Abstract
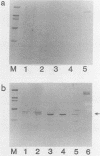
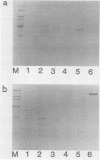
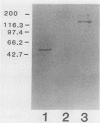
We isolated a glucan-binding domain of water-insoluble glucan synthase (GTF-I) of Streptococcus sobrinus B13. Mild trypsin digestion of GTF-I bound to a water-insoluble glucan (IG) produced one predominant large fragment (55 kilodaltons). The fragment was easily recovered in IG precipitate. The isolated fragment had the same degree of affinity to IG as did the native GTF-I but no glucan synthesis activity. By the same method, a similar 55-kilodalton fragment was protected for GTF-Sd but not for GTF-Si. Immunological comparisons using specific antisera against the purified glucan-binding fragment of GTF-I from strain B13 indicated that GTF-I and GTF-S have a distinct glucan-binding domain.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aoki H., Shiroza T., Hayakawa M., Sato S., Kuramitsu H. K. Cloning of a Streptococcus mutans glucosyltransferase gene coding for insoluble glucan synthesis. Infect Immun. 1986 Sep;53(3):587–594. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.3.587-594.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferretti J. J., Gilpin M. L., Russell R. R. Nucleotide sequence of a glucosyltransferase gene from Streptococcus sobrinus MFe28. J Bacteriol. 1987 Sep;169(9):4271–4278. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.9.4271-4278.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilpin M. L., Russell R. R., Morrissey P. Cloning and expression of two Streptococcus mutans glucosyltransferases in Escherichia coli K-12. Infect Immun. 1985 Aug;49(2):414–416. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.2.414-416.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamada S., Slade H. D. Biology, immunology, and cariogenicity of Streptococcus mutans. Microbiol Rev. 1980 Jun;44(2):331–384. doi: 10.1128/mr.44.2.331-384.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamada S., Torii M. Interaction of glucosyltransferase from Streptococcus mutans with various glucans. J Gen Microbiol. 1980 Jan;116(1):51–59. doi: 10.1099/00221287-116-1-51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCabe M. M., Alberts M., Stein J. Monoclonal antibodies to the extracellular glucosyltransferases from Streptococcus sobrinus 6715. Infect Immun. 1987 Aug;55(8):1900–1905. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.8.1900-1905.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mooser G., Shur D., Lyou M., Watanabe C. Kinetic studies on dextransucrase from the cariogenic oral bacterium Streptococcus mutans. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 10;260(11):6907–6915. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mooser G., Wong C. Isolation of a glucan-binding domain of glucosyltransferase (1,6-alpha-glucan synthase) from Streptococcus sobrinus. Infect Immun. 1988 Apr;56(4):880–884. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.4.880-884.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]