trichomoniasis: diagnosis and treatment. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1980 Oct 1;177(7):616–619. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieger J. N., Holmes K. K., Spence M. R., Rein M. F., McCormack W. M., Tam M. R. Geographic variation among isolates of Trichomonas vaginalis: demonstration of antigenic heterogeneity by using monoclonal antibodies and the indirect immunofluorescence technique. J Infect Dis. 1985 Nov;152(5):979–984. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.5.979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieger J. N., Ravdin J. I., Rein M. F. Contact-dependent cytopathogenic mechanisms of Trichomonas vaginalis. Infect Immun. 1985 Dec;50(3):778–786. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.3.778-786.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mårdh P. A., Westtöm L. Adherence of bacterial to vaginal epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1976 Mar;13(3):661–666. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.3.661-666.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsonson I. M., Clark B. L., Dufty J. H. Early pathogenesis and pathology of Tritrichomonas foetus infection in virgin heifers. J Comp Pathol. 1976 Jan;86(1):59–66. doi: 10.1016/0021-9975(76)90028-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsonson I. M., Clark B. L., Dufty J. The pathogenesis of Tritrichomonas foetus infection in the bull. Aust Vet J. 1974 Oct;50(10):421–423. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-0813.1974.tb06861.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schurig G. G., Duncan J. R., Winter A. J. Elimination of genital vibriosis in female cattle by systemic immunization with killed cells or cell-free extracts of Campylobacter fetus. J Infect Dis. 1978 Oct;138(4):463–472. doi: 10.1093/infdis/138.4.463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schurig G. G., Hall C. E., Corbell L. B., Duncan J. R., Winter A. J. Bovine veneral vibriosis: cure of genital infection in females by systemic immunization. Infect Immun. 1975 Feb;11(2):245–251. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.2.245-251.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shackelford P. G., Nelson S. J., Palma A. T., Nahm M. H. Human antibodies to group A streptococcal carbohydrate. Ontogeny, subclass restriction, and clonal diversity. J Immunol. 1988 May 1;140(9):3200–3205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman P. M., Houston W. L., Boedeker E. C. Functional heterogeneity of intestinal Escherichia coli strains expressing type 1 somatic pili (fimbriae): assessment of bacterial adherence to intestinal membranes and surface hydrophobicity. Infect Immun. 1985 Sep;49(3):797–804. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.3.797-804.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siber G. R., Schur P. H., Aisenberg A. C., Weitzman S. A., Schiffman G. Correlation between serum IgG-2 concentrations and the antibody response to bacterial polysaccharide antigens. N Engl J Med. 1980 Jul 24;303(4):178–182. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198007243030402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torian B. E., Connelly R. J., Stephens R. S., Stibbs H. H. Specific and common antigens of Trichomonas vaginalis detected by monoclonal antibodies. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):270–275. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.270-275.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virji M., Heckels J. E. The role of common and type-specific pilus antigenic domains in adhesion and virulence of gonococci for human epithelial cells. J Gen Microbiol. 1984 May;130(5):1089–1095. doi: 10.1099/00221287-130-5-1089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wartoń A., Honigberg B. M. Structure of trichomonads as revealed by scanning electron microscopy. J Protozool. 1979 Feb;26(1):56–62. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1979.tb02732.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widders P. R., Paisley L. G., Gogolewski R. P., Evermann J. F., Smith J. W., Corbeil L. B. Experimental abortion and the systemic immune response to "Haemophilus somnus" in cattle. Infect Immun. 1986 Nov;54(2):555–560. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.2.555-560.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodward M. P., Young W. W., Jr, Bloodgood R. A. Detection of monoclonal antibodies specific for carbohydrate epitopes using periodate oxidation. J Immunol Methods. 1985 Apr 8;78(1):143–153. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(85)90337-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zawaneh S. M., Ayoub E. M., Baer H., Cruz A. C., Spellacy W. N. Factors influencing adherence of group B streptococci to human vaginal epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1979 Nov;26(2):441–447. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.2.441-447.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]