Abstract
Urachal cysts are the most common urachal anomaly in the pediatric population. There is an increasing body of literature documenting successful management of urachal cysts using laparoscopic techniques. There may be an advantage, however, with the use of robot-assisted laparoscopy for reconstructive cases. We describe the techniques used for robot-assisted laparoscopic excision of a urachal cyst and bladder cuff with bladder repair in a female child. This approach is a safe and effective option for the minimally invasive management of pediatric urachal cysts.
Introduction
The urachus, a three-layered canal that connects the allantois to the fetal bladder, usually obliterates in the fifth month of gestation. Urachal anomalies in the pediatric population are rarely associated with malignancy. Urachal cysts represent up to 54% of pediatric urachal anomalies.1–4
Several recent reports have described successful management of urachal anomalies using minimally invasive techniques.5–11 For pediatric patients, minimally invasive approaches for urachal anomalies have been limited to traditional laparoscopic techniques.7–9 Robot assistance in laparoscopic surgery is increasingly being used for reconstructive procedures that are needed after extirpative surgery. To date, robot-assisted laparoscopy for urachal anomalies has only been described in adult patients.5,6 In this report, we present the techniques used in pediatric robot-assisted laparoscopic excision of a urachal cyst with a bladder cuff, with subsequent bladder repair.
Technique
We performed a robot-assisted laparoscopic excision of a previously infected urachal cyst in a 4-year-old girl who initially presented to the emergency department with midline abdominal pain. She was otherwise noted to be healthy, and there was no history of umbilical drainage. A CT scan of the abdomen and pelvis revealed an anterior midline urachal cyst located just superior to the bladder that measured 2.7 cm in its greatest diameter and which was associated with local inflammatory changes (Fig. 1). Her abdominal pain resolved after 2 weeks of oral antibiotics. After 2 months of observation to allow the inflammatory changes to subside, options for management of the urachal cyst were discussed with the family. The family elected to proceed with robot-assisted laparoscopic excision of the urachal cyst and bladder cuff with subsequent bladder repair.
FIG. 1.
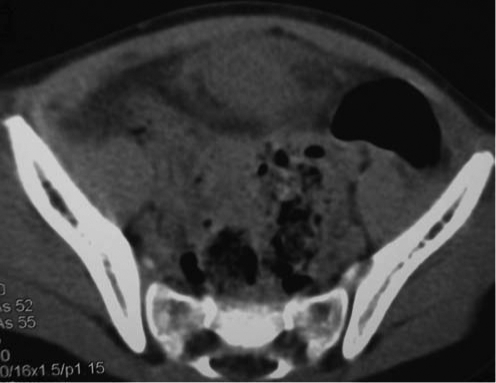
A CT scan of the abdomen shows a midline anterior cystic mass just superior to the bladder with local inflammation consistent with an inflamed urachal cyst.
Patient positioning and robot setup
Cystoscopy and cystography are performed initially to identify a possible connection from the bladder to the urachal cyst. The patient is placed in the supine position, padded at all pressure points, and secured to the table using wide tape. The Trendelenberg position is used to allow the abdominal contents to fall in a cephalad manner away from the pelvis. A Foley catheter is placed in a sterile fashion to allow for saline installation to achieve intermittent bladder distension.
Peritoneal access is obtained using the open Hasson technique,12 with placement of the 12-mm camera port in the midline using a vertical incision halfway between the umbilicus and the xyphoid process. Subsequent pneumoperitoneum of 12 to 15 mm Hg is applied, and the laparoscope is inserted. Two additional ports (5 mm or 8 mm) are inserted under direct vision at the anterior axillary lines just above the level of the umbilicus (Fig. 2). A box stitch is applied to all ports to secure them in place and for use during the port closures.13
FIG. 2.
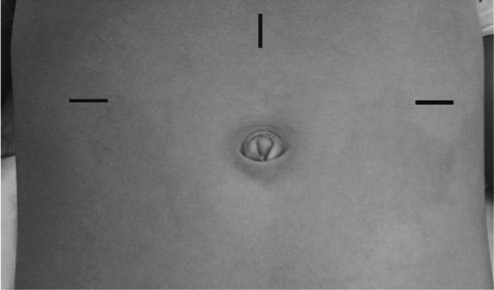
A 12-mm camera port is placed through a vertical incision at midline halfway between the umbilicus and the xyphoid process; 5- or 8-mm ports are placed through horizontal incisions at the anterior axillary lines just superior to level of umbilicus
The Da Vinci surgical robot system (Intuitive Surgical, Sunnyvale, CA) is brought over the legs from the caudal direction, and the robotic arms are engaged to the ports. Hook cautery or the hot scissors are used for dissection, and De-Bakey forceps are used for grasping. The 30-degree angled camera lens is positioned upward to visualize the bladder and anterior abdominal wall.
Initial approach
Dissection begins with lysis of the omental adhesions, which are often adherent to the cyst (Fig. 3). Once the adhesions are freed, one or both of the obliterated umbilical arteries are cauterized and divided to allow access to the anterior bladder wall (Fig. 4). The urachal remnant is cauterized and divided at its superior end near the umbilicus and then carefully dissected from the anterior abdominal wall using cautery. The dissection is carried down to the dome of the bladder, and the anterior bladder wall is mobilized from the anterior abdominal wall as well. The bladder can be distended partially or fully to assist with this dissection.
FIG. 3.
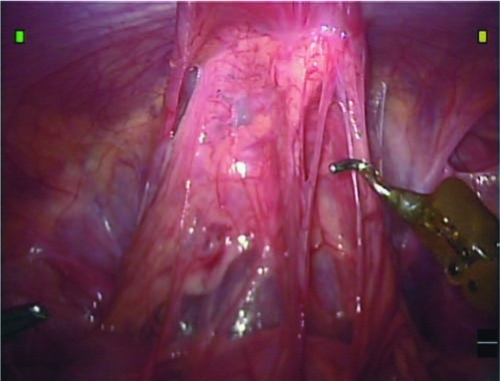
Omental adhesions cover the urachal cyst.
FIG. 4.
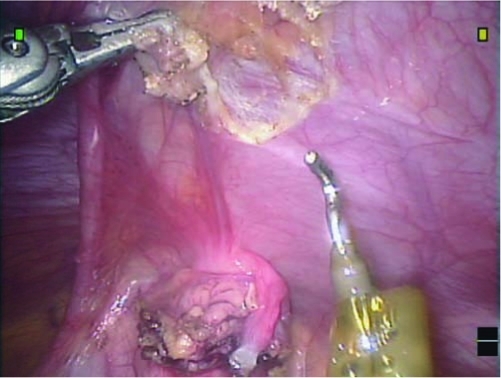
Dissection of the urachus from the anterior abdominal wall occurs after division of the right obliterated umbilical artery.
Hitch stitch
After mobilization of the urachal remnant, a holding stitch is passed through the abdominal wall above the bladder, then passed through the anterior bladder wall, and then out through the abdominal wall next to its initial insertion site, where it is clamped at the level of the skin (Fig. 5). The tension on this hitch stitch can then be adjusted to allow for better visualization of the surgical area, while providing countertraction during the cyst excision, as well as stability during suturing. Alternatively, an internal holding suture can be used to temporarily attach the anterior bladder wall to the anterior abdominal wall without passing the suture through the entire wall thickness.
FIG. 5.
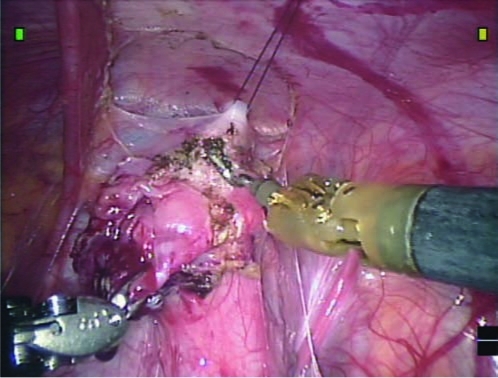
With the hitch stitch providing countertraction, the urachal cyst and bladder cuff are excised from the rest of the bladder.
Urachal cyst and bladder cuff excision
The urachal cyst and the bladder cuff are excised circumferentially using electrocautery; the hitch stitch and bladder distension via the Foley catheter can be adjusted as needed. A bladder opening is created once the urachal cyst and bladder cuff are excised as a single unit. Spillage of the bladder irrigant and urine is minimized because of the hitch stitch. The bladder defect is closed in a running fashion with two separate layers of 3-0 absorbable suture (Fig. 6). After closure, the bladder is distended via the Foley catheter to ensure a watertight anastomosis.
FIG. 6.
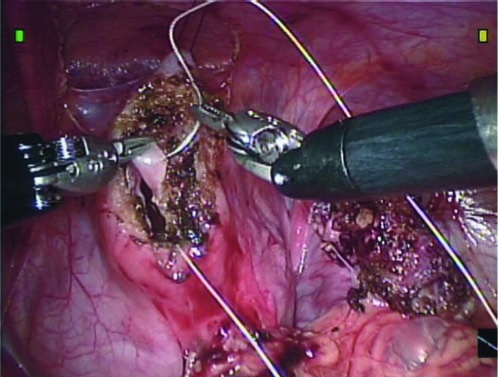
Two layer closure of the bladder opening is used after excision of the urachal cyst and bladder cuff.
Any spilled urine or blood is aspirated from the field. Once the robot is disengaged, the specimen is placed within a laparoscopic pouch and removed under direct visualization through one of the arm port sites after the arm port is removed. The other ports are removed under direct visualization, and the abdominal wall defects are closed in layers.
Foley catheter drainage for 24 to 48 hours is sufficient for complete bladder closure, similar to ureteral reimplantation surgery. Pathologic examination confirmed the presence of a benign urachal cyst with extensive acute and chronic inflammation.
Role in Urologic Practice
Minimally invasive robot-assisted surgery is a safe and viable option in a wide range of surgical conditions in children.14–16 Robot-assisted surgery is increasingly being applied to pediatric cases that involve urologic reconstruction and are of greater complexity.17 For pediatric urachal anomalies, minimally invasive management of pediatric urachal anomalies has so far been limited to traditional laparoscopic techniques. We present the first description of the techniques for a pediatric robot-assisted laparoscopic excision of a urachal cyst and bladder cuff with bladder repair.
Previously published reports of successful outcomes of laparoscopic surgery for urachal anomalies have alluded to the potential advantages in children, including shorter hospital stays, decreased pain medication usage, and improved cosmesis, all of which should apply to robot-assisted laparoscopic surgery as well.18 Robot-assisted laparoscopic surgery offers pediatric surgical specialists and their patients an effective minimally invasive tool for increased precision during complex pediatric surgical procedures that require reconstruction, such as the excision of a urachal cyst and bladder cuff with bladder repair.
Abbreviations Used
- CT
computed tomography
Footnotes
A video demonstrating this technique is available on the enclosed CD-ROM and online at www.liebertpub.com/end.
Disclosure Statement
No competing financial interests exist.
References
- 1.Ashley RA. Inman BA. Routh JC. Rohlinger RA. Husmann DA. Kramer SA. Urachal anomalies: A longitudinal study of urachal remnants in children and adults. J Urol. 2007;178:1615–1618. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2007.03.194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.McCollum MO. Macneily AE. Blair GK. Surgical implications of urachal remnants: Presentation and management. J Pediatr Surg. 2003;38:798–803. doi: 10.1016/jpsu.2003.50170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Bauer SB. Retik AB. Urachal anomalies and related umbilical disorders. Urol Clin North Am. 1978;5:195–211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Cilento BG., Jr Bauer SB. Retik AB. Peters CA. Atala A. Urachal anomalies: Defining the best diagnostic modality. Urology. 1998;52:120–122. doi: 10.1016/s0090-4295(98)00161-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Madeb R. Knopf JK. Nicholson C, et al. The use of robotically assisted surgery for treating urachal anomalies. BJU Int. 2006;98:838–842. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410X.2006.06430.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Yano H. Iwazawa T. Monden T. Excision of urachal sinus with use of a voice-controlled laparoscope. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A. 2003;13:45–49. doi: 10.1089/109264203321235476. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Khurana S. Borzi PA. Laparoscopic management of complicated urachal disease in children. J Urol. 2002;168:1526–1528. doi: 10.1016/S0022-5347(05)64510-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Yohannes P. Bruno T. Pathan M. Baltaro R. Laparoscopic radical excision of urachal sinus. J Endourol. 2003;17:475–479. doi: 10.1089/089277903769013612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Kojima Y. Hayashi Y. Yasui T. Itoh Y. Maruyama T. Kohri K. Laparoscopic management for urachal cyst in 9-year-old boy. Int Urol Nephrol. 2007;39:771–774. doi: 10.1007/s11255-006-9132-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Cadeddu JA. Boyle KE. Fabrizio MD. Schulam PG. Kavoussi LR. Laparoscopic management of urachal cysts in adulthood. J Urol. 2000;164:1526–1528. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Stone NN. Garden RJ. Weber H. Laparoscopic excision of a urachal cyst. Urology. 1995;45:161–164. doi: 10.1016/s0090-4295(95)97824-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Hasson HM. Open laparoscopy. Biomed Bull. 1984;5:1–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Poppas DP. Bleustein CB. Peters CA. Box stitch modification of Hasson technique for pediatric laparoscopy. J Endourol. 1999;13:447–450. doi: 10.1089/end.1999.13.447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Najmaldin A. Antao B. Early experience of tele-robotic surgery in children. Int J Med Robot. 2007;3:199–202. doi: 10.1002/rcs.150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Meehan JJ. Sandler A. Pediatric robotic surgery: A single-institutional review of the first 100 consecutive cases. Surg Endosc. 2008;22:177–182. doi: 10.1007/s00464-007-9418-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Volfson IA. Munver R. Esposito M. Dakwar G. Hanna M. Stock JA. Robot-assisted urologic surgery: Safety and feasibility in the pediatric population. J Endourol. 2007;21:1315–1318. doi: 10.1089/end.2007.9982. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Passeroti CC. Nguyen HT. Eisner BH. Lee RS. Peters CA. Laparoscopic reoperative pediatric pyeloplasty with robotic assistance. J Endourol. 2007;21:1137–1139. doi: 10.1089/end.2007.9929. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Peters CA. Laparoscopic and robotic approach to genitourinary anomalies in children. Urol Clin North Am. 2004;31:595–605. doi: 10.1016/j.ucl.2004.04.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


