Abstract
The Pseudomonas aeruginosa genome (G + C content 65–67%, size 5.5–7 Mbp) is made up of a single circular chromosome and a variable number of plasmids. Sequencing of complete genomes or blocks of the accessory genome has revealed that the genome encodes a large repertoire of transporters, transcriptional regulators, and two-component regulatory systems which reflects its metabolic diversity to utilize a broad range of nutrients. The conserved core component of the genome is largely collinear among P. aeruginosa strains and exhibits an interclonal sequence diversity of 0.5–0.7%. Only a few loci of the core genome are subject to diversifying selection. Genome diversity is mainly caused by accessory DNA elements located in 79 regions of genome plasticity that are scattered around the genome and show an anomalous usage of mono- to tetradecanucleotides. Genomic islands of the pKLC102/PAGI-2 family that integrate into tRNALys or tRNAGly genes represent hotspots of inter- and intraclonal genomic diversity. The individual islands differ in their repertoire of metabolic genes that make a large contribution to the pangenome. In order to unravel intraclonal diversity of P. aeruginosa, the genomes of two members of the PA14 clonal complex from diverse habitats and geographic origin were compared. The genome sequences differed by less than 0.01% from each other. One hundred ninety-eight of the 231 single nucleotide substitutions (SNPs) were non-randomly distributed in the genome. Non-synonymous SNPs were mainly found in an integrated Pf1-like phage and in genes involved in transcriptional regulation, membrane and extracellular constituents, transport, and secretion. In summary, P. aeruginosa is endowed with a highly conserved core genome of low sequence diversity and a highly variable accessory genome that communicates with other pseudomonads and genera via horizontal gene transfer.
Keywords: Pseudomonas aeruginosa, genome, genomic island, core genome, accessory genome, clonal complex, oligonucleotide signature
Introduction
The genetic repertoire of Pseudomonas aeruginosa reflects the lifestyle of this ubiquitous bacterial species. P. aeruginosa strains are found in various environmental habitats as well as in animal and human hosts, where they can act as opportunistic pathogens. The colonization of this broad spectrum of habitats goes along with the ability to exploit many different nutrition sources and a high potential for adaptation to new (or changing) environmental conditions (Ramos, 2004).
The metabolic versatility is provided by genes encoding not only the enzymes participating in metabolic pathways, but also by a very high number of transcriptional regulators and two-component regulatory systems. More than 500 regulatory genes were identified in the genome of strain PAO1 (Stover et al., 2000). The genomes of P. aeruginosa strains are larger than those of most sequenced bacteria. Within the species, the genome size varies between 5.5 and 7 Mbp (Schmidt et al., 1996; Lee et al., 2006).
The divergence in genome size is caused by the so-called accessory genome. The major part of the genome, the core genome, is found in all P. aeruginosa strains with the respective DNA generally collinearly arranged (Römling et al., 1995). The core genome, with few exceptions of loci subject to diversifying selection, is highly conserved among clonal complexes and shows sequence diversities of 0.5–0.7% (Spencer et al., 2003; Lee et al., 2006; Cramer et al., 2011). The accessory genome consists of extrachromosomal elements like plasmids and of blocks of DNA inserted into the chromosome at various loci. The elements of the accessory genome can be present in subgroups of the P. aeruginosa population but may also occur only in single strains (Klockgether et al., 2007; Wiehlmann et al., 2007). The individual composition of the accessory genome accounts for most intra- and interclonal genome diversity in P. aeruginosa. The elements of the accessory genome were apparently acquired by horizontal gene transfer from different sources including other species or genera. Upon integration into the host chromosome they appear as “foreign” blocks in the core genome. Therefore, a P. aeruginosa chromosome is often described as a mosaic structure of conserved core genome frequently interrupted by the inserted parts of the accessory genome.
The individual mosaics also show remarkable plasticity. Ongoing acquisition of new foreign DNA as well as larger or smaller deletion events, mutations of single nucleotides and even chromosomal inversions (Römling et al., 1997; Ernst et al., 2003; Kresse et al., 2003; Smith et al., 2006; Klockgether et al., 2010; Cramer et al., 2011) – all of them potentially affecting parts of the core and/or the accessory genome – continuously modify the genome, modulate the P. aeruginosa strain’s phenotype and differentiate it from others.
Genome diversity of P. aeruginosa was initially analyzed by low-resolution physical mapping techniques (Schmidt et al., 1996; Römling et al., 1997). Thanks to progress in DNA sequencing technologies P. aeruginosa genomes can nowadays be compared by the base (Kung et al., 2010; Silby et al., 2011).
Genome Sequences
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is ubiquitous in aquatic habitats and colonizes animate surfaces of humans, animals and plants. Complete genome sequences, however, are so far only available for P. aeruginosa isolates from human infections (Table 1).
Table 1.
Features of sequenced P. aeruginosa strains.
| Strain | PAO1 | PA14 | PA7 | LESB58 | PACS2 | 2192 | C3719 | 39016 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Source | Wound | Clinical | Clinical | CF-patient | Clinical | CF-patient | CF-patient | Keratitis |
| Genome size (Mbp) | 6.264 | 6.538 | 6.588 | 6.602 | 6.492 | 6.905 | 6.222 | 6.667 |
| GC-content (%) | 66.6 | 66.3 | 66.5 | 66.5 | 66 | 66.2 | 66.5 | 66 |
| No. of protein coding ORFs | 5570 | 5892 | 6286 | 5925 | 5676 | 6191 | 5578 | 6401 |
The first complete genome sequencing was performed for strain PAO1 (Stover et al., 2000), derived from an Australian wound isolate from the 1950s. The PAO1 strain has been and is still the major reference for genetic and functional studies on P. aeruginosa. The PAO1 genome consists of a 6.264-Mbp circular chromosome encoding 5,570 predicted protein coding sequences. Sequence and annotation are deposited at the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) genome database (Refseq. no. NC_002516) and in the Pseudomonas Genome Database (Winsor et al., 2009), which also documents ongoing annotation updates. Thanks to the recently developed deep cDNA sequencing more and more non-coding RNAs are currently being identified in bacterial genomes, and thus we can expect a large number of non-coding genes to be added to the annotation of P. aeruginosa genomes as has been executed for Helicobacter pylori and Pseudomonas putida (Sharma et al., 2010; Frank et al., 2011).
The second P. aeruginosa genome sequence was published for the ExoU-positive strain PA14 (NC_008463, Lee et al., 2006), a clinical isolate displaying higher virulence than PAO1. Fifty-four PAO1 regions of at least one open reading frames (ORFs) are absent in the PA14 genome, and 58 PA14 regions are absent in PAO1 including the PA14 pathogenicity islands PAPI-1 and PAPI-2 (He et al., 2004).
LESB58, a so-called “Liverpool epidemic strain,” was found to be highly transmissible among CF-patients and displayed the potential to cause severe infections even in non-CF human hosts (Cheng et al., 1996; McCallum et al., 2002). The LESB58 genome (NC_011770) contains previously unknown accessory genome elements (Winstanley et al., 2009).
PA7 is a clinical isolate from Argentina with a notably unusual antimicrobial resistance pattern. Strain PA7 (NC_009656) shares only 93.5% nucleotide identity in the core genome with the other sequenced strains confirming the previous assignment of strain PA7 as a taxonomic outlier within the species P. aeruginosa (Roy et al., 2010).
Almost complete genome sequences are also available for strains 2192 (NZ_AAKW00000000), C3719 (NZ_AAKV00000000), PACS2 (NZ_AAQW00000000; Mathee et al., 2008), and 39016 (AEEX00000000; Stewart et al., 2011). Eight additional P. aeruginosa genome sequences are listed at NCBI as “In Progress” (last checked on February 23rd, 2011) and numerous P. aeruginosa projects are deposited in the European Nucleotide Archive (ENA) hosted by EMBL-EBI1. With decreasing costs and increasing speed of sequencing we can expect an avalanche of novel P. aeruginosa genome sequence data. Published examples are the comparative sequencing of PAO1 sublines of divergent metabolic and virulence phenotypes (Klockgether et al., 2010), the identification of de novo mutations conferring antimicrobial resistance (Moya et al., 2009), the analysis of genomic gradients of sequence diversity in a pool of clinical isolates (Dötsch et al., 2010), and the intraclonal microevolution in the cystic fibrosis lung (Cramer et al., 2011).
The Accessory Genome
The accessory genome consists of DNA elements from within the range of a few hundred bases to more than 200 kbp. The minimum size of an accessory element was defined as a block of at least four contiguous ORFs that are not conserved in all P. aeruginosa (Mathee et al., 2008). Thirty-eight to 53 accessory elements were identified in the completely sequenced P. aeruginosa genomes (Table 2). The PAO1 genome only contains inserts of 14 kbp or smaller (Mathee et al., 2008), whereas the LESB58 genome harbors five genomic islands and five inserted prophages of 14–111 kbp in size (Winstanley et al., 2009). Table 3 lists the subset of genomic islands that were analyzed in detail in silico and/or in wet lab experiments.
Table 2.
Regions of genome plasticity (RGP) in seven sequenced P. aeruginosa genomes.
| RGP | Flanking loci | Strain | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Insertion Site | In PAO11 | In PA141 | PAO1 | PA14 | LESB58 | PA7 | 2192 | C3719 | PACS2 | |
| RGP1 | 0201/0208 | 02530/02550 | * | i | * | * | ||||
| RGP2 | tRNAArg | 0256/0264 | 03160/03420 | * | i | * | i | * | * | |
| RGP3 | 0611/0629 | 07960/08160 | * | * | i2 | i | + | + | ||
| RGP4 | 0641/0648 | 08300/08330 | * | i | i2 | i | * | i | i | |
| RGP5 | tRNAGly | 0714/0730 | 55100/54830 | i | i | i | i | i | ||
| RGP6 | tmRNA | 0819/0827 | 53680/53560 | i | i | i | i | i | i | i |
| RGP7 | tRNALys | 0976/0988 | 51670/51510 | i | i | i | ||||
| RGP8 | tRNASer | 1013/1014 | 51240/51220 | i | i | |||||
| RGP93 | 1087/1092 | 50340/50290 | * | * | * | i | i | * | i | |
| RGP10 | 1191/1192 | 49040/48870 | i | i | i | |||||
| RGP11 | 1222/1225 | 48520/48440 | * | i | * | i | * | * | * | |
| RGP12 | 1243/1244 | 48160/48150 | i | i | ||||||
| RGP13 | 1367/1373 | 46630/46490 | i | i | i | i | i | |||
| RGP14 | 1375/1376 | 46470/46540 | i | i | ||||||
| RGP15 | 1377/1394 | 46440/46390 | i | i | i4 | i | i | i | ||
| RGP16 | 1530/1531 | 44650/44640 | i5 | i | i | |||||
| RGP17 | tRNAHis | 1796/1797 | 41350/41280 | i | i | |||||
| RGP19 | 1964/1965 | 39130/39110 | i | |||||||
| RGP20 | 2024/2070 | 38340/37730 | i | * | * | i | i | i | ||
| RGP21 | 2099/2107 | 37360/37350 | * | * | ||||||
| RGP22 | 2181/2187 | 36370/36360 | * | * | i | * | * | |||
| RGP23 | 2217/2235 | 36050/35690 | i | i | i | i | i | i | i | |
| RGP24 | 2422/2423 | 33370/33290 | i | i | i | * | * | |||
| RGP25 | 2455/2464 | 32860/32770 | i | i | i | i | i | i | i | |
| RGP26 | tRNALeu | 2570/2571 | 31290/30840 | i | i | |||||
| RGP27 | tRNAGly | 2583/2584 | 30700/30670 | i | i | i | i | |||
| RGP28 | tRNAPro | 2727/2737 | 28895/28730 | i | i | i | i | i | i | i |
| RGP29 | tRNAGly | 2817/2820 | 27710/27590 | + | * | * | + | i | * | * |
| RGP30 | 2950/2951 | 25900/25880 | i | |||||||
| RGP316 | 3141/3160 | 23470/23360 | i | i | i | i | * | i | * | |
| RGP32 | 3222/3223 | 22560/22490 | i | |||||||
| RGP33 | 3239/3240 | 22290/22075 | i | |||||||
| RGP34 | 3496/3515 | 18870/18860 | i | |||||||
| RGP35 | 3536/3537 | 18620/18610 | i | |||||||
| RGP36 | 3768/3769 | 15670/15340 | i | i | i | |||||
| RGP37 | 3865/3870 | 13990/13850 | * | i | * | |||||
| RGP38 | 4162/4163 | 10130/10040 | * | * | ||||||
| RGP39 | 4190/4196 | 09700/09690 | * | * | * | * | * | |||
| RGP41 | tRNALys | 4541/4542 | 58900/60190 | i | i | i | i | |||
| RGP42 | tRNAMet | 4673/4674 | 61820/61840 | i7 | i | i | i | |||
| RGP43 | 2770/2773 | 28280/28220 | *8 | i | *8 | i | *8 | *8 | *8 | |
| RGP44 | 4100/4108 | 10850/10820 | * | i | * | * | * | * | * | |
| RGP46 | 0041/0042 | 00510/00530 | i | i | i | i | i | |||
| RGP47 | 1149/1153 | 49530/49500 | i | i | * | * | i | * | ||
| RGP48 | 1238/1242 | 48240/48170 | * | * | * | * | ||||
| RGP50 | 1655/1656 | 43110/43050 | i | |||||||
| RGP52 | 1934/1940 | 39500/39460 | i | i | i | i | i | i | i | |
| RGP53 | 2332/2337 | 34450/34440 | * | * | * | * | * | |||
| RGP56 | 2793/2795 | 28000/27980 | * | * | + | i | + | * | +9 | |
| RGP58 | tRNAArg | 3366/3368 | 20560/20490 | * | i | i | * | * | * | i |
| RGP6010 | tRNAThr | 4524/4526 | 58700/58750 | i | * | + | i | + | * | i |
| RGP62 | tRNAPhe | 5149/5150 | 68000/68040 | i | ||||||
| RGP63 | 006911 | 0081011 | i | |||||||
| RGP64 | 027811 | 0362011 | i | |||||||
| RGP65 | 0377/0378 | 04940/04950 | i | |||||||
| RGP66 | tRNAMet | 0574/0575 | 07450/07500 | i | i | |||||
| RGP67 | 3858/3859 | 14080/14100 | i | |||||||
| RGP6812 | 3840/3844 | 14290/14340 | * | i | * | i | * | * | * | |
| RGP69 | 3714/3715 | 16340/16350 | i | |||||||
| RGP70 | tRNAPro | 3031/3032 | 24860/24880 | i | ||||||
| RGP71 | 2650/2651 | 29820/29830 | * | i | * | * | ||||
| RGP72 | tRNACys | 2581/2582 | 30710/30730 | i | ||||||
| RGP7313 | 2397/2403 | 33600/33690 | * | * | i | + | i | + | + | |
| RGP74 | 2201/2202 | 36230/36250 | i | |||||||
| RGP75 | 1579/1580 | 44070/44080 | i | |||||||
| RGP76 | 1425/1428 | 45980/46010 | * | * | * | i | * | * | * | |
| RGP77 | 1397/1398 | 46330/46350 | * | * | ||||||
| RGP78 | 4466/4467 | 57980/57990 | i | |||||||
| RGP79 | 5290/5291 | 69840/69850 | i | |||||||
| RGP80 | 5454/5460 | 72000/72060 | * | * | * | i | * | * | * | |
| RGP81 | 4138/4139 | 10420/10380 | i | |||||||
| RGP82 | 3663/3664 | 16980/16970 | i | |||||||
| RGP83 | 3463/3464 | 19330/19320 | i14 | i | i14 | *14 | *14 | |||
| RGP84 | tRNASer | 2603/2604 | 30430/30410 | i | 15 | |||||
| RGP85 | 2593/2594 | 30550/30560 | i | 15 | ||||||
| RGP86 | 0831/0832 | 53510/53520 | i | |||||||
| RGP87 | tRNAThr | 5160/5161 | 68140/68170 | i | i | |||||
| RGP88 | 396116 | 1263016 | ||||||||
| RGP89 | 3834/3836 | 14440/14390 | * | i | * | + | i | * | + | |
Differentiation of accessory elements in the RGPs: i, strain-specific accessory element; *or +, identical accessory elements in two or more strains. RGPs 1–62 were defined by Mathee et al. (2008) and RGPs 63–80 by Roy et al. (2010). The novel RGPs 81–89 were extracted from the sequences of genomic islands in strain LESB58 (RGP 81–86; Winstanley et al., 2009) and strain PSE9 (RGP 87–89; Battle et al., 2009).
1Insertions are designated by the numbers of the flanking loci in the PAO1 and PA14 genomes (e.g., 0201 is PA0201, 02530 is PA14_02530).
2Insertion LESPP-1 between PA0612 and PA0648 homologs comprises RGP3 and RGP4.
3Region containing flagellin glycosylation genes (replacement island).
4Partial duplication of sequence of the core genome (between RGP27 and RGP28).
5No annotated ORF in this insertion.
6Region contains O-antigen gene cluster (replacement island).
7No insertion in PAO1 reference sequence but in variants PAO1-DSM and MPAO1 (Klockgether et al., 2010).
8Identical sequence with discordant ORF annotation for the different strains.
9Identical sequence with discordant annotation for PACS2 versus LESB58 and 2192.
10Region contains pilA gene (replacement island).
11Homologous ORF in PA7 disrupted by the insertion.
12Insertion contains exoS gene in PAO1, LESB58, 2192, C3719, and PACS2.
13Region contains pyoverdine synthesis gene cluster (replacement island).
14<1 kb insertion in PAO1, 2192, C3719, and PACS2 with no predicted ORF.
15Insertion in PA7 comprises RGP84 and RGP85.
16Homologous ORF in strain PSE9 disrupted by PAGI-7.
Table 3.
Genomic islands in P. aeruginosa strains described in literature.
| Genomic island | Host strain | Size (kb) | RGP locus | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PAPI-1 | PA14 | 108 | 41 | He et al. (2004) |
| PAPI-2 | PA14 | 10.8 | 7 | He et al. (2004) |
| LES-prophage 1 | LESB58 | 14.8 | 3 and 4 | Winstanley et al. (2009) |
| LES-prophage 2 | LESB58 | 42.1 | 81 | Winstanley et al. (2009) |
| LES-prophage 3 | LESB58 | 42.8 | 82 | Winstanley et al. (2009) |
| LES-prophage 4 | LESB58 | 26.8 | 83 | Winstanley et al. (2009) |
| LES-prophage 5 | LESB58 | 39.9 | 84 | Winstanley et al. (2009) |
| LES-prophage 6 | LESB58 | 7.6 | 10 | Winstanley et al. (2009) |
| LESGI-1 | LESB58 | 46.4 | 28 | Winstanley et al. (2009) |
| LESGI-2 | LESB58 | 31.7 | 85 | Winstanley et al. (2009) |
| LESGI-3 | LESB58 | 110.6 | 27 | Winstanley et al. (2009) |
| LESGI-4 | LESB58 | 39.4 | 23 | Winstanley et al. (2009) |
| LESGI-5 | LESB58 | 29.4 | 86 | Winstanley et al. (2009) |
| pKLC102 | C, SG17M | 103.5 | 41 | Klockgether et al. (2004) |
| PAGI-1 | X24509 | 48.9 | 23 | Liang et al. (2001) |
| PAGI-2 | C | 105 | 29 | Larbig et al. (2002) |
| PAGI-3 | SG17M | 103.3 | 29 | Larbig et al. (2002) |
| PAGI-4 | C | 23.4 | 7 | Klockgether et al. (2004) |
| PAGI-5 | PSE9 | 99.3 | 7 | Battle et al. (2008) |
| PAGI-6 | PSE9 | 44.4 | 87 | Battle et al. (2009) |
| PAGI-7 | PSE9 | 22.5 | 88 | Battle et al. (2009) |
| PAGI-8 | PSE9 | 16.2 | 62 | Battle et al. (2009) |
| PAGI-9 | PSE9 | 6.6 | 89 | Battle et al. (2009) |
| PAGI-10 | PSE9 | 2.2 | 25 | Battle et al. (2009) |
| PAGI-11 | PSE9 | 2 | 52 | Battle et al. (2009) |
| ExoU-A | 6077 | 81.2 | 7 | Kulasekara et al. (2006) |
| ExoU-B | 19660 | 29.8 | 7 | Kulasekara et al. (2006) |
| ExoU-C | X13273 | 3.7 | 7 | Kulasekara et al. (2006) |
Within the chromosomally integrated islands, very often phages, transposons, or IS-elements are found indicating that the majority of the accessory genome originates from mobile DNA elements which have been acquired and kept by the host strain. Many elements were irreversibly fixed by secondary mutation or deletions, but a few others have retained their mobility and can still leave the chromosomal insertion site and be transferred elsewhere, as shown for the elements PAPI-1 (Qiu et al., 2006) and pKLC102 (Klockgether et al., 2007). For a detailed description of the different types of accessory elements [integrative and conjugative elements (ICEs), prophages, transposons, etc.], the reader is referred to the recently published review by Kung et al. (2010).
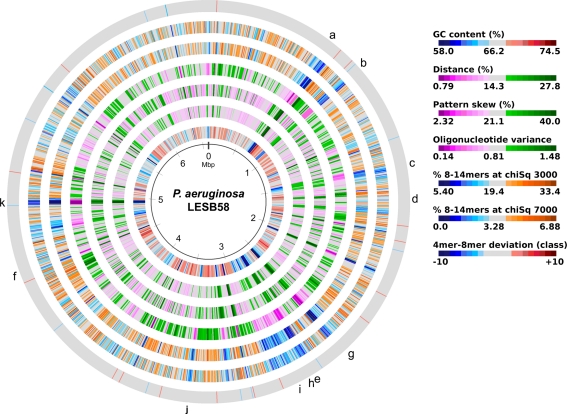
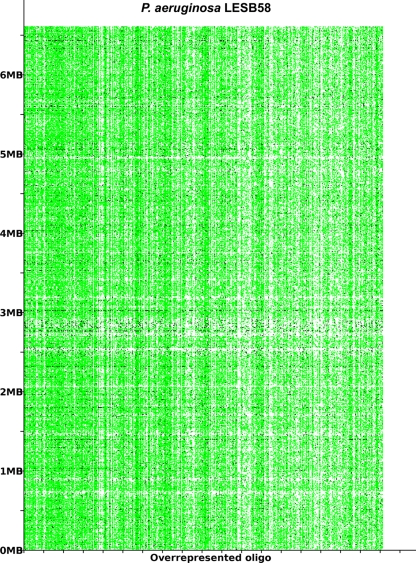
The acquisition of the elements of the accessory genome from other taxa is not only evident from the gene contents with its overrepresentation of mobile DNA elements, but also from global parameters like the oligonucleotide signature. The segments of the core genome share the same oligonucleotide usage, whereas the constituents of the accessory genome exhibit a divergent G + C content and oligonucleotide usage (Reva and Tümmler, 2004, 2005). In the genome atlas of P. aeruginosa LESB58 (Figure 1), the regions with an anomalous tetranucleotide composition and an underrepresentation of common octa- to tetradecanucleotides coincide with the segments of the accessory genome. Figure 2 shows the genome distribution of the most abundant 8- to 14mers in P. aeruginosa LESB58 (Davenport et al., 2009). Regions that lack these strain- or taxon-specific words represent those parts of the accessory genome that is most foreign from the core.
Figure 1.
Genome atlas representations of G + C content, tetranucleotide parameters and overrepresented 8- to 14mers in P. aeruginosa LESB58 (Davenport et al., 2009). Increasing divergence from average (up to an extreme value at ±3 SD) is indicated by progressively darker colors. G + C content and the three tetranucleotide parameters are plotted on the innermost four rings. Distance (second innermost circle) is the distance between global and local sliding window tetranucleotide patterns, pattern skew (third innermost circle) is the distance between tetranucleotide rankings on direct and reverse strands, and oligonucleotide variance (fourth innermost circle) is the numerical variance of oligomers, where a lower value indicates tetramer usage is more highly restricted (for example in repeat regions). Rings 5 (χ2 threshold 3000) and 6 (χ2 threshold 7000) display the number of bases occupied by overrepresented 8- to 14mers in a certain region, with overlaps only counted once, as a percentage. The outermost ring shows the difference (in classes) between a tetranucleotide parameter, oligonucleotide variance, and the 8- to 14mers in ring 5. Figures were created with JCircleGraph. Letters at the outermost ring indicate the regions of the six identified prophages (a–f) and five genomic islands (g–k; Winstanley et al., 2009).
Figure 2.
The most overrepresented 8- 14 bp oligomers in P. aeruginosa LESB58 sorted by decreasing χ2 values. The genome position of each oligo is plotted on the y-axis. A black dot is printed where an oligonucleotide occurs in non-coding regions and a green dot where an oligonucleotide occurs in coding regions. The figure was created with the program OligoViz (Davenport et al., 2009). The majority of the overrepresented 8–14 bp oligomers is located in coding sequences distributed all over the genome; only in the few cases of white vertical lines the respective oligonucleotide clusters in a few genome positions. Horizontal white lines indicate regions with an atypical oligonucleotide usage that lack these strain- or taxon-specific words and represent those parts of the accessory genome that are most foreign from the core.
Regions of Genome Plasticity
Elements of the accessory genome are located in all sections of the P. aeruginosa chromosome, not concentrated in some regions. Nevertheless, the uptake of accessory DNA apparently did not occur completely at random but at specific genomic loci that are prone to integration of special mobile elements.
A comprehensive comparison of the genomes of strains PAO1, PA14, 2192, C3719, and PACS2 (Mathee et al., 2008) led to the definition of so-called “regions of genome plasticity” (RGPs). Mathee and co-workers searched for segments of DNA not conserved in all five genomes and designated any region containing a block of four or more contiguous ORFs that is missing in at least one of the genomes as an RGP. For each of these RGPs they defined the DNA contained in the accessory blocks and the ORFs annotated within. Also the RGP flanking ORFs conserved in all five strains were listed, referred to as “anchors,” which describe the genomic site used for the integration of the foreign DNA.
The approach by Mathee et al. (2008) appears reasonable to describe accessory and core genome of P. aeruginosa strains, although small insertions are ignored and deletions affecting the core genome in some, but not all, compared strains will misassign the respective segment to the accessory genome. A secondary check of the oligonucleotide usage will correct these false positives.
Mathee et al. (2008) initially defined 52 RGPs (no. 1–62 in Table 2). With the advent of the PA7 genome sequence, a further 18 elements were identified (RGPs 63–80; Roy et al., 2010).
Table 2 moreover lists the novel RGPs 81–89 that comprise yet unknown RGPs from strains LESB58 (Winstanley et al., 2009) and PSE9 (Battle et al., 2009).
On average each sequenced P. aeruginosa strain carries about 40 RGPs with insertions. The outlier was strain PA7 with 53 occupied RGPs. tRNA genes serve as integration sites for 20 RGPs. The 3′ end of tRNA genes and the subsequent nucleotides are known to serve as integration sites for ICEs and phage-like elements (Dobrindt et al., 2004). In the majority of RGPs, however, other target sequences had been utilized for the insertion corresponding with the diverse type and origin of the elements of the accessory genome of P. aeruginosa (Kung et al., 2010). Most target sequences are located in intergenic regions, but in three RGPs a single ORF was disrupted (RGPs 63, 64, and 88; Table 2). Interestingly, insertions in each of these three RGPs were only detected for a single strain so far, while in all other tested genomes the non-fragmented anchor-ORF was present.
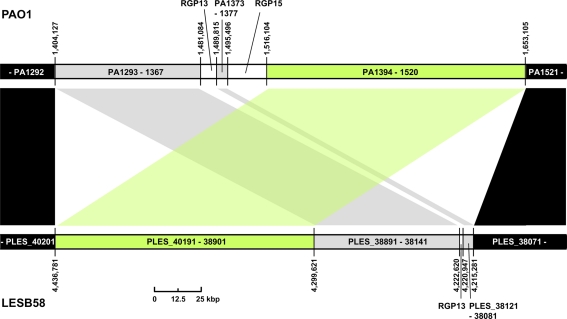
Three regions show an unusual local genome structure. Strains LESB58 and PA7 each carry hybrids of two adjacent RGPs. Moreover, in strain LESB58 a 137-kbp segment of the core genome 3′ to RGB15 was transposed upstream by 83 genes (84.3 kbp; Figure 3). No repeats flanking the segment or mobility-related genes such as transposase- or integrase-coding genes were identified so that the underlying mechanism of the transposition remains elusive.
Figure 3.
Transposition of core genome DNA in LESB58. The genomic region with different core genome architecture is shown for strains PAO1 and LESB58. One hundred thirty-seven kbp of DNA (green) are located upstream of other core genome DNA blocks (gray) in LESB58 while occurring downstream of them in PAO1 (and other genomes). Surrounding core genome DNA arranged collinearly in both strains is shown in black, strain-specific insertions are represented by white areas. Genome coordinates of the borders of the core genome DNA blocks and numbers of the ORFs within are given for both strains. Accessory DNA blocks are described by the RGP number (see Table 2).
The pKLC102/PAGI-2 ICE Family
Among the genomic islands of the P. aeruginosa accessory genome, members of the pKLC102/PAGI-2 family are highly prevalent. They represent a special group of ICEs that can be described as semi-conserved elements, as they generally consist of individual DNA blocks and sets of genes common to all members (Klockgether et al., 2008; Kung et al., 2010). pKLC102/PAGI-2 family islands have been detected in various bacterial species and genera, mainly in β- and γ-proteobacteria. The fact that a set of genes is conserved among all family members indicates a common origin from an ancient ancestor (Mohd-Zain et al., 2004). This conserved gene set accounts for structural and mobility-related features and conjugal transfer. Individual genes within the islands can encode a broad spectrum of different functions, among them catabolic pathways as well as virulence effectors. Existence of free episomal forms and/or transfer to other strains, even across species barriers, have been monitored for several pKLC102/PAGI-2-like islands, thus confirming their role for (ongoing) evolution of bacterial genomes and, due to the different “cargo” provided by these elements to the host strains, for the genome diversification within bacterial species and emergence of subgroup- or strain-specific phenotypes. For a detailed summary of the role of the common “backbone” genes for integration, mobilization and transfer of pKLC102/PAGI-2-like elements, the reader is referred to the recent review by Kung et al. (2010).
The role of pKLC102/PAGI-2-like islands within the P. aeruginosa accessory genome, and thus their contribution to genome diversity, is illustrated by the abundance of many different islands of this family within the population. Hybridization results have indicated the presence of such islands in a majority of strains isolated from different habitats (Klockgether et al., 2007; Wiehlmann et al., 2007). Similarly, searching the available P. aeruginosa genome sequences for the typically conserved genes revealed their presence in all strains but PAO1.
Six of the islands listed in Table 3 are members of that family: pKLC102, PAPI-1, PAGI-5, PAGI-2, PAGI-3, and LESGI-3. All of them are between 99 and 110 kbp in size. Clusters of typically conserved backbone genes were also detected in smaller islands like PAGI-4 or ExoU-A. As significant parts of the backbone, however, were missing, it was hypothesized that PAGI-4 and ExoU-A represent remaining fragments of formerly complete PAGI-2/pKLC102-like islands that underwent recombination and deletion events resulting in the loss of smaller (ExoU-A) or bigger parts (PAGI-4) of the original elements (Klockgether et al., 2004; Kulasekara et al., 2006).
The mentioned P. aeruginosa islands split up into two subtypes: PAGI-2-like islands (PAGI-2, PAGI-3, and LESGI-3) contain a phage P4-related integrase gene and are inserted at tRNAGly genes in RGPs 27 or 29. The well described clc element providing features for metabolizing chlorinated aromatic compounds could be assigned to that subtype as well. Present in other Pseudomonas species as well as in Ralstonia and Burkholderia strains, transfer of clc to P. aeruginosa PAO1 by conjugation was shown in vitro (Gaillard et al., 2008). Upon transfer, genomic integration occurred at the usual tRNAGly genes in RGP27 or RGP29.
The pKLC102-subtype islands (pKLC102, PAPI-1, PAGI-5) are endowed with a XerC/XerD-like integrase gene, and the two copies of a tRNALys gene in RGP7 and RGP41 can be used as insertion sites. Transfer of pKLC102-like elements from one RGP to the other has been demonstrated (Kiewitz et al., 2000; Qiu et al., 2006). The “fragmentary” pKLC102-like islands PAGI-4 and ExoU-A are also located in RGP7. The tRNALys gene in RP7 is also the insertion site for islands carrying the virulence-associated exoU gene and its cognate chaperone spcU gene, ExoU-B, ExoU-C, and PAPI-2. Although DNA typical for pKLC102-like islands is scarce in these exoU-positive islands, the common insertion site and a few motifs within their sequence indicate a descent from a pKLC102-like element as hypothesized for ExoU-A (Kulasekara et al., 2006).
Kung et al. (2010) described the two subtypes as two families of P. aeruginosa ICEs. Due to the conserved function and synteny of the backbone genes, however, we prefer to consider them as members of one family with common ancestry (Klockgether et al., 2007, 2008). The pKLC102/PAGI-2-like islands share 35 conserved orthologs with a variable degree of amino acid identity between 35 and 100%.
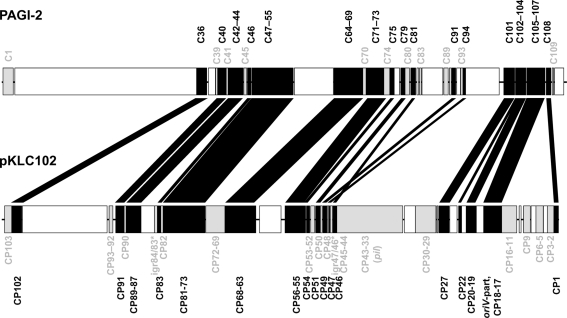
Divergent evolution from the ancestor might have caused the early formation of the two pKLC102- and PAGI-2 subtypes that exhibit higher average identity values among the conserved backbone genes and each carry a subfamily-specific set of genes (Figure 4). Eleven genes were specific for the PAGI-2-subtype and 39 genes specific for the pKLC102- subtype including a cluster of conjugative type IV sex pilin genes (Klockgether et al., 2004; Carter et al., 2010). Thus, pKLC102-/PAGI-2-family islands appear as mosaic pieces in P. aeruginosa genomes while they are small mosaics themselves, composed of conserved backbone, subtype-specific, and individual cargo genes.
Figure 4.
Conserved genes in pKLC102-/PAGI-2-like genomic islands. PAGI-2 (Larbig et al., 2002) and pKLC102 (Klockgether et al., 2004) were chosen as representatives for the respective subtypes among the pKLC102-/PAGI-2 family. The annotated ORFs are labeled according to their conservation. ORFs appearing in all P. aeruginosa islands of this family (“backbone genes”) are shown in black. ORFs conserved within one of the subtypes are colored in gray. White blocks represent ORFs specific for the single islands (“individual cargo”). Intergenic regions (igr) marked with an asterisk indicate loci with no ORF annotated for pKLC102 but for the highly homologous sequences in other islands from this subtype. Please note that ORF C105 of PAGI-2 is homologous to DNA in pKLC102 described as a part of the replication origin oriV of this element. The other part of oriV containing 16 57 bp repeats (Klockgether et al., 2004) is not conserved among the island family, not even in other islands from the pKLC102 subtype.
Due to their size, islands of this family can represent a major portion of the accessory genome. Strains with one or two large pKLC102/PAGI-2-family elements are common, but higher numbers per genome are possible. P. aeruginosa strain C harbors PAGI-2 and pKLC102, but two more sets of backbone ORFs have been identified in the chromosome indicating four related elements in total, with an overall DNA sequence length of more than 360 kbp (own unpublished data). Of the seven genomes presented in Table 2, six contain large pKLC102/PAGI-2-family islands. Strains PA14, C3719, and PA7 each harbor one pKLC102-like island in RGP41 or, in case of PA7, in RGP7. LESB58 also contains one island, but of the PAGI-2 subtype (LESGI-3 in RGP27). Two islands each are located in the 2192- and the PACS2 genomes. Both strains also harbor a pKLC102-like insertion in RGP41 and a PAGI-2-related island, which is in RGP29 for strain 2192 and in RGP27 in PACS2.
The island in 2192 inserted at RGP29 is a nearly identical copy of PAGI-2 itself but is interestingly accompanied by another island of comparable size, the so-called Dit-island which is distinct from the pKLC102/PAGI-2 family (Mathee et al., 2008). Thus an extremely large insertion of about 220 kbp is present in RGP29, which probably resulted from successive acquisition of two elements using the same chromosomal integration site. The RGP41-insertion in strain PA7 also provides hints for a combination of genome islands. Next to the pKLC102-like island with all typically conserved genes a DNA block with a second copy of some of the backbone genes is located, resembling a fragment of a second pKLC102-like element linked to the first one (Klockgether et al., 2008; Roy et al., 2010).
Replacement Islands
Table 2 also lists the loci in the core genome that are under diversifying selection, the so-called replacement islands: RGP9 (flagellin glycosylation genes), RGP31 (O-antigen biosynthesis genes), RGP60 (pilin gene), and RGP73 (pyoverdine gene cluster). The RGPs only encompass those genes that fulfill the definition of less than 70% nucleotide sequence identity between homologs and thus do not necessarily comprise the complete functional units (Mathee et al., 2008).
The types of each replacement island were identified by comparative sequencing of the respective gene clusters in P. aeruginosa strain collections. The 20 known O-antigen serotypes, for example, were assigned to 11 groups according to the criterion of more than 98% sequence identity in the major O-antigen biosynthesis gene cluster (Raymond et al., 2002).
RGP60, containing the pilA gene that encodes the major subunit for type IV attachment pili, was classified into groups I–V (Kus et al., 2004). This “major pilin” region adjacent to a tRNAThr gene contains, besides pilA for all groups but group II, several tfp genes that are involved in type IV pilus assembly and modification. More tfp genes are located downstream in the “minor pilin” region. Each of the five major pilin regions is associated with a specific set of minor pilins, and unrelated strains with the same major pilin type have identical minor pilin genes (Giltner et al., 2011). The absolute linkage disequilibrium between major and minor pilin groups provides evidence that both regions were derived from one large island. Consistent with this interpretation more pilin assembly genes are located between the major and minor pilin groups. These genes, however, were not subject of diversifying selection. Moreover a tRNA gene cluster is located between the major and the minor pilin region that serves as a hotspot for integration of large pKLC102-like islands (RGP41). Thus, the genome distance between major and minor pilin gene clusters varies between 136 kbp in strain PA14 and only 29 kbp in PAO1.
The pyoverdine gene clusters I, II, and III encode the three pyoverdine types and their specific receptor. Intratype divergence driven by recombination, positive selection, and horizontal gene transfer have enhanced the diversity of this genomic region (Smith et al., 2005).
The two flagellins a and b differ in their primary amino acid sequence and their glycosylation from each other (Spangenberg et al., 1996). b-type flagellins are conserved in sequence and glycosylation (Verma et al., 2006). In contrast, six fliC single nucleotide substitutions (SNPs) haplotypes (Spangenberg et al., 1996) and differential glycosylation patterns lead to a large diversity of a-type flagellins (Arora et al., 2004). The variability of the a-type glycosylation gene cluster (RGP9) is high, even within the subtypes A1 and A2 that were defined by phylogenetic relatedness of amino acid sequences.
The P. aeruginosa Pangenome
The pangenome represents the complete gene pool of a bacterial species. Thus the description of a pangenome depends on the amount of sequence data available. For species with an extended accessory genome like P. aeruginosa, the addition of each new genome sequence will enlarge the overall pool of genes. The size of the core genome that is present in all strains will decrease concurrently.
To define the core genome and pangenome, the genomes are sequentially screened for orthologs by searching for reciprocal best BLAST hits. Genes that lack an ortholog in the already investigated gene pool are added to the pangenome.
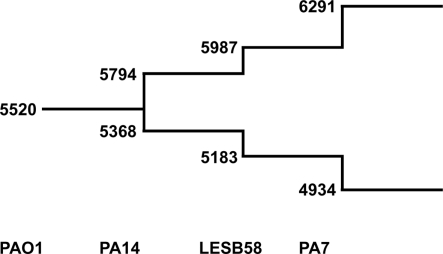
We used the tool “Comparative Genome Search” provided by the Pseudomonas Genome Database2 to define the number of orthologs representing reciprocal best blast hits in the four fully sequenced genomes of PAO1, PA14, LESB58, and PA7 (BLASTP comparisons, E-value cutoff: 1 × 10−4). The tool also allows the determination of individual genes per genome, so the number of genes contributing to the pangenome could be counted with paralogs excluded. The results are shown in Figure 5. Please note that the PAO1 gene pool is lower than the overall number of ORFs in this genome (5520 compared to 5570) due to this exclusion of paralogs. As expected the core genome decreases and the pangenome increases each by a few hundred genes with the addition of a new genome. Although the analysis of just four genomes is insufficient for the extrapolation of the gene pool of core genome and pangenome of P. aeruginosa, we can assume that the pangenome does not approach a saturation value. Each novel genome sequence will contribute a yet unknown gene set to the pangenome. The large genomic islands of the pKLC102/PAGI-2 family contribute a broad variety of cargo to the species. Each strain possesses an individual set of islands that is acquired by horizontal gene transfer preferentially from beta- and gamma-proteobacteria (Klockgether et al., 2008). In other words, P. aeruginosa has wide, but not unrestricted access to the gene pool of prokaryotes.
Figure 5.
The P. aeruginosa pangenome. The extent of the P. aeruginosa core- and pan-genome is shown as a stepwise development going along with the availability of complete genome sequences. The numbers at the lower branch give the amount of genes identified as best reciprocal blast hits in the indicated genomes (core genome). Numbers of the upper branch describe amount of genes making up the pangenome. For each genome the number of genes are added that are neither ortho- nor paralogs of genes from the existing pool.
Intraclonal Genome Diversity
The comparison of published genome sequences of clonally unrelated strains uncovered an interclonal sequence diversity of the P. aeruginosa core genome of 0.5–0.7% (Spencer et al., 2003; Cramer et al., 2011). The intraclonal diversity of members of the same clonal complex, however, is yet unknown. Of the strains with completely sequenced genomes, only strain PA14 belongs to a common clonal complex in the P. aeruginosa population (Wiehlmann et al., 2007). Hence we decided to sequence another strain of the PA14 clonal complex by Illumina sequencing-by-synthesis technology [study accession number ERP000390 at the Nucleotide Read Archive (ENA) of the EBI]. This strain RN3 was isolated from the first P. aeruginosa-positive airway specimen of an individual with cystic fibrosis who was living in North–West Germany. Strain PA14 is a clinical isolate from California. Thus the two strains are of unrelated geographic origin.
The strain PA14 and strain RN3 genomes match in genome size and differ in 231 SNPs from each other (Table 4) which corresponds to a sequence diversity of 3.5 × 10−5. Transitions (n = 148) occurred significantly more frequently than the expected ratio of transitions to transversions of 55: 176 of a random distribution (χ2 = 206.3; P < 0.001). The number of SNPs in inter- and intragenic regions roughly corresponded with their proportions in the genome. Within the coding regions synonymous SNPs were significantly overrepresented (χ2 = 23.2; P < 0.001) indicating that de novo amino acid substitutions had been subject to purifying selection.
Table 4.
Single nucleotide substitutions in RN3 sequence (compared to PA14 reference).
| Intragenic position | nt | Locus_tag | aa | Gene name | Encoded product |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 72440 | T – C | PA14_00740 | K – E | Putative lipoprotein | |
| 96307 | A – C | PA14_00970 | syn. | Hypothetical protein | |
| 273734 | C – T | PA14_03110 | D – N | Hypothetical protein | |
| 477483 | G – A | PA14_05410 | syn. | chpC | putative chemotaxis protein |
| 480880 | T – C | PA14_05450 | syn. | 16S ribosomal RNA methyltransferase RsmE | |
| 480915 | T – C | PA14_05450 | K – E | 16S ribosomal RNA methyltransferase RsmE | |
| 522777 | G – T | PA14_05890 | E – stop1 | putative stomatin-like protein | |
| 741080 | G – A | PA14_08660 | tRNAGly | ||
| 747764 | G – A | PA14_08760 | G – D | rpoB | DNA-directed RNA polymerase subunit beta |
| 791890 | A – G | PA14_09280 | N – D | pchF | Pyochelin synthetase |
| 8880382 | C – T | PA14_10290 | P – L | acoR | Transcriptional regulator AcoR |
| 8880392 | T – G | PA14_10290 | P – L | acoR | Transcriptional regulator AcoR |
| 927917 | T – C | PA14_10770 | I – T | Putative sensor/response regulator hybrid | |
| 982940 | A – G | PA14_11290 | syn. | Putative permease | |
| 1071133 | G – C | PA14_124303 | ladS | Homolog to lost adherence sensor LadS | |
| 1082958 | A – G | PA14_12630 | syn. | Putative ATP-dependent helicase | |
| 1356548 | G – C | PA14_15920 | R – G | yhjE | Major facilitator transporter |
| 1441164 | T – C | PA14_16820 | syn. | Putative efflux transmembrane protein | |
| 1468998 | C – T | PA14_17130 | syn. | dxr | 1-deoxy-d-xylulose 5-phosphate reductoisomerase |
| 1551564 | G – A | PA14_18080 | A – V | TetR family transcriptional regulator | |
| 1558205 | A – G | PA14_18150 | syn. | acsL | Putative acetyl-CoA synthetase |
| 1612742 | A –G | PA14_18740 | syn. | argG | Argininosuccinate synthase |
| 1640196 | G – T | PA14_18985 | P – H | Hypothetical protein | |
| 1640394 | A – G | PA14_18985 | F – S | Hypothetical protein | |
| 1880872 | C – G | PA14_21690 | A – G | lhr1 | Putative ATP-dependent DNA helicase |
| 1960256 | C – A | PA14_22520 | R – L | Hypothetical protein | |
| 2027678 | C – G | PA14_23360 | P – R | wzz | O-antigen chain length regulator |
| 2149425 | T – C | PA14_24600 | syn. | Putative carboxypeptidase | |
| 2156146 | C – A | PA14_24665 | Q – K | Hypothetical protein | |
| 2209674 | A – G | PA14_25250 | K – E | gapA | Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase |
| 2318606 | A – G | PA14_26600 | syn. | RNA polymerase sigma factor | |
| 2407435 | C – G | PA14_27755 | syn. | yliJ | Glutathione S-transferase |
| 2407463 | A – G | PA14_27755 | K – E | yliJ | Glutathione S-transferase |
| 2510099 | A – G | PA14_29030 | T – A | Putative FMN oxidoreductase | |
| 2545609 | T – C | PA14_29390 | syn. | Hypothetical protein | |
| 2545663 | T – C | PA14_29390 | syn. | Hypothetical protein | |
| 2553747 | T – C | PA14_29440 | D – G | LysR family transcriptional regulator | |
| 2651339 | T – C | PA14_30600 | F – L | Putative permease | |
| 2651357 | A – G | PA14_30600 | N – D | Putative permease | |
| 2762006 | A – G | PA14_31750 | K – E | Putative acyltransferase | |
| 2787777 | C – G | PA14_320153 | czcA | Homolog to RND efflux transporter CzcA | |
| 2787784 | T – G | PA14_320153 | czcA | Homolog to RND efflux transporter CzcA | |
| 2807266 | G – C | PA14_32300 | V – L | Putative kinase | |
| 2885933 | G – C | PA14_32985 | syn. | gcvH2 | Glycine cleavage system protein H |
| 2955357 | A – G | PA14_33600 | syn. | Hypothetical protein | |
| 2955433 | A – G | PA14_33600 | syn. | Hypothetical protein | |
| 2955468 | A – G | PA14_33600 | syn. | Hypothetical protein | |
| 2985345 | A – G | PA14_33650 | K – E | pvdD | Pyoverdine synthetase D |
| 3198441 | T – G | PA14_35940 | syn. | Acyl-CoA synthetase | |
| 3373667 | G – C | PA14_37830 | syn. | iscS | Putative pyridoxal-phosphate dependent enzyme |
| 3374601 | A – G | PA14_37830 | F – S | iscS | Putative pyridoxal-phosphate dependent enzyme |
| 3387854 | A – C | PA14_37965 | Y – S | cynS | Cyanate hydratase |
| 3387881 | A – C | PA14_37965 | M – L | cynS | Cyanate hydratase |
| 3387884 | T – C | PA14_37965 | F – L | cynS | Cyanate hydratase |
| 3387941 | A – C | PA14_37965 | M – L | cynS | Cyanate hydratase |
| 3390498 | A – C | PA14_38000 | Stop – S4 | Hypothetical protein | |
| 3423281 | A – G | PA14_38410 | syn. | amrB/mexH | Multidrug efflux protein |
| 3423414 | C – G | PA14_38410 | Q – E | amrB/mexH | Multidrug efflux protein |
| 3424176 | A – G | PA14_38410 | T – A | amrB/mexH | Multidrug efflux protein |
| 3424199 | A – G | PA14_38410 | syn. | amrB/mexH | Multidrug efflux protein |
| 3425614 | A – T | PA14_38410 | H – S | amrB/mexH | Multidrug efflux protein |
| 3442543 | G – A | PA14_38580 | G – D | Hypothetical protein | |
| 3443292 | C – G | PA14_38580 | P – A | Hypothetical protein | |
| 3541978 | G – A | PA14_39750 | syn. | Putative amino acid permease | |
| 3543662 | A – G | PA14_39770 | T – A | Putative regulatory protein | |
| 3558172 | A – G | PA14_39910 | F – L | phzE2 | Phenazine biosynthesis protein PhzE |
| 3559401 | T – C | PA14_39925 | K – E | phzD2 | Phenazine biosynthesis protein PhzD |
| 3566716 | A – G | PA14_40020 | Q – R | Hypothetical protein | |
| 3566730 | A – G | PA14_40020 | K – E | Hypothetical protein | |
| 3566749 | A – G | PA14_40020 | Q – R | Hypothetical protein | |
| 3566751 | A – G | PA14_40020 | N – D | Hypothetical protein | |
| 3566769 | A – G | PA14_40020 | K – E | Hypothetical protein | |
| 3566788 | A – G | PA14_40020 | Q – R | Hypothetical protein | |
| 3670384 | A – G | PA14_41150 | syn. | Putative permease of ABC transporter | |
| 3711749 | T – C | PA14_41563 | syn. | cobA | Uroporphyrin-III C-methyltransferase |
| 3711791 | G – C | PA14_41563 | V – L | cobA | Uroporphyrin-III C-methyltransferase |
| 3764383 | A – G | PA14_42220 | I – M | Membrane sensor domain-containing protein | |
| 3769180 | C – G | PA14_42250 | syn. | pscL | Type III secretion system protein |
| 3879553 | A – G | PA14_43570 | F – L | Hypothetical protein | |
| 3906764 | G – C | PA14_43870 | R – G | Hypothetical protein | |
| 3933352 | C – G | PA14_44190 | syn. | Putative sugar MFS transporter | |
| 4346242 | C – G | PA14_48890 | syn. | Hypothetical protein | |
| 4346254 | G – A | PA14_48890 | syn. | Hypothetical protein | |
| 4346325 | A – G | PA14_48890 | syn. | Hypothetical protein | |
| 4346329 | G – A | PA14_48890 | syn. | Hypothetical protein | |
| 4346413 | G – A | PA14_48890 | syn. | Hypothetical protein | |
| 4346434 | G – A | PA14_48890 | syn. | Hypothetical protein | |
| 4346485 | A – G | PA14_48890 | syn. | Hypothetical protein | |
| 4346497 | G – A | PA14_48890 | syn. | Hypothetical protein | |
| 4346500 | G – A | PA14_48890 | syn. | Hypothetical protein | |
| 4346665 | C – T | PA14_48890 | syn. | Hypothetical protein | |
| 4346713 | C – T | PA14_48890 | syn. | Hypothetical protein | |
| 4346731 | T – C | PA14_48890 | syn. | Hypothetical protein | |
| 4346763 | A – G | PA14_48890 | syn. | Hypothetical protein | |
| 4346845 | A – G | PA14_48890 | syn. | Hypothetical protein | |
| 4346890 | A – C | PA14_48890 | syn. | Hypothetical protein | |
| 4346926 | G – A | PA14_48890 | syn. | Hypothetical protein | |
| 4346938 | C – T | PA14_48890 | syn. | Hypothetical protein | |
| 4347034 | C – T | PA14_48890 | syn. | Hypothetical protein | |
| 4347190 | A – G | PA14_48890 | syn. | Hypothetical protein | |
| 4347211 | G – A | PA14_48890 | syn. | Hypothetical protein | |
| 4347241 | G – A | PA14_48890 | syn. | Hypothetical protein | |
| 4347256 | C – T | PA14_48890 | syn. | Hypothetical protein | |
| 4347283 | T – C | PA14_48890 | syn. | Hypothetical protein | |
| 4347289 | G – C | PA14_48890 | syn. | Hypothetical protein | |
| 4347310 | T – C | PA14_48890 | syn. | Hypothetical protein | |
| 4347322 | T – C | PA14_48890 | syn. | Hypothetical protein | |
| 4347346 | C – G | PA14_48890 | syn. | Hypothetical protein | |
| 4347358 | G – A | PA14_48890 | syn. | Hypothetical protein | |
| 4347376 | C – G | PA14_48890 | syn. | Hypothetical protein | |
| 4347642 | G – A | PA14_48900 | A – V | Hypothetical protein | |
| 4347673 | T – A | PA14_48900 | T – S | Hypothetical protein | |
| 4347701 | C – A | PA14_48900 | syn. | Hypothetical protein | |
| 4347825 | G – T | PA14_48910 | P – T | Hypothetical protein | |
| 4348119 | C – T | PA14_48910 | A – T | Hypothetical protein | |
| 4348192 | A – G | PA14_48910 | syn. | Hypothetical protein | |
| 4348221 | G – A | PA14_48910 | P – S | Hypothetical protein | |
| 4348224 | T – C | PA14_48910 | T – A | Hypothetical protein | |
| 4348308 | G – A | PA14_48910 | syn. | Hypothetical protein | |
| 4348378 | G – T | PA14_48910 | syn. | Hypothetical protein | |
| 4348501 | A – G | PA14_48910 | syn. | Hypothetical protein | |
| 4348684 | A – G | PA14_48910 | syn. | Hypothetical protein | |
| 4348966 | T – G | PA14_48910 | syn. | Hypothetical protein | |
| 4349128 | A – C | PA14_48920 | syn. | Bacteriophage protein | |
| 4350200 | A – T | PA14_48930 | syn. | Putative coat protein A of bacteriophage Pf1 | |
| 4350213 | G – C | PA14_48930 | A – G | Putative coat protein A of bacteriophage Pf1 | |
| 4350484 | T – C | PA14_48930 | N – D | Putative coat protein A of bacteriophage Pf1 | |
| 4350502 | T – C | PA14_48930 | T – A | Putative coat protein A of bacteriophage Pf1 | |
| 4350656 | G – A | PA14_48930 | syn. | Putative coat protein A of bacteriophage Pf1 | |
| 4350884 | A – G | PA14_48940 | syn. | coaB | Coat protein B of bacteriophage Pf1 |
| 4350911 | G – C | PA14_48940 | syn. | coaB | Coat protein B of bacteriophage Pf1 |
| 4350917 | A – G | PA14_48940 | syn. | coaB | Coat protein B of bacteriophage Pf1 |
| 4350941 | A – G | PA14_48940 | syn. | coaB | Coat protein B of bacteriophage Pf1 |
| 4350959 | T – C | PA14_48940 | syn. | coaB | Coat protein B of bacteriophage Pf1 |
| 4351186 | C – T | PA14_48950 | A – T | Hypothetical protein | |
| 4351199 | G – A | PA14_48950 | syn. | Hypothetical protein | |
| 4351316 | A – G | PA14_48950 | syn. | Hypothetical protein | |
| 4351503 | G – A | PA14_48970 | syn. | Helix destabilizing protein of bacteriophage Pf1 | |
| 4351563 | T – C | PA14_48970 | syn. | Helix destabilizing protein of bacteriophage Pf1 | |
| 4351617 | A – G | PA14_48970 | syn. | Helix destabilizing protein of bacteriophage Pf1 | |
| 4351641 | C – G | PA14_48970 | syn. | Helix destabilizing protein of bacteriophage Pf1 | |
| 4351722 | A – G | PA14_48970 | syn. | Helix destabilizing protein of bacteriophage Pf1 | |
| 4351857 | G – A | PA14_48970 | syn. | Helix destabilizing protein of bacteriophage Pf1 | |
| 4352075 | A – G | PA14_48980 | syn. | Hypothetical protein | |
| 4352106 | T – C | PA14_48980 | D – G | Hypothetical protein | |
| 4352113 | C – A | PA14_48980 | D – Y | Hypothetical protein | |
| 4352144 | G – C | PA14_48980 | S – R | Hypothetical protein | |
| 4352234 | G – A | PA14_48980 | syn. | Hypothetical protein | |
| 4352294 | G – C | PA14_48980 | syn. | Hypothetical protein | |
| 4352384 | C – T | PA14_48980 | syn. | Hypothetical protein | |
| 4352465 | G – T | PA14_48990 | syn. | Hypothetical protein | |
| 4352471 | G – A | PA14_48990 | syn. | Hypothetical protein | |
| 4352545 | C – A | PA14_48990 | A – S | Hypothetical protein | |
| 4352560 | G – A | PA14_48990 | P – S | Hypothetical protein | |
| 4352594 | C – G | PA14_48990 | syn. | Hypothetical protein | |
| 4352607 | C – T | PA14_48990 | R – Q | Hypothetical protein | |
| 4352676 | G – C | PA14_48990 | A – G | Hypothetical protein | |
| 4352700 | T – C | PA14_48990 | H – R | Hypothetical protein | |
| 4352821 | T – C | PA14_49000 | I – V | Hypothetical protein | |
| 43528652 | A – C | PA14_49000 | I – G | Hypothetical protein | |
| 43528662 | T – C | PA14_49000 | I – G | Hypothetical protein | |
| 4352921 | C – A | PA14_49000 | M – I | Hypothetical protein | |
| 4450619 | T – G | PA14_50060 | L – R | Hypothetical protein | |
| 4565005 | C – G | PA14_51360 | G – A | phnA | Hnthranilate synthase component I |
| 4565040 | A – G | PA14_51360 | syn. | phnA | Hnthranilate synthase component I |
| 4565093 | C – G | PA14_51360 | G – R | phnA | Hnthranilate synthase component I |
| 4707658 | G – C | PA14_53110 | syn. | Hxidoreductase | |
| 4707787 | G – C | PA14_53110 | syn. | Oxidoreductase | |
| 4760743 | A – G | PA14_53670 | L – P | Hypothetical protein | |
| 4901696 | A – G | PA14_55180 | M – V | migA | Glycosyl transferase |
| 4912690 | C – T | PA14_55330 | D – N | Hypothetical protein | |
| 4947683 | A – G | PA14_55600 | H – R | Hypothetical protein | |
| 4997786 | T – C | PA14_55980 | K – E | yjgR | Hypothetical protein |
| 5041775 | A – T | PA14_56550 | syn. | Hypothetical protein | |
| 51032242 | A – C | PA14_57275 | P – L | ftsZ | Cell division protein FtsZ |
| 51032252 | G – A | PA14_57275 | P – L | ftsZ | Cell division protein FtsZ |
| 5103259 | T – G | PA14_57275 | M – L | ftsZ | Cell division protein FtsZ |
| 5103291 | C – T | PA14_57275 | G – D | ftsZ | Cell division protein FtsZ |
| 5103303 | G – T | PA14_57275 | T – N | ftsZ | Cell division protein FtsZ |
| 5103322 | G – T | PA14_57275 | P – T | ftsZ | Cell division protein FtsZ |
| 5236534 | A – G | PA14_58760 | syn. | pilC | Type 4 fimbrial biogenesis protein pilC |
| 5404627 | C – T | PA14_60630 | L – F | Hypothetical protein | |
| 5464577 | C – T | PA14_61200 | G – D | Hypothetical protein | |
| 5530315 | A – G | PA14_62000 | F – L | hitA | Ferric iron-binding periplasmic protein HitA |
| 5722900 | A – C | PA14_64230 | D – A | retS/rtsM | RetS, regulator of exopolysaccharide and type III Secretion |
| 5757525 | G – C | PA14_64620 | Q – E | Putative oxidoreductase | |
| 5757527 | G – C | PA14_64620 | P – R | Putative oxidoreductase | |
| 5809365 | T – C | PA14_65190 | K – E | yjfH | TrmH family RNA methyltransferase, group 3 |
| 5866730 | T – G | PA14_65860 | syn. | Putative two-component sensor | |
| 5905079 | A – G | PA14_66270 | syn. | glnE | Glutamine-synthetase adenylyltransferase |
| 5968025 | C – G | PA14_66820 | P – A | phaC1 | Poly(3-hydroxyalkanoic acid) synthase 1 |
| 6070122 | T – C | PA14_680203 | Homolog to hypothetical protein PA5149 | ||
| 6076066 | G – C | PA14_68100 | syn. | Hypothetical protein | |
| 6412470 | G – C | PA14_71930 | R – G | wbpX | Glycosyltransferase WbpX |
| 6441338 | T – C | PA14_72300 | L – P | Hypothetical protein |
| Intergenic position | nt | Intergenic region |
|---|---|---|
| 151966 | A – G | igrPA14_01660-01670 |
| 187759 | G – T | igrPA14_02050-02060 |
| 208430 | T – G | igrPA14_02310-02330 |
| 208433 | G – C | igrPA14_02310-02330 |
| 888497 | A – C | igrPA14_10290-10300 |
| 966217 | T – C | igrPA14_11110-11120 |
| 1144646 | C – G | igrPA14_13320-13330 |
| 1375947 | A – G | igrPA14_16150-16160 |
| 1725505 | A – G | igrPA14_20020-20030 |
| 1748240 | T – C | igrPA14_20290-20300 |
| 1923008 | C – T | igrPA14_22080-22090 |
| 2354149 | A – G | igrPA14_27090-27100 |
| 2362330 | A – C | igrPA14_27180-27190 |
| 2362363 | G – C | igrPA14_27180-27190 |
| 2589402 | C – T | igrPA14_29890-29900 |
| 2840442 | T – C | igrPA14_32700-32710 |
| 2840444 | T – C | igrPA14_32700-32710 |
| 3281477 | G – C | igrPA14_36810-36820 |
| 3356495 | G – C | igrPA14_37680-37690 |
| 3515863 | T – C | igrPA14_39480-39500 |
| 3662614 | T – C | igrPA14_41070-41080 |
| 4347602 | G – C | igrPA14_48890-48900 |
| 4351470 | T – G | igrPA14_48960-48970 |
| 4352019 | T – G | igrPA14_48970-48980 |
| 4352023 | C – G | igrPA14_48970-48980 |
| 4352432 | G – A | igrPA14_48980-48990 |
| 4352433 | G – A | igrPA14_48980-48990 |
| 4407236 | A – G | igrPA14_49540-49560 |
| 4659805 | A – G | igrPA14_52530-52540 |
| 4708161 | A – G | igrPA14_53110-53120 |
| 5198405 | T – C | igrPA14_58360-58375 |
| 5200474 | A – C | igrPA14_58380-58390 |
| 5565118 | A – G | igrPA14_62380-62390 |
| 5648548 | A – G | igrPA14_63280-63290 |
| 5648573 | A – G | igrPA14_63280-63290 |
| 5792010 | A – G | igrPA14_64980-64990 |
1Protein length 180 aa instead of 264.
2Two SNPs in one codon.
3Annotated as probably inactive protein fragment/putative frameshift gene.
4Next stop 18 codons downstream.
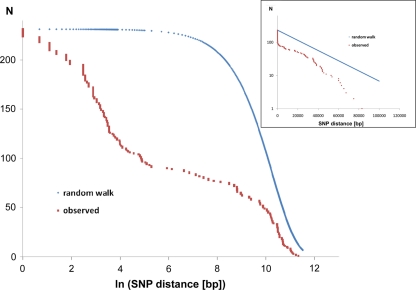
Of the 231 SNPs, only 33 SNPs followed the statistics of a random distribution in the genome (Figure 6). In other words, 198 SNPs were non-randomly distributed in the genome implying that the affected loci had been subject to diversifying selection.
Figure 6.
Intraclonal SNP diversity of the P. aeruginosa PA14 clone: distribution of nearest SNP neighbors in the RN3 genome. Mapping of the RN3 genome onto the PA14 genome uncovered 231 SNPs. The figure depicts the genomic distribution of the distance between two adjacent SNPs (nearest neighbors). The red graphs show the observed distribution that is compared with a random genomic distribution of the same number of 231 SNPs (blue graphs, one-dimensional random walk statistics). The two semilogarithmic plots visualize the deviation from a random distribution at either a global scale (insert) or with focus on the hotspots of sequence diversity (large figure).
The major hotspot is the phage Pf1-like gene cluster (PA14_48890–PA14_49000) with 87 SNPs, i.e., 38% of all SNPs. Thus phage Pf1 seems to be the most rapidly evolving part of the PA14 genome consistent with the view that phages span a high degree of genetic diversity and are prone to frequent horizontal transfer (Hatfull, 2008).
Non-synonymous SNPs were mainly found in the functional categories of transcriptional regulators, membranes, cellular appendages, transport, and secretion (Table 4). Hotspots of sequence diversity in single genes between the PA14 and RN3 genomes are ftsZ, armB (mexH), and cynS with six, five, and four SNPs, respectively. FtsZ is the major tubulin-like cytoskeletal protein in the bacterial cytokinesis machine (Erickson et al., 2010) and hence we noted with surprise that the FtsZ proteins of strains PA14 and RN3 differ at five positions in their amino acid sequence. The substitutions P-L, M-L, G-D, T-N, and P-T are located within a stretch of 35 amino acids of the 394 aa protein and are all not neutral (Table 4). MexH is a component of the MexGHI-OpmD efflux pump that is required for biofilm formation (Southey-Pillig et al., 2005), facilitates cell-to-cell communication and promotes virulence and growth in P. aeruginosa (Aendekerk et al., 2005). MexH of strains PA14 and RN3 differ by three amino acid substitutions (Q-E, T-A, and H-S) in three distant domains of the protein from each other. CynS encodes a cyanase (EC 4.2.1.104) that catalyzes the decomposition of cyanate into CO2 and ammonium (Luque-Almagro et al., 2008). The intraclonal diversity of cyanase between RN3 and PA14 of four amino acid substitutions is similar in number and localization to that of the completely sequenced P. aeruginosa strains, i.e., 5–11 amino acid substitutions clustering in the N-terminal region of CynS.
Key genes were also affected by non-synonymous SNPs that may modulate the function of the gene products. The DNA-directed RNA polymerase RpoB of strain RN3 carries a substitution of a glycine by an aspartate, and the global regulator RetS of the sessile and planktonic lifestyle of P. aeruginosa, which is involved in the transition from acute to chronic infections (Goodman et al., 2004), harbors a substitution of an aspartate by an alanine.
Of the 34 observed amino acid substitution types, nine are classified by the Dayhoff (1978) matrix as uncommon and associated with an impact on protein function. In contrast, only 12 of the 20 most common neutral amino acid changes were seen. In summary, SNPs non-randomly targeted elements of the cell surface and uncommon non-neutral substitutions (e.g., K-E) were overrepresented in the affected proteins. These facts suggest that in the investigated case the intraclonal diversity did not evolve by random drift, but was driven by selective forces.
Strain RN3 was isolated from the first P. aeruginosa-positive specimen taken from an individual with cystic fibrosis. Thus the portion of adaptive mutations that typically emerge during chronic colonization of cystic fibrosis airways (Smith et al., 2006) should be low. Nevertheless some sequence differences between RN3 and PA14 could provide RN3 with selective advantage to adapt and persist in cystic fibrosis airways. Obvious candidates are loci encoding efflux pumps (mexH), major transcriptional regulators (retS), and siderophore (pvdD), cyanide (cynS), or quinolone (phnA) biosynthesis, respectively.
The major take home message of our endeavor to compare the intraclonal genome diversity of strains of distant geographic origin was the unexpectedly low substitution rate. Statistical analysis provides strong evidence that nucleotide substitutions in coding regions were under purifying selection so that only a low number of substitutions was fixed. This versatile, ubiquitous and phylogenetically ancient organism apparently does not need many de novo mutations if it conquers a new habitat. The next step to understand the molecular evolution of intraclonal diversity would be the determination of the relative contributions of de novo mutation versus recombination. To accomplish this task, a larger collection of clone PA14 strains than just two isolates will have to be studied (see Spratt, 2004, for an appropriate study design).
Perspectives
Only four completely sequenced P. aeruginosa genomes are officially deposited as finished genomes in GenBank. Draft genomes exist for a five further genomes and several dozen P. aeruginosa projects are deposited in the ENA hosted by EMBL-EBI (see text footnote 1). Many of the projects were done for the purpose of (re)sequencing variants of already known strains. Thorough genome assemblies and functional annotations are probably intended only in a minority of cases. But nevertheless an immense increase in P. aeruginosa genome data is expected to become available in the near future due to the on-going revolution of sequencing technologies. In particular, the sequencing of strains from environmental habitats should provide us with an unbiased overview of the genetic repertoire of the P. aeruginosa population.
Conflict of Interest Statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (SFB 900: Chronic Infections: Microbial Persistence and its Control; project A2).
Footnotes
References
- Aendekerk S., Diggle S. P., Song Z., Høiby N., Cornelis P., Williams P., Cámara M. (2005). The MexGHI-OpmD multidrug efflux pump controls growth, antibiotic susceptibility and virulence in Pseudomonas aeruginosa via 4-quinolone-dependent cell-to-cell communication. Microbiology 151(Pt 4), 1113–1125 10.1099/mic.0.27631-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arora S. K., Wolfgang M. C., Lory S., Ramphal R. (2004). Sequence polymorphism in the glycosylation island and flagellins of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Bacteriol. 186, 2115–2122 10.1128/JB.186.7.2115-2122.2004 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Battle S. E., Meyer F., Rello J., Kung V. L., Hauser A. R. (2008). Hybrid pathogenicity island PAGI-5 contributes to the highly virulent phenotype of a Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolate in mammals. J. Bacteriol. 190, 7130–7140 10.1128/JB.00785-08 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Battle S. E., Rello J., Hauser A. R. (2009). Genomic islands of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 290, 70–78 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2008.01406.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter M. Q., Chen J., Lory S. (2010). The Pseudomonas aeruginosa pathogenicity island PAPI-1 is transferred via a novel type IV pilus. J. Bacteriol. 192, 3249–3258 10.1128/JB.01426-09 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng K., Smyth R. L., Govan J. R., Doherty C., Winstanley C., Denning N., Heaf D. P., van Saene H., Hart C. A. (1996). Spread of beta-lactam-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa in a cystic fibrosis clinic. Lancet 348, 639–642 10.1016/S0140-6736(96)05169-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cramer N., Klockgether J., Wrasman K., Schmidt M., Davenport C., Tümmler B. (2011). Microevolution of the major common Pseudomonas aeruginosa clones C and PA14 in cystic fibrosis lungs. Environ. Microbiol. 13, 1590–1604 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2011.02470.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davenport C. F., Wiehlmann L., Reva O. N., Tümmler B. (2009). Visualization of Pseudomonas genomic structure by abundant 8-14mer oligonucleotides. Environ. Microbiol. 11, 1092–1104 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2008.01839.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dayhoff M. O. (1978). Atlas of Protein Sequence and Structure, Observed Frequencies of Amino Acid Replacements Between Closely Related Proteins, Vol. 5, Suppl. 3 Washington, DC: National Biomedical Research foundation [Google Scholar]
- Dobrindt U., Hochhut B., Hentschel U., Hacker J. (2004). Genomic islands in pathogenic and environmental microorganisms. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2, 414–424 10.1038/nrmicro884 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dötsch A., Klawonn F., Jarek M., Scharfe M., Blöcker H., Häussler S. (2010). Evolutionary conservation of essential and highly expressed genes in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. BMC Genomics 11, 234. 10.1186/1471-2164-11-234 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson H. P., Anderson D. E., Osawa M. (2010). FtsZ in bacterial cytokinesis: cytoskeleton and force generator all in one. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 74, 504–528 10.1128/MMBR.00021-10 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernst R. K., D’Argenio D. A., Ichikawa J. K., Bangera M. G., Selgrade S., Burns J. L., Hiatt P., McCoy K., Brittnacher M., Kas A., Spencer D. H., Olson M. V., Ramsey B. W., Lory S., Miller S. I. (2003). Genome mosaicism is conserved but not unique in Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates from the airways of young children with cystic fibrosis. Environ. Microbiol. 5, 1341–1349 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2003.00518.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank S., Klockgether J., Hagendorf P., Geffers R., Schöck U., Pohl T., Davenport C. F., Tümmler B. (2011). Pseudomonas putida KT2440 genome update by cDNA sequencing and microarray transcriptomics. Environ. Microbiol. 13, 1309–1326 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2011.02430.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaillard M., Pernet N., Vogne C., Hagenbüchle O., van der Meer J. R. (2008). Host and invader impact of transfer of the clc genomic island into Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 105, 7058–7063 10.1073/pnas.0801269105 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giltner C. L., Rana N., Lunardo M. N., Hussain A. Q., Burrows L. L. (2011). Evolutionary and functional diversity of the Pseudomonas type IVa pilin island. Environ. Microbiol. 13, 250–264 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2010.02327.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman A. L., Kulasekara B., Rietsch A., Boyd D., Smith R. S., Lory S. (2004). A signaling network reciprocally regulates genes associated with acute infection and chronic persistence in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Dev. Cell 7, 745–754 10.1016/j.devcel.2004.08.020 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatfull G. F. (2008). Bacteriophage genomics. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 11, 447–453 10.1016/j.mib.2008.09.004 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He J., Baldini R. L., Déziel E., Saucier M., Zhang Q., Liberati N. T., Lee D., Urbach J., Goodman H. M., Rahme L. G. (2004). The broad host range pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain PA14 carries two pathogenicity islands harboring plant and animal virulence genes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 101, 2530–2535 10.1073/pnas.0304622101 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiewitz C., Larbig K., Klockgether J., Weinel C., Tümmler B. (2000). Monitoring genome evolution ex vivo: reversible chromosomal integration of a 106 kb plasmid at two tRNA(Lys) gene loci in sequential Pseudomonas aeruginosa airway isolates. Microbiology 146(Pt 10), 2365–2373 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klockgether J., Munder A., Neugebauer J., Davenport C. F., Stanke F., Larbig K. D., Heeb S., Schöck U., Pohl T. M., Wiehlmann L., Tümmler B. (2010). Genome diversity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 laboratory strains. J. Bacteriol. 192, 1113–1121 10.1128/JB.01515-09 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klockgether J., Reva O., Larbig K., Tümmler B. (2004). Sequence analysis of the mobile genome island pKLC102 of Pseudomonas aeruginosa C. J. Bacteriol. 186, 518–534 10.1128/JB.186.2.518-534.2004 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klockgether J., Würdemann D., Reva O., Wiehlmann L., Tümmler B. (2007). Diversity of the abundant pKLC102/PAGI-2 family of genomic islands in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Bacteriol. 189, 2443–2459 10.1128/JB.01688-06 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klockgether J., Würdemann D., Wiehlmann L., Binnewies T. T., Ussery D. W., Tümmler B. (2008). “Genome diversity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa,” in Pseudomonas Genomics and Molecular Biology, ed. Cornelis P. (Norfolk: Caister Academic Press; ), 19–42 [Google Scholar]
- Kresse A. U., Dinesh S. D., Larbig K., Römling U. (2003). Impact of large chromosomal inversions on the adaptation and evolution of Pseudomonas aeruginosa chronically colonizing cystic fibrosis lungs. Mol. Microbiol. 47, 145–158 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2003.03261.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulasekara B. R., Kulasekara H. D., Wolfgang M. C., Stevens L., Frank D. W., Lory S. (2006). Acquisition and evolution of the exoU locus in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Bacteriol. 188, 4037–4050 10.1128/JB.02000-05 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kung V. L., Ozer E. A., Hauser A. R. (2010). The accessory genome of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 74, 621–641 10.1128/MMBR.00027-10 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kus J. V., Tullis E., Cvitkovitch D. G., Burrows L. L. (2004). Significant differences in type IV pilin allele distribution among Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates from cystic fibrosis (CF) versus non-CF patients. Microbiology 150(Pt 5), 1315–1326 10.1099/mic.0.26822-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larbig K. D., Christmann A., Johann A., Klockgether J., Hartsch T., Merkl R., Wiehlmann L., Fritz H. J., Tümmler B. (2002). Gene islands integrated into tRNA(Gly) genes confer genome diversity on a Pseudomonas aeruginosa clone. J. Bacteriol. 184, 6665–6680 10.1128/JB.184.23.6665-6680.2002 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee D. G., Urbach J. M., Wu G., Liberati N. T., Feinbaum R. L., Miyata S., Diggins L. T., He J., Saucier M., Déziel E., Friedman L., Li L., Grills G., Montgomery K., Kucherlapati R., Rahme L. G., Ausubel F. M. (2006). Genomic analysis reveals that Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence is combinatorial. Genome Biol. 7, R90. 10.1186/gb-2006-7-10-r90 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liang X., Pham X. Q., Olson M. V., Lory S. (2001). Identification of a genomic island present in the majority of pathogenic isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Bacteriol. 183, 843–853 10.1128/JB.183.3.843-853.2001 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luque-Almagro V. M., Huertas M. J., Sáez L. P., Luque-Romero M. M., Moreno-Vivián C., Castillo F., Roldán M. D., Blasco R. (2008). Characterization of the Pseudomonas pseudoalcaligenes CECT5344 cyanase, an enzyme that is not essential for cyanide assimilation. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 74, 6280–6288 10.1128/AEM.00916-08 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathee K., Narasimhan G., Valdes C., Qiu X., Matewish J. M., Koehrsen M., Rokas A., Yandava C. N., Engels R., Zeng E., Olavarietta R., Doud M., Smith R. S., Montgomery P., White J. R., Godfrey P. A., Kodira C., Birren B., Galagan J. E., Lory S. (2008). Dynamics of Pseudomonas aeruginosa genome evolution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 105, 3100–3105 10.1073/pnas.0711982105 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCallum S. J., Gallagher M. J., Corkill J. E., Hart C. A., Ledson M. J., Walshaw M. J. (2002). Spread of an epidemic Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain from a patient with cystic fibrosis (CF) to non-CF relatives. Thorax 57, 559–560 10.1136/thorax.57.6.559 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohd-Zain Z., Turner S. L., Cerdeño-Tárraga A. M., Lilley A. K., Inzana T. J., Duncan A. J., Harding R. M., Hood D. W., Peto T. E., Crook D. W. (2004). Transferable antibiotic resistance elements in Haemophilus influenzae share a common evolutionary origin with a diverse family of syntenic genomic islands. J. Bacteriol. 186, 8114–8122 10.1128/JB.186.23.8114-8122.2004 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moya B., Dötsch A., Juan C., Blázquez J., Zamorano L., Häussler S., Oliver A. (2009). Beta-lactam resistance response triggered by inactivation of a non-essential penicillin-binding protein. PLoS Pathog. 5, e1000353. 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000353 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qiu X., Gurkar A. U., Lory S. (2006). Interstrain transfer of the large pathogenicity island (PAPI-1) of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 103, 19830–19835 10.1073/pnas.0602208103 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramos J. L. (ed.). (2004). Pseudomonas Volume 1: Genomics, Life Style and Molecular Architecture. New York: Kluwer Academics/Plenum Publishers [Google Scholar]
- Raymond C. K., Sims E. H., Kas A., Spencer D. H., Kutyavin T. V., Ivey R. G., Zhou Y., Kaul R., Clendenning J. B., Olson M. V. (2002). Genetic variation at the O-antigen biosynthetic locus in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Bacteriol. 184, 3614–3622 10.1128/JB.184.13.3614-3622.2002 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reva O. N., Tümmler B. (2004). Global features of sequences of bacterial chromosomes, plasmids and phages revealed by analysis of oligonucleotide usage patterns. BMC Bioinformatics 5, 90. 10.1186/1471-2105-5-90 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reva O. N., Tümmler B. (2005). Differentiation of regions with atypical oligonucleotide composition in bacterial genomes. BMC Bioinformatics 6, 251. 10.1186/1471-2105-6-251 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Römling U., Greipel J., Tümmler B. (1995). Gradient of genomic diversity in the Pseudomonas aeruginosa chromosome. Mol. Microbiol. 17, 323–332 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1995.mmi_17020323.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Römling U., Schmidt K. D., Tümmler B. (1997). Large genome rearrangements discovered by the detailed analysis of 21 Pseudomonas aeruginosa clone C isolates found in environment and disease habitats. J. Mol. Biol. 271, 386–404 10.1006/jmbi.1997.1186 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy P. H., Tetu S. G., Larouche A., Elbourne L., Tremblay S., Ren Q., Dodson R., Harkins D., Shay R., Watkins K., Mahamoud Y., Paulsen I. T. (2010). Complete genome sequence of the multiresistant taxonomic outlier Pseudomonas aeruginosa PA7. PLoS ONE 5, e8842. 10.1371/journal.pone.0008842 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt K. D., Tümmler B., Römling U. (1996). Comparative genome mapping of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO with P. aeruginosa C, which belongs to a major clone in cystic fibrosis patients and aquatic habitats. J. Bacteriol. 178, 85–93 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma C. M., Hoffmann S., Darfeuille F., Reignier J., Findeiss S., Sittka A., Chabas S., Reiche K., Hackermüller J., Reinhardt R., Stadler P. F., Vogel J. (2010). The primary transcriptome of the major human pathogen Helicobacter pylori. Nature 464, 250–255 10.1038/nature08756 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silby M. W., Winstanley C., Godfrey S. A., Levy S. B., Jackson R. W. (2011). Pseudomonas genomes: diverse and adaptable. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 35, 652–680 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2011.00269.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith E. E., Buckley D. G., Wu Z., Saenphimmachak C., Hoffman L. R., D’Argenio D. A., Miller S. I., Ramsey B. W., Speert D. P., Moskowitz S. M., Burns J. L., Kaul R., Olson M. V. (2006). Genetic adaptation by Pseudomonas aeruginosa to the airways of cystic fibrosis patients. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 103, 8487–8492 10.1073/pnas.0508169103 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith E. E., Sims E. H., Spencer D. H., Kaul R., Olson M. V. (2005). Evidence for diversifying selection at the pyoverdine locus of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Bacteriol. 187, 2138–2147 10.1128/JB.187.6.2138-2147.2005 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southey-Pillig C. J., Davies D. G., Sauer K. (2005). Characterization of temporal protein production in Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. J. Bacteriol. 187, 8114–8126 10.1128/JB.187.23.8114-8126.2005 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spangenberg C., Heuer T., Bürger C., Tümmler B. (1996). Genetic diversity of flagellins of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. FEBS Lett. 396, 213–217 10.1016/0014-5793(96)01099-X [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer D. H., Kas A., Smith E. E., Raymond C. K., Sims E. H., Hastings M., Burns J. L., Kaul R., Olson M. V. (2003). Whole-genome sequence variation among multiple isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Bacteriol. 185, 1316–1325 10.1128/JB.185.4.1316-1325.2003 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spratt B. G. (2004). Exploring the concept of clonality in bacteria. Methods Mol. Biol. 266, 323–352 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart R. M., Wiehlmann L., Ashelford K. E., Preston S. J., Frimmersdorf E., Campbell B. J., Neal T. J., Hall N., Tuft S., Kaye S. B., Winstanley C. (2011). Genetic characterization indicates that a specific subpopulation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa is associated with keratitis infections. J. Clin. Microbiol. 49, 993–1003 10.1128/JCM.02036-10 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stover C. K., Pham X. Q., Erwin A. L., Mizoguchi S. D., Warrener P., Hickey M. J., Brinkman F. S., Hufnagle W. O., Kowalik D. J., Lagrou M., Garber R. L., Goltry L., Tolentino E., Westbrock-Wadman S., Yuan Y., Brody L. L., Coulter S. N., Folger K. R., Kas A., Larbig K., Lim R., Smith K., Spencer D., Wong G. K., Wu Z., Paulsen I. T., Reizer J., Saier M. H., Hancock R. E., Lory S., Olson M. V. (2000). Complete genome sequence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1, an opportunistic pathogen. Nature 406, 959–964 10.1038/35023079 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verma A., Schirm M., Arora S. K., Thibault P., Logan S. M., Ramphal R. (2006). Glycosylation of b-type flagellin of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: structural and genetic basis. J. Bacteriol. 188, 4395–4403 10.1128/JB.01642-05 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiehlmann L., Wagner G., Cramer N., Siebert B., Gudowius P., Morales G., Köhler T., van Delden C., Weinel C., Slickers P., Tümmler B. (2007). Population structure of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 104, 8101–8106 10.1073/pnas.0609213104 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winsor G. L., Van Rossum T., Lo R., Khaira B., Whiteside M. D., Hancock R. E., Brinkman F. S. (2009). Pseudomonas Genome Database: facilitating user-friendly, comprehensive comparisons of microbial genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 37, D483–D488 10.1093/nar/gkn861 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winstanley C., Langille M. G., Fothergill J. L., Kukavica-Ibrulj I., Paradis-Bleau C., Sanschagrin F., Thomson N. R., Winsor G. L., Quail M. A., Lennard N., Bignell A., Clarke L., Seeger K., Saunders D., Harris D., Parkhill J., Hancock R. E., Brinkman F. S., Levesque R. C. (2009). Newly introduced genomic prophage islands are critical determinants of in vivo competitiveness in the Liverpool epidemic strain of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Genome Res. 19, 12–23 10.1101/gr.086082.108 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]